- September 26, 2018
- Gastroenterology
- Smirnova Alexandra
Currently, gastrointestinal diseases have a strong upward trend. Most experts believe that the reason lies in constant stress, poor nutrition, and poor environmental conditions.
If you don’t pay attention to your own health and don’t follow the basic rules of a balanced diet, then a problem can develop in your body that you may not be aware of for a long time, and it will only manifest itself during a period of exacerbation. In this article we will try to understand what a disease such as atrophic hyperplastic gastritis is, what are the causes of its occurrence, what symptoms does it manifest, and also consider treatment methods.
About hyperplastic gastritis
Doctors note a rather rare manifestation of this pathology compared to other gastrointestinal diseases. Hyperplastic gastritis accounts for about 5% of cases of the total number of chronic gastric diseases. A characteristic feature of this disease is excessive and rapid proliferation of epithelial tissues, resulting in the formation of rigid folds and polyps. Hyperplastic gastritis develops as a result of hyperplasia of the gastric epithelium.
Medicine knows that men are susceptible to pathology four times more often than women. When it develops in children, comprehensive and effective treatment allows for complete regression of the disease and restoration of the gastric mucosa. Hyperplastic gastritis in adults most often leads to mucosal atrophy.
Symptoms
The disease is considered dangerous and does not manifest itself in any way at the initial stage of development. Patients feel the disease when the condition of the gastric mucosa has already undergone irreversible changes, and in the acute stage. A characteristic symptom is considered to be severe aching pain in the stomach, heartburn, rotten belching, and bad breath. Nausea or vomiting, heaviness, fever, gas formation in the intestines, and diarrhea are indicative. There is a complete lack of appetite and severe weight loss of the patient.
Symptoms depend on the form of hyperplastic gastritis and on the level of acidity of the digestive juice. With certain types of disease, gastric bleeding can occur, then the patient feels weak. As a result, chronic anemia and protein deficiency in the body develop.
Patients diagnosed with hyperplastic gastritis are at risk of developing stomach cancer, which occurs as a complication of the disease in question.
An additional danger of the disease is its chronic nature; patients are exposed to long-term hypovitaminosis and disorders of the digestive tract.
Main types
Hyperplastic gastritis comes in several types:
- Atrophic hyperplastic gastritis. Characterized by the formation of many polyps on the gastric mucosa.
- Superficial hyperplastic gastritis. It is the mildest form of this disease. Only the upper layers of the gastric mucosa are exposed to pathological processes.
- Diffuse hyperplastic gastritis. Such a diagnosis occurs if multiple changes are present on the gastric mucosa that have different etymologies.
- Focal hyperplastic gastritis. This form of the disease is characterized by the development of a slowly growing benign tumor.
- Granular hyperplastic gastritis. A characteristic feature of this form of pathology is the presence of multiple semicircular growths. As a result of their appearance, the mucous membrane swells and becomes lumpy.
- Erosive-hyperplastic gastritis. It is characterized by the formation of erosive areas and nodular formations on the gastric mucosa. Hypertrophy of the folds cannot be ruled out.
- Chronic active atrophic hyperplastic gastritis. As a result of the chronic course of the pathology, thickening of the walls of the stomach occurs.
- Antral hyperplastic gastritis. This disease is characterized by decreased gastric motility. Changes in the structure of the gastric mucosa are observed.
Causes of the disease
The specific cause of this stomach pathology has not been identified. Doctors believe that they are similar to those that provoke diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Let us highlight the causes of hyperplastic gastritis:
- Poisoning with chemicals and alcohol.
- Chronic food allergies.
- Chemical and thermal burns of the mucous membrane.
- Past viral diseases: typhoid, influenza, hepatitis.
- Dysfunction in the functioning of the endocrine glands.
- Violation of metabolic processes.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages, smoking.
- Hereditary predisposition to pathology.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Lack of vitamins in the body.
In the presence of several provoking factors, the risk of developing pathology increases.
Causes of pathology
Until now, doctors have not found out the specific reason as a result of which this stomach disease develops. Some experts are of the opinion that the etymology of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis is similar to the etymology of gastrointestinal diseases.
The following factors can provoke the development of hyperplastic gastritis:
- Poisoning with alcohol or chemicals.
- Chemical or thermal burn of the mucous membrane.
- Vitamin deficiency in the body.
- NS diseases.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Abuse of smoking and alcoholic beverages.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine system.
- Diseases of a viral nature, for example, hepatitis, influenza, typhoid.
- Chronic food allergies.
If several of these factors are present at once, the risk of developing atrophic hyperplastic gastritis increases significantly. Symptoms and treatment are often interrelated.
Hyperplastic gastritis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
In the modern world, gastrointestinal diseases tend to increase. Many believe that the reason for this is constant stress, poor nutrition, and poor environmental conditions. Without paying attention to our body, without following the basic rules of rational nutrition, we may not even suspect that a problem is brewing inside the body. Hyperplastic gastritis - what it is, what are the causes and symptoms of the disease, as well as how to treat it, we will consider further.
Symptoms
Most often, the initial stage of the disease is asymptomatic. Moreover, any signs may be absent for quite a long time. The development of the pathological process is characterized by the manifestation of the following symptoms:
- Pain in the epigastric region.
- Belching and heartburn.
- Bloating. The symptoms of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis are similar to those of other types of disease, but there are still some differences.
- Rapid weight loss despite the fact that the diet remains the same.
- Drowsiness.
- General malaise.
- Digestive disorders.
- Change in stool color.
- Nausea.
- The occurrence of a feeling of overeating with a small amount of food eaten.
If any suspicious signs appear, you should be wary and consult a doctor. This will facilitate timely detection of the disease and, as a result, more productive treatment.
How to identify chronic hyperplastic atrophic gastritis? More on this below.
Complications
The danger of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis is the development of complications and severe irreversible consequences for the body. With advanced gastropathology, a stomach ulcer or a malignant tumor may develop. There are other, no less serious complications of the disease:
- hypochlorhydria (low hydrochloric acid content in gastric secretions);
- dysfunction and atony (decreased peristalsis and loss of tone) of gastric motility, causing persistent dyspepsia and gastroparesis;
- hypoproteinemia (significant decrease in protein levels in the blood plasma);
- sudden weight loss, exhaustion;
- anemia;
- deterioration of digestive functions and hydrochloric acid production;
- changes in the structure of epithelial tissues and subsequent atrophy of varying severity.
References: med.vesti.ru/articles/zabolevaniya/atroficheskij-gastrit-zheludka/ https://www.rmj.ru/articles/bolezni_organov_pishchevareniya/Atroficheskiy_gastrit_chto_my_ponimaem_pod_etim_sostoyaniem_Sovremennye_podhody_k_diagnostike_i_lecheniyu/ https://www.ob ozrevatel.com/health/bolezni/giperplasticheskij -gastrit.htm Nutrition for gastric diseases, Ilya Melnikov 2009 crbusman48.ru/prevention-gastritis/ https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gastroenterologia/hyperplastic-gastritis Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/18/2020
Diagnosis of pathology
If problems related to the stomach occur, you should contact a specialist such as a gastroenterologist. In order to establish the reasons that resulted in disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, the following clinical studies are carried out:
- Helicobacter test;
- biochemical examination of stool, blood and urine;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- intragastric pH-metry;
- X-ray of the stomach;
- endoscopic biopsy;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Having the results of these studies, the specialist is able to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy, taking into account all the nuances.
Diagnostics
It is important to diagnose hyperplastic gastritis in time to avoid the mentioned possible complications. Diagnosis and treatment of gastritis is performed by a gastroenterologist. To make a correct diagnosis, the following types of patient examinations are used:
- fluoroscopic examination using a contrast agent;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopic examination;
- study of gastric tissue or histology;
- blood tests - general, biochemical;
- analysis for the detection of Helicobacter bacteria;
- study of pH levels in the stomach;
- ultrasound examination of the patient's abdominal cavity;
- stool test for occult blood;
- gastroscopy.
Gastroscopy of the stomach
Treatment
Due to the fact that the etymology of the disease is not fully understood, with the development of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis, complex therapy should be carried out, which takes into account the manifested symptoms.
Taking into account the form of the disease and its course, the gastroenterologist develops a special drug therapy regimen. Most often, in the treatment of this pathology, drugs belonging to the following pharmacological groups are used:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Ranitidine.
- Antibacterial agents, which include Clarithromycin.
- Antispasmodic drugs: Buscopan or No-shpa.
- Enzymatic preparations. Allows you to significantly improve digestion. The most commonly used are Pepsin or Mezim.
- Proton pump inhibitors, for example, Omez.
- Antacids. The most commonly used drug is Gaviscon.
- Medicines that help normalize digestion, for example, Motilium.
- Products that have an enveloping effect, for example, Almagel or Phosphalugel.
- In advanced cases, hormonal drugs can be used to treat atrophic hyperplastic gastritis of the stomach.
The rapidly developing disease provokes the rapid proliferation of cells that transform into polyps. Treatment in this case does not exclude the possibility of surgical intervention.
How to treat
Due to the fact that the causes of the development of hyperplastic gastritis are not fully known, treatment is carried out comprehensively, taking into account the manifesting symptoms of the disease.
Taking into account the form of the disease and its course, appropriate medications are prescribed. We list the groups of drugs that are used in the treatment of hyperplastic gastritis of the stomach:
- Proton pump inhibitors: Omez.
- Drugs that normalize digestion: Motilium.
- Antacids: Gaviscon.
- Enzymes to improve digestion: “Mezim”, “Festal”.
- Enveloping agents: “Phosphalugel”, “Almagel”.
- Artificial substitutes for hydrochloric acid: “Acidin”, “Pepsin”.
- Antispasmodics: “No-shpa”, “Buscopan”.
- Hormonal drugs in advanced cases.
- Antibacterial drugs: Clarithromycin.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Ranitidine.
The progressive development of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis leads to the rapid proliferation of cells developing into polyps. Treatment may require surgery.
In what cases is surgery indicated:
- In the presence of polyps, cysts.
- For frequent stomach bleeding.
- With a sustained decrease in serum protein in plasma.
Nutritional Features
There is no special diet for such a disease, however, taking into account its type and course, the attending physician will be able to advise the appropriate diet. If there is increased gastric secretion, then you should adhere to diet No. 1, if reduced, then No. 2. During periods of exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to follow diet No. 16.
In addition, there are general recommendations:
- You should eat in small portions.
- Fruits and vegetables must be subject to preliminary heat treatment.
- Dishes should not be too cold or hot.
- When cooking, steaming should be preferred.
- You need to eat slowly, chewing your food thoroughly.
Smoked products, pickles, carbonated drinks, too spicy and fatty foods, all baked goods, as well as food prepared by frying should be completely excluded from the diet. It will not be possible to cope with stomach pathology without following an appropriate diet. What other methods are used to treat atrophic hyperplastic gastritis?
Therapeutic diet for hyperplastic gastritis
When prescribing proper nutrition, exclude junk fast food, confectionery, fresh baked goods, canned foods and fried foods from the diet. At the same time, salt and spices are added to a minimum. The therapeutic diet involves split meals up to 5 times a day.
Dishes are steamed, boiled or baked. Many vegetables and fruits are not allowed to be eaten raw. Chew food thoroughly and monitor its temperature. If you are sick, you should not eat hot or too cold food.
For gastritis with increased secretion, follow diet No. 1. If the inflammation goes away with reduced secretion, the doctor prescribes table No. 2. When the patient experiences an exacerbation of the disease, then menu No. 16 is followed.
Treatment with traditional methods
Traditional medicine also has means to treat the disease. Most often, herbal therapy is assumed. It is recommended to take decoctions of the following plants:
- Blooming Sally.
- Loosestrife.
- Roots of Lyubka bifolia.
- The plantain is big.
- Thyme.
- Calendula officinalis.
- Pharmaceutical camomile.
The roots, flowers or leaves of plants must be brewed as follows: one spoon of the mixture is poured with two hundred milliliters of boiling water and left for 20 minutes. It is better to take infusions before meals, about twenty minutes.
Folk remedies
People have many recipes for the treatment of hyperplastic gastritis of the stomach. As a rule, this is a herbal treatment. It is recommended to take decoctions of the following plants:
- Pharmaceutical camomile.
- Calendula officinalis.
- Thyme.
- The plantain is big.
- Decoction of the roots of Lyubka bifolia.
- Loosestrife.
- Blooming Sally.
Brew flowers and herbs in the following ratio: for 200 ml of water you will need a tablespoon of the mixture. Leave for 20 minutes and take 20 minutes before meals.
Folk remedies help restore appetite and gastric mucosa, relieve inflammation and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. But it is worth remembering that you cannot self-medicate. Before using herbs, consult a doctor. The main thing is not to harm your body, but to help cope with the disease.
Recommendations
Traditional medicine helps restore the mucous membrane, improve appetite, relieve inflammation and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. However, it is important to remember that you should not self-medicate, and folk remedies can only be used with the permission of the attending physician and only as part of complex therapy. That is, traditional medicine cannot be used as the only treatment for this pathology. We reviewed the symptoms and treatment of atrophic hyperplastic gastritis.
How to treat chronic atrophic hyperplastic gastritis
Treatment is prescribed immediately after receiving diagnostic results. The earlier it starts, the more significant the results will be. Since hyperplastic gastritis is usually accompanied by other diseases of the internal organs, treatment is prescribed comprehensively and taking them into account. In addition, the stage of the disease is always taken into account. Unfortunately, atrophy of the glands of the antrum of the stomach is not completely cured, so the main goal of treatment is to stop the atrophic process and restore the basic functions of the stomach.
The treatment complex consists of the following components:
- drug therapy;
- therapeutic diet;
- physical therapy and other aids;
- treatment with folk remedies;
- surgical intervention (in extreme cases).
Drug therapy
Treatment with medications has the following goals:
- destruction of Helicobacter pylori bacteria using antibiotics or special anti-Helicobacter pylori agents (Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, De-Nol, Ulcavis, etc.);
- relieving irritation and protecting against it with the help of enveloping agents (“De-Nol”, “Ulkavis”, “Almagel”, etc.);
- increased acidity level (natural gastric juice, etc.);
- restoration of motor skills (“Trimedat”);
- improving the digestion and absorption of food using enzyme replacement therapy (Pepcidin, Creon, Mezim, Festal, etc.);
- pain relief (“No-shpa”, “Papaverine”, “Drotaverine”, etc.);
- elimination of dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, constipation and diarrhea);
- increasing the level of vitamins and minerals with the help of special vitamin complexes and medicinal preparations.
Therapeutic diet
A therapeutic diet for atrophic hyperplastic gastritis is not just proper healthy eating, it is part of therapy. The success of treatment largely depends on how well the diet is organized and followed. At the beginning of treatment it will be the most strict, then gradually soften. However, a patient with such a diagnosis will have to adhere to the basic principles of this diet throughout his life.
The diet is primarily aimed at restoring the mucous membrane, as far as possible, and normalizing the acidity of gastric juice. With this type of gastritis, foods that can injure the mucous membrane and that take a long time to digest in the stomach are prohibited, that is, rough, heterogeneous foods rich in fiber.
Basic principles of the diet:
- regular split meals (5 – 6 times a day);
- small portions that do not cause heaviness in the stomach;
- eating at the same time, which helps the production of gastric juice;
- dishes and drinks should be warm, but in no case hot or cold;
- You should exclude foods that can injure the mucous membrane and will take too long to digest in the stomach: anything spicy, smoked, salted, fried, pickled, as well as carbonated drinks, alcohol, strong coffee, whole milk, fresh bread, baked goods, confectionery, etc. d.
- food should be easily digestible and rich in protein, nutrients, vitamins and minerals;
- You should choose steamed or boiled dishes.
Recommended dishes and products:
- lean meats and fish, steamed, baked or boiled;
- low-fat broths;
- vegetable puree soups;
- stewed or boiled vegetables;
- slimy porridge;
- pureed cottage cheese;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- omelettes;
- souffle;
- jelly;
- dried bread;
- from confectionery products - marshmallows, marshmallows, marmalade;
- vegetable and butter.
Auxiliary therapeutic agents
As an additional treatment, various methods of healing the body in general and the gastrointestinal tract in particular are used. Physiotherapy is widely used and produces positive results. No less popular is treatment with mineral waters, which can be carried out both at specialized resorts and at home. Massage is useful for gastritis. It can be carried out not only by specialists, but also independently, daily before meals, massaging the abdominal area clockwise. This procedure will increase the secretion of gastric juice and will be especially effective if, after the massage, you take a medicinal decoction or infusion recommended for gastritis with low acidity.
Treatment with folk remedies
This treatment is prescribed in addition to the main one. For example, using traditional medicine, you can increase the level of acidity (white cabbage juice) or protect the gastric mucosa from negative influences (linseed oil). When treating this type of gastritis, herbs such as chamomile, calendula, plantain, dandelion, St. John's wort, yarrow, sage, mint, as well as calamus and chicory roots are used. Honey is added to many decoctions and infusions. Take these medications before meals.
Important! Atrophic hyperplastic gastritis cannot be cured with folk remedies alone! All prescriptions should be made only by the attending physician!
Surgical intervention
In advanced cases, surgery may be required to remove the most damaged part of the stomach. As a rule, doctors try to avoid this extreme measure and limit themselves to therapeutic methods.
Possible complications of the disease
Lack of timely treatment can provoke the development of some complications. These include:
- Stomach carcinoma.
- Cancer tumor.
- Ulcer development.
- Reduced whey protein.
- Decline of digestive functions as a result of damage and a decrease in the number of parietal cells.
- Gastrointestinal motility disorder.
- Fast weight loss.
- Development of anemia.
- Varying degrees of mucosal atrophy.
- Damage to the mucous membrane.
When the first unpleasant symptoms of antral atrophic hyperplastic gastritis with symptoms of exacerbation appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
What kind of disease is hyperplastic gastritis?
In clinical gastroenterology, hyperplastic gastritis is considered a rather rarely detected pathology of the stomach, which, among chronic gastric diseases, accounts for about 3.7-4.8% of diagnosed cases.
Hyperplastic gastritis is a rare form of chronic gastric disease.
When areas of increased mitosis of the cells of the mucous membrane lining its cavity are identified as a result of an endoscopic examination of the stomach, gastroenterologists can make a diagnosis of hyperplastic gastritis.
Experts call such risk factors for the development of hyperplastic gastritis as:
- eating disorders;
- allergies to certain foods;
- deficiency of essential vitamins;
- toxic effects of alcohol and carcinogenic compounds, severe renal failure and hyperglycemia.
And when treating hyperacid gastritis and gastroesophageal reflux disease with the help of potent drugs that inhibit acid secretion (Omeprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, etc.), the risk of increased growth of polyps that appear in the areas of the main glands and foveoli (gastric pits into which the ducts of the glands emerge) increases. . Probably, this localization of the pathological process is due to the fact that regeneration of the gastric mucosa when it is damaged occurs precisely due to the cells of the mucosa covering the areas of the gastric pits.
The symptoms of hyperplastic gastritis are not specific and vary greatly, but gastroenterologists include in the list of possible clinical manifestations of this pathology: heartburn, belching with a rotten taste, plaque on the back of the tongue, nausea, increased gas formation, pain in the epigastric region (aching, pressing or cramping), vomiting .
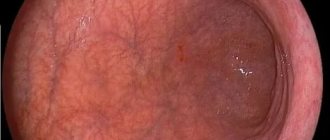
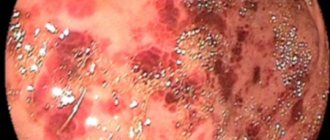
The main method on which the diagnosis of hyperplastic gastritis is based is endogastroscopy (endogastroduodenoscopy). Endoscopic instrumental diagnostics allows not only to visualize pathologically changed areas of the gastric mucosa, but also to perform a biopsy: take tissue particles for subsequent histochemical examination. X-rays, ultrasound of the stomach, and electrogastrography are also used.
The main method on which the diagnosis of hyperplastic gastritis is based is endogastroscopy
Advanced hyperplastic granular gastritis threatens the development of gastric ulcers and even cancer. Giant hypertrophic gastritis leads to hypochlorhydria; experts note the ability of this form of pathology to degenerate into a cancerous tumor of the stomach. With focal hyperplasia of enterochromaffin-like mucosal cells, gastric carcinoma can also develop. Polypous hyperplastic gastritis, according to some data, becomes malignant in almost 20 cases out of a hundred.
The most common consequences and complications of hyperplastic gastritis:
- changes in the structure of the gastric mucosa with atrophy of varying severity;
- damage and reduction in the number of parietal cells, decreased acid synthesis and deterioration of the digestive functions of the stomach;
- atony and impaired gastric motility, leading to persistent dyspepsia and partial gastroparesis;
- hypoproteinemia (drop in serum protein levels);
- anemia;
- weight loss.
Disease prevention and prognosis
The presence of hyperplastic gastritis requires constant monitoring by a specialist. In addition, the patient must strictly adhere to the diet and prescribed treatment regimen. Especially if there are polyps. Complete restoration of the mucous membrane in adults is a very rare occurrence, but absolute recovery in childhood is possible. The prognosis of the pathology depends entirely on the form of the disease and the degree of hyperplasia.
As such, prevention does not exist due to the unknown reasons influencing the development of the disease. However, following the general rules for preventing stomach diseases will not be superfluous. The following recommendations must be followed:
- Compliance with diet.
- You should eat often, in small portions.
- You need to eat enough vegetables and fruits, drink vitamin complexes.
- Nutrition should be moderate.
- You should not abuse fatty and fried foods, flour products, and carbonated drinks.
- It is necessary to give up bad habits such as alcohol and smoking.
- You should take medications strictly as prescribed by your doctor.
- It is recommended to periodically drink herbal remedies for the stomach.
- Do not neglect protective equipment in hazardous industries.
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly.
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
In the article we looked at atrophic hyperplastic gastritis. What this is is clear from the information above.
Description of the disease
Hyperplastic gastritis is understood as a special type of damage to the mucous layer of the gastric organ. It is characterized by increased proliferation of epithelial cells, in which the volume and mass of mucus greatly increases. This leads to the formation of polyps, folds and cysts on the inner surface of the stomach. Inflammation can have varying degrees of severity and affect different areas of the stomach, being localized in one place or affecting the entire area of the organ. Diagnosis of the disease is greatly complicated by the fact that in the initial stage it often occurs without severe symptoms. Symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and internal bleeding appear in later stages.
Hyperplastic gastritis can be classified as a rare type of chronic gastric disease. Moreover, it is not a separate disease, but covers a whole complex of gastrointestinal pathologies. The basis of this is not inflammation of the mucous membrane, as happens in other types of gastritis, but another process - the excessive formation of new epithelial cells. This phenomenon is called hyperplasia.
Under the influence of external negative factors, a failure occurs in the regenerative system of the epithelium. The mucous layer is designed in such a way that its cells are constantly renewed, and the outdated ones are replaced by new ones. When the regeneration process is disrupted, normal cells are replaced by damaged ones.
Damaged cells cannot perform their functions; they only secrete a large amount of mucus, which covers the walls of the stomach. In this case, gastric motility is disrupted and the secretory gland malfunctions. Epithelial cells in undamaged areas begin to intensively produce hydrochloric acid to compensate for its deficiency.
These areas in the stomach alternate with atrophied areas that are unable to function normally. As a result of the increased growth of damaged cells, the mucous layer of the stomach greatly increases in volume, folds and multiple polyps appear on it.
The peculiarity of this disease is that in childhood this process can result in the regeneration of the mucosa, which restores its functions. In adults, this pathology always develops into a chronic atrophic form of gastritis, which is often given a precancerous prognosis.
Methods for diagnosing granular gastritis
Granular gastritis is diagnosed using ultrasound, probing and fibrogastroscopy with biopsy. An ineffective diagnostic method is fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS), since with such an examination the gastroenterologist-endoscopist can clearly see neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the stomach wall. FGDS shows the location of the “grains”, their size and quantity. During the procedure, a special tube with a video camera is used that films what is inside the stomach - a fibrogastroscope.
Why is granular gastritis dangerous?
Granular gastritis is a serious disease, the danger of which is a high risk of complications. Against the background of swelling of the mucous membrane, gastric motility may be impaired. This causes serious deviations in metabolic processes, which also disrupts metabolism. Granular gastritis can easily cause internal gastric bleeding. If you do not respond to this problem in a timely manner, death may occur. In this case, it is necessary to immediately perform gastric resection.
Granular gastritis is treatable if diagnosed in the early stages. Only with an integrated approach will you be able to prevent complications from occurring. The particular danger of this pathology is that it can easily lead to stomach tumors.
Granular gastritis is a disease that, if treated incorrectly, can lead to the development of serious complications. Due to hypertrophy of the gastric mucosa, bleeding may occur or a tumor may form. It is for this reason that when the first signs of pathology appear, you should immediately consult your doctor.
Sources:
- https://gastritinform.ru/xozyaika.com/zernistyj-gastrit-vidy-simptomy-lechenie-i-dieta/
- https://zhkt.ru/zheludok/gastrit/zernistyj.html
- https://gastritinform.ru/gastromedic.ru/gastrit/zernistyj-gastrit.html
- https://zhkt.guru/gastrit/vidy/zernistyy-1
- https://www.passion.ru/health/zhkt/hronicheskiy-ochagovyy-gastrit-86156.htm
- https://gastrit.guru/lechenie/zernistyj-gastrit.html