What is bulbit
Bulbit is an inflammation of the duodenal bulb. The disease is one of the forms of duodenitis.
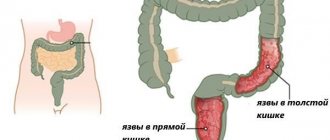
The duodenal bulb is located in the proximal part and is shaped like an ampulla. This is an important anatomical site that is involved in the movement of food from the epigastrium to the intestine.
The disease develops at any age. More often, gastric bulbitis develops in adults. Children suffer from the disease less often; this is most likely due to genetic predisposition.
The chronic type of this disease leads to damage to this part of the duodenum with subsequent destruction.
Bulbit is difficult to diagnose; more often, pathological conditions are discovered by chance during a gastrological or x-ray examination of the stomach.
This pathology can cause significant discomfort and prevents a person from living a full life. If you respond to the disease in a timely manner, you will be able to get rid of it completely. And if you follow preventive measures, you will be able to prevent a relapse.
Causes of bulbitis in adults
Having an understanding of the nature of the inflammatory process of the duodenum, it is easier to prevent possible complications and the development of the disease itself.
The following conditions and factors can provoke bulbitis:
- bacterium Helicobacter pylori . The bacterium resides in the stomach without causing any symptoms. When acidity in the stomach decreases, liver and pancreatic enzymes damage the mucous membrane. Helicobacter pylori penetrates into an aggressive acidic environment, provoking the development of an inflammatory process;
- absence of duodenal mesentery . It is an anatomical structure considered as continuous. Covers the intestine from the duodenum to the rectum. With various anomalies of embryonic development, the mesentery remains, a loop is formed from the intestine, in which stagnation of acidic contents begins. This leads to erosion of the mucous membrane;
- nutrition . Bulbit often develops as a result of poor nutrition. The occurrence of the disease is influenced by the consumption of spicy, fried foods and cravings for sweets;
- hereditary predisposition , due to stagnation, the acid in the food bolus leads to damage to the mucous membrane.
In addition to the main causes of the development of the disease, doctors identify other factors and compare them with different types of pathology.
Table. Reasons for the development of various forms of bulbitis.
| Type | Causes |
| Erosive | Radiation treatment, chemotherapy for oncology, duodenogastric reflux, immune deficiency, liver cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus. |
| Catarrhal | Outgrows from the superficial form. Develops as a result of weakened immunity with the development of other chronic gastrointestinal pathologies. |
| Surface | Peptic ulcer (stomach ulcer), intoxication, unsystematic alcohol abuse, chronic gastritis and pancreatitis, short bowel syndrome. |
| Focal | Long-term food retention, gastritis, colitis, pancreatitis, disorders of the gallbladder, kidneys and liver. Risk factors for the development of the focal form are:
|
| Follicular | Smoking, state of psycho-emotional stress, frequent consumption of caffeine-containing drinks. |
Classification
Depending on the characteristics of the course, acute and chronic forms of pathology are distinguished. The inflammatory process can be focal or diffuse in nature, if the mucous membrane of the duodenal bulb is completely affected.
According to the degree of activity, they are distinguished:
- catarrhal - under the influence of a disturbed pH balance, irritation develops, which later develops into inflammation. The walls of the bulb swell, more mucus is released, and the digestion process suffers. If you contact a specialist in a timely manner, this form has a favorable prognosis;
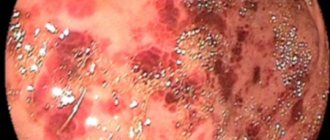
- erosive-ulcerative - develops as a result of inflammation occurring for a long time and is characterized by the formation of single or multiple lesions on the mucous membrane;
- follicular - provokes tissue changes at the micro level: the follicles covering the walls of the duodenum become larger, the mucous membrane acquires a nodular structure.
Symptoms of bulbitis
Symptoms of bulbitis depend on the clinical type. In this way, doctors are able to promptly determine the type of disease and begin treatment before diagnosis in order to prevent deterioration and complications.
However, there are common symptoms of bulbitis in adults and children. They do not differ depending on age categories.
Clinical signs:
- discomfort in the upper part of the peritoneum;
- nausea;
- vomiting, in severe cases with blood;
- belching after eating or between meals;
- during an exacerbation, body temperature rises;
- diarrhea begins and flatulence worries.
Sometimes bulbitis occurs in a hidden form. Many patients are unaware of the existence of the disease, and some symptoms are similar to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, so it is difficult to independently differentiate the pathology.
Diet food
First of all, the patient needs to give up rough food. Eating hot, smoked, spicy, pickled, salted, fried, too hot or cold food is not allowed. Meals should be eaten in small portions, at least 6-8 times a day, and should be eaten in small portions.
The patient's diet should consist of liquid and puree dishes, and their temperature should not be lower than room temperature. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, you can eat fermented milk products, jelly, boiled meat, and broths.
The therapeutic diet includes the use of herbal preparations, which should contain leaves and inflorescences of celandine, chamomile, yarrow, St. John's wort, fennel, and linden. In a state of remission of the acute form of bulbitis, it is recommended to use the mineral waters “Essentuki No. 4”, “Essentuki No. 17” and “Borjomi”.
Basic forms of bulbite
There are several types of bulbit. Treatment also depends on the type of disease. Bulb happens:
- erosive - this type of disease provokes dyspepsia and loss of appetite, dizziness, weakness, discoloration of stool, and increased stomach acidity. The pain radiates to the back and chest. The erosive appearance is characterized by the presence of erosion of the duodenal bulb. Hunger pain in this type is observed on an empty stomach and at night. An unpleasant taste appears in the mouth, which is explained by the entry of bile into the esophagus as a result of reflux. Assessing the clinical picture of chronic erosive bulbitis is often difficult;
- superficial - this type of bulbitis can be acute or chronic. The main symptom of both forms is pain in the epigastric region. Chronic bulbitis is characterized by aching pain, morning sickness and heartburn;
- catarrhal - this form is manifested by pain radiating to the right hypochondrium. At night there is a sharp pain radiating to the umbilical region. After eating, vomiting appears, hyperhidrosis and insomnia bother me. The patient becomes irritable and nervous. The catarrhal form provokes constipation and muscle weakness;
- focal - in most cases they are chronic. The main signs include diarrhea, vomiting, headache and decreased activity, hunger and sweating;
- follicular - this type of bulbitis is a rare species. Characterized by hand tremors, chills, weakness, and low performance. The clinical picture is complemented by problems with defecation, bloating, vomiting, and the onset of pain several hours after eating.
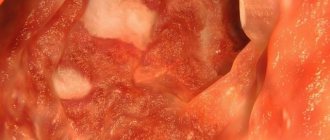
Diagnostics
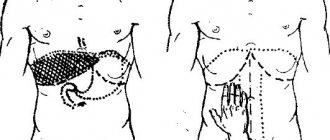
The initial diagnosis is carried out in the doctor's office. This is a visual inspection of the abdominal area and palpation. The doctor makes a preliminary conclusion based on the clinical picture.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is given a referral for instrumental diagnostic methods and laboratory tests.
Only after a comprehensive diagnosis does the doctor make a final diagnosis of bulbitis and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics includes the following instrumental techniques and analyses:
- manometry. The study is carried out to measure pressure during contraction of the stomach;
- FGDS - used to determine swelling, bleeding and hemorrhage in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum;
- fractional duodenal intubation;
- stool analysis for the detection of Helicobacter pylori;
- pH-metry and electrogastroenterography of the gastrointestinal tract are performed.
Diagnosis and treatment of focal gastric bulbitis
The primary diagnosis of inflammation of the duodenal bulb is determined by palpation. In the presence of the disease, it is easy to detect tension in the abdominal wall in the umbilical region, while the patient feels mild pain.
In addition, the presence of the disease is indicated by a specific yellow coating on the tongue.
If during the initial examination symptoms of bulbitis are revealed, then gastroenterologists will prescribe the necessary studies of the functioning of the stomach to confirm the diagnosis.
Using certain diagnostic methods, the cause of bulbitis is determined.
Treatment for such a stomach disease is usually complex. It consists of the use of medications, physiotherapy, herbal medicine , and adherence to special therapeutic diets .
Since the main cause of the disease is Helicobacter, to eradicate the pathogen, therapy with antibiotics and drugs that accelerate the process of tissue repair in the gastrointestinal tract is usually prescribed. Bismuth preparations are no less effective in this case.
Complications
In advanced cases, bulbitis is fraught with serious complications.
The focal form can cause disruptions in the functioning of the digestive system. Without proper treatment it becomes erosive. When ulcers form, food may enter the abdominal cavity, which leads to the development of peritonitis.
With the erosive type of bulbitis, duodenal ulcers may form. If it is in the bulb, there is a risk of perforation and bleeding.
Superficial chronic bulbitis is characterized by bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract; about 10% of bleeding develops due to this type of disease. The second complication is the development of cancer of the major duodenal papilla.
Delayed treatment leads to death.
Treatment
In the case of an acute form of the disease, painkillers are prescribed. A person who has become ill with bulbitis is admitted to a hospital and the duodenum is lavaged, and a drip with saline is placed for detoxification. As a rule, to cure this disease, anti-Helicobacter antibiotics and gastro- and enteroprotectors are prescribed. The entire treatment process is accompanied by a strict diet that excludes an abundance of spicy foods, alcoholic and highly carbonated drinks.
Treatment of bulbitis
If signs of bulbitis appear and the diagnosis is confirmed by a doctor, it is advisable to immediately begin treatment. Therapy for inflammation localized in the duodenal bulb is based on taking medications and herbal infusions.
The main and constant method of treating bulbitis is diet. In difficult situations, surgery is performed.
Medications
Patients are prescribed medications. Prescribed medications aimed at relieving pain, antacids (for example: Almagel, Maalox, Rennie ) - medications can be taken independently, according to the dosage indicated in the instructions. They are prescribed for high acidity and ulcerative complications.
If the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is detected, treatment of bulbitis is based on the use of antibacterial agents. At the same time, the same antacids are prescribed; they regulate the process of acid secretion.
If Giardia is detected, anti-Giardia therapy is prescribed. If a stool test shows helminthic infestation, the patient is prescribed anthelmintic drugs (for example, Pirantel, Vermox, Praziquantel, Decaris ).
For complications of bulbitis, for example, Crohn's disease, the doctor prescribes steroid hormones, zinc salts and vitamin C. If the cause of inflammation is intoxication, sorbents ( activated carbon ) are prescribed that neutralize the effect of the caustic toxic substance.
Therapy is used to treat chronic bulbitis with infection. If the disease is associated with increased stress, it is necessary to exclude the influence of a psychological factor. Sedative medications are prescribed.
Treatment at home is carried out in the absence of ulcers, bleeding and other complications of acute or chronic bulbitis.
Surgery
If symptoms worsen, treatment does not help, bleeding is detected, and surgery is prescribed. Most often, these conditions are characteristic of erosive bulbitis.
Ligation of the bleeding vessel or vagotomy with intersection of the trunks of the vagus nerve is performed.