What it is
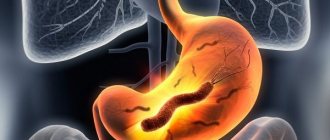
Hemorrhagic gastritis is one of the forms of gastritis, in which erosions (superficial tissue lesions) often form in the gastric mucosa as a result of inflammation. Therefore, it is also called erosive or corrosive. The occurrence of erosions is accompanied by severe pain.
Hemorrhagic gastritis is one of the forms of gastritis, in which erosions (superficial tissue lesions) often form in the gastric mucosa as a result of inflammation.
In this case, the pain is persistent and long-lasting. Relief of painful manifestations usually occurs during long-term treatment. Hemorrhagic gastritis is dangerous because superficial lesions of the stomach tissue can develop into a muscle plate defect (ulcer). Therefore, it is extremely important to identify this disease as early as possible and undergo appropriate treatment to avoid unwanted consequences.
The peculiarity of this type of disease is that at the initial stage there is a disruption of the functioning of the vessels of the gastric mucosa. As a result, hemorrhage begins in the inner membrane, which leads to the formation of blood clots (thrombi). This becomes the beginning of the inflammatory process of tissues, which leads to the formation of erosion.
Hemorrhagic gastritis may not always take an erosive form. But, since such consequences occur quite often, correct diagnosis at an early stage of the disease is very important. Erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis can develop in two variants: acute and chronic.
The acute form is characterized by intense symptoms of the disease. The pain is felt more vivid and sharp. The disease is of this nature when it appears for the first time or occurs repeatedly, with the rapid development of inflammation. The acute form of hemorrhagic gastritis can occur due to injuries, burns, blood loss, etc., when the body experiences severe shock. The chronic form of the disease is characterized by constantly recurring inflammatory processes. It is characterized by the appearance of gastric bleeding.
Forecast
The main thing is timely diagnosis. Hemorrhagic gastritis is not fatal; treatment at the initial stage depends only on the patient. Based on the work done by the patient, the doctor decides on more conservative methods, considering, for example, surgical intervention.
Otherwise, complications are possible - the transition of an acute form of the disease to a chronic one: stomach ulcers, cancer and bleeding.
It is worth remembering that hemorrhagic gastritis is a disease compatible with life, but it is better to prevent the disease than to treat it.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of hemorrhagic gastritis is made only after a series of studies and tests to confirm the presence of the disease. Thanks to the following actions, you can confidently say about the type of gastritis, assess the condition of the diseased organ, impaired functions and the degree of damage to the stomach.
The diagnosis of hemorrhagic gastritis is made only after a series of studies and tests to confirm the presence of the disease.
Clinical diagnosis. The very first study conducted with the patient. It includes the collection of information and analysis of the patient’s complaints, examination data, and the patient’s condition. On these grounds a preliminary diagnosis is made. The most important thing is that at this stage a further plan for diagnosis and treatment is drawn up.- Endoscopic diagnosis (gastroscopy) and biopsy. Gastroscopy is performed using a special flexible tube, inside of which there is a fiber optic system (gastroscope). It is administered through the mouth and esophagus. The condition of the stomach is observed. During a biopsy, cells and tissues are collected to accurately determine the cellular composition of the entire stomach.
- Laboratory diagnostics. This type of study includes a general and biochemical blood test, a clinical analysis of urine and feces, as well as a fecal test to determine occult blood. The presence of infection in the body is determined.
- Ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas. In addition to gastritis, there may be concomitant diseases that require treatment.
- Electrogastroenterography. Behind this long, incomprehensible name lies a fairly simple definition. Let's take it in order. The motor-evacuation function of the stomach is the process of moving food through the digestive tract, processing, mixing with gastric juice. In fact, one of the most important functions of the gastric tract. Electrogastroenterography examines how much the stomach is able to work.
Diagnostics and necessary examinations
In addition to the external examination and history taking, the patient is prescribed the following diagnostic tests.
Lab tests:
- blood chemistry;
- blood test to detect anemia;
- stool occult blood test;
- bacteriological and toxicological analysis of vomit, food debris, feces.
Instrumental studies:
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) with targeted biopsy - performed to assess the condition of the mucous membrane and exclude the oncological nature of the disease;
- X-ray of the stomach - study of the relief of the walls of the stomach;
- intragastric pH-metry – assessment of the acid-forming function of the stomach;
- breath test for helicobacteriosis.
Additionally, immunological studies, tests for syphilis and tuberculosis may be prescribed.
Clinical picture
The manifestations of hemorrhagic gastritis coincide with other types of gastritis, but have several additional signs that are unique to it. All symptoms of gastritis are divided into two categories - local and general. Local - only processes occurring in the affected part, in the stomach. General - appearing throughout the body. The body reacts sharply to a failure in any organ and tries with all its might to send a signal that not everything is okay with it.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic gastritis:
- heaviness;
- nausea;
- heartburn;
- general weakness of the body;
- fast fatiguability;
- increased irritability;
- pallor;
- sweating;
- drowsiness;
- intestinal disorder;
- stomach bleeding;
- vomiting (looks like coffee grounds);
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus.
Diet menu for erosive gastritis
We present to your attention an approximate diet menu for erosive gastritis for seven days.
- Breakfast. 2 soft-boiled eggs, a cup of weakly brewed tea with breadcrumbs.
- Snack. Banana.
- Dinner. Celery puree soup, steamed meatballs, rosehip tea, crackers.
- Afternoon snack. Berry-fruit mousse.
- Dinner. Sea fish fillet from a steamer with potatoes.
- A glass of kefir at night.
- Breakfast. A plate of oatmeal with honey, chamomile tea.
- Snack. Biscuits, jelly.
- Dinner. A bowl of cereal soup, fish cutlets, a cup of fruit compote, crackers.
- Afternoon snack. Berry soufflé.
- Dinner. A plate of meat stew.
- At night - yogurt.
- Breakfast. Steamed cottage cheese, a cup of compote.
- Snack. Sweet pear.
- Dinner. Vegetarian beetroot soup, chicken fillet with vegetables, toasted bread, herbal tea.
- Afternoon snack. Baked apple.
- Dinner. Buckwheat side dish with liver, tea.
- At night - a glass of tea with milk.
- Breakfast. Steamed omelette, plum jelly.
- Snack. A handful of dried apricots.
- Dinner. A serving of rice and potato soup, fish and vegetable casserole, crackers, weak tea.
- Afternoon snack. A glass of compote with dry cookies.
- Dinner. Vegetarian pilaf, a piece of dried bread, herbal tea.
- Before bed – a glass of fermented baked milk.
- Breakfast. Curd and berry casserole with jam, tea.
- Snack. Berry mix with yogurt.
- Dinner. A plate of tomato soup, a steamed cutlet with barley, a glass of prune compote, a piece of dried bread.
- Afternoon snack. Cottage cheese with low-fat yogurt.
- Dinner. A piece of boiled fish with vegetables, crackers.
- Before bed - a glass of kefir.
- Breakfast. Lazy dumplings with low-fat yogurt, a cup of weak tea.
- Snack. Fruit soufflé.
- Dinner. Barley soup, carrot-beet cutlets with boiled fish, a glass of compote, crackers.
- Afternoon snack. A handful of any dry fruit.
- Dinner. Fish and vegetable casserole, weak tea, a piece of dried bread.
- At night - yogurt.
- Breakfast. Rice pudding, compote.
- Snack. Sweet apple.
- Dinner. Beetroot soup, steamed chicken cutlets, boiled potatoes, weak tea, crackers.
- Afternoon snack. Galette cookies.
- Dinner. A portion of vegetable side dish, boiled fish, a piece of dried bread, a cup of herbal tea.
- Before bed – tea with milk.
Hemorrhagic gastritis: causes
This disease is due to its high polyetiology.
Most often, the development of hemorrhagic gastritis is associated with the incorrect use of certain medications and the consumption of poor-quality food products. This disease is due to its high polyetiology. Most often, the development of hemorrhagic gastritis is associated with the incorrect use of certain medications and the consumption of poor-quality food. In addition, Helicobacter, salmonella and diphtheria bacilli can also cause erosive gastritis. Improper nutrition can initiate the occurrence of defects in the gastric mucosa; exposure to high temperatures associated with eating too hot food plays a certain role in the development of the pathological process. In most cases, mucosal defects occur after suffering stress, especially against the background of chronic psychotrauma.
One of the main causes of hemorrhagic gastritis during chronic exposure to damaging factors is an increase in the permeability of vascular walls and microcirculation, as well as intracellular metabolic processes, accompanied by the development of cellular degeneration. The development of bleeding is directly due to the presence of multiple erosions, as well as the leakage of blood plasma and cellular elements into the lumen of the stomach.
Diet for erosive reflux gastritis
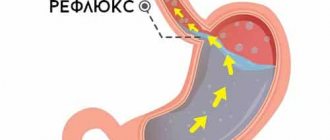
Erosive reflux gastritis occurs with the contents of the duodenum entering the stomach cavity. As a result, erosions appear on the gastric mucosa, which are not easy to cure. The reasons for this are the abuse of unhealthy foods, drinks, and overeating.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to prepare the stomach: for this, fasting is prescribed for 1-2 days. During these days, you are allowed to drink only still mineral waters and lightly brewed tea without sugar. During these two days, the stomach will be able to recover and rest.
Further diet for erosive reflux gastritis will consist of frequent and small portions of food. These will be only boiled or steamed dishes, mainly vegetables, a variety of cereals and slimy soups, ground white meat.
The duration of treatment for the disease is about 1 month.
It is imperative to exclude strong drinks (alcohol, beer, strongly brewed tea and coffee), as well as salt, spices, animal fat, fried foods, marinades, vinegar, dyes, soda and sauces. Under no circumstances should overeating be allowed.
Why does hemorrhagic gastritis occur?
The acute form of the disease develops as a result of:
- renal or liver failure;
- mechanical injuries to the stomach, for example, surgery;
- chemical burns due to contact with acids or alkalis on the mucous membrane;
- sepsis.
The impetus for the occurrence of chronic hemorrhagic gastritis can be:
- long-term use of NSAIDs;
- severe stress to which the body is regularly exposed;
- Crohn's disease;
- alcohol abuse;
- non-compliance with diet for chronic catarrhal gastritis;
- The bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which enters the stomach with food or water.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a tube equipped with a miniature video camera is inserted into the patient's esophagus. Thanks to the device, the doctor examines the walls of the stomach, sees all the redness, swelling and erosion, and determines the source of bleeding.
Prognosis: what will happen if left untreated?
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilievna
Practicing gastroenterologist
In the absence of gastric bleeding and timely treatment, the prognosis for recovery in patients diagnosed with erosive gastritis is quite favorable . If the disease is diagnosed for the first time, and treatment measures are carried out in accordance with the therapeutic plan, a complete cure can be achieved even on an outpatient basis.
With delayed diagnosis, the acute form of the disease becomes chronic , which is difficult to treat and often relapses even after surgery.
On our website: How to cure focal antral gastritis?
Symptoms
Taking into account the duration of the course of the disease, acute and chronic forms of hemorrhagic gastritis are distinguished.
Taking into account the duration of the disease, acute and chronic forms of hemorrhagic gastritis are distinguished. The types of disease differ in that acute erosions are caused by a healing period of 4 to 10 days, while chronic ones can exist for quite a long time. In addition, primary and secondary hemorrhagic gastritis are distinguished. The primary form of the disease develops in practically healthy people against the background of an unchanged mucous membrane; the secondary form is a consequence of the patient’s existing stomach diseases. Depending on the location of the pathological formations, erosions of the fundus, body and antrum of the stomach are distinguished.
Most often, the main sign of pathology is not intense dyspeptic complaints. In some cases, hemorrhagic gastritis debuts with gastric bleeding.
Patients with this pathology complain of decreased appetite, dull pain in the epigastric zone, a feeling of fullness and pressure in the stomach, nausea, heartburn, sour belching, and an unpleasant, metallic taste in the mouth. Pain may occur immediately after eating. The patient may experience vomiting of undigested food, diarrhea, followed by constipation. When palpating the abdomen, pain in the stomach area is determined, and symptoms of peritoneal irritation may not be detected, however, with acute hemorrhagic gastritis, tension in the abdominal muscles may be detected.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic gastritis are presented in table form.
| Complaints |
|
| Inspection data |
|
| Diagnostic data |
|
Specific signs of the disease are symptoms of acute or chronic gastric bleeding. In the case of an acute process, patients complain of general weakness, dizziness, and nausea. The classic symptom of the disease is vomiting “coffee grounds.” With profuse blood loss, consciousness may be impaired. The skin and visible mucous membranes become pale, tachycardia and decreased blood pressure are detected. The patient experiences the passage of black liquid feces; chronic bleeding is characterized by complaints of general weakness, headache, fatigue, dizziness; in addition, the patient may exhibit pallor of the skin, brittle nails and hair. Such patients are characterized by the development of posthemorrhagic iron deficiency anemia.
What kind of disease is this
Pathology refers to complications of chronic or acute gastritis. It is characterized by the appearance of foci of cell damage on the gastric mucosa. As the pathological process develops, bleeding erosions form.
The following reasons can provoke hemorrhagic erosive gastritis:
- long-term use of antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- the predominance in the diet of products that have an aggressive effect on the gastric mucosa (chips, crackers, low-quality sausages, smoked and spicy foods, sweet carbonated drinks);
- contamination of the stomach lining with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- alcohol and nicotine abuse;
- state of chronic stress;
- work in hazardous production.
If you experience discomfort in the stomach after eating or drinking hot drinks, you should not delay going to the doctor. These may be the first signs of the development of gastritis.
Symptoms
A preliminary diagnosis can be made based on the following signs:
- pain in the epigastric region that occurs during the day on an empty stomach, as well as at night;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- bad breath;
- heartburn;
- belching with a sour taste;
- vomiting at the peak of an attack of pain, often mixed with blood;
- constipation followed by diarrhea.
One of the characteristic signs of erosive gastritis is gastric bleeding. Its development is accompanied by general weakness, dizziness, pale skin, and fainting. Minor bleeding may not cause significant symptoms. It can be detected using a stool occult blood test.
Erosive gastritis, which is caused by taking medications, occurs in a latent form for a long time. The patient may experience minor symptoms of dyspepsia, such as heartburn and heaviness in the stomach. At this stage, symptomatic treatment is carried out. At the same time, the process of erosion development continues.
Treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis
Treatment can take place on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. Patients with signs of gastrointestinal bleeding are subject to mandatory hospitalization.
Treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis begins with diet therapy: meals should be frequent, fractional, in small portions, food should be consumed pureed and semi-liquid, warm. However, if there is bleeding, the Meulengracht diet is prescribed - pureed chilled food. Coffee, rich broths, spicy and fried foods, smoked foods, alcoholic drinks and freshly squeezed juices are not recommended.
Pharmacotherapy is carried out individually, taking into account the characteristics of the disease. In accordance with the standards of treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis, acidity correctors are prescribed (H2-histamine receptor blockers - cimetidine, ranitidine; M-anticholinergics - pirenzepine; proton pump inhibitors - omeprazole, pantoprazole; antacids - aluminum hydroxide + magnesium hydroxide, aluminum phosphate). Enveloping, astringent drugs (bismuth subcitrate, aluminum hydroxide + sucrose octasulfite), antibiotics (in the case of bacterial etiology of the disease), mucus formers (licorice root extract, licurazide + quercetin) and reparants (methyluracil, sea buckthorn oil) are also used.
In case of bleeding with hemorrhagic gastritis, hemostatic therapy is prescribed: oral solution of aminocaproic acid with adrenaline, tranexamic acid; Vikasol and etamsylate intramuscularly, intravenously. In hemorrhagic shock, blood loss is replenished with anti-shock blood substitutes, and sometimes with drugs and blood components. It is advisable to use vegetable oils: sea buckthorn, carotene and rosehip oil. These drugs have anti-inflammatory and reparative effects. In the remission stage, herbal medicine is indicated: a decoction of flax seeds, yarrow, plantain, St. John's wort and chamomile inflorescences.
In some cases, surgical treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis is performed. Unfortunately, even with the availability of modern equipment and surgeons’ knowledge of the latest surgical techniques, postoperative mortality in hemorrhagic gastritis is quite high, in addition, recurrent bleeding occurs in 20-30% of patients.
Today there is no consensus on what volume of surgical intervention is optimal, therefore the operation is performed only when all possibilities of conservative therapy and endoscopic treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis have been exhausted. The methods of endoscopic injection with an alcohol-adrenaline mixture, irrigation with hemostatic solutions and electrocoagulation of the bleeding area, and the method of prolonged hemostasis using a barium-thrombin mixture are quite effective.
Diet for chronic erosive gastritis
Nutrition and diet for chronic erosive gastritis depends on the stage of the disease. During the period of exacerbation, a strict diet is prescribed, the same as for acute erosive gastritis. During the period of remission, the diet expands slightly, but meals still remain fractional, with small portions of food, about 6 times a day.
It is recommended to start every morning with a glass of clean, not cold water. Food should be as gentle as possible: spicy, pickled, smoked, dishes with salt and preservatives should be avoided. Fruits must be eaten without peeling.
Avoid butter, replace it with any vegetable oil.
Forget about buns, creams and alcohol.
If there is an increase in stomach acid, it is recommended:
- skimmed milk;
- white bread croutons;
- dishes from liver, tongue, white meat;
- low-fat fish;
- boiled eggs;
- stewed or boiled vegetables;
- vegetable soup or puree;
- pureed side dishes from cereals (preferably rice, oatmeal or semolina);
- freshly squeezed non-acidic juices, diluted in half with boiled water.
For low stomach acid, the following are recommended:
- broths, soups;
- fermented milk products;
- boiled and stewed vegetables;
- low-fat meat, fish;
- side dishes made from cereals without adding milk and butter (vegetable oil can be added);
- homemade jam, natural honey, dried apricots, figs, raisins (instead of dessert);
- fruit and vegetable salads;
- strong brewed tea, or herbal tea (chamomile, St. John's wort, lemon balm);
- dried dark bread or crackers (not made from white flour).
This diet should be followed for several months until stable remission.
Diet for illness
During the treatment of gastritis, the patient must exclude fried, spicy, fatty foods, as well as smoked foods from the diet.
To achieve the maximum effect, treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis should be carried out comprehensively. A set of measures to restore normal activity of the gastric mucosa includes taking medications in combination with a special diet.
Since digestion of food is the main function of the stomach, diet is an important component of treating the inflammatory process. Proper nutrition is also of great importance for the prevention of this disease. The diet should be balanced and include all the necessary foods for the body.
During the treatment of gastritis, the patient must exclude fried, spicy, fatty foods, as well as smoked foods from the diet. Baked goods, coarse hard foods, and raw vegetables should be avoided.
The diet involves eating soft foods such as cereals, soups, boiled or steamed foods. In this case, the food should be at normal temperature, not too hot or cold.
This diet allows the intake of lean meat and chicken, fermented milk products, eggs, processed fruits and berries. You need to eat food several times a day (5 or 6), in small portions. Dieting for the purpose of losing weight is completely unacceptable.
Diet for acute erosive gastritis
The principles of dietary nutrition for acute erosive gastritis are based on eliminating inflammation in the tissues of the stomach.
On the first day of an exacerbation, it is recommended to stop eating altogether. From the second day, it is allowed to gradually introduce semi-liquid well-cooked porridge, natural jelly, and boiled eggs into the menu. This is a fairly strict diet, which will gradually soften as the acute process subsides.
You should eat meals in small portions, 5-6 times daily. Dishes should be cooked primarily by steaming, and food should be chopped and pureed as much as possible. For several days after the inflammatory process has normalized, biscuits, steamed omelettes, non-acidic and low-fat cottage cheese, vegetable soup, dietary white meat, and weak tea with added milk can be added to the menu.
For acute erosive gastritis, a strict diet lasts 15-25 days. After the inflammatory reaction is removed, the diet can be expanded somewhat, but you cannot abandon the diet altogether. As we said above, to consolidate the results, the diet must be followed for at least 3 months. When acidity increases, it is allowed to gradually include vegetable oils in the menu; when low - broths, a small amount of salt, lemon juice.
Spicy foods, bread and buns, fatty and fried foods, sauces and marinades, lard and sausages remain prohibited throughout the diet.
[11]
Treatment with drugs
The patient must take a set of medications prescribed by the doctor. Various medications act on specific processes in the body.
The complex may include drugs to reduce the secretion of gastric acid. Such medications include Kvamatel, Omeprazole, Nolpaza, etc. Additionally, the patient must take substances that normalize the activity of the stomach. This could be Maalox, Almagel, etc. The doctor prescribes the patient various enzymes that help digest food and ease the work of the stomach: Mezim, Pancreatin. In the presence of bleeding erosions, hemostatic drugs are prescribed.
In addition, the body needs substances that strengthen the immune system. In this regard, it is recommended to take vitamins and various restoratives.
Diet recipes for erosive gastritis
Here are a few recipes to diversify the weekly menu outlined above.
- Apple pudding for breakfast
We will need: half a glass of apple juice, 5 yolks, 300 ml of milk, 100 g of sugar, 25 g of gelatin.
Add gelatin to apple juice and leave for half an hour. Meanwhile, beat the yolks, put the milk on the stove, and bring to a boil. Add sugar and mix. After this, add the juice with gelatin to the milk, and finally the yolks. Stirring continuously, cook over low heat for 15 minutes. Turn off the heat, pour the mixture into molds and place in the refrigerator to harden for 8 hours. If you prepare the pudding in the evening, then by morning you will have an unusual and healthy breakfast ready.
- Meatballs with milk sauce
We will need: 0.5 kg of minced chicken, an onion, 3 slices of bread, 200 ml of milk, 2 tablespoons of flour, 3 tablespoons of vegetable oil, herbs.
Grind a small onion and bread into minced meat.
Prepare the sauce separately: 1 tbsp. pour a spoonful of flour into a frying pan, add vegetable oil, mix, pour in milk, cook for about 10 minutes.
We make meatballs from the minced meat and put them in the sauce, simmer until cooked (
35 minutes). When serving, sprinkle with herbs.
We will need: 3 tablespoons sunflower oil, 200 g pumpkin pulp, one sweet bell pepper, 1 small zucchini, 250 ml water, 150 g couscous, 1 small onion.
Wash the zucchini, pepper and pumpkin pulp, peel the pepper in the middle. Chop the vegetables and onions into small cubes and simmer over low heat. In a separate pan, boil 250 ml of water, pour boiling water over the couscous, add tbsp. a spoonful of sunflower oil and let it swell for about 5 minutes. After that, combine the couscous and vegetables. Simple and delicious.
[14]
Folk remedies
A folk remedy such as yarrow, which has an anti-inflammatory and hemostatic effect, is very helpful in treating gastritis.
This disease is treated quite effectively with folk remedies - using herbal decoctions and collections of medicinal plants.
A folk remedy such as yarrow, which has an anti-inflammatory and hemostatic effect, is very helpful in treating gastritis. A tablespoon of chopped dried herb is brewed in a glass of hot water. You need to drink a few tablespoons of the broth half an hour before meals.
The leaves of the aloe plant are a well-known anti-inflammatory folk remedy. The pulp needs to be crushed and a decoction made from it. Take the composition two teaspoons before meals, half an hour before.
Gastritis of the hemorrhagic type is well treated with such a natural substance as propolis. A small amount of propolis should be chewed thoroughly in the morning on an empty stomach. The substances contained in it have a positive effect on the functioning of the stomach and help restore the mucous membrane.
If you find signs of gastritis, do not delay its diagnosis and treatment. This will help you avoid serious stomach complications in the future. Do not neglect diet as an additional measure to treat the disease.
Folk recipes for herbal decoctions
When there were still no medications, people had the only option to alleviate their suffering - the use of herbs both externally and internally. This is due to the medicinal properties of plants. Among them there are cultures with antibacterial properties, others with wound healing and painkillers. Hemorrhagic gastritis can be treated using herbs. Official medicine does not reject such options. Among the medicinal plants for gastritis, you can use yarrow. It has anti-inflammatory and hemostatic properties. For pain, use infusions of valerian root, chamomile flowers, peppermint leaves, and fennel fruits.
Any herbal preparations should be used warm so as not to irritate the walls of the stomach.
Prevention
Prevention of hemorrhagic gastritis comes down to a healthy lifestyle, proper daily routine, regular nutrition, stress prevention, timely treatment of stomach diseases, as well as quitting smoking and drinking alcohol.
Sources
https://www.obozrevatel.com/health/bolezni/gemorragicheskij-gastrit.htm
https://gastritinform.ru/www.harbor.ru/med/chto-takoe-erozivno-gemorragicheskiy-gastrit-i-kak-ego-lechit.htm
https://simptomi.online/bolezni/zheludochno-kishechnyj-trakt/gemorragicheskij-gastrit.html
https://gastritinform.ru/bezgastritov.ru/gastrit/ostryj-gemorragicheskij-gastrit-s-krovotecheniem/
Diet for erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis
Erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis occurs with periodic bleeding, which is associated with damage to the vascular walls in the gastric mucosa. The difficulty of treating this form of erosive gastritis is that the erosive surfaces can bleed until the erosion is completely healed. But even after this, not in all cases we can say with confidence that the disease has been cured.
Drug treatment of erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis will not be effective unless you change your lifestyle and reconsider your diet.
Diet for erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis is the basis for a speedy recovery. The patient should completely avoid fried, canned or pickled foods, as well as spices, salt and smoked foods. Sweets, baked goods, white bread, cocoa, coffee, alcoholic and carbonated drinks, sour varieties of fruits and berries are prohibited.
What does the diet consist of? The menu should include light dishes that do not burden the stomach:
- vegetable soup;
- oatmeal, as well as buckwheat, rice and pearl barley;
- vegetable puree with vegetable oil;
- stew of vegetables and herbs;
- fresh fermented milk products (low-fat cottage cheese, kefir).
Steamed or boiled fish or eggs are perfect for protein foods. As for eggs, you can eat them raw, boil them soft-boiled, or make a steamed omelet from them.
To replenish blood loss, it is recommended to eat liver dishes and bake sweet varieties of apples.
Great attention is paid to the daily routine and food intake. You need to eat 6 times a day in small portions. Products should be crushed as much as possible, and while eating, chew well, so as not to damage the mucous membrane of the diseased stomach with unchewed pieces.
Instead of tea, it is recommended to drink a herbal decoction, adding a small amount of oak bark, St. John's wort or chamomile.
Treatment
Therapy for reflux lesions of the stomach is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the inflammatory process, improving the functional state of the digestive tract, increasing the protective functions of the body, normalizing the acidity of gastric juice and reducing the aggressiveness of bile. Such results are achieved using an integrated approach. Treatment of the disease is carried out with medications, physiotherapeutic procedures and diet. Additionally, you can use some traditional medicine methods. In case of complications, the patient may undergo surgery.
Drug treatment
If you have reflux damage to the gastrointestinal tract, you should not self-medicate. Drugs are prescribed depending on the degree of damage to the gastric epithelium, the spread of the inflammatory process and the general clinical picture of the patient’s health. Only a specialist can correctly draw up a drug therapy regimen.
Examples of drugs:
drugs for stopping excess bile production (Urdoxa, Ursofalk, Ursosan);- medicines with an enveloping effect (Pariet, Omez, Omeprazole);
- bismuth-based preparations (De-Nol);
- medications to reduce the acidity of gastric juice (Almagel, Phosphalugel);
- enzyme agents (Creon, Mezim);
- antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Drotaverine);
- antibiotics for infection (Amoxiclav);
- probiotics (Linex, Bifiform, Bifindumbacterin);
- drugs to restore intestinal motility (Motilak, Motilium).
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative medicine prescriptions should not be used as the primary treatment for reflux gastritis. Folk remedies improve the digestion process and strengthen local immunity, but they are not able to cure the disease. Recipes based on herbal ingredients can only be used as an addition to drug therapy.
Examples of folk remedies:
- dandelion syrup (plant flowers should be placed in a jar in layers with sugar, crush the mixture until the juice appears, dilute a tablespoon of juice in 100 ml of water, take several times a day);
- herbal mixture (combine yarrow, mint and St. John's wort in equal proportions, pour three tablespoons of the preparation into a liter of boiling water, leave for several hours, take the product in small portions throughout the day);
- potato juice (grate potatoes, squeeze out the juice, take the product in small portions several times a day).
Physiotherapy
Electrophoresis is highly effective in the treatment of reflux lesions of the digestive tract. The standard course of therapy is ten to fourteen days. If there are complications, the doctor may prescribe repeat procedures. Electrophoresis accelerates the tendency to recovery and increases the effect of drug therapy.
Video: Heartburn, reflux - causes and treatment.
Surgery
Surgery is used only in the presence of complications of reflux gastritis. Indications for operations are malignant and benign formations, deep ulcers and erosions, internal bleeding or insufficient activity of the pylorus. The decision about the need for surgical intervention is made by the doctor.
Diet and nutrition
A diet for reflux gastritis implies the exclusion of mechanical, thermal, and physical factors affecting the gastrointestinal tract. Food is consumed only warm. To prepare dishes, methods of steaming, boiling, stewing or baking are used. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, food should have a liquid or semi-liquid consistency. Meals are provided in fractions (at least five times a day). Drinking medicinal mineral water without gas is considered a good addition to the diet.
Other nutritional principles:
- exclusion from the diet of salted, fried, pickled, smoked, fatty, spicy foods;
- sweet pastries, fresh bread and confectionery are prohibited;
- during the period of remission, the menu is supplemented with fermented milk products;
- It is allowed to include vegetarian soups, water-based porridges, steamed cutlets, heat-treated vegetables, and juices into the diet.
Diet for reflux gastritis
Traditional methods of treatment
To reduce the severity of symptoms of hemorrhagic gastritis, teas with honey are used. Milk is also diluted in a glass of warm water and given to the patient to drink several times a day. For prevention, infusions of chamomile, calendula, yarrow, hay, and nettle are also used.
A popular recipe is boiling flax seeds. This remedy can practically replace antacid drugs.
Symptoms of reflux gastritis
For a long time, the signs of the disease are mild. Only when reflux gastritis progresses do the symptoms begin to bother the patient. If they appear, you should contact a specialist for timely diagnosis and treatment. Inflammation of the stomach, which is accompanied by the reflux of food chyme from the duodenum, is characterized by the following manifestations:
- aching pain and discomfort after eating;
- feeling of heaviness in the upper abdomen;
- belching sour or bitter;
- vomiting mixed with partially digested food;
- loss of body weight;
- nausea;
- changes in stool such as diarrhea or constipation.
If reflux gastritis is accompanied by dysfunction of the biliary tract, there is a reflux of bile into the stomach. The presence of bile acids causes a specific inflammatory process, in which a bitter taste in the mouth and vomiting mixed with bile are noted.
Symptoms of reflux esophagitis
In case of insufficiency of the sphincter of the cardial part of the stomach, reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus is observed.
This often occurs during sleep, when a person is in a horizontal position, during pregnancy. Reflux gastritis with reflux esophagitis gradually develops with the following clinical signs:
- heartburn in the evening or at night;
- belching sour or bitter;
- a feeling of a lump and pain behind the sternum, radiating to the back, neck, which intensifies with physical activity, jumping, forced breathing;
- frequent hiccups;
- drooling;
- cough;
- shortness of breath.
The aggressive effect of hydrochloric acid on the mucous membrane of the esophagus eventually leads to scarring and narrowing.
Symptoms of duodenitis
The inflammatory reaction in the duodenum is rarely isolated. Basically, there is a chronic course of the disease, which occurs against the background of dysfunction of the sphincters of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms of reflux gastritis are accompanied by manifestations of duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum) and bulbitis (inflammatory process in the duodenal bulb):
- discomfort in the upper abdomen after eating;
- pain on palpation of the pyloroduodenal area;
- flatulence;
- decreased appetite;
- nonspecific signs such as irritability, increased fatigue.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you suspect gastritis, you should seek help from a qualified doctor. He should ask the patient about his complaints, the nature of the pain, the presence of changes in the color of stool or vomiting with blood. After this, a physical examination (examination) of the patient is performed. Pay attention to the condition of the oral cavity, pallor of the skin, pain when pressing on the epigastric region.
Laboratory diagnosis of erosive gastritis necessarily includes a general blood test. In the chronic form of the disease, anemia is diagnosed using this test. Gastritis is also characterized by an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and an increase in the number of leukocytes (due to neutrophils).
To determine the presence of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, a specific test is performed that allows you to determine even a small amount of hemoglobin in the stool.
The basis for diagnosing gastritis is fibrogastroduodenoscopy. In this case, the attention of the endoscopist is drawn to pronounced redness and swelling of the mucous membrane. It also has a large number of small defects (erosions) from which blood leaks. Atrophic changes appear as the disease becomes chronic. An example of the mucous membrane in hemorrhagic gastritis can be seen clearly in the photo.
During FGDS, express diagnostics of Helicobacter pylori invasion of the mucous membrane is mandatory. Acidity indicators (pH) and the presence of reflux from the duodenum are also studied.
If necessary, a biopsy of suspicious areas of the mucous membrane is performed for cytological examination. It allows you to determine the morphological structure of epithelial cells and turn off/confirm the malignant process in the stomach.
Principles of treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis
Typically, drug treatment of chronic hemorrhagic gastritis takes place on an outpatient basis. If there is a suspicion of gastric hemorrhage, the patient must be hospitalized in the surgical department of the hospital.