- September 8, 2018
- Gastroenterology
- Elena Klimova
The life of a modern person is characterized by stress and psychological overload, unhealthy diet, snacking on the go and abuse of fast food. With such a rhythm of life, we sometimes have no time to pay attention to our health, for example, getting rid of bad habits, learning to avoid stressful situations, cooking and eating healthy foods and dishes. The consequence of an unhealthy lifestyle is stomach diseases that are common among the population. One of the most common pathologies is erythematous gastritis.
A few years ago, only 20% of people were diagnosed with such a diagnosis; today the percentage of patients has tripled. Among the patients there are more young people, even teenagers (14-15 years old). Pathological processes in the stomach, resulting from poor nutrition, provoke the onset of the disease.
Erythematous gastritis - what is it?
First of all, it is necessary to find out the nature of this disease. As mentioned earlier, it is a gastric pathology. The stomach is an organ that plays a significant role in the digestion process, producing acids necessary for the breakdown of food. The walls of this organ are covered with a mucous film that protects it from the harmful effects of acids. When this membrane is damaged, acids have a destructive effect on the stomach and cause irritation and painful symptoms.
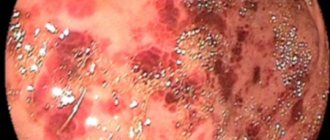
Erythematous gastritis is characterized by the appearance of red or pink spots (“erythrema” - redness) of an oval shape on the gastric mucosa; underlying pathological changes in the organ are not observed. Redness in this form of the disease is a consequence of dilation of blood vessels and a manifestation of the inflammatory process. With timely treatment, pathological phenomena quickly disappear.
Antral erythematous gastritis and other types of chronic gastritis
There are several forms of the disease. One type is antral erythematous gastritis. How is it characterized?
First of all, it is necessary to answer the question: antral erythematous gastritis - what is it and what are its features? This form of pathology occurs if the disease manifests itself in the antrum (the area in which the stomach passes into the duodenum).
Other types of gastritis:
- Erythematous exudative gastritis is inflammation of certain areas of the gastric mucosa due to an increased level of eosinophils in the blood or parasitic invasion.
- Diffuse gastritis, or pangastritis, is a total lesion of the mucous membrane of an organ or most of it.
- Focal erythematous gastritis is a partial lesion of the surface of the stomach walls. Appears due to poor nutrition and alcoholism. It is dangerous due to the occurrence of complications in the form of ulcers.
- Atrophic gastritis is an inflammation that results in atrophy of the glands.
Why does gastritis occur?
Everyone probably knows the expression: “Forewarned is forearmed.” Knowing the possible causes of diseases, you can prevent them through preventive measures. What is the reason for the appearance of gastric pathologies?
Among the factors that provoke erythematous gastritis are:
- Stress factor (severe stress or chronic stressful situations).
- Drug treatment (some medications, for example, hormonal drugs, antibiotics, NSAIDs, have a destructive effect on the gastric mucosa).
- Non-compliance with diet, frequent consumption of unhealthy foods (hot or cold foods, fatty, spicy foods, smoked foods).
- Unfavorable heredity (presence of relatives with gastrointestinal pathologies).
- Metabolic disease.
- Fungal, viral and bacterial infections.
- Bad habits - smoking and alcoholism (nicotine and ethanol irritate the lining of the stomach).
- Other negative impacts.
Causes
Like any other diseases associated with stomach problems, erythematous gastritis is provoked by one or several factors, depending on existing diseases and lifestyle.
In order for treatment to be competent and timely, you should know about the causes of the disease:
- stressful situations;
- uncontrolled use of hormones and antibiotics;
- poor nutrition;
- bacterial or viral infections;
- hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of erythematous inflammation may hardly appear at the onset of the disease. The main symptom of erythematous gastritis is stomach pain. Most often, this is an aching pain, it appears in the morning or at night, and disappears after eating.
Other characteristic manifestations of pathology are:
- nausea (especially after eating pickles, smoked, fried, fatty or spicy foods);
- vomiting, which brings relief to patients;
- decreased appetite and weight loss.
Belching, heartburn and a burning sensation in the stomach, pain in the esophagus, a feeling of a lump in the throat, diarrhea and constipation are often observed. This symptomatology negatively affects the nervous system, causing depression and constant fatigue.
The presence of at least one of the above signs is a reason to consult a doctor, because early diagnosis and treatment makes it possible to completely get rid of gastritis.
Characteristic symptoms
Dangerous signs indicating the onset and progression of the disease are often missed, since digestive disorders such as heartburn and stomach pain are often associated with poor diet and stress.
The patient is confident that as soon as the stressful situation stops, the digestive process will return to normal. But more often it happens that such a provoking factor makes itself felt not for the first time. And in combination with a hereditary factor, pathological changes in the organ manage to reach a stage where it is no longer possible to do without a course of treatment.
That is why the following symptoms should not be ignored and they should be a reason to visit a gastroenterologist and undergo a medical examination.
Schedule a visit to your doctor if:
- Began to experience heartburn frequently,
- A burning sensation occurs even when the stomach is empty,
- Do you notice rapid fatigue?
- Worried about irritability and mood swings,
- A white coating appears on the surface of the tongue,
- Belching occurs, leaving a pronounced unpleasant aftertaste,
- After eating there is a strong feeling of fullness, heaviness,
- Body temperature rises slightly but regularly,
- Completely lost or very weak appetite.
Diagnosis of gastritis
To identify pathology and select adequate therapy and diet for treatment, it is important to carry out diagnostic procedures.
If chronic gastritis is suspected, the following types of medical examinations are used:
- Ultrasound examination.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Fibroesophagogastroscopy.
- Laboratory tests (general blood and urine tests are ordered to measure the pH of the cavity).
An important diagnostic method is endoscopic examination; it reveals the presence of exudative gastritis and identifies foci of inflammatory processes. During the examination, a probe is inserted into a person’s stomach to see the condition of the gastric mucosa. Sometimes the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic procedures, for example, electrogastroenterography (if reflux is suspected).
Treatment of the disease: drug therapy
Treatment of erythematous gastritis includes the following techniques:
- Drug therapy.
- Physiotherapy.
- Spa treatment.
The most important aspect of treating pathology is drugs to restore the gastric mucosa. Based on the cause of gastritis, appropriate medications are prescribed, for example:
- Antibacterial if gastritis is caused by Helicobacter bacillus (Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin, Metronidazole).
- Antiparasitic drugs (“Trichopol”) are prescribed for parasitic infestations.
- Stomach-coating drugs (“Vicalin”, “De-nol”).
- Medicines to reduce stomach acidity (Omez, Ranitidine).
- Preparations to increase acidity (“Enzistal”, “Abomin”, “Penzital”).
- To relieve symptoms, antidiarrheals (Smecta, Enterosgel), antispasmodic painkillers (Drotaverine), and antiemetics (Cerucal, Motilium) are prescribed.
Diet is the key to recovery
The main task of patients is to adhere to a diet that will need to be followed throughout their lives. Proper and regular nutrition will help avoid unwanted complications and chronic inflammation.
During exacerbation of gastritis, seasonings, baked goods, pickles, and fatty foods are prohibited; Light, simple dishes are recommended; you need to steam them, it is advisable to eat pureed and boiled food.
It is important to include protein and easily digestible fiber in your diet so that the food is both healthy and nutritious. After the end of the acute period, you can eat stewed vegetables, cereals and jelly, casseroles, omelettes, light salads, fermented milk drinks, salt, sugar (in small quantities).
Another prerequisite for recovery is giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol). You should also try to avoid chronic stress.
Let's talk about the reasons
It is impossible to single out any special causes that are unique to erythematous gastritis. Traditional provoking factors that can cause any other form of stomach inflammation are important. These include:
- improper and irrational nutrition;
- parasitic diseases, acute and chronic intestinal pathologies;
- inadequate rest, intense work schedule, frequent stress;
- hereditary predisposition;
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- bad habits;
- addiction to strong coffee and tea, carbonated drinks, spices and marinades;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications;
- chronic metabolic disorders, endocrine diseases.
In fact, the risk of stomach inflammation is present in every person, regardless of age, gender and type of employment. However, whether the process will be chronic in most cases depends on the patient.
Folk remedies
In addition to medications, you can use folk recipes to treat stomach diseases. From time immemorial, people have known the healing properties of plants, which can be used to alleviate the conditions of patients with various diseases.
But, despite this, traditional treatment methods can only be used after diagnosis and consultation with a doctor.
The following are most often used as folk recipes for the treatment of gastritis:
- Gastric collection (a complex of herbs to restore the mucous membrane).
- Kyzyl May oil (has an anti-inflammatory effect).
- White cabbage juice or freshly squeezed potato juice.
- Propolis tincture (eliminates acidity problems).
- Burdock root decoction.
- Calamus root.
- Aloe juice.
- A decoction of a mixture of medicinal herbs (chamomile, mint, linden and flax seeds).
- Medicinal herbs: marshmallow, St. John's wort, calendula.
How to treat
If the diagnosis of “erythematous gastritis” is confirmed, then first of all the doctor will advise you to improve your diet and go on a therapeutic diet that will help normalize the condition of the mucous membrane, relieve inflammation and prevent complications.
Diet rules
The therapeutic diet primarily involves the total exclusion of all dishes and products that irritate the walls of the gastric mucosa.
The therapeutic diet primarily provides for the total exclusion of all dishes and products that irritate the walls of the gastric mucosa. It is necessary to exclude hot seasonings, fried foods, sour fruits and vegetables, desserts with butter creams, strong brewed tea, and coffee. Taking into account how the disease progresses, the following dietary options are offered:
- If stomach acid is secreted in insufficient quantities, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that contain large amounts of coarse fiber, as well as pickles, smoked meats and spicy foods. You should not eat hot or very chilled dishes; food should be at a comfortable temperature. You also need to reduce the consumption of dairy products, legumes, hot onions and garlic, and mushrooms.
- If acid secretion is increased and the patient suffers from severe heartburn, then it is worth removing fatty, spicy, fried, and sour foods from the diet. It is undesirable to eat various kinds of pickles in sour marinades, strongly brewed coffee and tea, alcohol and beer.
It is advisable to give preference to vegetables that need to be steamed, boiled or baked in the oven. Among fruits, green apples, bananas, pears, grapes, peaches, nectarines and others are allowed.
If necessary, the doctor will also prescribe medications. Most often these are antacids, which normalize the condition of the mucous membrane, relieve inflammation and swelling, and promote rapid healing of the affected areas.
Traditional methods
A good remedy for the treatment and prevention of gastritis is the juice of potatoes and carrots, which can be taken separately or mixed.
The use of folk remedies in combination with drug therapy also has a proper effect in eliminating the disease. First of all, herbal decoctions and infusions are effective in curing gastritis, which have an anti-inflammatory, soothing, and antibacterial effect.
A good remedy for the treatment and prevention of gastritis is the juice of potatoes and carrots, which can be taken separately or mixed. For low acidity, it is recommended to drink white cabbage juice, which is drunk several times a day before eating.
An infusion of birch bark relieves attacks of heartburn, reflux and belching. The product is taken every time before meals. Chamomile decoction also has an analgesic, antispasmodic and calming effect. The product can be drunk as tea, the preparation of which requires 1 tsp. dried chamomile flowers, which are poured with a glass of boiling water and allowed to brew for 10 minutes.