Causes of intestinal spasms
Spasmodic, cramping pain in the intestinal tract is caused by impaired motor function. The pathogenesis of the condition consists of the following processes :
- stretching of the inner lining of the intestine;
- irritation of nerve endings;
- disorder of smooth muscle tone;
- congestion, foreign bodies, fecal stones.
Factors contributing to the appearance of pain and spasms are psychoemotional disorders, ulcerative-erosive lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, intoxication, anatomical features and congenital developmental anomalies. Irritable bowel syndrome often accompanies intestinal spasms.
Intestinal spasm: symptoms
The muscle tissue of the intestinal walls provides peristalsis and the movement of food through the digestive tract. Under normal conditions, the functioning of this organ is coordinated and rhythmic. Disturbances in the functioning of the wall muscles can lead to intestinal spasm and retention of its contents.
The most common symptoms of intestinal spasm are:
- false urge to defecate;
- phenomena of flatulence and bloating;
- discomfort and cramping pain in the intestines;
- constipation and feeling of incomplete emptying;
- violation of stool character.
All of the above manifestations of spasm can occur simultaneously, they can periodically disappear and appear again. Concomitant symptoms of intestinal spasm may include headache, sleep problems, weakness, malaise, frequent urination in small portions, nausea, etc.
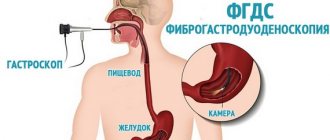
With intestinal spasm, other symptoms may be observed depending on the reasons that caused it. They have important diagnostic value. In addition to collecting anamnesis, to determine the causes of intestinal spasm, the doctor may prescribe urine and blood tests, stool examination for the presence of helminths, and examination of the digestive tract using various methods.
Antispasmodics for the intestines
Antispasmodics are a group of synthetic drugs that relieve spasms in various organ structures and associated pain . Simultaneous use with painkillers enhances the therapeutic effect of NSAIDs and other analgesics.
Classification
Classification involves the division of antispasmodics according to the type and duration of exposure , the mechanism of blocking nerve impulses:
- Neurotropic (m-anticholinergics). Neurotropic intestinal antispasmodics are aimed at stopping the nervous excitability of the smooth muscles of the intestinal tract and preventing the spread of impulses through the autonomic nervous system. If a muscle does not receive a signal from the brain to contract, rapid relaxation occurs. Popular products in this category: “Chlorosil”, “Atropine”, “Neostopan”, “Platifillin”, “Metacin”.
- Myotropic . The drugs affect the processes that occur during a spasm in already contracting muscles. Drugs from the myotropic group can be taken for a long time without subsequently worsening muscle contractility. In clinical practice, Drotaverine (No-shpa), Dicetel, Duspatalin, and Papaverine are widely used.
- Neuromyotropic . Combined antispasmodics, combining neurotropic and myotropic components. The substance kamilofin has a dual effect. Drugs in this group: “Bendazol”, “Nitroglycerin”, isosorbide dinitrate, “Gimecromon”.
- Complex . Such medications contain several active components that relieve spasm, pain, fever, and improve tissue trophism. Among the complex drugs are Pentalgin, Spazmalgon, Novigan, Trigan.
- Plant origin . Plant-based antispasmodics contain one natural component that helps normalize intestinal motility. Popular drugs: Altalex, Azulan, Prospan, Iberogast.
Attention ! Even relatively safe medications are not recommended to be taken for a long time without medical indications. Constant symptoms are evidence of a pathological process.
List of antispasmodics for intestinal pain
Antispasmodics are a group of drugs that, differing in their mechanism of action, relieve spasms and pain in various organs (bronchi, gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels, etc.).
Types and list of drugs for gastrointestinal antispasmodics
Antispasmodics, depending on the mechanism of action, are divided into two large groups:
Myotropic antispasmodics
The mechanism of action is based on relieving spasm by direct action on smooth muscle cells. Drugs in this group can be used for a long time.
The following myotropic antispasmodics are distinguished, which are used in gastroenterology:
- Papaverine hydrochloride (Papaverine). The mechanism of action is associated with blocking phosphodiesterase, an enzyme that is involved in the transport of calcium ions into smooth muscle cells. Excess calcium inside the cell leads to its contraction; when this process is blocked, relaxation and spasm relief occur. The drug is approved for use in children and pregnant women. Widely used in gastroenterological practice. Quickly relieves spasms and relieves pain, but is 5 times weaker than drotaverine.
- Drotaverine (Drotaverine, No-Shpa, Spazmol). Papaverine-like antispasmodic. The mechanism of action does not differ from papaverine, but has a more pronounced antispasmodic effect, which in duration exceeds the effect of papaverine. Does not penetrate the central nervous system. It is a universal antispasmodic and is well tolerated. In therapeutic dosages it does not cause side effects. It quickly penetrates tissues and organs and has an effect regardless of the cause that caused the spasm. Included in the standards of medical care for abdominal pain.
- Pinaveria bromide (Dicetel). Selective calcium channel blocker. By preventing the penetration of calcium into the cell, it leads to its relaxation. It is used primarily to relieve spasms in the large intestine. Long-term use does not cause intestinal hypotension. Due to low absorption from the intestine, it does not have a systemic effect on the body and practically does not cause adverse reactions. Clinical efficacy and safety have been confirmed by multicenter studies. Does not affect the cardiovascular system.
- Otilonium bromide (Spasmomen). According to the mechanism of action and pharmacodynamics (distribution in the body, excretion, side effects) it is practically no different from Dicetel, but in Russia the demand for this drug is not high.
- Mebeverine hydrochloride (Duspatalin). It is a sodium channel blocker. Sodium is involved in the contraction of muscle cells. When sodium channels are blocked, its penetration is limited and cell contraction is suppressed. The main site of action is the large and small intestines. The drug does not accumulate in the body, therefore it does not require adjustment of the therapeutic dose in elderly patients. It has proven itself in the treatment of spastic pain in people with irritable bowel syndrome.
Neurotropic antispasmodics
The mechanism of action of drugs from this group is associated with blocking the conduction of excitation from nerve endings or ganglia to the smooth muscle cells of internal organs.
Most drugs are M-anticholinergic drugs. The antispasmodic effect is associated with blocking M-cholinergic receptors in the human body. These receptors are responsible for the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, the functioning of the salivary and sweat glands, increase the tone of smooth muscles in the digestive tract, and reduce the heart rate.
When they are blocked, the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract relax, especially the upper sections (esophagus, sphincter of Oddi, stomach, gall bladder).
M-cholinergic receptors are practically not found in the intestines, so most drugs in this group do not have an effect on abdominal pain caused by diseases of the lower digestive tract, which limits their use.
Preparations:
- Atropine sulfate (Atropine). It is a plant alkaloid of a number of poisonous plants (henbane, datura). It affects M-cholinergic receptors located on the periphery and in the central nervous system. It affects the functioning of a large number of organs (digestive system, respiratory, cardiovascular, endocrine glands, brain, iris, etc.). Use is limited by the frequent development of adverse reactions from various organs and systems. It has a low range of therapeutic doses, which increases the risk of overdose.
- Platiphylline hydrotartrate (Platifillin). Plant alkaloid of ragwort. It is 5 times weaker than atropine in its effect on the gastrointestinal tract. Causes less side effects compared to atropine. Used in emergency care to relieve pain spasms.
- Hyoscine butyl bromide (Buscopan, Neoscopan). One of the most studied antispasmodics, which has an optimal effectiveness-safety ratio. The drug acts on the subtypes of M-cholinergic receptors, which are located in the gastrointestinal tract, and therefore does not affect the central nervous system, bronchi and blood vessels. The antispasmodic effect on the gastrointestinal tract is 44 times stronger than the effect of drotaverine. The main application is spastic conditions of the upper digestive tract (esophagus, stomach). When taking the drug, dry mouth, drowsiness, increased heart rate and other atropine-like effects that do not require special treatment may rarely occur.
- Metacin . Does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Reduces the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Reduces the tone of the upper digestive tract. Causes atropine-like side effects (dry mouth, paralysis of accommodation, etc.). It is used mainly for the treatment of gastric ulcers as part of complex therapy.
- Chlorosyl . It differs little from Metacin in pharmacological action and side effects.
Release forms and indications
Medicines for intestinal colic in children and adults are available in various forms and are used according to indications:
- rectal suppositories - suppositories are prescribed in pediatrics and when oral administration is not possible, suitable for self-medication for periodic spasms;
- injections for intramuscular administration - a hospital form of treatment necessary for acute intestinal pathologies with a pronounced clinical picture;
- suspensions, syrups - a children's form of the drug to facilitate administration due to its pleasant taste, suitable for short-term and long-term treatment;
- tablets, capsules - the traditional form of release of antispasmodics for adults; after entering the gastrointestinal tract, it is quickly absorbed into the blood and penetrates the tissues of the intestinal tract.
The main indications for the use of antispasmodics are exacerbations of intestinal diseases (paraproctitis, irritable bowel syndrome, enterocolitis, colitis), periodic pain in the chronic form of gastrointestinal diseases, high intestinal sensitivity. Antispasmodics can be used to reduce pain after diagnostic and treatment studies.
Antacids
These are acid-neutralizing drugs that deactivate pepsin, envelop and bind bile acids. The cytoprotective effect of antacids containing aluminum compounds has also been discovered - it is used to prevent peptic ulcers when long-term treatment with NSAIDs is necessary.
Antacids also bind epithelial growth factor, stimulating tissue regeneration. The quality of scarring after the use of antacids is significantly higher than after the use of proton pump inhibitors.
Drugs in this group are prescribed for exacerbations of gastric and duodenal ulcers with mild pathology. They are used as an anesthetic for chronic or acute gastritis, for the prevention of ulcerative and erosive pathologies.
Common antacids include:
- Maalox;
- Phosphalugel;
- Almagel;
- Compensated;
- Gastal;
- Rennie.
Available in the form of tablets and suspensions for oral use.
Selective anticholinergics
Anticholinergics are used as antiulcer drugs, as they affect the very process of development of this pathology. They reduce acid production and inhibit gastrin secretion. When used, the production of pepsin is reduced and the effect of antacid medications is prolonged.
Anticholinergics are able to inhibit the release of hydrochloric acid, but somewhat reduce the tone of the esophageal sphincter. Currently used for the healing of duodenal ulcers and pain relief for gastritis.
Of this group, Gastrocepin and Telenzepin have found the most use. The latter is a very powerful inhibitor of hydrochloric acid secretion and is administered intravenously.
Gangleron
In addition to effective pain relief, the drug enhances motor functions. It is used in capsules or as injections.
Gastrozem
Reduces the functionality of the stomach to produce acid, the root cause of pain. To achieve positive results, take it for at least 2 weeks.
Histodil
It has a similar effect to gastrozem, blocking cholinergic receptors. Use at night or during meals.
Histamine blockers
These are the most common antiulcer anesthetics. They suppress the production of hydrochloric acid by blocking histamine receptors located in the mucous membranes of the stomach. Among the drugs in this group:
- Cimetidine;
- Roxatidine;
- Nizatidine;
- Ranitidine;
- Famotidine.
These drugs can reduce the production of pepsin, increase the secretion of gastric mucus and prostaglandins, improving microcirculation in the mucous membranes of the stomach. The use of drugs in this group leads to stimulation of reparative processes.
The disadvantage is the potential risk of developing hypergastrinemia and rebound syndrome. Available in the form of tablets or injections.
Proton pump inhibitors
These are the main antiulcer drugs. They exhibit antisecretory activity and create favorable conditions for anti-Helicobacter therapy. Currently, the drugs of choice for ulcers from this group are Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, Lanzoprazole, Omez, Loseprazole, Omealox, Rabeprazole, Esomeprazole, Dexlansoprazole.
Eight weeks are sufficient for ulcer scarring when treated with proton pump inhibitors. Also used to prevent relapses. They have a high safety profile, which guarantees good tolerability.
Contraindications and side effects
Restrictions on use:
- tuberculosis;
- Crohn's disease;
- acute infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- some types of acute colitis;
- allergic reactions;
- surgical conditions.
Pregnancy, lactation and childhood are relative contraindications ; medications can be prescribed by a doctor. The most common side effects include shortness of breath, dizziness, bowel movements, and allergies.
Causes of intestinal spasm
The most common causes of intestinal cramps:
- Nervous strain and stress. Such conditions do not require special treatment. Bowel function will improve when the person completely calms down.
- Pathologies of the digestive system, for example, gastritis, pancreatitis and others.
- Irritation of the intestinal walls by various poisons or parasites.
- Eating poor quality food.
- Various helminthiases; other symptoms of this pathology include abdominal pain, sudden weight loss, loss of appetite, and nausea.
- Overeating or eating on the run.
- Sometimes intestinal spasms occur during infectious diseases of a viral nature.
Instructions for use
Instructions for use in the treatment of intestinal spasms in children and adults are attached to each drug. There are some general recommendations for use in various categories of patients :
- newborns and children up to one year old - in pediatrics and neonatology, m-anticholinergic agents are used in the form of rectal suppositories and syrup, the dosage varies from 1 to 10 ml every 6-8 hours (it is recommended to take natural antispasmodics: a decoction of dill seed, fennel);
- pregnant women - the prescription should be determined by the potential benefits for the mother compared to the risks to the fetus, the dose is prescribed with caution 1-2 times a day (use Dicycloverine, Bencyclane, hyoscine butyl bromide);
- persons with intestinal pain and colitis of any nature - tablets for intestinal colic are taken 30-50 mg several times a day, pinaveria bromide is more often used as an active substance, the course of treatment is 7-10 days until the symptoms are eliminated;
- elderly people - when prescribing, concomitant symptoms and current diseases are taken into account; the use of drugs that enhance or reduce the effect of other drugs is unacceptable.
Attention! When prescribing, various criteria are taken into account; single use at home is acceptable. It is better to start therapy with herbal and natural antispasmodics.
Other methods of pain relief
Non-drug methods of relieving painful spasms include physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Electrophoresis with novocaine, platyphylline, atropine, papaverine.
- Paraffin therapy. Heat reduces pain, dilates blood vessels, and relaxes muscle cells.
Spasms are contractions of smooth muscle that occur rapidly. Against the background of this condition, severe pain appears - intestinal colic. To understand which medications to use for intestinal spasms, you need to know what causes them to appear.
Remedies for intestinal colic and spasms
In clinical practice, for spasms and pain in the intestinal tract, drugs from the following list are most often prescribed :
- Papaverine hydrochloride . Quickly and permanently eliminates spasms of blood vessels, muscle structures in the intestines, and increases blood flow. Widely used in cardiological practice to relieve myocardial excitability. Available from pharmacy chains in the form of injections and tablets, rectal suppositories. The average cost is 40-80 rubles.
- "Drotaverine" . It has a prolonged and strong effect on intestinal spasms, does not penetrate the brain, has high bioavailability and absorption rate into the systemic bloodstream. Quickly reduces intestinal motility and dilates blood vessels. Not used for organ failure, pregnancy and lactation, atherosclerosis. Side effects are headache, disturbances in heart rhythm and stool, nausea and vomiting. The average cost is 130-150 rubles per pack of tablets.
- "Mebeverine" . It has a good therapeutic effect for intestinal spasms against the background of hypersensitivity syndrome. The general course of therapy is until recovery and relief of symptoms. Side effects include nausea, stool upset, dizziness, and allergic reactions. Not used during pregnancy and lactation due to insufficient research. Trade names: “Sparex”, “Meverin” (300 rubles), “Duspatalin” (500 rubles), “Niaspam” (300-400 rubles).
- "Spazmalgon" . A mixed preparation containing metamizole sodium, pitofenone hydrochloride, fenpiverinium bromide. All active components reinforce each other, which leads to a high therapeutic effect. The drug is contraindicated in case of angina pectoris, heart and kidney failure, high sensitivity of the body to the components, in childhood (only according to indications). Sold from pharmacy chains in tablets and ampoules (average cost - from 35 to 200 rubles).
- "Meteospasmil" . An antispasmodic drug from the myotropic group, it reduces gas formation, normalizes intestinal motility, and relieves pain. Contains alverine and simethicone. It is recommended not only for the treatment of spasms, but also as a preparation for diagnostic procedures. Contraindications: pregnancy, lactation, organ failure of any nature. Side effects are usually associated with individual intolerance. The cost of capsules varies from 380 to 450 rubles.
- Hyoscine butyl bromide . The drug blocks the transmission of nerve impulses in intestinal smooth muscle cells. In addition to relieving spasms, it normalizes the secretion of the digestive organs. There is no direct effect on the central nervous system and does not have an atropine-like effect. The drug is contraindicated in glaucoma, pulmonary edema, pregnancy and lactation, myasthenia gravis, and vascular atherosclerosis. The drug enters the systemic circulation after 30 minutes, and the maximum concentration is reached after two hours. Side effects include dry mouth, shortness of breath, and tachycardia. The average cost of tablets is 300-350 rubles, rectal suppositories are 350 rubles.
All products are incompatible with alcoholic beverages, some hormonal and painkillers . If there is no therapeutic effect, the use is stopped or other medications are prescribed.
Gastritis and how to relieve pain
Gastritis is a degenerative-inflammatory process in which irreversible organic and dystrophic changes appear in the mucous membrane lining the stomach.
It is not considered a dangerous disease and is often consulted by a doctor when urgent hospitalization is already required. Tablets for stomach pain due to gastritis are purchased on the recommendation of a pharmacist. Gastritis is considered a precancerous condition, regeneration of the organ surface and secretory function are disrupted, epithelial cells partially atrophy, and glands may be replaced by fibrous fibers. General signs of the disease are pain and burning in the epigastric region and stomach, nausea, frequent heartburn, flatulence, and unpleasant taste in the mouth.
To quickly relieve gastritis pain, it is necessary to determine the cause of its occurrence. Factors causing exacerbation: violation of the regime and quality of nutrition, emotional instability and frequent stress, increased activity of Helicobacter pylori.
The most dangerous forms of pathology are hypertrophic, atrophic, phlegmous and fibrous. In this case, pain medications will not help; assistance is provided in a hospital setting.
Pharmaceutical agents have an analgesic effect:
- Antispasmodics and analgesics that eliminate stomach tone and spasms are the most popular painkillers for gastritis. Disadvantage: short-term effect.
- Gastroprotectors are enveloping and astringent drugs. Restore stomach function and have antimicrobial activity.
- Antacids - normalize the acidity of gastric juice, eliminate heaviness and burning.
- Enzyme agents speed up the digestion of food and reduce stress on the stomach.
- Anticholinergic blockers - simultaneously stop spasms and reduce the production of hydrochloric acid. The synthesis of protective mucus is not disrupted.
Traditional medicine helps to restore the condition faster. When using a home method, it is advisable to inform your doctor.