Among diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, biliary dyskinesia is the most common disease. This disease does not pose a threat to human life, but it still brings with it many unpleasant surprises.
Knowing the symptoms of the disease allows you not to confuse it with other serious diseases. In addition, dyskinesia is often accompanied by complications and requires timely treatment.
In case of illness, the outflow of bile from the liver into the bladder and through the ducts is significantly hindered. But at the same time, no pathological changes occur in the structure of the liver and gallbladder with ducts.
During examinations, doctors find two variants of disturbances in the functioning of the gallbladder in patients: it can contract very quickly and often, or, conversely, too slowly. In general, every third person in the world suffers from dyskinesia.
What it is?
Gallbladder dyskinesia is a decrease in the tone and motility of the gallbladder and ducts. The disease is divided into two main types: hypokinetic and hyperkinetic . The latter option most often occurs in young people. The first is for people with unstable mental health and people over 40 years old.
Brief medical history
The concept of dyskinesia first appeared at the beginning of the 20th century, when a patient with severe pain in the right hypochondrium was operated on. An autopsy revealed no inflammation or stones in the gall bladder. Then therapists began to deal with this disease.
Prevalence and significance
Every third person on the planet suffers from this disease. But not all patients seek medical help, which makes it impossible to accurately calculate their number.
Women suffer from dyskinesia much more often than men. This is explained by the peculiarities of hormonal and metabolic processes in their body. Most often, the disease develops in women of asthenic physique at a young age. The disease often occurs even in children during adolescence.
Dyskinesia accounts for approximately 12.5% of diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. In most cases, it is a secondary disease after pancreatitis, gastritis or other gastrointestinal disease. In approximately 70% of all cases, dyskinesia has a hypotonic form.
Is hypotonicity of the gallbladder dangerous?
Reduced wall contractility causes discomfort associated with eating. Patients are constantly bothered by unpleasant sensations in the epigastrium.
Complications of hypotension pose a danger to life:
- Constant stagnation of bile causes precipitation of bile salts. First, suspension and sand are formed, then stones appear. Calculous cholecystitis (this is the name of this disease) is a direct indication for removal of the bladder.
- Microorganisms enter the bile that remains in the bladder for a long time from the intestines. They cause inflammation of the gallbladder - cholecystitis. Patients relieve mild attacks of cholecystitis on their own, at home. Severe inflammation requires hospitalization. When inflammation passes into a gangrenous form, removal of the bladder in emergency mode is indicated.
Hypotension of the gallbladder in a child is more pronounced. His parents notice that after eating he complains of abdominal pain and nausea. Children under 3 years of age often vomit.
A feature of the course of the disease in childhood is the absence of formation of gallstones.
Causes
Dyskinesia can be primary or secondary depending on the causes of the disease.
The reasons for the primary option are:
- constant stress;
- disruption of cholecystokinin production;
- psychosomatic diseases;
- imbalance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system;
- eating disorders;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- asthenic body type;
- allergic diseases.
The disease of the secondary type develops after a number of diseases or conditions:
- disruption of the production of intestinal hormones. The motility of the gallbladder and biliary tract depends on this;
- gastritis, colitis and other gastrointestinal diseases;
- inflammatory processes in the abdominal organs, for example, pyelonephritis or ovarian cyst;
- cholangitis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, hepatitis;
- gastrointestinal diseases that arise due to pathogens;
- helminthic infestation;
- endocrine diseases;
- congenital anomaly of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Symptoms of the disease
Impaired motor activity of the gallbladder and its ducts is expressed in various symptoms. When the organ's ability to contract is insufficient, hypotonic dyskinesia occurs.
With increased contraction of the gallbladder, hypertensive dyskinesia may develop. With hypotonic-hyperkinetic dyskinesia, the patient has symptoms of two forms of the disease.
With hypomotor dyskinesia of the gallbladder, a characteristic symptom is prolonged pain in the right upper abdomen. With errors in nutrition and after stress, the pain may intensify. Belching may occur after meals or between meals.
If you eat improperly, vomiting or nausea occurs. After physical activity and in the morning, an important symptom of this type of dyskinesia is bitterness in the mouth. As a result of insufficient flow of bile into the lumen of the small intestine, the patient's appetite worsens.
A characteristic symptom of this type of dyskinesia is also constipation, as a result of which the density of stool increases. Due to a disruption in the process of fat breakdown, the patient often develops obesity. Also, with this form of the disease, disorders of the autonomic nervous system appear. They are expressed as:
- poor sleep;
- increased salivation;
- lowering blood pressure.
With hypermotor dyskinesia of the gallbladder, acute pain in the form of colic occurs in the right hypochondrium. In some cases, it can radiate to the heart area and resembles the pain of angina pectoris. Due to the uneven flow of bile into the lumen of the small intestine, the patient develops decreased appetite and decreases body weight in the case of a long course of the disease.
During an attack, nausea or vomiting and loose stools often occur. When the disease worsens, the patient also experiences disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. They manifest themselves in high blood pressure, headaches, rapid heartbeat, and sweating. When there was no attack, the following was recorded in patients:
- aching pain in the heart area;
- fast fatiguability;
- irritability.
Clinical course: signs and symptoms
The clinical picture of hypokinetic type GIB differs from the signs of hypermotor function of the gallbladder, so it is necessary to know the features of this type of pathology and the main symptoms. This will allow you to consult a doctor in a timely manner and avoid serious consequences.
Tell your doctor about any accompanying symptoms
Pain syndrome
Pain with any type of bile duct dyskinesia is the main diagnostic sign. They can occur after eating or exercising, lifting heavy objects, or bending over. The nature of the pain depends on the degree of hypotension (slight decrease in tone or complete absence of peristalsis) of the gallbladder and dietary habits (a large volume of food requires an increased volume of bile). In most cases, patients complain of dull pain of moderate or high intensity occurring in the right hypochondrium. At home, it is almost impossible to differentiate these pains from liver diseases, so self-diagnosis with such localization of pain is unacceptable.
Palpable pain may indicate serious acute or chronic diseases
Features of pain with hypokinetic arthroplasty also include:
- exacerbation of a painful attack after overeating or prolonged fasting (differential diagnosis with a stomach ulcer is necessary);
- displacement of sensations into the epigastric space - the area under the xiphoid process of the sternum (can blur the clinical picture, which will lead to an incorrect diagnosis without specialized diagnostics);
- irradiation to the right shoulder blade, arm or shoulder (less often to the neck);
- sharp pain on palpation of the right upper quadrant.
The use of antispasmodics for hypokinetic disorders of gallbladder peristalsis is ineffective
Note! The absence of an analgesic effect from the use of antispasmodics can also be regarded as a diagnostic sign of hypotonic type VAD.
Digestive disorders
Digestive disorders are typical symptoms for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and organs of the hepatobiliary system. After food enters the duodenum, a portion of bile is needed for further digestion and breakdown.
Structure of the human gastrointestinal tract
If bile does not enter the small intestine, typical symptoms of functional dyspepsia appear:
- bowel dysfunction (mainly diarrhea);
- pain and bloating in the abdomen;
- feeling of painful fullness after eating;
- flatulence syndrome (the passage of large amounts of intestinal gas with a pungent odor);
- nausea not associated with food intake;
- causeless vomiting (most often one-time).
Bitterness in the mouth can be a symptom of serious illnesses
Along with these signs, the patient may complain of bitterness in the mouth, bad breath, weakness and headaches. Heartburn is not typical for this pathology.
Blistering symptoms
This is a set of diagnostic signs named after the doctors who discovered and described them. These symptoms may indicate diseases of the bile ducts and gallbladder, which allows the doctor to correctly prescribe a set of primary diagnostics and begin the necessary treatment in a timely manner.
Pain points for gallbladder diseases
Table 1. Blistering symptoms
| Name of the symptom (syndrome) | Description or characteristics |
| Risman's symptom | The patient needs to hold his breath during the inhalation phase. At this time, the doctor performs percussion or tapping with the edge of the palm along the lower border of the twelfth rib on the right side. A symptom is defined as positive when pain appears at the point of tapping. |
| Ker's symptom | The patient needs to take a deep breath, during which the doctor taps the area of the gallbladder. A symptom is considered positive when acute pain occurs. |
| Boas's sign | It is a hypersensitivity reaction (mild pain, tingling, numbness, “pins and needles”) in the lumbar region on the right side. |
| Lepen's symptom | It is considered positive if the patient experiences a pain reaction in response to tapping with the index finger at the point of projection of the gallbladder (the finger should be bent). |
| Vasilenko's symptom | The patient needs to take a deep breath. At this time, the doctor taps the lower costal arch on the right side with his palm. The appearance of pain is regarded as a positive sign of hypotonic type VA. |
| Frenicus symptom | The doctor palpates the space between the sternoclavicular muscles, located behind the saphenous cervical muscle. Pain with a positive symptom can radiate to the lower abdomen and thigh. |
| Murphy's sign | Pain appears with uniform pressure on the area of the gallbladder during the inhalation phase. |
| Grekov's symptom | It is considered positive if, when tapping along the lower edge of the ribs, severe dull or dagger-shaped pain appears. |
Ker's symptom
Note! The symptoms of Kehr, Boas and Risman are the main diagnostic symptoms, the appearance of which by 90% indicates diseases of the gallbladder. In total, there are 8 syndromes included in the complex of cystic symptoms, but the determination of positive reactions in at least three of them is considered sufficient to make a preliminary diagnosis.
Liver changes
Changes in the liver with dyskinesia of the bile ducts do not always appear. Most often, such symptoms occur when the cause of hypotension of the gallbladder is liver disease: cirrhosis, parasitic liver infections, hepatitis, fatty degeneration. During palpation, the doctor can detect an increase in the organ and a change in its structure, as well as a slight displacement.
Stages of development of liver cirrhosis
This symptom can only be considered as a manifestation of ADHD in conjunction with other signs, since liver enlargement itself can be a manifestation of other diseases, for example, infectious mononucleosis.
Cholestatic syndrome
Cholestatic syndrome (cholestasis) is a pathology in which the cause of slow or insufficient flow of bile into the duodenum is a violation of bile formation. Clinically, cholestatic syndrome can manifest itself as yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes, itching, constipation, and a bitter or metallic taste in the mouth.
Cholestasis - general information
Pain syndrome with cholestasis can change its localization and radiate to the posterior wall of the right rib and spine. With cholestasis, the liver is always enlarged, and the urine becomes cloudy and dark brown in color (many compare it to the color of beer).
Important! One of the most typical signs of delayed bile formation is lightening or discoloration of stool.
Diagnosis
A variety of methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- Ultrasound helps determine the degree of emptying of the gallbladder, its shape and congenital developmental anomalies.
- General blood analysis.
- Blood chemistry.
- X-ray studies (cholecystography; infusion cholecystography; cholangiography).
Doctors also prescribe laboratory tests:
- duodenal intubation;
- study of bile composition;
- examination of bile for the presence of parasites;
- biochemical study of bile portions “B” and “C”;
Diagnostics
Additional diagnostics are necessary to make a diagnosis and determine the type of functional disorder. The examination protocol includes the following methods, which are reflected in Table 1.
Table 1. Diagnosis of biliary dyskinesia
| Kinds | Indicators |
| General clinical blood test | Detailed leukocyte formula, ESR |
| Biochemical blood test | Level of bilirubin, its fraction, alkaline phosphatase, ALT, cholesterol, y-glutamyl transpeptidase |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder | Reflects the type of dyskinesia and the state of the organ |
| Dynamic cholescintigraphy | Detects initial changes in the biliary tract, impaired contraction of the gallbladder, manifestations of reflux |
| Sphincter of Oddi manometry | Determines the level of pressure in the area of smooth circular muscle on the papilla of Vater |
Treatment
Treatment of dyskinesia should be aimed at improving the flow of bile and reducing inflammation in the gallbladder. Attention is also paid to the fight against parasites and normalization of the nervous system. When choosing medications, the type and form of the disease must be taken into account.
Drugs
The following drugs are used to stimulate the secretory function of the liver:
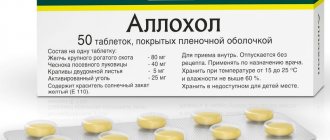
- Allohol based on animal and plant components. It promotes the production of bile, eliminates putrefaction processes, and improves the motility of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Plant-based Flamin with anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects.
- Hepatoprotective agent Ursosan, which has an excellent choleretic effect and reduces the concentration of cholesterol in the blood.
- The natural choleretic drug Holosas improves metabolic processes in the liver and enhances the secretion of bile.
- Magnesium Sulfate with choleretic and laxative effects.
- Oxafenamide to eliminate cholesterol stones and eliminate pain.
In addition to choleretic medications, other groups of drugs are also used: Papaverine, Besalol, No-Shpa, Duspatalin and others.
Surgery
For biliary dyskinesias, surgical treatment is not indicated. If cholecystectomy is done incorrectly, it can lead to post-cholecystectomy syndrome.
Folk remedies
A good effect is obtained by using:
- medicinal plants in the form of decoctions and infusions (St. John's wort, calendula flowers, sage leaves and others);
- carrot juice combined with spinach, parsley, celery juice;
- milk with fresh carrot juice (can be taken every day for a month);
- a mixture of red wine, honey and aloe;
- applying cold compresses to the liver area before bedtime (for hypotonic form);
- hot compresses (for hypertensive form of the disease);
- laying down thick slabs of blue clay;
- enemas with corn oil (for hypertensive dyskinesia).
Diet
For such a disease, a special diet is indicated. Success in treatment depends on it, and it must be followed for a long time, sometimes up to a year. The goal of dietary nutrition is to normalize the function of the biliary tract, liver and gastrointestinal tract.
During an exacerbation of the disease, it is forbidden to eat smoked, fatty, salty, fried and sour foods. You should also not eat hot seasonings, radishes, sorrel, onions, garlic, or alcohol.
All foods that increase gas formation, such as rye bread and peas, are prohibited. You should not eat chocolate, cocoa, black coffee, pastries with cream, whole milk, or marinades. In addition, it is important to eat small portions and several times a day.
Treatment of dyskinesia at home - folk remedies and diet for dyskinesia
Treatment of the disease in question should begin with diet. This will not only speed up the recovery process, but will also protect against the development of various exacerbations: gallstone pathologies, acute cholecystitis.
Diet therapy for dyskinesia of the gallbladder and ducts includes several nuances.
General aspects
Relevant for any form of this disease.
To ensure complete emptying of the gallbladder, patients should follow several rules:
- You need to eat often (up to 5 rubles per day), in small portions.
- The interval between meals should be at least 3 hours.
- During the evening meal, the amount of meat products should be minimized.
- Dishes should be warm: in no case hot, but not cold either.
- Fermented milk products in the morning and evening are an excellent prevention against dysbiosis (which negatively affects the functioning of the gallbladder).
- Food can only be heated in vegetable oils.
| Products that need to be excluded entirely | Foods that should not be consumed during exacerbations | Products that can be included in the diet |
|
|
|
Nutrition for the hypomotor form of the disease in question should be aimed at enhancing the motility of the bile ducts
The daily menu may include the following products:
- Fresh fruits.
- Baked or boiled vegetables. Stewed vegetables are also allowed.
- Dairy products: cream, sour cream.
- Bread only black varieties.
- Eggs.
In addition to vegetable fats, small quantities of butter are also allowed.
The main task of the diet for hypermotor dyskinesia is to exclude from the daily menu foods that accelerate the processes of bile formation.
Patients with this form of the disease should avoid:
- Fatty broths.
- Black bread varieties.
- Animal fats.
- Sodas.
- Fermented milk products with a high percentage of fat.
- Fresh vegetables.
As an additional method of treatment, you can use traditional medicine. There are many medicinal herbs and herbs, decoctions of which will help improve the functioning of the gallbladder and ducts.
However, all these points must be agreed with the attending physician , because the choice of a specific herbal medicine will be determined by the form of the disease in question and the individual characteristics of the body.
| Hypertensive form | Hypotonic form | |
| Medicinal herbs, juices that are used to prepare a decoction. Often several herbs are used at once. |
|
|
Prevention
To prevent this disease, it is necessary to follow a balanced diet. It is important to maintain intervals between meals. Avoid drinking alcohol, carbonated drinks, pickled and spicy foods. It is important to normalize the work and rest schedule and engage in physical exercise. It is also necessary to avoid stress and psycho-emotional stress.
It is necessary to promptly treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, chronic infections, neuroses and allergic diseases.
Medicines for the treatment of hypotonic dyskinesia
For dyskinesia of the hypotonic type, which is characterized by a deterioration in the tone of the muscle tissue of the bile ducts, the following medications are usually prescribed:
- Allohol
This medicine belongs to the group of choleretic drugs. The basis of its composition is of natural origin (animal bile).
Treatment with Allochol helps improve liver function and prevent stone formation in the gallbladder cavity, which is caused by stagnation of bile in this organ. In addition, with the help of this drug, the chemical composition of bile is normalized, and the motility of the digestive system is also stimulated. The following diseases are contraindications to the use of this medicine:
- obstructive jaundice;
- peptic ulcer of the intestines and stomach;
- hepatic dystrophy;
- acute form of hepatitis;
- individual intolerance to the components included in the drug.
This natural remedy can be prescribed to pediatric patients and women during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Nikodin
This drug has choleretic, choleretic, anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, antimicrobial and bacteriological effects. Nicodine contains substances that are derivatives of nicotinic acid amide and formaldehyde.
Its intake helps to increase liver secretion, increase the concentration of bile acids and facilitate the flow of bile into the duodenum.
Contraindicated for people with individual intolerance to the components of this product. Increased caution in its use should be observed in cases of bile stagnation (cholestasis) and in antacid forms of gastritis.
Side effects when using Nicodin are: disorders of the digestive system; allergic reactions to the drug and the possibility of severe pain. As a result, only a qualified doctor can prescribe it.
- Holenzym
This medicine contains components such as natural animal bile and digestive enzymes. “Cholenzim” also belongs to the drugs of combined action, and has not only a choleretic effect, but also has a beneficial effect on the digestive process due to the enzymes included in its composition.
Taking this medicine is prohibited in the following cases:
- acute pancreatitis;
- obstructive jaundice;
- peptic ulcer of the intestines and stomach (during its exacerbation).
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should be especially careful when using this medicine. The following negative side effects may occur:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | heartburn |
| 2 | itchy skin |
| 3 | skin rashes |
| 4 | diarrhea |
| 5 | increase in blood transaminase levels |
- Cerucal
Its purpose is to prevent nausea and vomiting in a patient with this diagnosis.
A similar effect is achieved by blocking the urge to vomit, transmitted to the brain by impulses. Available both in the form of tablets and in liquid dosage form (injection solution).
Contraindications to the use of Cerucal are:
- pheochromocytoma;
- intestinal obstruction;
- presence of intestinal bleeding;
- perforation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- tumor-like formations;
- epilepsy and other convulsive conditions.
Pregnant women and nursing mothers are strictly prohibited from taking this medication. If an emergency arises, a Cerucal injection is allowed.
Possible side effects of this drug include:
Read also: Is it possible to take Ursosan and Ursofalk after removal of the gallbladder?
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- headache;
- increased fatigue;
- depression;
- tachycardia;
- agranulocytosis;
- sudden changes in blood pressure;
- dry mouth;
- stool disorders;
- allergic reactions;
- spastic colitis.
- Hofitol
This drug belongs to the group of hepatoprotectors (protectors of liver cells - hepatocytes), and also has a choleretic effect.
Taking Hofitol helps normalize the production of liver enzymes, improve metabolic processes in the body and reduce cholesterol levels in bile. In addition to the above, this medicine contains a complex of vitamins and biologically active substances that help normalize the functioning of the biliary system (liver + gall bladder). Since its composition is based on natural ingredients, Hofitol can be prescribed to patients regardless of their age category. Dosage forms – tablets and solutions (both for injection and for internal use).
Contraindications:
- cholelithiasis;
- obstruction of the bile ducts;
- kidney pathologies;
- severe liver failure;
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
As a rule, there are no adverse reactions to Hofitol, but the following negative symptoms may appear:
- diarrhea;
- allergic reactions;
- swelling of the skin;
- swelling of the subcutaneous tissue.
To treat dyskinesia, experts also recommend blind probing (tubage) of the gallbladder.
For this purpose: mineral water, sorbitol or magnesia are used. Similar procedures must be performed three times a year. In the evening before the tubing day, you should perform a cleansing enema of the intestines, or cleanse it with laxatives. The pre-prepared tubage solution is drunk the next morning, after which a warm heating pad is placed on the right side of the abdomen and held there in a supine position for one and a half to two hours. All day after the procedure, you must follow a gentle fruit and vegetable diet.
Prognosis and prevention
The earlier treatment begins, the better the prognosis. Timely complex therapy allows you to put the disease into stable remission. The situation becomes more complicated with late diagnosis and concomitant diseases of the gallbladder.
To prevent hypomotor dyskinesia, adhere to the following recommendations:
- promptly identify and treat diseases that lead to disruption of the outflow of bile;
- give preference to moderate physical activity: yoga, swimming, daily walking of at least 7000-10000 steps, running, breathing exercises;
- eliminate the source of stress, take magnesium supplements to restore the psycho-emotional state;
- observe the drinking regime: the daily norm is calculated using the formula - 30-50 ml multiplied by body weight;
- normalize body weight;
- adhere to the basic principles of a healthy lifestyle.
At the first symptoms of a disorder, it is important to promptly seek medical help.
Causes
Hypomotor dyskinesia can be caused by the following reasons:
- hormonal changes: pregnancy, taking COCs, which help reduce organ contractility;
- a diet in which fatty foods predominate, irregular meals, consumption of high-calorie foods quickly, as a snack;
- systemic pathologies: myasthenia gravis, scleroderma, amyloidosis, diabetes mellitus, celiac disease (gluten intolerance);
- pathologies of inflammatory origin, the influence of which changes the composition of bile: cholelithiasis, cholangitis, cholecystitis, spasm of the sphincter of Oddi;
- allergic reactions;
- helminthic infestation;
- regular exposure to stress.
The disorder can also occur as a complication of gastritis, enteritis, after surgery.
Under the influence of the described factors, the outflow of bile is disrupted. Congestion in the area of the gallbladder is fraught with the development of secondary inflammation and digestive disorders.
Biliary dyskinesia
This disease is an imbalance in the contraction of the biliary tract, as well as the sphincter of Oddi located on the papilla of Vater, which regulates the release of bile into the lumen of the duodenum.
The pathology itself does not cause any particular harm to the human body, but can lead to the development of gallstone disease.
Most people suffering from this disease are representatives of the fairer sex. Characteristic signs of biliary dyskinesia of the hypomotor type include dull pain throughout the right hypochondrium, poor appetite, constipation, bloating, and bitterness in the mouth. The hypermotor type is characterized by attacks of acute pain with vomiting and loose stools. With a mixed type, both one and other manifestations may occur.
Complications
The lack of high-quality, timely medical care is fraught with complications:
- cholelithiasis;
- chronic cholecystitis - with the addition of secondary infections;
- obstructive jaundice, which occurs against the background of bile stagnation;
- cholangitis caused by the influence of infectious pathogens on the bile ducts;
- with insufficient supply of bile to the intestines, malabsorption develops - impaired absorption of vitamins and nutrients with the subsequent development of deficiency conditions.
Severe intoxication of the body and hepatic encephalopathy are also possible. To prevent complications, at the first signs of a disorder, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Video: Gallbladder dyskinesia - symptoms, causes, treatment