If, against the background of inflammation of the gastric mucosa, accumulations of leukocytes form on the walls of the organ, follicular gastritis develops. Often the disease occurs due to damage to the body by Helicobacter pylori. Since the mucous membrane is unable to perform its functions, lymphocytes are produced that are designed to fight the pathogen. The accumulation of cells and the formation of follicles interferes with the secretion of gastric juice and impairs digestion.
What kind of pathology is this
The pathological process manifests itself in the appearance of follicles on the gastric wall, which are formed from leukocytes. They disrupt digestion and cause dysfunction in the gastrointestinal tract. Pathologists consider chronic gastritis caused by H. pillori to be the main cause of development.
Bacteria penetrate the epithelial cells of the gastric mucosa, and the acids they secrete disrupt the functioning of the digestive tract. Motility and secretory activity of the gastrointestinal tract decreases. The human immune system, trying to protect the stomach from the harmful effects of microbes, tries to destroy them by sending leukocytes to the sites of damage.
As a result, an accumulation of leukocytes occurs on the lining of the stomach, which turn into follicles, sometimes reaching large sizes. By inhibiting the vital activity of bacteria, such formations harm the functioning of the digestive system, since they reduce the secretory ability of the glands of the gastric epithelium. As gastritis progresses, the follicles cover the inner walls with a dense layer, significantly thickening them. This reduces the release of hydrochloric acid necessary for digesting food.
Treatment of lymphoid gastritis
Treatment of the disease is as follows:
- Taking antibacterial drugs that affect pathogenic microorganisms. The patient usually takes antibiotics for 2 weeks.
- If a patient complains of heartburn, he is prescribed medications that help reduce the acidity of the stomach.
- Taking drugs that restore damaged cells of the mucous membrane, drugs that coat the walls of the stomach from aggressive influences.
- In case of severe pain, the patient additionally takes painkillers.
- To improve digestive functions, certain enzymes are prescribed.
Causes
The follicular form of gastritis is a secondary pathology and is formed on the basis of damaged mucosa caused by a chronic type of disease. The main reason for its appearance is considered to be damage to the inflamed membrane by the bacterium X. pylori. But there are other factors that can provoke the onset of the development of this rare form of gastritis:
- errors in nutrition (a lot of fatty foods, fast food);
- improper diets (fasting);
- stress;
- constant emotional stress;
- dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
In addition, the development of follicular gastritis is provoked by addiction to alcohol and smoking, constant snacking “on the go”, as a result of which food is poorly chewed and systematically irritates the stomach wall.
Gastritis is different from gastritis
According to localization on the inner surface of the stomach, chronic gastritis is:
- Antral. It affects the antrum, then spreads in the form of ulcers to other parts and the duodenum.
- Fundal. Affects the fundus of the stomach (fundus). It is localized in the body and fundus, significantly increasing the risk of cancer.
- Pangastritis. Inflammation affects the mucous membrane of the fundic and antral zones.
Clinics diagnose 3 types of this disease:
- “A” – primary autoimmune (fundal). The body produces antibodies to its cells, so the mucous layer of the stomach dies, and the number of glands that produce secretions is reduced.
- “B” – bacterial, antral. The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is found in 90% of cases of gastritis. The results of its vital activity are ulcers and erosive damage to the walls of the stomach.
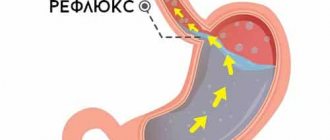
- “C” – chemical or reflux gastritis. Due to disturbances in the functioning of the pylorus, duodenogastric reflux occurs - the contents of the duodenum end up in the stomach. Other provoking factors are alcohol abuse and taking a number of medications.
Chronic gastritis is also distinguished:
- According to the stage of the course - in the phase of remission or inflammation.
- According to the effect on the mucous membrane - erosive (atrophic, wears out the epithelium) and non-erosive (hyperplastic, modifies cells, causing them to grow). Useful video about atrophic gastritis here ↗.
- According to the amount of gastric secretion - reduced secretion (hypacidal), increased secretion (hyperacidic) and normal secretion.
There are specific types of chronic gastritis: radiation, lymphocytic, allergic, granulomatous.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of follicular gastritis is similar in symptoms to other forms of pathology and manifests itself in the form of:
- heartburn;
- burps sour;
- “ hunger pain ” that occurs in the morning or some time after eating;
- bowel dysfunction ( constipation , diarrhea );
- lack of appetite (due to stagnation of food in the gastrointestinal tract).
Digestive disorders lead to the formation of stagnant processes in the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, patients complain of heaviness in the stomach that appears after eating, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. Due to decreased gastrointestinal motility, such patients often alternate between diarrhea and constipation. Due to poor breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients, patients are visually noted to have pale skin, brittle hair and nails, emaciation, and a white coated tongue. In addition, their appetite decreases and they feel constantly tired.
Main symptoms of the disease
It is difficult to identify any specific signs that characterize this particular form of inflammation of the gastric mucosa - for the most part they are common to all types of the disease. Symptoms of lymphoid gastritis may include the following sensations and processes:
- frequent and prolonged heartburn;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- sour belching;
- morning stomach pain, usually occurring 1-3 hours after breakfast;
- loss of appetite - to the point that the patient refuses to eat;
- both frequent constipation and diarrhea;
- heaviness in the stomach, bloating;
- nausea, often ending in vomiting.
With advanced forms, the following may also be observed:
- conspicuous thinness;
- weakness;
- pale and dry skin;
- dense white coating on the tongue;
- jams, cracks in the corners of the lips.
Diagnostic procedures
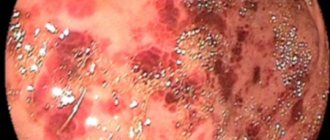
The difficulty in establishing an accurate diagnosis is that this type of gastritis is rare and does not have specific manifestations characteristic only of it. Therefore, during diagnosis, it is necessary to distinguish the follicular form of gastritis from atrophic and hypertrophic, since round formations and folds with erosions appear on the surface of the gastric epithelium, as in these pathologies.
To clarify the diagnosis, endoscopy is mandatory and the affected area of the gastric mucosa is examined using a probe. In addition, material is collected for histological examination. Cytology is performed to exclude oncology, as well as to determine the type of gastritis.
After questioning and collecting anamnesis, the patient is prescribed:
- general and biochemical analysis of urine and blood;
- abdominal echocardiogram;
- stool analysis.
Studies help identify deviations from the norm in the blood formula, as well as the presence of foreign impurities in feces and urine.
Gastritis with lymphoid hyperplasia of the stomach
The danger of hyperplasia is that tumors can form as a result of the pathological process. This can happen due to the fact that not only increased division occurs at the cellular level, but sometimes their structural change, which leads to the formation of a tumor.
In this case, the division process looks normal. This leads to the mucous membrane growing in a certain place. Gastric hyperplasia can occur in epithelial tissue cells, mucous membranes and other tissues of the organ.
Lymphoid disease refers to pseudolymphatic lesions, most often it occurs against the background of peptic ulcer infection or inflammation of the lymph node itself
Symptoms in the initial stages of the disease are most often absent or mild. This justifies the danger, since the disease develops without the patient being aware of it. Therefore, hyperplasia is predominantly detected when the disease becomes chronic and advanced.
Lymphoid hyperplasia is the process of excessive formation of lymphocytes in the lymph nodes . This is inflammation of the lymph node, which leads to it becoming larger. Lymphoid anomaly affects not only the lymph node, but also the organ.
Lymphoid disease refers to pseudolymphatic lesions. Most often it occurs against the background of a peptic ulcer, infection or inflammation of the lymph node itself. Hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa or deeper globules of the organ is possible.
Diagnosing a lymphoid abnormality is difficult, since there are no atypical cells, nodes form in the submucosa and muscular layer, and fibrous stroma is present. The localization of lymphoid disease may vary.
To confirm gastric hyperplasia, you need to undergo a series of tests, since the symptoms of the disease are absent or similar to other gastrointestinal diseases. Treatment of hyperplasia in the stomach can be carried out with medications, diet or surgery, or traditional medicines.
Treatment
If the diagnosis of follicular type of gastritis is confirmed by research, then treatment should be started immediately. Self-medication should not be carried out, because, despite the fact that the disease passes without pronounced symptoms and periods of exacerbation, it is dangerous. The follicles themselves do not degenerate into oncology, but the glands of the mucous membrane, which atrophy due to pathological processes occurring on the walls of the stomach, can transform into an oncological form. Therefore, you should strictly follow the doctor’s advice and the outcome of the disease will be positive.
Treatment of follicular gastritis involves the following steps:
- drug therapy;
- dietary nutrition;
- diet;
- folk treatment during remission.
To relieve symptoms, therapy is carried out with medications, the action of which is aimed at eliminating the bacterium H. pylori and restoring the gastric mucosa.
- Two types of antibiotics are used. They contribute to the inhibition of the vital functions of microbes and their death. The course of treatment is 10-14 days. If the effect is not complete, then one group of drugs is replaced by another ( Metronidazole , Klacid , Amoxiclav ).
- Antacids. Their action is aimed at reducing the acidity of hydrochloric acid and reducing the aggressive effect on the walls of the stomach ( Almagel , Phosphalugel ).
- Enzymatic medications are prescribed to improve the digestion process and normalize the gastrointestinal microflora ( Panzinorm , Mezim ).
- Alginates create a protective film that can protect the walls of the stomach from the harmful effects of food and hydrochloric acid ( Gaviscon ).
- Antispasmodics relax smooth muscles, relieve pain ( No-shpa , Spazmolgon ).
- Vitamin preparations help accelerate the processes of regeneration of mucous tissue and increase the immune properties of the body.
Treatment with medications should be carried out strictly according to the regimen suggested by the doctor. Antibiotics for X. pylori infection are taken for the period prescribed by the doctor. It is not worth stopping the medications on your own, even if your general condition improves, since the bacteria have not completely died, but only the process of their reproduction has slowed down.
Interrupting the use of antibiotics contributes to the development of microbial addiction to this medicine.
Treatment methods for follicular gastritis
There is almost no information on the Internet about the follicular type: this form of gastritis is secondary, is a concomitant disease and is diagnosed extremely rarely. But such a diagnosis exists, which means that those who suffer from this disease do too.
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori causes inflammation of the stomach
Any form of gastritis is inflammation.
Depending on the subtype, inflammation can occur only in the gastric mucosa or penetrate into deeper layers.
Follicular gastritis appears against the background of already existing gastritis of any other form. The highest risk is in patients who have had Helicobacter pylori infection.
Reference : Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that causes an infection, as a result of which gastritis develops in the patient’s stomach. Infection occurs through household items, dirty hands, unwashed fruits and vegetables, etc.
The development of the disease can occur several years after infection, when favorable factors coincide (low immunity, poor nutrition, etc.). Before this, the bacterium is in a dormant state, and humans do not notice it.
The presence of bacteria can be detected using various tests.
The nature of the disease, its development and several anatomical facts
When gastritis begins to develop in the stomach, the body throws all its strength into resisting the unpleasant process. In order for harmful bacteria to be defeated, lymphocytes are called upon in large quantities, which often quite successfully protect the body and “hold the line.”
But in this case, everything happens a little differently. The affected tissue (and gastritis always destroys stomach tissue) attracts too many lymphocytes. They accumulate in large quantities on already injured areas.
This leads to natural blockage of the glands through which enzymes are released. As a result, the quality of food digestion in the stomach decreases (which is already present due to primary gastritis), which leads to an exacerbation of symptoms and a decrease in the patient’s quality of life.
Establishing diagnosis
A painful symptom in the stomach area is a reason to go to the doctor
The patient consults a doctor with very subtle symptoms, which can suggest many different diseases. For example:
- acid in the mouth after waking up;
- heartburn immediately after eating;
- persistent flatulence;
- a combined feeling of a full stomach and hunger;
- pain symptoms.
Standard methods are used to make an accurate diagnosis.
- Determination of primary symptoms, identification of the nature of hypertrophy as a result of thickening.
- FGSD - endoscopy - is a not very pleasant procedure that involves swallowing a small camera, with which the doctor will examine the patient’s stomach from the inside, examine its condition and find damage. It is often combined with a biopsy - in this case, a piece of tissue from suspicious thickenings will be pinched off for their detailed examination. With the help of this study, tumors (malignant and benign) will be excluded, with which seals in follicular gastritis can easily be confused.
- Blood, urine, stool tests.
Antral gastritis (the second name for follicular gastritis based on its location - in the antrum of the stomach) is detected quite simply. After research and diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
Treatment: traditional, alternative methods and diet
Antral gastritis is treated with three approaches at once: medication, using natural remedies (traditional medicine) and diet. None of these methods should be excluded, because the triple blow helps to relieve unpleasant symptoms more quickly.
Medicines
Drug treatment is prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation. Roughly speaking, medications are used symptomatically.
- In case of pain, the use of analgesics is recommended, but in doses strictly limited by the treating gastroenterologist (they negatively affect the gastric mucosa).
- For actively developing inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed.
- Flatulence and stool disorders are treated with appropriate medications.
- And if food is poorly digested, the doctor prescribes additional use of enzymes.
Important! Self-medication may not only not help, but also aggravate the situation. Consult your doctor about each drug you use.
A couple more important nuances
Gastritis goes hand in hand with stress. Remember this! You must closely monitor your psycho-emotional state so as not to provoke accelerated development of the disease and exacerbation.
Excessive physical activity is contraindicated for antral gastritis. You should not reach a state of physical fatigue. This applies not only to fatigue during a particular workout, but also to the number of sports activities during the week. Everything is good in moderation!
Sleep at least seven hours a night. Be sure to set a bedtime clock and stick to it at all times (even on weekends!). The same applies to nutrition - set a convenient schedule and stick to it with minimal occasional deviations due to circumstances.
Traditional medicine methods
Traditional medicine offers many ways to relieve unpleasant symptoms.
The main advantage of these methods is that they all work on natural ingredients, but the action is formed by the same chemicals as pharmaceutical drugs.
The main drawback is about the same. Many people do not take “herbs” seriously, believing that they can be consumed in any quantity and without specifying safety. This is fundamentally wrong.
The use of herbal infusions should be agreed with a doctor
Any most harmless prescription should be agreed with your doctor. Don't add more work to him!
There are many different recipes that combat certain symptoms. For example, potato juice is used for heartburn, and tincture of wormwood and plantain for diarrhea.
Such recipes are much older than the oldest medicines and are based on observation of certain properties of natural components. Therefore, if your doctor approves of the tincture you like, drink it boldly and without fear.
Gastritis is a disease of modern man. Poor nutrition, problems with daily routine, and ignoring the initial symptoms lead to the fact that a person consults a doctor not at the initial stage of the disease, but when the symptoms significantly worsen the quality of life.
Timely treatment and strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions allows you to put any form of gastritis into remission and make the symptoms completely invisible.
Source: https://PobediGastrit.ru/lechsimpt/kak-lechit-follikulyarnyj-gastrit.html
Proper nutrition
Diet is of great importance in the therapy. It is developed individually by a nutritionist or gastroenterologist, depending on the clinical picture and condition of the patient.
But there are certain rules that must be followed by all patients with follicular gastritis, without exception.
- Meals should be frequent (5-6 times a day), but in small portions (200-250 g) so as not to create a burden on the digestive tract. For the same reason, you should chew your food well and take your last meal 3 hours before bedtime. Under no circumstances should you overeat.
- Preference should be given to boiled, baked or stewed dishes. The food should be light, tasty and aesthetically presented in order to awaken the patient’s appetite, since during illness it is absent.
- The diet should be dominated by vegetable fats, lean meat, free of coarse fibers, and low-fat fish.
- Patients can eat puree soups, stews, porridges, casseroles, jellies, mousses and soufflés.
- It is better to steam or bake meat products without using fat.
- Vegetable oil is used only in salads, but is not subjected to heat treatment.
- It is advisable to eat vegetables boiled, and when choosing fruits and berries you should pay attention to the content of fruit acids in them (sour varieties are not allowed).
For follicular gastritis, the following should not be included in the diet:
- green pea;
- beans;
- radish, radish;
- peas, beans;
- corn;
- mushrooms;
- sour berries and fruits;
- onion garlic;
- spices;
- fatty and spicy foods;
- baked goods and sweets with cream.
Also, patients are strictly prohibited from smoking, drinking alcohol, strong tea and coffee.
Difficulties in diagnosis
Diagnosis of gastritis is often difficult due to the lack of specific manifestations of lymphoid pathology, and at the initial stage – very disturbing symptoms. Follicular gastritis is easily confused with the hypertrophic or atrophic form.
Competently prescribed and performed comprehensive diagnostics play an important role in establishing a diagnosis and further treatment
Advanced lymphoid gastritis can lead to a disease of the lymphatic tissues of the stomach, which at the initial stage of examination is sometimes confused with cancer, but with timely treatment, the chances of recovery are much greater.
Diagnosis of lymphoid gastritis necessarily includes:
- collecting information about the medical history, previous health problems, dietary habits, and habits of the patient, which may be the cause of the development of the disease;
- conducting gastroscopy, which allows you to examine in detail the tissues of the stomach, esophagus, duodenum, assess the degree of their damage, and also identify oncological tumors even in the embryonic state;
- mandatory biopsy, which will confirm or refute the likelihood of cancer development;
- detailed blood and urine analysis;
- a blood test, which includes determining a set of indicators regarding the anatomical state of the stomach (gastropanel), which makes it possible to assess the condition of the tissues of the organ, the degree of its functioning, determine the presence of Helicobacter, assess the risk of pathology transforming into an ulcer, oncology, as well as other serious disorders;
- echocardiogram, ultrasound examination.
Prevention
In order to exclude relapses of follicular gastritis, during the period of remission you should not violate the menu suggested by the doctor, and also use infusions of herbs that can improve the regeneration processes of the gastric mucosa. A decoction of medicinal plants (chamomile, calamus, St. John's wort, mint), propolis tincture (10 drops per 100 ml of water 3 times a day before meals), honey helps in this case.
Sea buckthorn oil has a healing effect (drink 1 tsp 30 minutes before meals). A glass of freshly prepared potato juice, drunk on an empty stomach, neutralizes the effect of hydrochloric acid.
In addition, people with gastritis need to avoid stressful situations and try to always be in a good mood. Exercise daily, lead an active lifestyle, but do not overwork. You should also eat on time to prevent the release of gastric juice “idly”.
Very important. It is necessary to get rid of bad habits, undergo regular examinations with your doctor, and if unwanted symptoms appear, then visit him unscheduled. There is no need to self-medicate, since at the wrong time, the follicular type of gastritis threatens to develop into a more serious disease.
Treatment and prevention
The duration and effectiveness of treatment for gastritis depends on how long the sick person decided to seek help from a doctor, on a full examination, and on following all prescribed therapeutic recommendations. Follicular gastritis, which appears against a background of chronic gastritis, requires the use of various medications that relieve inflammation of the gastric mucosa, eliminate pain, have an enveloping effect, the ability to reduce and regulate the production of hydrochloric acid, and help break down food with the help of enzymes. If Helicobacter is detected in the gastric environment, a course of antibiotics is prescribed to suppress pathogenic microorganisms.
A course of treatment for follicular gastritis should be prescribed by a qualified specialist. Ignoring the symptoms of a developing dangerous disease, waiting for everything to “resolve” on its own, and self-medicating is unacceptable
Taking the recommended medications strictly according to the prescribed regimen allows you to effectively fight gastritis and quickly improve your well-being. In addition to the use of medications, it is important to exclude all factors that provoked the development of gastritis:
- establish a meal schedule, optimize the composition of food products, eliminate heavy meals, stick to a diet;
- not just minimize bad habits, but get rid of them, no matter how difficult it may be;
- maintain a sleep and rest schedule;
- try to provide a comfortable emotional environment at home and at work that is favorable for healing;
- spend more time outdoors.
Traditional medicine reference books have a huge number of recipes to help overcome this unpleasant disease. Whether it is worth resorting to unconventional methods is something everyone has the right to decide for themselves, but this issue must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Reasons for appearance
Pathology does not develop independently and appears on the basis of existing diseases. The causes of follicular gastritis can be:
- vegetative-vascular hypertension, disrupting the functionality of the whole organism;
- bad habits that affect the mucous membrane;
- Helicobacter pylori infection that affects the antrum, which contains the most favorable habitat;
- psycho-emotional instability and frequent stress, leading to disturbances in digestive processes, decreased appetite and immunological defense;
- overeating, abuse of fast foods and instant food force the spleen and stomach to work in emergency mode;
- irregular meals;
- rough or poorly chewed food that irritates mucous surfaces.
The following can provoke the development of pathology in a person who adheres to proper nutrition:
- HIV infection;
- presence of parasites;
- cytomegalovirus;
- candidiasis;
- autoimmune balance.
Attention! The development of pathology occurs gradually, without the presence of severe symptoms, which greatly complicates diagnosis.