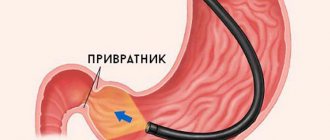
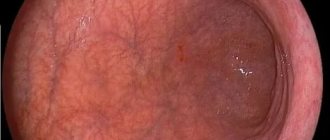
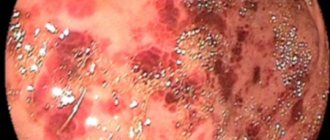
Features of the disease
The duodenum has an alkaline level. The contents received there are processed with substances:
- bile acids;
- pancreatic enzymes;
- lysolecithin.
The duodenal environment also includes components of salts and other elements. These substances are necessary for complete digestion of food. When the contents processed by the duodenal components move in the opposite direction, the mucous membrane of the upper digestive tract is damaged. Since the stomach and esophagus have an acidic environment, alkali injures their walls.
Duodenogastric reflux occurs regularly in healthy people. Normally, this process occurs mainly at night. If reflux occurs more often than physiology allows, chronic reflux gastritis develops.
Bile can only reach the stomach or reach the esophagus and oral cavity.
Chronic atrophic gastritis
Chronic atrophic reflux gastritis most often occurs in older people. This type of disease develops over a long period of time, inhibiting the gastric mucosa. Inflammation in the upper part of the esophagus in the presence of unfavorable factors lasts for years.
There are many reasons that provoke the chronic form of gastritis. Bacterial infection is one of the main factors in the occurrence of the disease. During gastritis, the functioning of the pylorus of the stomach is disrupted. As a result, acid begins to rise up the esophagus. This process is accompanied by chest pain.
Causes
Backflow of food occurs when the lower valve of the stomach does not close completely. Rejection of contents into the upper sections also occurs when the sphincter opens after food enters the duodenum. The chronic form of gastritis with bile reflux develops for the following reasons:
- malfunctions of the sphincter apparatus;
- violation of the coordination of the functions of the digestive departments;
- surgical interventions;
- taking hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs.
When duodenal juice and pancreatic enzymes enter the upper sections, they damage the mucosa. Especially when a person eats food that increases acidity in the stomach. The pH level affects the degree of epithelial damage. Prolonged duodenogastric reflux eventually provokes chemical gastritis type C.
Normally, the gastric mucosa is protected by a bicarbonate barrier. It is destroyed by exposure to too acidic or alkaline contents. The gastric mucosa becomes inflamed, which leads to gland atrophy.
Gastritis duodenitis-reflux is provoked by factors:
- poor closure of the pyloric opening;
- increased pressure and systematic inflammation in the duodenum;
- impaired motility of the digestive organs;
- activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- peptic ulcer;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- birth defects.
The release of contents can also be caused by external factors: consumption of heavy food, alcohol.
In 50% of reported cases, reflux gastritis is caused by inconsistency between the antrum and duodenum.
The main cause of stomach inflammation is the microbe Helicobacter pylori. Reflux gastritis is rare; this type of pathology accounts for less than 5% of cases.
Symptoms of the disease
Reflux gastritis, the symptoms and treatment of which differ depending on the form, can be asymptomatic or mild in most people. A typical manifestation of the disease is accompanied by the following conditions:
- pain appears in the stomach, which intensifies after eating;
- general weakness;
- bloating;
- feeling of a full stomach;
- heartburn;
- pain in the stomach;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- nausea;
- weight loss;
- belching with a sour smell and bitter taste;
- loss of appetite;
- pain when swallowing;
- burning in the stomach;
- dry mouth.
If there is an acute form of the disease and severe inflammation of the gastric mucosa, the patient’s temperature rises. Hidden forms of symptoms include conditions identical to pulmonary ailments - difficulty exhaling and inhaling, dry cough. Symptoms characteristic of laryngitis may appear - sore throat, hoarse voice.
The chronic form of gastritis is accompanied by the reflux of bile into the stomach. This causes diffuse atrophic lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. The production of gastric juice decreases. These disorders lead to the appearance of cancer cells. The disease is accompanied by vitamin deficiency and anemia, which manifest themselves in the form of fatigue, dry skin and cracks in the corners of the lips.
Types of reflux gastritis
Based on the nature of fluid reflux, there are 2 forms of gastritis:
- bile (biliary);
- duodenal.
Bile reflux gastritis is caused by weak contraction of the pyloric muscles, chronic stagnation in the duodenum. Long-term exposure of the components to the mucous membrane leads to the development of this pathology. Duodenal reflux with reflux gastritis develops due to inflammation in the intestine and increased pressure in it.
Based on the severity of symptoms, acute and chronic forms of the disease are distinguished. Reflux gastritis is characterized by long-term remission. Exacerbation occurs when infected with Helicobacter pylori against a background of weakened immunity and after surgery in the gastrointestinal tract.
Depending on the causes and the extent of inflammation, several types of disease are distinguished.
Surface
Gastritis caused by bile reflux begins with diffuse changes in the epithelium. Inflammation is distributed over the entire surface of the mucous membrane of the antrum of the stomach. Then the upper parts of the organ are affected. To protect the walls of the stomach from bile, new cells with a changed structure are formed in damaged areas. Superficial reflux gastritis is dangerous due to the degeneration of transformed elements into a cancerous tumor.
Since the antrum is anatomically lower than the body of the stomach and esophagus, reflux gastritis primarily affects its glands.
Focal
Inflammation in this form of the disease covers isolated areas of the mucous membrane. With focal reflux gastritis, the walls of the stomach are not completely affected. Inflammation is localized in one or several areas. With exacerbation, the lesions expand and deepen.
Erythematous
Erythema is redness of the epithelium. During instrumental examination, expansion of the capillaries is observed in the affected area. Erythematous gastritis, when consuming spicy, heavy foods, or alcohol, becomes an erosive type of the disease.
Inflammation of the areas is aggravated if parasite infestation occurs. This form is not a diagnosis, but a statement of fact. In the results of the study, the term “erythematous” refers to the existing inflammatory process in the form of foci.
Erosive
With frequent reflux of bile, the gastric mucosa loses its protective properties. Over time, the epithelium becomes very sensitive. Bile and enzymes corrode it, erosions and small ulcers appear. The inflamed areas bleed, causing severe pain. The erosive form of reflux gastritis with prolonged exacerbation provokes the development of stomach ulcers.
Reactive
Chemical gastritis type C provokes a chronic release of fluid into the stomach. The constant movement of refluxate in the opposite direction over time causes irreversible changes in the epithelium. Metabolic processes in cells are disrupted, tissue structure changes. The mucous membrane loses its ability to regenerate. Changes in the cell nucleus during reactive gastritis lead to loss of organ functions.
Atrophic
Chronic motility disorders weaken the stomach over time. The atrophy process lasts for years. Permanent damage causes the parietal cells to die. They are replaced by transformed elements that produce protective mucus instead of gastric juice. Continuous division of altered cells leads to proliferation of the epithelium. The accumulation of such elements forms polyps and cysts. The atrophic type of reflux gastritis can lead to the formation of a cancerous tumor.
Esophagitis
When the release of duodenal contents regularly reaches the esophagus, inflammation of the mucous membrane of this organ is diagnosed. This process is called duodenogastroesophageal reflux or esophagitis. The pathology develops due to imperfection of the lower esophageal sphincter. It serves as a flap that closes the organ from reflux of contents.
Normally, the esophageal sphincter opens several times a day. As the number of episodes increases, the protective mucosal barrier is destroyed. The inflammatory process begins. The sphincter opens due to increased pressure on the esophagus during pregnancy, overeating, and excess weight. Frequent reflux is also caused by surgery, trauma, hiatal hernia, and medications (beta blockers, nitrates, calcium channel blockers).
Etiology
Reflux gastritis is a special form of the disease in which an aggressive liquid, namely bile juice, acts on the surface of the stomach. Predisposing factors to the formation of such a process may be:
- maintaining an unhealthy lifestyle;
- poor nutrition;
- the course of the inflammatory process in the duodenum. In the medical field, this condition is called chronic duodenitis;
- long-term use of certain medications, in particular anti-inflammatory drugs;
- complications after surgery in the gastrointestinal tract;
- the occurrence of pathological processes or dysfunction of the pylorus;
- increased pressure in the duodenum;
- genetic predisposition.
In addition, the formation of such a disease is influenced by high or low secretion of hydrochloric acid. This disrupts the functioning of enzymes, which are significantly activated in an acidic environment, thereby causing insufficient protein digestion and the appearance of an inflammatory process. This process is called reflux, which causes the formation of chronic reflux gastritis.
The mechanism of formation of reflux gastritis
Signs
During the period of remission, the disease may occur without symptoms or they may be mild. Reflux gastritis is recognized by the presence of signs:
- stomach ache;
- heaviness during and after eating;
- belching with the smell of eaten food;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- increased gas formation;
- bitterness in the mouth.
Features of exacerbation: yellow coating on the tongue, loss of appetite, stool disorders, vomiting with bile. The long course of the disease is accompanied by anemia and vitamin deficiency. Cracks appear in the corners of the lips - jams. A person quickly gets tired and becomes irritable.
After physical exertion or against a background of stress, burning pain in the epigastric region may appear, which is accompanied by general weakness.
The acute phase of pathology is understood as a one-time exposure to chemical irritants. Painful manifestations of another kind are called an exacerbation period. The severity of symptoms does not always correspond to the stage of damage to the mucous membrane. Even in advanced cases, when the walls of the stomach become thinner, reflux gastritis can occur without symptoms. Pathology often manifests itself only as heartburn or belching.
If superficial inflammation is left unattended and untreated, the disease develops. First, atrophied lesions appear. They are combined with glands that still cope with their functions. Over time, improper cell formation and changes in their structure completely cover the antrum. Signs of atrophy with reflux gastritis:
- intolerance to eggs, dairy products, meat;
- sudden weight loss;
- loss of appetite.
The cells of the mucous membrane stop regenerating and are replaced by a layer of epithelium, which is similar in structure to the tissue lining the intestines.
Symptoms and complications of biliary gastritis
The clinical picture of the disease is very diverse. Symptoms depend on the extent of damage to the walls of the stomach, that is, they differ in the forms listed above. The main signs of any form are pain, which is most often felt in the right hypochondrium or epigastric region, but can radiate to the spine.
With a long course of the disease, a favorable environment arises for the development of gastric ulcer
Usually occur during meals or after heavy overeating. The pain is predominantly dull. Every time after eating, patients note a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach. Dyspeptic symptoms occur: nausea; belching sour; vomit. Due to intestinal dysfunction, stool becomes unstable, and constipation is replaced by diarrhea.
Since nutrients are less absorbed, a person loses weight and develops painful “stubs” in the corners of his mouth. Anemia and dry skin are noted. With a long course of reflux gastritis, a general deterioration in well-being occurs, weakness occurs, sleep is disturbed, and the person becomes irritable.
Complications of the condition are not only esophagitis. When gastric contents, along with bile acids, enter the vocal cords or trachea, laryngospasm occurs, and even asphyxia develops. With a long course of the disease, a favorable environment arises for the development of gastric ulcer.
Since the symptoms of biliary reflux gastritis are nonspecific, additional studies are prescribed. This is fibrogastroduodenoscopy, which helps to visualize changes in the gastric mucosa. An X-ray of the organ is performed with the introduction of a contrast agent. Laboratory tests are also necessary.
Diagnostics
If discomfort associated with digestion is detected, consult a gastroenterologist. He studies the medical history and gives directions for research and analysis. Diagnosis is aimed at studying the cause of the disease and the degree of involvement of the mucous membrane in the inflammatory process. Particular attention is paid to patients with signs of atrophy.
Diagnostics includes studies:
- endoscopy - performed using an optical device with a long tube;
- X-ray of the digestive organs;
- Ultrasound;
- antroduodenal manometry - study of motility and coordination of departments;
- daily analysis of stomach contents (ph-gram);
- blood chemistry.
People who undergo surgery in the gastrointestinal tract are at risk.
During instrumental diagnostics, a focal or diffuse inflammatory process is detected using an endoscope. The stomach contents have a yellowish tint. Most often, the lesions are located in the antrum, less often they reach the body and upper part of the stomach. When inflamed, the epithelium looks swollen, the lesions rise above the healthy mucosa. The sphincter located between the stomach and duodenum is expanded.
During endoscopy, a histological analysis (mucous membrane particles) is taken from a person. The material is examined under a microscope. The data obtained allows us to identify:
- the presence of hyperplastic changes;
- degree of inflammation;
- change in cell structure;
- replacement of glandular tissue with intestinal epithelium.
The presence of duodenal reflux is determined using an x-ray using a contrast agent or a ph-gram.
Diagnosis and drugs for the treatment of biliary reflux gastritis
The symptoms and treatment of gastritis are somewhat different from other forms of inflammation. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately understand the problem and establish the correct diagnosis. Gastroendoscopy will help determine “biliary reflux gastritis”. When examining the mucous membrane of the digestive organs, you can find a picture characteristic of this pathology.
To confirm the diagnosis, an X-ray examination of the stomach using a contrast agent is also prescribed. Stool analysis is a necessary test to establish the disease. The presence of blood clots and bile inclusions allows one to suspect improper functioning of the digestive sphincters and prescribe a more detailed study.
The first place to start treatment is to normalize proper nutrition and select a diet that helps the stomach easily and quickly digest the food it receives. Food should only be boiled, preferably in a liquid state. Avoid taking spices, hot and salty foods.
The first thing to start treatment with is the normalization of proper nutrition and the selection of a diet that helps the stomach easily and quickly digest the food it receives.
Foods such as eggs, white and brown bread, legumes, mushrooms, and sour fruits should be removed from your diet for a very long time. Unhealthy and heavy food slows down the digestion process, deteriorates the quality of digested food, slows down the transition of food chyme into the intestines, thereby provoking the reflux of food gruel back into the stomach.
When the disease develops, it is simply impossible to do without drug treatment. Experts immediately prescribe a whole range of medications aimed at reducing the symptoms of the disease and normalizing proper digestion.
There are several groups of drugs to eliminate bile stagnation and complete digestion of food:
- choleretic drugs: Ursosan, Ursohol, Holosas;
- agents that coat the stomach: De-nol, Almagel;
- drugs that regulate the production of gastric juice: Omeprazole, Panzinorm;
- drugs that improve peristalsis of the stomach and intestines: Motilium, Itomed;
- enzymes that help digest food: Festal, Creon;
- products that normalize the natural balance of the intestines and restore the regular release of digestive residues: Linex, bifidumbacteria;
- if necessary, antibacterial agents;
- complex of vitamins to restore immunity.
To restore proper motility of the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to include physical therapy, which will tone muscle tissue and weakened sphincters, and also strengthen the functioning of the digestive glands. Procedures such as electrophoresis and phonophoresis can be prescribed by specialists only during a period of deep remission.
A comprehensive massage will enhance metabolism, improve blood circulation in all organs and tissues, and help relieve muscle tension. In extreme cases, if therapeutic treatment is ineffective, surgery may be performed. It is indicated for sphincter insufficiency, neoplasms, scar changes that do not ensure proper intestinal motility and provoke the reflux of food back into the stomach.
Traditional treatment for biliary reflux gastritis
For the treatment of biliary gastritis, herbal infusions or decoctions of various herbs are used.
Herbal infusions or decoctions of various herbs are used for treatment. The recipes include sedative, antispasmodic, choleretic and anti-inflammatory herbs. Under the influence of alternative treatment, the gallbladder with its ducts begins to function normally, its motor function and the outflow of bile improve.
It is necessary to take folk remedies regularly and for quite a long time: 1–2 months. You should not stop treatment only if the symptoms of the disease have passed and no longer bother you. For therapy with traditional drugs, it is better to use several recipes and alternate them every 2-3 weeks, otherwise addiction may develop and the drug will stop working.
Traditional medicine recipes:
- dandelions: gastritis can be treated with syrup from the flowers of this plant. Dandelion flowers are placed in a three-liter jar and poured into 0.5 kg of sugar. It is best to add layers. Then the flowers need to be crushed until a syrup appears. For half a glass of boiled water, take 1 tbsp. l. syrup. Take the drug 2-3 times a day;
- chamomile: prepare syrup from chamomile flowers according to the same procedure as described above for dandelion flowers. Dilute 1 tsp in half a glass of water. chamomile syrup. Drink three times a day;
- Potatoes: You can treat it with either raw potato juice or potato broth. Drink juice from mashed peeled potatoes, half a glass, twice a day before meals. It is necessary to prepare fresh juice every time. To prepare the decoction, potatoes along with their peel are cut into pieces and boiled for an hour. The strained broth is taken six times a day, half a glass, on an empty stomach.
Sources:
- https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gastroenterologia/bile-reflux
- https://medaboutme.ru/zdorove/publikacii/stati/sovety_vracha/vospalenie_pri_biliarnom_reflyuks_gastrite/
- https://dvedoli.com/liver/gallbladder/biliarnyy-reflyuks.html
- https://rabbitprom.ru/what-is-reflux-gastritis-and-whether-it-can-be-cured-forever-symptoms-and-treatment-of-biliary-reflux-gastritis.html
- https://pobedigastrit.ru/lechsimpt/kak-lechitsya-biliarnyj-reflyuks-gastrit.html
- https://sammedic.ru/333489a-biliarnyiy-reflyuks-gastrit-prichinyi-simptomyi-i-osobennosti-lecheniya
- https://gastritinform.ru/ozhkt.com/zheludok/gastrit/lechenie-biliarnogo-reflyuks-gastrita.html
- https://gastritinform.ru/nmed.org/kak-lechit-biliarnyjj-reflyuks-gastrit.html
Treatment with medications
The goal of therapy is to restore gastric motility and prevent the destructive effect of the release of contents on the gastric epithelium.
Treatment of reflux gastritis in adults includes drugs:
- prokinetics to stimulate gastrointestinal motility - Cerucal, Motilium, Trimedat, Itoprid, Primer;
- proton load inhibitors - Nexium, Sanpraz, Lanzoptol;
- dopamine D2 receptor blockers – Cimetidine, Famotidine, Roxatidine;
- antacids – Phosphalugel, Almagel, Gaviscon, Hydrotalcide;
- products based on ursodeoxycholic acid - Ursosan, Ursohol.
Medicines are chosen depending on the cause of the disease and symptoms. To maintain the tone of the gastric muscles, prokinetics are prescribed. Duration of treatment is 2–3 weeks.
Diffuse superficial reflux gastritis is accompanied by increased formation of hydrochloric acid. Antacids are taken to neutralize this substance. For example, tablets Hydrotalcide, Rutacid. They help with heartburn, normalize acidity and protect the walls of the stomach during biliary gastritis. Preparations based on aluminum and magnesium also have the properties of sorbents - they absorb bile and lysocytin, which is toxic to the stomach. Hydrotalcide can be taken by children from 6 years of age.
Gastroduodenitis is treated with:
- antibiotics to destroy Helicobacter pylori;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- drugs that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid.
Stomach pain is relieved with antispasmodics and enveloping medications: No-Shpa, Almagel, Papaverine.
For nausea and vomiting, take Motilium, Metoclopramide, Torekan. Medicines are taken with the permission of a doctor.
Green tea and mint will help cope with mild nausea. Continuous vomiting is a reason to call an ambulance, as dehydration may occur.
In children, treatment of reflux gastritis is carried out:
- antibiotics;
- prebiotics;
- enzymes;
- dopamine receptor antagonists.
If the symptoms are severe, the child is treated in a hospital. The safest drug from the group of antagonists is Domperidone. It is approved for use by children from birth. Antibiotics are included in the treatment regimen if helicobacteriosis is detected.
Surgery for reflux gastritis is performed very rarely. Indications for surgery are non-healing ulcers, erosions, sphincter dysfunction, tumors.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Gastric pathology with signs of reflux can be caused by the following reasons:
- weakening of sphincter muscle motility;
- surgical removal of part of the stomach;
- operations to narrow the duodenum;
- removal of the gallbladder;
- plastic and other operations on the epigastrium;
- anatomical displacement of the stomach;
- chronic forms of gastrointestinal pathologies;
- malignant neoplasms in the digestive organs;
- duodenal obstruction;
- increased pressure in the intestines;
- congenital pathologies in the structure of the gastrointestinal tract and valves.
Important information: What is hypoacid gastritis
Factors that provoke the development of biliary gastroreflux:
- eating disorder;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products;
- inflammatory pathologies of the pancreas and gallbladder;
- formation of stones in the biliary tract, bladder and kidneys;
- long-term and uncontrolled use of medications that affect the coolant;
- emotional overload and stressful situations.
Diet
Treatment will not bring the expected effect without following a special diet. The diet includes gentle dishes that reduce and normalize the level of acidity in the stomach. Nutrition rules for reflux gastritis:
- during an exacerbation, follow diet No. 1;
- exclude spicy, fried foods from the diet;
- do not eat 3 hours before bedtime;
- eat 5-6 times a day in small portions;
- exclude cold and too hot dishes - take food only warm.
table No. 1 (click on the picture to enlarge)
Compliance with the regime promotes recovery. It is advisable that meals be taken without haste, at certain hours. If you have reflux gastritis, you can eat:
- viscous porridges - buckwheat and oatmeal are especially useful;
- soups with minced meat;
- steam cutlets;
- low-fat fish;
- well-cooked vegetable stew;
- low-fat dairy products;
- eggs (no more than 2 times a week);
- yesterday's bread (fresh increases acidity);
- crackers;
- butter, olive oil;
- jelly;
- herbal tea;
- for dessert - marmalade, soufflé, pastille, baked apples.
Nutrition for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
During the period of remission, it is recommended to drink medicinal mineral water. Tonic drinks, seasonings, rich broths, and gas-forming products are excluded from the diet.
2) Mixed gastritis
Mixed gastritis is when a patient suffers from several types of gastritis at once, for example, erosive, hemorrhagic and superficial.
If you periodically experience nausea, vomiting (sometimes with blood), lack of appetite, heartburn, pain in the ribs, which often radiates to the back, then you may be suffering from a mixed form of the disease. Of course, to make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a medical examination, and, therefore, special treatment, which is recommended to be combined with folk remedies:
- Green apples. The recipe is simple: finely chopped or grated fruits (without peel) should be eaten in unlimited quantities. It is important to remember that five hours before and after the procedure you are prohibited from consuming other foods.
- Honey (necessarily fresh harvest, preferably flower or mountain). One teaspoon in the morning on an empty stomach and one before bed. You can drink tea or still water. After this procedure, you can start eating, but not earlier than fifteen minutes later.
- the egg whites until foamy and drink the resulting cocktail on an empty stomach in the morning.
- mumiyo with water in equal proportions. Drink a tablespoon three times a day before meals.
Herbal treatment
Homeopathy is used in the treatment of reflux gastritis. Herbal remedies are usually used as an addition to treatment and are considered a folk remedy. There are medications that a homeopathic doctor selects individually, taking into account the cause of the disease and a thorough analysis of the symptoms. These include Baptisia, Bryonia, Hamomilla, Conium and others. These drugs can lead to stable remission even in advanced stages of reflux gastritis.
Conium is recommended for people with high levels of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, a tendency to nausea, heartburn, and sour belching. For severe pain, Argentum nitricum is suitable. It should be noted that homeopathic medicines are often not suitable for people with allergies.
Biliary reflux gastritis and reflux esophagitis symptoms and treatment
The disease is a chronic inflammation of the esophagus, which occurs due to the constant entry of acidic stomach contents into it. The pathology is associated with insufficiency of the lower esophageal sphincter, which normally protects the esophagus from the penetration of gastric juice into it.
The main symptoms of reflux esophagitis are heartburn and sour belching, which usually occur after eating, as well as when bending forward. In addition to this is discomfort in the epigastric region.
Biliary reflux gastritis has a more intense clinical picture. Symptoms of this disease include pain and other disorders. Often patients are bothered by a feeling of fullness and bloating, as well as heaviness usually appear on an empty stomach, and their intensity can vary - from severe acute to aching. Vomiting is often observed.
Biliary reflux gastritis and reflux esophagitis require immediate treatment. This will help improve the patient's condition and avoid possible complications. If esophagitis is detected, you should give up bad habits, as well as intense physical activity on the abdominal area.
Drug therapy is based on prescriptions that will reduce the aggressive effect of gastric juice on the mucous membrane of the esophagus. Among them are “Almagel” and “Maalox”, used in a course. They coat the walls of the stomach and reduce acidity.
In addition, it is recommended to use drugs that reduce the secretion of gastric juice (Omeprazole). Prokinetics improve the tone of the sphincter, which is protection against the reflux of acidic contents. Among such drugs are Motilium and Motilak. If conservative therapy does not produce results, surgical intervention may be required, which is performed using endoscopic equipment.
Folk remedies
If cholecystitis is diagnosed along with bile reflux, folk remedies are used along with the main treatment for gastritis:
- eat 2 pears daily on an empty stomach;
- take a decoction of oats before meals - 500 ml, pour 1 liter of boiling water and leave for 40 minutes;
- drink ¼ glass of rowan juice 30 minutes before meals.
To eliminate heartburn when the contents of the duodenum are released into the stomach, celery root is used. Drink a tablespoon of juice before meals.
An effective remedy for the treatment of reflux gastritis is flaxseed. It can be purchased at a pharmacy. Pour 2 tablespoons of the product into a glass of boiling water and leave for 10 minutes. Drink 100 ml of decoction before meals.
To prevent food from moving in the opposite direction, you need to sleep on high pillows and do not lift heavy objects.
Surgical operations
Surgeries are performed extremely rarely. Surgery is performed only when:
- scarring process;
- formation of neoplasms;
- the presence of deep ulcers and erosions;
- pyloric insufficiency;
- bleeding.
Atrophic reflux gastritis most often does not prevent a person from leading a normal lifestyle. The disease complicates life mainly during periods of exacerbation. Nevertheless, gastritis must be treated, and the sooner the better. If you do not see a doctor in time, cancer cells may begin to form, which may be incurable.
It is always easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. To avoid the appearance of gastritis, you must be wary of stress and nervous irritation. It is very important to follow a proper diet and nutrition regimen. You can't snack on the go. It is advisable to get rid of bad habits.
Half an hour before meals you need to drink a glass of water. This not only prevents overeating, but also reduces the acidity of gastric juice. At the first signs of gastritis, you should immediately consult a doctor and get diagnosed. Often the disease develops asymptomatically and is noticed late.
Forecast
Reflux gastritis can be cured when the disease is not advanced and only the upper part of the epithelium is damaged. Simply taking heartburn medications will only make the situation worse. The right treatment that targets the cause will help get rid of reflux.
Basic lifestyle recommendations for GERD
Even advanced types of the disease can be successfully treated, but it will not be possible to get rid of it completely. When the glands are damaged, you can only prolong the period of remission.
Exacerbation of the disease occurs with overeating, poor nutrition, long-term treatment, and alcohol consumption. If you exclude these unfavorable factors and follow a gentle diet, this will be a good prevention. The risk of exacerbation of reflux gastritis will be minimized.
We recommend: What is the danger of ulcerative gastritis and how to treat it?
Types of reflux gastritis and their features
Reflux gastritis is divided into three main types. They differ in the causes and course of the disease. Types of reflux gastritis:
- Superficial affects the upper layer of epithelium and cells. In this case, digestion is disrupted and there is a risk of developing a malignant tumor.
- Erosive manifests itself in the form of small ulcers on the gastric mucosa. The development of the disease is accompanied by pain. If left untreated for a long time, an ulcer may form on the stomach.
- Atrophic reflux gastritis is one of the most dangerous types. During illness, serious changes occur in the gastric mucosa. The atrophic appearance refers to the precancerous period and can lead to the appearance of a malignant neoplasm.
Preventive actions
You can prevent the occurrence or exacerbation of gastric reflux pathology by following certain rules:
- healthy eating at regular times;
- diet;
- timely treatment of concomitant diseases of the abdominal organs;
- active lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits;
- immune support.
For any manifestations of dysfunction of the digestive system (bitterness in the mouth, dyspepsia, stool disorders, stomach pain), it is better to visit a doctor and undergo qualified treatment. It is important to remember that biliary gastroreflux is a disease that requires immediate treatment.