Features of the disease
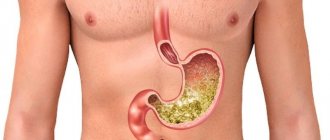
Inflammation of the esophagus is commonly called esophagitis. Since the cause of the pathology is the willful reflux of stomach contents, the prefix “reflux” appears. Provoking factors can be external or internal; the disease progresses differently in each case. The pathological process involves the upper part of the mucosa or deep tissues. In this regard, esophagitis is distinguished as catarrhal, edematous, erosive, hemorrhagic, necrotic.
The initial form of the disease is catarrhal. The inflammatory process is superficial or in certain parts of the esophagus. As the disease progresses, in the absence of proper therapy, an edematous form appears, which causes noticeable pain. Against the background of increased acidity, erosions develop over time, which become inflamed, bleed, and irritated during the passage of food. The lack of qualified therapy leads to the appearance of compactions, ulcers, deformations, and narrowing of space. In severe forms of the disease, cells mutate and become cancerous.
Inflammation of the esophagus, which occurs as a result of temporary exposure to negative factors - trauma, accidental ingestion of objects, acid burns, is treated fairly quickly and rarely causes complications. Internal factors are often associated with other gastrointestinal pathologies; in order to achieve a therapeutic effect, the root cause must be eliminated. Which can be problematic.
How to detect a connection between a sore throat and stomach
To determine the relationship between sore throat and gastrointestinal problems, it is necessary to analyze the existing symptoms.
If discomfort in the throat (for example, a lump) appears in the morning, goes away after two to three hours and occurs again every day for a week, then this is likely evidence of the presence of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
It is necessary to exclude other manifestations observed during infections of viral origin. If there are symptoms such as fever, sore throat, reflux esophagitis, it can be excluded.
You should not try to diagnose yourself and choose therapy yourself.
This is the prerogative of the doctor; it is for this reason that at the first manifestations of the disease the patient should go to the doctor, who will write a referral to the necessary specialists (in the field of gastroenterology or otolaryngology).
The appropriate doctor will probe the patient’s stomach, collect information about the patient’s medical history, living conditions and past illnesses.
In addition to carrying out timely diagnosis, you should be a supporter of a healthy lifestyle, in which there is no place for alcohol and cigarettes.
The key to health is compliance with basic rules, namely proper nutrition, rich in vitamins and minerals, avoidance of fried and fatty foods, minimal consumption of sweet foods, coffee and strong teas.
You need to eat more fruits and vegetables, make juices and purees from them. Stress, emotional stress, physical inactivity can only contribute to the development of gastritis and negatively affect the stomach. In this regard, it is advisable to be less nervous and exercise more.
It is also extremely important to visit medical specialists on a regular basis and undergo examinations.
This will facilitate the prompt detection of diseases that do not have pronounced symptoms. Only a strong immune system can effectively fight the disease.
To this end, it is important to ensure adequate sleep and rest, a balanced diet and moderate physical activity.
Strengthening the immune system is possible through hardening, taking a contrast shower during water procedures.
Causes
The main cause of inflammation of the esophagus is increased acidity in the stomach. Under normal conditions, the esophagus is protected by a special sphincter, which prevents the contents of the digestive organ from moving in the opposite direction. An increased amount of hydrochloric acid causes inflammation of the stomach and reduces the tone of the sphincter muscles. As a result, acid enters the esophagus and burns the mucous membrane. There are no significant painful sensations, but the main symptom is a sour taste in the mouth. Belching and heartburn may occur.
Experts say the main provoking factor is a disrupted diet and poor diet. Direct inflammation of the throat occurs with frequent consumption of hot drinks, carbonated drinks, alcoholic drinks with a high alcohol content. Spicy, fatty, salty foods, sweets provoke an increase in acidity, the development or exacerbation of gastritis. Then the esophagus becomes inflamed. Since everything in the digestive system is interconnected, gastritis, gastroduodenitis, and colitis can provoke esophagitis.
Recently, experts keep reminding that the cause of gastritis is the bacteria Helicobacter pylori, which, with reduced immunity, begin to multiply. They, as well as a reduced protective reaction, can be provocateurs of inflammation of the esophagus. Esophagitis can be caused by an infection or virus. The situation is especially common with prolonged vomiting.
The cause of esophagitis can be instrumental methods of examining the gastrointestinal tract. A device with a hose is inserted through the mouth, which is lowered into the stomach and small intestine. If the size is incorrectly selected or the specialist is poorly qualified, side effects appear after the procedure. In addition, esophagitis can be the cause of allergies, autoimmune transformations - food, contact, bronchial asthma.
Provoking factors:
- Spicy, fatty, too hot food;
- Overweight, obesity;
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- Sphincter pathology;
- Metabolic disorders, endocrine diseases;
- Medicines;
- Chronic inflammatory processes in the body.
All diseases manifest themselves and worsen when the body’s protective functions decrease, so weak immunity can also be called the cause.
If your throat hurts due to gastritis, conclusions
If you suffer from a sore throat, sore throat, or secretion of a large amount of mucus in the morning, think carefully about whether you also have problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Gastritis, ulcers, in the end, even the individual anatomical features of the gallbladder - its uncharacteristic “curvature” - is already a reason to think about the nature of a sore throat. Remember that the main symptom of reflux esophagitis is heartburn.
The peak of discomfort in the throat with reflux esophagitis occurs in the morning, when gastric juice refluxes into the esophagus and further onto the back wall of the pharynx. In such cases, the picture is as follows: the throat hurts in the morning, and after breakfast the pain goes away. And this is not surprising: at breakfast a person drinks, for example, a glass of tea. The liquid washes away the acid - and it becomes easier.
Despite the seeming absurdity of the situation, gastroenterologists perfectly understand what complaints about a sore throat mean and are able to accurately find the right solution.
Bad breath is also a reason to be wary. It can be the result of “fermentation” in the stomach, a collision of bile and gastric juice. If you cough up a large amount of mucus in the morning, this is also an alarming sign. After all, you need to somehow protect yourself from the reflux of gastric juice into the mucous membrane of the back wall of the pharynx. As a result, she is intensively engaged in her direct task - mucus production.
Sources:
- https://pobedigastrit.ru/lechsimpt/mozhet-li-bolet-gorlo-pri-gastrite.html
- https://viplor.ru/gorlo/mozhet-li-ot-zheludka-bolet
- https://gastritinform.ru/ogastrite.ru/konsultacii/mozhet-li-bolet-gorlo-iz-za-bolezni-zheludka/
- https://aif.ru/health/life/40761
Types of disease
Esophagitis can be acute or chronic. In the first case, the symptoms are pronounced, in the second they are mild, but are recurrent. According to the degree of involvement of organ tissues in the pathological process, several types are distinguished:
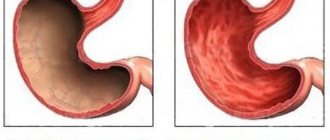
- Catarrhal. Inflammation of the mucous membrane on the upper layer occurs. There is redness and irritation. It responds well to treatment.
- Erosive. Wounds and erosions appear on the surface of the mucous membrane as a result of a long-term inflammatory process and increased acidity. Long-term therapy with special medications and diet are required. Erosion heals, but when exposed to unfavorable factors, relapses occur.
- Hemorrhagic. Inflammation is associated with mechanical, chemical, and infectious damage. The mucous membrane peels off and bleeds, which causes significant discomfort and pain.
- Necrotic. The severe stage of the disease is characterized by the formation of fibrous tissue and purulent plaque. The ulcers heal poorly, bleed, scar tissue forms, which narrows the lumen of the esophagus, and the cells degenerate. Necrotizing esophagitis is life-threatening and often transforms into cancer.
Any form of the disease requires qualified therapy, but if in the first stages folk remedies cope with the symptoms, in the last stages the most effective drugs do not help much. It is very important to diagnose the disease in a timely manner to prevent complications.
Symptoms
Manifestations of inflammation of the esophagus:
- Lump in the throat;
- Painful swallowing;
- Increased salivation;
- Pressure behind the sternum;
- Dry cough;
- Belching;
- Sour taste in mouth.
Since the irritated mucous membrane becomes inflamed, the lumen of the esophagus narrows, and a sensation of coma appears. When swallowing food and passing it into the stomach, discomfort and painful sensations of varying degrees of severity are felt. Increased salivation is a consequence of high levels of hydrochloric acid.
Causes and symptoms of sore throat
The throat can hurt not only due to the reflux of gastric secretions into the esophagus. The following diseases may be the cause:
Symptoms of the disease
In order to associate a sore throat with problems of the digestive tract, a clearer clinical picture and the presence of additional symptoms are necessary:
- the throat usually hurts in the morning;
- pain persists for several weeks;
- after a person gets out of bed, the pain goes away after a few minutes or hours;
- there are no symptoms characteristic of a viral disease;
- cough due to irritated larynx;
- heartburn and dryness in the larynx;
- nausea and problems swallowing food;
- sour taste in the mouth, especially in the morning;
- belching after each meal, becoming more intense in the evening;
- you feel a lump in your throat;
- labored breathing;
- chest pain.
If there is a cough, a sore throat, a fever, a person feels unwell, this is a viral disease that is not associated with the stomach. The reflux of gastric juice into the throat occurs when the diet and diet are violated. Fatty and fried foods often provoke gastric reflux.
Consequences of a sore throat due to stomach
When gastritis worsens, especially due to bad habits, the pain that occurs in the stomach can radiate to the throat. Reflux does not go away without a trace, gastric secretions cause irritation of the larynx and this has a bad effect on the mucous membrane of the throat.
An inflammatory process in the larynx may begin, so if characteristic symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. The human body is designed in such a way that all internal organs are interconnected, so digestive problems can lead to serious problems with the throat.
The acidic environment of gastric juice can corrode the mucous membrane of the larynx, which will cause the appearance of ulcers and erosions.
Pathogenic microbes, getting on the loose, inflamed mucous membrane, begin to multiply and provoke the development of various diseases, these can be:
- focal sore throat;
- throat cancer;
- laryngitis;
- inflammation of the vocal cords;
- viral diseases of the respiratory system.
Diagnosis must be carried out in a clinical setting by a gastroenterologist. Additional measures are needed to make an accurate diagnosis and identify the causes of sore throat.
Can my stomach hurt my throat?
At first glance, it seems that the digestive organs and the throat are in no way connected. However, it is not. The esophagus borders on one side with the stomach, on the other with the pharynx. In the absence of qualified treatment of the stomach, the inflammatory process involves the small and large intestines, pancreas, gallbladder, as well as the esophagus, larynx, and throat.
Painful sensations are pronounced during sleep, in the morning. In a lying position, the sphincter muscles relax, acid enters the esophagus, increasing unpleasant symptoms.
How to tell if your throat hurts from your stomach
Throat diseases are caused by bacteria and viruses. This is one of the main symptoms of acute respiratory infections, flu, and intestinal infections. Since many stomach diseases are associated with the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria Helicobacter pylori, it is very easy to associate discomfort in the throat. Against the background of decreased immunity, microorganisms begin to multiply on various mucous membranes, including the throat.
To choose the right treatment, you need to find out the root cause of the pain - a cold or gastritis.
Main distinctive features:
- It hurts at night, in the morning, and subsides during the day;
- There is an unpleasant soreness;
- It does not increase, does not decrease, everything is at the same level, even when using standard remedies for sore throat;
- There are no other cold symptoms, but nasal discharge may appear;
- There is increased salivation, which is a symptom of inflammation of the esophagus;
- There is pressure in the stomach, there is nausea;
- Sour taste in mouth.
The sore throat does not subside after using antibacterial sprays, lozenges, gargles, and subsides after a dose of antacids. With a sore throat, the pain intensifies every day, then weakens. In general, all signs of a cold disappear within a week. With a sore throat caused by gastritis, everything remains at the same level, the pain condition can be assessed as average.
Treatment of sore throat with gastritis of the stomach
If the appearance of a sore throat can be correlated with eating, then it is possible that the cause lies in problems with the digestive system or impaired motility of the esophagus. For example, with a disease such as gastroesophageal reflux, intestinal contents reflux into the esophagus, a feeling of discomfort in the stomach appears, a sour taste in the mouth, and an unpleasant lump rolls up in the throat.
Irritation of the esophagus (spicy foods, alcohol, swallowing a probe during endoscopic examination), as well as hiatal hernia, can also manifest themselves in a similar way. Treatment of food reflux should be carried out simultaneously with changes in diet and lifestyle.
If your throat hurts due to stomach problems, then getting results is possible only after changing your eating habits and lifestyle. Otherwise, taking pharmacological drugs and medications can only provide a short-term effect and the cause of the problem of sore throat will not be solved.
Therapy and prevention of the disease aims to normalize the functioning of the digestive system and reduce the effects of stomach acid. Features of treatment and prescription directly depend on the causes of disruption of the digestive system and the severity of the patient’s symptoms.
Several different groups of drugs are prescribed medicinally:
- blockers of H2 histamine receptors that produce hydrochloric acid - Ranitidine, Famotidine, Cimetidine, should be taken before meals for gastric reflux or after meals for heartburn;
- drugs of the inhibitor group: Omeprazole, Omez, which stop acid production, are taken for 14 days, eliminate the symptoms of gastric reflux and heal the mucous membrane of the esophagus;
- anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of gastritis and other digestive problems;
- drugs that protect mucous membranes;
- prokinetics to provide pressure on the lower esophagus and enzymes to improve digestion.
If there are no other pathologies of the digestive system, then it is enough to neutralize the effect of stomach acid after eating, and the throat will stop hurting.
A necessary action to normalize the patient’s condition is to ensure proper nutrition and eliminate foods from the diet that lead to increased acidity levels. These include any types of citrus fruits, onions, garlic. It is necessary to exclude all fatty and fried foods, pickles, and sweets from the diet.
Treatment with folk remedies for sore throat with gastritis
Not only medications, but also folk remedies are effective for therapy and prevention. Good results are observed with regular drinking of herbal decoctions: yarrow; linden; chamomile; St. John's wort; calendula.
Such medicinal plants improve digestion and help relieve pain in the stomach, which has a beneficial effect on the larynx area and eliminates discomfort in this area. It is recommended to use dry herbs or special teas for recipes, since when using alcohol-containing tinctures, the mucous membranes become irritated and the stomach begins to ache.
For pronounced symptoms, it is recommended to use a herbal decoction recipe. The product is prepared as follows: 2 tbsp. l. flax seed; 200 ml boiling water. The seed mixture is poured with water and left for 8 hours. After filtering, the infusion is taken 0.5 cups for a month before meals.
If your throat hurts due to heartburn or gastritis, then a good effect is observed from using potato juice. It is worth considering that the product must be freshly prepared, otherwise its effectiveness is reduced significantly. This natural medicine is taken ¼ cup 20 minutes before meals.
Symptoms, treatment of “lump in throat” sign
The inflammatory process leads to swelling of the mucous membrane, which causes the walls to thicken and the lumen of the esophagus to narrow. A person feels this as the presence of a foreign body or a lump in the throat. In addition, a similar phenomenon occurs with muscle spasm. In the latter case, to eliminate unpleasant symptoms, antispasmodics are used - No-Shpa, Drotaverine, Meverine, Papaverine or sedatives - tincture of motherwort, valerian, glod, Nova-Passit.
To get rid of a lump in the throat completely, you need to stop the inflammation. To do this, you need to undergo a course of therapy from 7 to 30 days. Antacids temporarily relieve the condition, especially with an analgesic effect.
In addition, a lump in the throat can occur with diseases not related to the digestive system, so treatment is different.
- Stress;
- Pathologies of the endocrine system, enlarged thyroid gland;
- Osteochondrosis;
- Spinal hernia;
- Oncological tumor;
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
In each case, different medications are prescribed. In severe cases, surgery is indicated.
Treatment of the disease
Antacids are used in therapy if the cause of the disease is in the digestive organ.
Restoration of organs takes a long period and is treated comprehensively. First, the cause of the disease is established. If your throat hurts due to your stomach, the main methods of treatment include:
- Drug treatment: proton pump blockers;
- antacids;
- sedatives.
- fractions - 5-7 times a day;
- decoction of calamus root;
It is recommended to exclude all physical activity and heavy lifting. However, a course of gymnastics or physical therapy will be useful for reducing pain and normalizing the mental state. It is important to know and be able to distinguish the symptoms of sore throat due to respiratory ailments and pathologies of the esophagus and not to delay diagnosis. Timely treatment will prevent initial manifestations from developing into chronic pathologies.
Gastroesophageal reflux
It is the main provocateur of esophagitis. The reflux of acidic contents occurs regularly, causing the mucous membrane to become inflamed. Belching can be bitter, sour, airy, accompanied by heartburn, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Esophageal reflux is caused by the following factors:
- Gastrointestinal diseases;
- Spicy, fried foods;
- Coffee;
- Chocolate;
- Sweets;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Bad habits;
- Tight clothes, uncomfortable bra;
- Pregnancy;
- Lifting weights;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Stress;
- Exhaustion of the nervous system;
- Physical activity immediately after eating;
- Dry food.
Usually, esophagitis is caused by diseases of the digestive tract, but an unhealthy lifestyle, diet, and tight clothing can contribute to the development of inflammation.
Diagnostics
You can determine the presence of inflammation of the esophagus yourself by the characteristic symptoms. However, to choose the right treatment, you need to determine the root cause. To do this, you should seek help from specialists.
Making a diagnosis begins with a conversation. The specialist evaluates the clinical picture, listens to complaints, as well as the version of the appearance of symptoms. Performs abdominal palpation. In conclusion, he makes an assumption about a possible diagnosis and prescribes an examination.
It is mandatory to take blood, urine, and feces tests. A general blood test allows you to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, a biochemical test evaluates the functioning of certain internal organs. Urinalysis makes it possible to assess the functioning of the excretory system. Feces can tell about the presence of parasites in the body, internal bleeding, and the ability of the intestines to digest food.
The main diagnostic method is endoscopic examination. A special device is inserted into the esophagus through the mouth, allowing images to be transmitted to the monitor screen. During the study, the stage of the disease, type, and severity are determined. If there are ulcerative formations, material is taken for another research method - biopsy. Analysis of the contents of the esophagus allows you to determine or exclude oncological transformations. Additionally, fluoroscopy is prescribed, which allows you to see the accumulation of mucus, the appearance of tumors, and changes in relief.
Features of treatment
Therapy is aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms and preventing relapses. Carry out complex treatment with folk remedies and medications. The main condition for a quick recovery is adherence to a diet and diet. Methods and remedies are selected based on the complexity of symptoms and causes of esophagitis. You definitely need to reconsider your lifestyle and bad habits.
Treatment rules:
- Normalize your diet. The last meal should be at least 2 hours before bedtime. Avoid overeating and prolonged fasting.
- Eliminate foods that cause fermentation and increased gas formation from the diet.
- For the first 14 days of therapy, you must follow a strict diet. After the disappearance of painful symptoms, continue proper nutrition to prevent relapses.
- It is recommended to take sorbents - they remove toxins, reduce acidity, and help restore the mucous membrane.
- If you have a sore throat, rinse and treat with antiseptic solutions. Effective safe products - Chlorophyllipt, Orasept. For rinsing, use Furacilin and Streptocide tablets.
- Avoid bad habits - alcohol, smoking, coffee on an empty stomach.
- Direct all efforts to strengthen the body's protective functions.
- Normalize acidity. For this purpose, antacids, sorbents, probiotics, prokinetics, proton pump inhibitors, and gastroprotectors are used. Your doctor will help you choose the right treatment regimen.
If all instructions are followed, esophagitis can be cured fairly quickly; lack of therapy leads to serious complications. One of them is a narrowing of the esophagus. The lumen of the esophagus can narrow to 1 mm in diameter, which makes the passage of food, water and even saliva impossible.
Diagnostic features
Most often, therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating problems with the gastrointestinal tract and includes the mandatory cessation of bad habits, in particular, smoking as the main irritant for both the stomach and throat.
In parallel, medications can be prescribed to treat stomach problems, the choice of which depends on the stage of evolution of gastritis. These can be analgesics or antispasmodics, histamines and antacids; in more complex situations, antibiotics are prescribed.
If the symptoms discussed above are present, it is necessary to seek advice from a therapist, who, if necessary, will give a referral to a more specialized specialist - a gastroenterologist, as well as an otolaryngologist to determine the cause of the sore throat.
If you have symptoms of reflux, when gastric juice enters the esophagus, it is recommended to consult a physician. In most cases, the patient is given referrals to two specialists:
- gastroenterologist;
- otolaryngologist.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following studies are prescribed:
- FGDS to identify inflammatory processes, erosive changes in the stomach;
- X-ray of the esophagus to rule out a hernia;
- stomach acidity analysis;
- biopsy if there is a suspicion of cancer in the pharynx.
When a patient informs a doctor about a symptom such as a lump in the throat, it becomes necessary to exclude the possible development of all diseases that have this symptom. For a consultation you will need to visit:
- ENT doctor;
- endocrinologist;
- neurologist;
- psychotherapist;
- gastroenterologist.
The gastroenterologist prescribes a series of examinations and finds out whether the patient has inflammation of the gastric mucosa. When diagnosing gastritis, urine and stool tests are done.
It indicates which parts of the digestive tract are affected by pathology and what its nature is. It is mandatory to determine the acidity of gastric juice and test for bacterial infection in the stomach.
Of the instrumental methods, the most informative are abdominal ultrasound and gastroendoscopy.
Treatment with medications
In case of inflammation of the esophagus, provoked by temporary exposure to negative factors - trauma, instrumental examination, burn, rough food, antacids are used. The choice is extremely large, but Almagel in the form of a suspension is considered the most effective. The product envelops the mucous membrane, protects against irritation, stops the inflammatory process, and promotes healing of the mucous membrane. Take the drug 20 minutes before a meal or half an hour after a meal. Initially 4 times a day. As painful symptoms disappear, reduce the dosage to once. The duration of therapy is from 1 week to a month.
Other antacids:
- Maalox;
- Phosphalugel;
- Gaviscon.
Sorbents reduce acidity, remove toxins from the body, improve overall well-being, and protect the mucous membrane. The most common is Smecta. Sold in bags in powder form, it smells pleasantly of caramel. Before use, dilute in 100 ml of warm water, drink between meals up to 4 times a day. Smecta normalizes stool, thickens stool, and in case of an overdose, constipation can occur.
Other sorbents:
- Activated carbon;
- Enterol;
- Enterosgel.
When esophagitis develops against the background of gastritis with high acidity, proton pump inhibitors are taken. The drugs inhibit the production of hydrochloric acid, heal erosions, wounds, cracks, and restore the mucous membrane. The course of therapy is long - at least 2 weeks. The most common remedy is Omez. You should drink 1 capsule per day.
Other drugs to reduce acidity and heal ulcers:
- Omeprazole;
- Ranitidine;
- Pantoprozole.
Improves sphincter function, increases muscle elasticity - Domrid, restores microflora, reduces acidity, strengthens the immune system - Hilak Forte, relieves muscle spasms No-Shpa, Drotaverine.
Diet
During therapy, you should exclude foods that irritate the esophageal mucosa, cause an increase in the amount of gastric juice, and stimulate gas formation. Include easily digestible foods in your diet. It is recommended to eat first courses, porridges, stewed and boiled vegetables, and fermented milk products. It is better to make meat dishes from minced meat to make it easier to chew. Try to chew thoroughly and not swallow in lumps. Dishes should be served at a comfortable temperature; too cold or too hot is prohibited.
Allowed products for the first week of therapy:
- Potato;
- Carrot;
- Boiled onion;
- Zucchini;
- Pumpkin;
- Beet;
- Rice;
- Buckwheat;
- Oatmeal;
- Egg;
- Yogurt;
- Low-fat kefir;
- Cottage cheese;
- White bread toast;
- Cracker cookies;
- Dried fruits – dried apricots, raisins, figs, prunes;
- Melon;
- Watermelon;
- Banana;
- Still mineral water;
- Butter.
In the second week, with a positive trend towards recovery, it is allowed to consume in moderation:
- Cheese;
- Kefir;
- Yogurt;
- Fish;
- Meat;
- Raw vegetables;
- Green tea;
- Compote;
- Shortbread cookies;
- Fresh white bread;
- Loaf;
- Candies;
- Cocoa;
- Milk.
Consume sweets, coffee, chocolate, and alcoholic beverages in limited quantities, even if the unpleasant symptoms have completely disappeared.
Traditional methods
Esophagitis is treated with herbs with anti-inflammatory, wound-healing, acid-lowering, antispasmodic, and analgesic effects.
- Chamomile. Soothes, relieves inflammation, heals wounds, relieves pain. Can be purchased at the pharmacy in packaged form. Pour boiling water over, leave for 5 minutes, drink like regular tea.
- Peppermint. Relieves nausea, relieves spasms, soothes mucous membranes. For therapy, use a dry potion or a fresh leaf. In the first case, pour boiling water for 5 minutes, in the second, add it to green tea.
- Melissa. Removes toxins, soothes, relieves pain, stops the inflammatory process. It is allowed to mix with chamomile and mint in equal proportions. Drink instead of tea.
- Potato juice. An effective acid reducer. It has an enveloping effect, anti-inflammatory, wound healing, and analgesic. Grate the potatoes on a fine grater and squeeze out the juice. Take 50 ml fresh 20 minutes before meals. Definitely in the morning, before bed. Carrot juice works similarly. Allowed to be combined in equal proportions.
Decoctions based on medicinal herbs should be taken warm. Relief occurs almost immediately, but for a lasting effect, therapy is required for at least 10 days.