Classification and varieties
It is customary to distinguish several types of intestinal hernias. Classification depends on the location of the hernial sac:
- Inguinal. Develops in the area of the inguinal canal. It can form inside, go under the skin, or be diagnosed in both places at the same time.
- Umbilical. This type of education is typical for newborn babies. Caused by an underdeveloped umbilical ring. Also, a hernia can form in women during pregnancy and after childbirth.
- Femoral. Located in the upper part of the anterior thigh. Typical for older people.
- Linea alba. In most cases, it is represented by several small hernias located in close proximity to each other.
- Ventral (postoperative). Formed in an area of thinned scar tissue.
- Sliding. Formed as a result of partial overlap of the intestine with peritoneal tissue.
Patient management tactics depend on the type of hernia
Prognosis and prevention
In case of intestinal cysts, the prognosis is generally favorable if there are no complications. After surgical treatment, complete recovery occurs. Relapses occur in rare cases.
If a hernia is strangulated, the further prognosis depends on the timeliness of the operation, the method of treatment and the removal of necrotic parts of the intestine.
Prevention of hernias that form in the intestines consists of proper and rational nutrition, which ensures daily bowel movements and maintaining the patient’s weight. It is also necessary to maintain a sufficient level of physical activity, which will maintain the muscular frame of the abdomen.
A hernia that has formed in the intestines is not so dangerous, provided it does not provoke complications. However, it can greatly deteriorate a person's quality of life. In the early stages, the disease is easily treated.
Therefore, it is so important to contact a specialist in a timely manner. There is only one way to get rid of hernias - through surgery.
Causes
The development of pathology can be provoked by any conditions that to one degree or another affect intra-abdominal pressure, as well as thinning of the muscle layer of the anterior wall of the peritoneum or the formation of gaps in muscle tissue.
An intestinal hernia can form during the period of bearing a child as a result of the active pressure of the growing uterus on the surrounding organs; with ascites - stretching of the abdominal cavity and an increase in intra-abdominal pressure occurs due to the accumulation of a significant volume of free fluid, against the background of sudden weight loss, with physiological thinning of the walls of the abdominal cavity in as a result of age-related changes.
One of the following conditions can be a provoking factor:
- labor pains and pushing;
- pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- severe, prolonged cough;
- vomit;
- significant physical activity;
- lifting weights;
- bloating.
In some cases, the disease is caused by congenital defects in the structure of the abdominal organs.
Reasons for development
Any conditions that in one way or another affect pressure fluctuations, thinning or gaps in tissues can provoke the disease. An intestinal hernia occurs:
For the development of the disease, a certain “trigger” is required. The final reason provoking the formation is:
It may occur against the background of chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma, biliary dyskinesia, peritonitis, gastritis, cholecystitis, mechanical or traumatic effects on the peritoneal area. Sometimes it is caused by congenital defects of internal organs.
Symptoms of the disease
At the very beginning of its formation, pathology does not announce itself in any way. And only later, as the condition worsens, characteristic symptoms appear, which gradually intensify. Typical symptoms of a hernia formation are as follows:
- the appearance of a ball-shaped protrusion on the surface of the abdomen, which disappears when lying on the back;
- pain in the area where the hernial sac appears, appearing during exercise - the pain can be dull, cramping, tingling, occur periodically or not stop at all.
An intestinal hernia requires mandatory surgery.
It is possible that general weakness and increased body temperature may develop.
Symptoms
The main symptoms include:
- severe increasing pain in the peritoneal area, sometimes it can be of the nature of colic, cramps or contractions;
- a feeling of “fullness” of the intestines and bladder; after visiting the toilet, the patient has a feeling of incomplete bowel emptying;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- constipation, belching, nausea, vomiting;
- obstruction of intestinal loops, increased body temperature (observed when a hernia is strangulated);
- exacerbation of diseases of the genitourinary system.
One of the symptoms of an intestinal hernia is the hernial protrusion beyond the anus. This manifestation is often confused with hemorrhoids. The patient may feel pain and phlegm in the perineum, constant nagging pain. If you do not consult a doctor in time, intoxication of the body may begin.
Note!
In women with an intestinal hernia, the protrusion can be visible through the vaginal lumen. With a large formation, the patient feels pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Diagnosis of pathology
When the first signs of an intestinal hernia appear, you should consult a specialized specialist. This could be a surgeon or a gastroenterologist. Diagnosis of pathology is based on the following methods:
Symptoms of hernia of the white line of the abdomen
- Patient interview. Helps to create a general picture of the disease, collect existing complaints and make a preliminary diagnosis.
- Palpation (feeling the hernia area). One of the methods to determine the presence of a hernia formation.
- MRI. The technique helps to identify pathology in the early stages, and also allows you to obtain the exact size and detailed structure of the hernia.
- Ultrasound examination. Used to determine the size of the hernial sac and its location.
- Radiography.
To get a complete picture of an intestinal hernia, the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination (using several techniques).
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms and discomfort in the abdominal area appear, the patient should consult a doctor. Depending on the location of the hernia, the surgeon prescribes an additional examination by a specialized specialist: proctologist, gynecologist, gastroenterologist.
The primary stage of diagnosing the disease includes ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, radiography of barium passage through the intestines and diagnostic laparoscopy.
In addition, the doctor conducts a diagnostic examination using the cough jerk method. Putting your hand on the protrusion, the patient needs to cough. If the formation moves and changes in size, then the diagnosis of a hernia is confirmed. This type of study is not used as the main diagnostic procedure, since a strangulated hernia cannot be detected by palpation.
How to determine a peri-umbilical hernia, read here.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment of gastrointestinal hernias in adult patients is carried out surgically. Conservative methods do not bring the necessary therapeutic results. The exception is newborn children. As a rule, umbilical hernias are diagnosed in infants, which go away on their own by about 3–5 years of the child’s life.
Surgical treatment
The operation takes place under general anesthesia. During the procedure, the intestinal loop is reduced and the hernial orifice is sutured. In case of necrosis of the contents of the hernial sac, the dead area is removed, followed by connection of the intestine.
Surgeons correct the intestinal loop that has protruded beyond the anterior wall and suture the hernial orifice, preventing re-formation of the hernia
Conservative techniques
If it is impossible to perform a herniotomy operation, the following options are used:
- Wearing a bandage. The use of corrective medical underwear helps support weak muscles and slows down the progression of pathology. Each model is equipped with a solid part that provides high-quality support for the hernia.
- Physiotherapy. Effective in the early stages of pathology.
- Physiotherapy. Recommended in the initial stages.
The absence of relapse largely depends on competently performed plastic surgery. To eliminate the hernial orifice, the patient’s own tissue or a special medical mesh can be used. The second option is more functional. In addition, the body reacts positively to its material and rejection does not occur.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine recipes help alleviate current symptoms, but cannot be an alternative to surgical treatment. The following recipes have worked well. Applying oven-baked onions to the surface of the hernia. Course duration – 3 weeks. Pour boiling water (200 ml) over horse sorrel roots (10 grams) or oak bark (10 grams) and cook for 10 minutes.
The resulting decoction is used for compresses for 10 days. The duration of the procedure is 30 minutes. This prevents the hernia from increasing in size. The following methods are also used. Wash the plantain seeds, dry until flowable and grind. Eat a pinch every day.
Nettle leaves can be applied to the surface of the hernia. The duration of treatment is no less than a calendar month. You need to take a leaf of sauerkraut and apply it to the site of the hernial sac. Or soak a piece of soft cloth in brine and use it as a compress.
Treatment
There is only one radical treatment method - surgery. The exception is infants. Their education often disappears on its own during the first years of life, leaving no traces and without negative consequences.
Operation
The operation to remove an intestinal hernia is performed under local, conscious or general anesthesia. After dissection of the affected area, the intestine is moved into the cavity, followed by plastic surgery. If the intestinal loop dies as a result of blood supply problems, then it must also be removed.
If there are contraindications to the use of surgical intervention, use:
- Bandage. The use of special therapeutic underwear gives good results in maintaining weakened muscles and prevents the progression of the disease. Depending on the location, the bandage can be made in the form of a belt, shorts or pantaloons. In any case, any model must have a special hard part that supports the hernia (pelota).
- Physiotherapy. It is used only when diagnosing the disease in the first stages. It does not give any positive results in the future.
- Physiotherapy. It is used in a number of cases when a disease is detected at the inception stage. Later stages of the disease are not treated in this way.
The absence of relapse of the disease largely depends on successful and competent plastic surgery after removal of the hernia. To restore tone, patient tissue or an artificial mesh are used. The second method is modern and effective. The operation time is reduced, its efficiency increases and treatment is simplified. In addition, the body does not reject such materials.
Folk remedies
Apply an onion baked in the oven to the affected area. The vegetable is left for no more than 12 hours. The duration of onion treatment is three weeks.
When treating intestinal hernia, a decoction of horse sorrel roots is also used:
For this pathology, compresses are also made with oak bark tincture. They need to be left for half an hour. Thanks to such compresses, the hernia does not increase in size. You can take note of this recipe: a small amount of crushed oak bark and a few acorns are placed in a glass container, the mixture should be poured with wine. The product must be infused in a dry place where sunlight does not penetrate. After three weeks, the product is taken out into the light of day and filtered. Compresses are made from this tincture. When using them, your well-being noticeably improves.
You can eat plantain: its crushed seeds are used daily in small quantities. Nettle leaves should be applied to the affected area. Duration of treatment – at least 30 days.
Sauerkraut also helps in treating hernia. You need to take one leaf of the vegetable and apply it to the place where it is located. The procedure must be done regularly. You can simply soak a cotton cloth with sauerkraut brine. This compress should be applied to the hernia.
Is it worth buying a bandage?
For intestinal diseases, you need to perform massage and do appropriate exercises. It is recommended to purchase a bandage. It can also be worn after surgery. When using this product, the risk of relapse is reduced and pain is eliminated. It is used during pregnancy: during this period any surgical intervention is undesirable. The bandage is also used at the initial stage of the disease. The product reduces the likelihood of hernia strangulation. It must be worn every day: the bandage is removed before going to bed. The area where the hernia is located can be secured with a bandage.
This orthopedic product cannot be used in the following cases:
It is not recommended to wear a bandage in case of severe heart pathologies or a tendency to allergic reactions.
There are special postoperative bandages. They are used after surgery. Such products are made in the form of a belt. They are made of elastic material and equipped with a convenient clasp. The bandage does not put pressure on postoperative sutures. It reliably fixes the abdominal organs, accelerating the wound healing process. The duration of wearing the product is determined by the doctor. It depends on the patient's condition.
To prevent unwanted complications, you need to maintain good physical shape. The patient should monitor her weight and avoid constipation. When performing simple physical exercises, the pelvic floor muscles become stronger. No need to lift heavy objects.
Is wearing a bandage justified?
The use of a bandage for a diagnosed intestinal hernia is mandatory during pregnancy, since surgical intervention during this period is completely contraindicated for a woman. The use of a bandage shows good results at the initial stage of pathology and prevents strangulation of the hernial sac. You need to put it on while lying down and be sure to take it off before going to bed.
Contraindications to use of the product are:
- the presence of any type of damage on the surface of the skin;
- dermatitis and other skin diseases;
- strangulated hernia;
- heart pathologies that occur in severe form.
Wearing a bandage as a therapeutic measure is justified only in the initial stages of hernia development.
Wearing a special bandage will help prevent the formation of a postoperative intestinal hernia after intervention on the abdominal organs. It looks like an elastic belt and provides reliable support for the anterior abdominal wall.
Complications
An intestinal hernia, if not properly treated, can lead to a lot of complications. First of all, this is the formation of an irreducible protrusion. If in the initial stages of the disease the hernia tends to hide when a person takes a horizontal position, then over time adhesions form and the contents of the hernial sac no longer return to the abdominal cavity. This entails topographical changes in internal organs, circulatory disorders and intestinal dysfunction.
Strangulated hernia
Another complication of the disease is strangulated hernia. In this case, the intestinal loops are compressed and the normal functioning of the internal organs, which end up in the hernial sac, is disrupted. This pathology can only be removed through surgery, but even after the operation the person retains paresis of the intestinal wall. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, tissue necrosis and intestinal gangrene occur.
Injury to an intestinal hernia can be no less dangerous to the patient’s health. Injuries can be either closed or open, when the integrity of the skin is damaged. The complication manifests itself in the form of pain, swelling at the site of the hernia, and bruising. With open injuries, the hernial sac can retain its structure, but the mechanical impact on the hernia will not pass without leaving a trace. In such cases, it is necessary to contact a surgeon for a more detailed examination.
In some cases, the patient may develop tuberculosis of the hernial contents or a tumor. Neoplasms can be both benign and malignant, for example, carcinomas and sarcomas. At the first manifestations of such complications, you should immediately seek medical help; untimely treatment or its absence can lead to death.
Intestinal hernia in children
The main symptom indicating the development of an intestinal hernia in a child is the appearance of a pathological protrusion. The size of the formation may be different, since they depend on the size of the intestinal loop trapped in the hernial sac. There are three types of intestinal hernias:
- Reducible. If, when lying on your back or pressing a finger on the surface of the formation, it decreases in size or completely disappears, then this is a reducible hernia.
- Unfolded, unguided. In the absence of pain, but the impossibility of reducing the hernia, we are talking about an uncomplicated unreducible form.
- Disadvantaged.
Uncomplicated unreducible hernias may be accompanied by the following symptoms: aching pain, disruption of the digestive system - nausea, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea, difficulty urinating. The greatest danger is a strangulated hernia. Its signs are the development of sharp pain in the area where the hernial sac is located, a rapid rise in body temperature, the development of vomiting, the hernia cannot be reduced, becomes painful to the touch and tense.
The use of conservative treatment methods is possible only for umbilical hernias, since they tend to heal on their own. Other types of formations are operated on as planned. Temporary contraindications include inflammation of the skin, periods of exacerbation of chronic diseases, acute respiratory viral infections and colds.
Emergency surgery is performed when symptoms of strangulation of the hernial sac appear.
Umbilical hernia in a child
Treatment of intestinal hernia in a child
Intestinal hernias in children (inguinal or umbilical) are most often congenital or appear shortly after birth. Children's umbilical hernias are determined by straining, screaming, and restless behavior of the child. They are easy to reduce and rarely become pinched. For this reason, it is worth holding off on surgery in newborns in cases where the hernia is easily reducible and does not cause any discomfort to the child in terms of pain, digestion and urination. In addition, this pathology can resolve itself within up to 5 years with the reduction and closure of the umbilical ring.
Treatment methods for umbilical hernia pathology in children under 5 years of age are conservative: massage, special therapeutic exercises. At an older age, if the hernia does not disappear, surgical intervention is indicated. It should not be postponed, since over time the pathology will develop further, and pinching and inflammation may occur, which will reduce the effect of the operation. The possibilities of hernia repair and laparoscopy in case of prolonged delay will be reduced to nothing.
Note!
Be careful when using adhesive bandages for the umbilical ring on newborns, as their skin is very vulnerable and can become infected.
Also, mostly among boys, an indirect inguinal hernia is common, often accompanied by retention of the testicle in the inguinal canal or abdominal cavity. The protrusion appears in the groin area when straining or the child cries; it is easily pushed back into the abdominal cavity in a supine position. In case of strangulation of an inguinal hernia, the child becomes restless due to severe pain, the muscles are tense, and the protrusion ceases to be reduced. Although the pain may decrease after a couple of hours, the child will remain lethargic and will also experience symptoms of intestinal obstruction. In such a situation, surgery is urgently needed. During the first 10 hours from the moment of infringement, it is possible to use conservative measures (administration of antispasmodics, warm bath, etc.).
At different ages, the treatment of intestinal hernial pathologies, which are part of various abdominal hernias, has its own characteristics. If you notice their symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment, since in case of strangulation, an intestinal hernia can turn into a time bomb.
(Total 741, today 1)
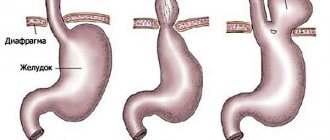
Symptoms
Signs of such a disease can manifest themselves in different ways, but most often we are talking about pain in the upper abdomen, and the diaphragm area also hurts. Most often, the pain intensifies after eating. Additional symptoms are the following: a person suffers from heartburn and belching. It should be noted that in addition to pain, there is another sign that may indicate the presence of a hernia - the feeling of a certain “lump” in the throat when a person quickly swallows food, as well as when it comes to swallowing hot, cold and liquid foods. If there are problems with the normal functioning of the heart, then these may also be symptoms of a hernia. However, it is heart pain that confuses many old people, since they believe that they have heart disease, since the symptoms of angina pectoris are very similar.
If the disease progresses, blood is found in the stool and it is difficult to swallow food. Then it becomes difficult for the person to breathe. However, the insidiousness of such a disease also lies in the fact that there are often cases when there are no symptoms at all. And a person learns about the presence of the disease only during a medical examination, which was carried out for a completely different reason. Hernia symptoms are often disguised as other ailments, so you should consult a doctor in a timely manner.
What is an intestinal hernia, symptoms and treatment
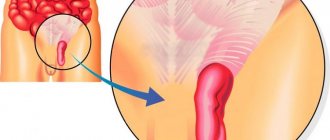
An intestinal hernia is a prolapse of the rectum from the anus due to pathological weakening of the pelvic muscles. Due to poor fixation by the muscular frame, intestinal loops come out through the abdominal cavity or abdominal walls.
Symptoms of a rectal hernia in women and men may differ slightly, but this pathology can develop in both sexes. Due to the structure of the female body and the ability to become pregnant, women are more often susceptible to this disease. However, weakened muscle tone can occur in anyone.
- Description
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
Description
The reasons for this weakening of the muscles in the pelvic area can be various pathologies: constipation, late stage hemorrhoids, diarrhea, intestinal erosion, mechanical trauma in the anal area. When the pelvic floor becomes weakened and muscle tone in it is disturbed, the appearance of a hernia can be the result of even a simple sneezing or coughing.
When pushing during defecation, a pathological flexible formation appears, which anticipates the appearance of a hernia. However, it is not always possible to correctly determine the risk, so the symptoms and treatment of a duodenal hernia, like that of a large intestine, may require additional tests.
A hernia appears when there is a gap in the muscles of the abdominal wall and a surge in pressure inside the abdominal cavity
Diagnosis of such pathology is often carried out using ultrasound or radiography.
Treatment of a rectal hernia is carried out only by performing a surgical operation to correct or remove the hernia, strengthening the muscle walls and closing the so-called hernial orifice through which the intestine prolapsed.
Under normal conditions, the intestinal loops are held together by the ligamentous apparatus, and intracavitary pressure encounters an obstacle in its path in the form of the muscles of the abdominal wall. The absence of heavy loads and weak points in the muscle structure allows you to avoid the development of a hernia.
Classification
The main classification is topographical - according to their location. Usually inguinal, umbilical, femoral hernias develop, and much less often - sciatic, lumbar and other hernias. Experts in the field of modern herniology distinguish the following types of hernias:
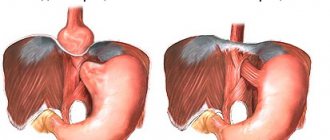
- Inguinal.
The most common option. It can be direct (a section of intestine exits through the outer ring of the inguinal canal, and when a finger is inserted into the hernial canal, it goes straight) or oblique (the hernial contents exit through the internal inguinal opening, the finger inserted into it is directed obliquely). Often, an inguinal hernia forms on both sides. - Umbilical.
It can develop in young children due to the structural features of the umbilical ring; among adult patients, this disease most often affects women after pregnancy and childbirth. The development of an umbilical hernia is predisposed by the presence of a peritoneal diverticulum in the area of the umbilical ring. - Femoral.
Usually formed due to weakness of the deep femoral ring in female patients after forty years. Femoral hernias rarely reach large sizes, but are more often strangulated than others. They can be complete or incomplete when the hernial contents do not extend beyond the fascia and are located in the femoral ring. - Linea alba.
It is typical for male patients, with gaps in the white line of the abdomen acting as hernial orifices. Hernias of the white line are often multiple, located one above the other, and can occur hidden. - Postoperative.
It is formed between separated aponeuroses or muscles, mainly after purulent inflammatory processes in the area of a postoperative wound and the introduction of tampons into it. Postoperative hernias can reach significant sizes and require abdominal wall repair.
Rare forms include sciatic, obturator, lateral and perineal hernias. Internal intestinal hernias can also form when loops of intestine get into intra-abdominal pouches (for example, Treitz's hernia, which forms in the area of the transition of the duodenum to the jejunum). In some cases, the peritoneum only partially covers the intestine - sliding hernias develop.
Features of the pathology
An intestinal hernia is a pathology in which part of the intestine comes out through defects in the abdominal wall. If there are no defects in the abdominal muscles, a hernia may appear as a “migration” of intestine within the abdominal cavity. Defects in the abdominal wall can develop as a result of surgery, tissue or muscle problems.
In a healthy person, the intestinal loops are held in place by the abdominal wall, which is made up of muscles and connective tissue. Therefore, a healthy area can withstand even strong pressure. An intestinal hernia occurs when weakness occurs in certain areas of the abdominal wall or during an increase in intra-abdominal pressure.