A disease caused by pathogens that are localized in the intestines is called an intestinal infection. There are two types of this infection:
- Bacterial. Pathogenic bacteria enter the body through contaminated hands, objects, food, and water. These are salmonellosis, dysentery, E. coli, staphylococci, typhoid fever, coli infection, Klebsiella, intestinal yersiniosis, Proteus, fungi.
- Viral. Transmitted by the fecal-oral route, caused by viruses such as rotavirus (intestinal flu), enterovirus, Noruwalk group, adenovirus, astrovirus, coronavirus.
The main causes of intestinal infections in both cases are violations of basic hygiene standards:
- improper storage of food;
- products that have not undergone heat treatment (raw meat, eggs, cakes with cream);
- dirty hands;
- insects (flies, ants, cockroaches);
- raw water;
- use of shared towels, dishes, toys.
When viruses and bacteria enter the human body, they disrupt the digestion process, causing the cells of the intestinal mucosa to become inflamed.
Symptoms of intestinal infection
How to identify an intestinal infection? It is necessary to know its symptoms and how it manifests itself in humans. Develops from six to forty-eight hours.
Here are the most common signs of this disease:
- Intoxicating:
- be sick;
- weakness;
- headache and dizziness;
- body aches.
- Temperature increase.
- Gastritis:
- my stomach hurts;
- vomit;
- loss of appetite.
- Enteritic:
- mild diarrhea.
- Colitic:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during defecation.
Sometimes these symptoms can be combined with each other.
Nutrition depending on the disease
Intestinal infections can be caused by viruses and bacteria. Symptoms, and therefore treatment, may differ in each case.
Salmonellosis
The causative agent of the disease is Salmonella bacilli. These bacteria most often affect children. Salmonella can be found anywhere, for example in food. The stick can last up to four months in meat and sausages, and up to six months in frozen meat.
At the same time, the appearance and taste of the product most often remain unchanged. The disease manifests itself in the form of weakness, chills, fever, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Every minute there is more and more bacterial infection in the body. In childhood, salmonellosis can be fatal.
Diet for adults
Adults with intestinal infection are recommended to use diet No. 4.
Products should not irritate the stomach; they should be steamed (preferably using a double boiler) or boiled. Dishes are served pureed and warm. In this case, the diet is as follows: six times a day in small portions. As for calorie content, it is advisable not to exceed the threshold of 1980 kilocalories.
General recommendations when using a diet for adults infected with intestinal infection (daily values):
- sugar – 40 g;
- salt – 10 g;
- fats – 70 g;
- carbohydrates – 250 g;
- proteins – 100 g.
If the patient’s condition has improved, he is transferred to the 4B diet, which is characterized by an increase in the consumption of kilocalories (3000) and carbohydrates (400 g).
What foods are allowed for consumption? This:
- crackers (unsweetened);
- meat (lean), steamed;
- porridge (oatmeal, millet, buckwheat) with water;
- scrambled eggs;
- soups (liquid, pureed);
- skim cheese.
You should not eat, so as not to aggravate the course of the disease:
- smoked products (fish, meat, sausage, cheese);
- milk;
- semi-finished products;
- baked goods;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- sweets (sweets, cakes, ice cream, halva, marmalade, cookies, waffles);
- fruit juices from concentrates and the like.
Diet rules
In order for food to have a beneficial effect on the digestive system during an intestinal infection, adhere to the following rules:
- The menu includes a variety of easily digestible dishes, but they should not be irritants to the mucous membranes of the esophagus and intestines.
- For heat treatment of products, boiling or steaming is used.
- Dishes are eaten in pureed puree form.
- Limit the consumption of salt, carbohydrates and fats.
- Reduce the number of calories.
- Eat warm dishes (food temperature should be between 33-36°C), but in small portions. The optimal volume is 150-300 g.
Diet for a child with an intestinal infection
As a parent, you are concerned about the health of your child and must remember that it is necessary to exclude from your baby’s diet those foods that can cause loose stools:
- green vegetables;
- fresh fruits;
- fried food;
- fatty foods;
- dairy products;
- salinity;
- salads.
It is recommended that if an appetite appears, to restore the baby’s intestinal function, give him:
- vegetables (baked or boiled);
- rice - porridge without oil;
- white bread (dried);
- bananas;
- potato;
- meat (lean);
- chicken bouillon;
- jelly;
- strong and unsweetened tea.
When the condition of a sick child improves, new foods should be introduced into his diet with extreme caution to prevent an exacerbation of the disease.
Diet during the acute period of illness
2-3 days after the onset of the development of the pathology, the acute stage begins. It lasts no more than a week. During this period, patients refuse food due to loss of appetite. Some are simply afraid to eat, so as not to provoke an attack of vomiting.
If you have no appetite, you don’t need to force yourself to eat. If you really want to eat, then with intestinal flu you need to remove familiar foods from your diet. You can and should eat:
- First meal. If the body requires soup, then you should give preference to jelly-like consistencies. For cooking, you can use potatoes, zucchini or carrots. You can add rice or durum wheat pasta to soups.
- Rice water. Boil the washed cereal in a small container until it reaches a jelly-like consistency. Drain the liquid into a separate container and add salt if desired. Rice broth can be drunk in small portions, alternating with saline solutions. The liquid has a strengthening effect and soothes an irritated stomach.
- Meat dishes. Doctors advise giving up meat during the acute period of the disease. If you really want to eat, you can choose chicken, rabbit or turkey. Meat can only be cooked by boiling. Other options are unacceptable.
- Kissel. The drink coats the walls of the stomach and soothes the mucous membrane. It is better to cook jelly yourself. The drink should not contain chemical dyes or flavors.
- Fruits are strictly prohibited. An exception may be bananas, but you can eat no more than 1 banana per day.
Dietary food should be gentle. You need to avoid grapes, figs, apricots, prunes, and alcoholic beverages. To effectively fight an intestinal virus, the body requires a lot of strength.
Sample diet menu for intestinal infection
As already noted, the regimen for this diet includes six meals a day:
- First breakfast: porridge with water, fresh cottage cheese made from low-fat milk, weak tea with one spoon of sugar.
- Second breakfast: fruit puree (apples, bananas, mixed).
- Lunch: meat broth (beef, chicken, rabbit) with the addition of cereals (rice, oatmeal, semolina), steamed meatballs, berry jelly.
- Afternoon snack: decoction of dried fruits (apples, dried apricots, rose hips, raisins).
- Dinner: steamed omelette, porridge with water (buckwheat, semolina, oatmeal), herbal tea.
- Second dinner: oat bran jelly.
How to create a menu?
At the initial stage of an intestinal infection, they completely refuse food if there is severe vomiting and diarrhea, and they are frequent. Now, the main thing is to avoid dehydration, so the patient should drink a lot. The following drinks are recommended during this period:
- not strong black or green tea;
- cocoa brewed in water without adding dairy products;
- decoctions made from bird cherry or blueberries;
- dried fruits compote;
- pharmacy (or homemade) rehydration products.
When clinical symptoms decrease, products are introduced that help replenish nutrients, strengthen the immune system and restore mucous membranes. It is good to introduce fermented milk drinks with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli into your diet. Preference can be given to kefir and acidophilus, which is due to two facts:
- They are rich in beneficial bacteria, which help increase the amount of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and B vitamins and improve digestion processes.
- They have a bactericidal effect, which allows them to fight pathogenic microflora and remove toxic substances from the body.
If you prefer dairy products, then choose those that do not contain lactose or its amount is very low.
After reducing the intoxication of the body, the menu is drawn up taking into account the following rules:
- For first courses, a variety of slimy soups are desirable. They are cooked in a low-fat broth using fish or meat with the addition of meatballs, meat quenelles or egg flakes.
- Instead of bread products, it is allowed to eat crackers made from premium white loaf or biscuits.
- For lunch you can serve cutlets, souffle, meatballs, which are cooked only by steaming. For minced meat, use chicken, turkey or beef. The meat is ground in a meat grinder with a fine mesh, turning it up to 4 times.
- Eggs are allowed for breakfast, boiled soft-boiled or steamed into an omelet. Fresh cottage cheese and cottage cheese soufflé are also allowed.
- Porridges must be pureed. For a sick person, porridge made from buckwheat, rice, semolina or oatmeal will bring the greatest benefit. They are boiled in water or weak meat broth.
- Among the drinks, the most beneficial are jelly and rosehip decoctions. Kissel envelops the mucous membranes of the digestive system and soothes it, and the starch included in its composition is a natural sorbent that removes toxic substances from the body. A decoction of rose hips is rich not only in minerals and vitamins, but also in tannins.
- For dessert, you can serve blueberry or bird cherry jelly.
Nutrition after recovery
For adults and children, the diet after an intestinal infection is the same. The diet should contain:
- meat and fish (low-fat varieties);
- soups (chicken broth with vegetables);
- vegetable purees;
- berry and fruit jelly;
- decoctions of herbs and dry berries.
Portions are small, food consumption is frequent.
Such a diet will contribute to a quick recovery, normalize intestinal function, and bring stool back to normal.
What can you eat
The following list of products is recommended for adult patients in the acute stage of the infectious process and during the recovery period:
- rice, buckwheat, semolina;
- low-fat cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt;
- vegetable or light chicken soups, especially slimy ones;
- homemade jelly;
- watermelons;
- bananas;
- apples and pumpkin baked with honey;
- boiled vegetables;
- dietary varieties of meat, fish - horse meat, chicken, turkey.
What can children eat after an intestinal infection? The therapeutic diet depends on the baby’s usual diet:
- If the child feeds exclusively on mother's milk, no special changes in the diet are needed. Doctors recommend putting it to the breast more often, but not overfeeding.
- A bottle-fed baby should be fed lactose-free formulas - Frisopep, Alfare, Nutrimigen. If complementary foods have already been introduced into the diet, the addition of new foods should be temporarily limited.
- It is useful for older children to give fermented milk products and acidophilus mixtures. They contain a high concentration of vitamin B and C, amino acids, bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. But it is not advisable to use one type of yogurt or kefir - you need to combine different lactic acid products.
- During the recovery stage, it is important to introduce boiled vegetables and baked fruits into the diet. They are rich in dietary fiber, which plays the role of natural sorbents - they absorb the remains of enterotoxins, improve peristalsis, and also help restore digestion in a short time.
Expert advice
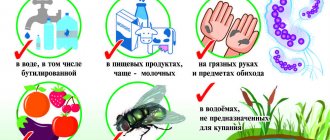
Take preventive measures:
- wash your hands after going outside, in public places, going to the toilet, before eating;
- heat-treat food and water before eating;
- adhere to food storage rules (ready meals should be kept in the refrigerator);
- boil the milk;
- do not eat raw eggs (be sure to wash them before cooking);
- check the expiration date of products before purchasing;
- do not feed your babies undiluted milk, both cow's and goat's;
Experts also advise isolating patients and providing them with separate dishes and personal hygiene products.
Principles of therapeutic nutrition
- Individuality . The diet is prescribed taking into account the prevailing symptoms, severity of the disease, age, concomitant pathology, and taste preferences.
- Avoiding hunger breaks . Previously, in the acute stage of the disease, doctors recommended a tea and water break for 1-2 days. Recent research has shown that fasting slows down the recovery of intestinal function. Refusal to eat leads to nutritional and energy deficiencies. Vomiting during intestinal infections lasts no more than 6 hours. After vomiting stops, start eating.
- Gentle principle . For 2-5 days, the most gentle diet is prescribed. The basis of the diet consists of foods that do not irritate the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, are quickly digested, and are easily absorbed. Avoid foods that cause increased gas formation, stimulate the production of bile, and gastric secretion. Food is ground using a blender, boiled or steamed. As your health improves, the diet is gradually expanded. The diet includes cutlets, meatballs, and dishes baked in the oven.
- Temperature regime. The recommended food temperature is not lower than 15 °C and not higher than 60 °C.
- Fractional nature of nutrition. Eating small portions 5-6 times a day facilitates digestion and absorption. In the acute stage of the disease, the amount of food is reduced, and the missing volume is replenished with liquid.
- Eating according to appetite . Eating forcefully provokes vomiting and worsens diarrhea.
- Drinking regime . To prevent dehydration from vomiting and diarrhea, drink at least 2 liters of fluid throughout the day.
Be sure to read: Culture for intestinal dysbiosis: details about the analysis
Drinking regime
Vomiting and diarrhea cause the body to lose fluid and electrolytes. If they are not replenished, dehydration will develop, so normalize your drinking regime at the first signs of illness. To avoid causing repeated vomiting, take 1-2 sips of liquid every 10-15 minutes.
What drink?
- Salt-free solutions : sweetened tea, rice broth, dried fruit compote, raisin broth, liquid jelly.
- Glucose salt solutions (compensate for the loss of electrolytes): buy Oralit, Regidron, Glucosolan at the pharmacy or prepare the mixture yourself.
Glucose salt solution recipe
Take 1 liter of warm boiled water, add a teaspoon of salt, 6 teaspoons of sugar, half a teaspoon of baking soda;
stir. Instead of regular table salt, you can use a special dietary supplement called “cardiosol”, which in addition to sodium chloride contains magnesium and potassium. Be sure to read:
Enterobacteriaceae in a child’s stool: is it dangerous and how to treat it?
Take at least 2 liters of fluid per day. Alternate salt-free solutions with glucose-salt solutions. Drinking only salt-free liquids will not replace lost electrolytes. A large dose of glucose-salt composition will increase the concentration of salts in the intestines and increase diarrhea.
Diet after an intestinal infection: diet, prohibited and permitted foods
A few days of rest with a suitable diet and drinking regime is usually enough to eliminate the symptoms of an intestinal infection. But the treatment doesn't stop there. After the acute symptoms have subsided, a recovery process follows, often lasting longer than the disease itself.
The infection weakens and depletes the body. Therefore, it is important that the return to normal nutrition occurs slowly, gradually.
Start with crackers and sautéed carrots
First courses should contain only easily digestible, low-fat foods that do not irritate the stomach and intestines. Suitable:
- banana;
- stewed carrots;
- apple compote;
- rice;
- crackers;
- stale bread.
Later you can add mashed potatoes, stewed vegetables, lean ham. But in small quantities. Eat slowly and try to chew your food thoroughly to save your stomach from overworking itself when digesting food. Recommended drinks include black, herbal tea, clean still water.
Temporarily avoid sugar and lactose
Some foods should be avoided altogether. These include dairy products - the lactose (milk sugar) they contain is difficult to digest, and a weakened intestine cannot cope with it sufficiently. For a few weeks, switch to low-lactose products: kefir, half-fat, low-fat cottage cheese, sour cream.
Also temporarily give up sugar (including sweetened drinks), which irritates a weakened stomach. Instead of lemonade, drink a glass of water with a slice of lemon or orange.
Do not hurry. Each person is individual. Some people take less than a week to recover, others 2 weeks. Be patient and try to avoid further health problems.
Provide your body with beneficial bacteria
After diarrhea, the intestinal bacterial balance is disrupted. Therefore, the diet after intestinal infection in adults and children includes the use of probiotics. These are living microorganisms that form a natural part of the balanced, properly functioning intestinal microflora that covers the intestinal mucosa.
You can get probiotics into your body through regular foods. These include:
- yoghurts;
- buttermilk;
- kefir;
- sauerkraut;
- fermented vegetables;
- fermented soy products (miso, tempeh);
- Korean kimchi salad;
- some cheeses (eg Gouda, mozzarella, cheddar).
Nutritional supplements containing a suitable combination of probiotic bacteria and yeast are also available in pharmacies and online stores. These may include fructooligosaccharides, which serve as food and energy for friendly bacteria.