Frequent heartburn is a phenomenon known to many. There is a home remedy - soda, there are tablets, gels for heartburn. All these are means of self-medication. They can help once, twice. Then everything can go away. Or maybe it won't pass. Moreover, symptoms may increase, in which case doctors talk about the development of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Our expert in this field:
Ryabov Konstantin Yurievich
Chief surgeon, oncologist, endoscopist
Call the doctor
What is reflux and why is it dangerous?
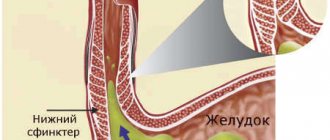
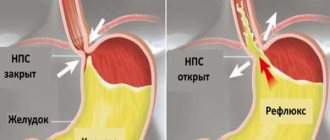
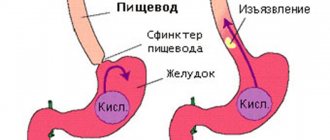
The backflow of the contents of a hollow organ is called reflux. This is the reverse flow of fluid, against the direction of its natural movement. The most common type of reflux is the backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus.
Food in the stomach is digested by hydrochloric acid. When its contents enter the esophagus, it causes severe irritation of the mucous membrane. The acid burns her. If this happens often, regularly, such an irritating effect leads to inflammation and then ulceration of the mucous membrane.
The cause of reflux is the weak functioning of the sphincter that locks the esophagus and separates it from the stomach. Normally, this valve should prevent the acidic gastric environment from entering the esophageal mucosa.
In addition to the fact that constant heartburn reduces the quality of life, ulceration and inflammation of the esophageal mucosa increases the risk of developing cancer.
In some cases, this gives reason to regard reflux esophagitis as a precancerous condition, namely with the formation of ulcers, degeneration of epithelial tissues and the development of Barrett's disease. The result of this process can be the formation of adenocarcinoma, esophageal cancer.
Folk remedies or how to relieve inflammation of the esophagus
Treatment of inflammation of the esophagus with traditional methods is effective using the following recipes:
- Treatment with potatoes. To do this, you need to grate several raw potatoes on a fine grater and squeeze out the liquid from the resulting mass. You need to drink the finished juice (2-3 tablespoons) in one gulp and eat it with a teaspoon of sugar. This will help get rid of the burning sensation in your chest.
- Treatment with teas. It is best to use chamomile, mint and raspberry tea. They need to be brewed immediately before taking. Drink twenty minutes before meals.
- Dill recipe to relieve inflammation in the esophagus. To prepare it, you need to take two teaspoons of dill seeds and crush them in a mortar. Pour a glass of boiling water and leave for two hours. Take a tablespoon three times a day before meals.
- Jerusalem artichoke remedy. To prepare it, you need to grate a couple of tubers of this vegetable on a fine grater. Mix with 1 grated apple and take a tablespoon twice a day.
- Herbal remedy:
- take a teaspoon of crushed oak bark;
- a tablespoon of chopped walnut leaves;
- 1 tbsp. l. St. John's wort color.
Pour this mixture with 3 glasses of cold water and leave for three hours. After this, the product must be strained and brought to a boil. Take two tablespoons twenty minutes before meals.
You should also sleep on a high pillow to prevent stomach acid from rising up the esophagus and causing heartburn.
Symptoms and diagnosis of reflux esophagitis
The main, painful symptom of reflux is burning, pain behind the sternum. Heartburn is accompanied by sour or bitter belching. After eating, there may be heaviness in the stomach.
Symptoms usually intensify with physical activity, as well as after a heavy meal, or while lying down. With the development of reflux esophagitis, swallowing becomes difficult, and esophageal obstruction develops.
Chronic heartburn, especially if it does not improve and does not go away after taking antacids, is an indication for esophagogastroscopy. A miniature device with a video camera descends on a flexible tube into the esophagus. With its help, the doctor examines the mucous walls and takes a tissue sample - a biopsy.
The biopsy is sent for morphological examination. At this stage, Barrett's disease or its complication, adenocarcinoma, can be diagnosed.
X-rays are performed to visually examine the esophagus. On an x-ray, the doctor sees ulceration of the walls of the esophagus (if any), a narrowing of its lumen.
If necessary, additional examinations may be prescribed to study the complex picture of the disease - esophageal sphincter manometry, electromyography. To assess acidity, pH monitoring is carried out.
Diagnostics
If the discomfort does not go away and the intensity of pain increases, you should consult a doctor. Without treatment, catarrhal esophagitis can lead to degeneration of mucosal cells, necrosis and cancer. Therefore, consultation with a gastroenterologist is very important. But it is difficult to diagnose “catarrhal esophagitis” based on symptoms alone. The doctor collects anamnesis, talks with the patient about the causes of discomfort, and finds out what gastrointestinal diseases he has.
After this, he can diagnose esophagitis, but the condition of the esophageal mucosa can only be determined with the help of an instrumental examination. In this case, x-rays are ineffective, since they can only show the presence of edema, erosions or areas of necrosis. But it is definitely prescribed to exclude malignant tumors and stenosis of the esophagus.
The condition of the esophageal mucosa can be assessed during esophagoscopy.
Basic information about the condition of the esophageal mucosa can be obtained by performing esophagoscopy. Probing reveals hyperemia and swelling. But it is recommended to carry out this examination after the acute stage of catarrhal esophagitis has subsided. After all, the endoscope can additionally injure the mucous membrane, which will aggravate the patient’s condition. Therefore, esophagoscopy is most often performed in the chronic form of the disease. In this case, a section of the mucous membrane is often taken for analysis to exclude malignant neoplasms.
In addition, when diagnosing pathology, intraesophageal pH-metry is performed. It allows you to detect the presence of gastroesophageal reflux. And esophageal manometry determines the insufficiency of the sphincter and motility of the esophagus.
Indications and benefits of surgery
Surgical treatment of reflux esophagitis is indicated in the presence of ulcers, bleeding, Barrett's disease, precancerous condition or cancer of the esophagus. In these cases, conservative therapy is useless.
Other indications for surgery: narrowing of the esophagus, diaphragmatic hernia.
Surgical treatment helps to return to normal life and get rid of painful symptoms when the use of medications does not work.
Another advantage of the operation is that it helps prevent the development of cancer or eliminate it at an early stage. In this case, conservative treatment methods may cause lost time.
Often a person undergoes surgery on his own, desperate to get rid of chronic heartburn and unable to endure it any longer. Unlike drug therapy, which only relieves symptoms, surgical treatment eliminates the cause of reflux esophagitis.
According to the experience of our clinic, in more than 90% of cases, surgical treatment of reflux esophagitis gives positive results. The symptoms go away, the swallowing process normalizes, and the risk of developing cancer, ulcers and other complications disappears. The need to take antacids and other medications disappears.
Our doctors will help you
Leave your phone number
Drug treatment
Therapy against inflammation of the esophagus is primarily aimed at eliminating acute pain in the patient. To do this, he is prescribed various antacid drugs that have a pronounced gentle and enveloping therapeutic effect (Almagel, Vikaira, Vikalin, Enteros gel).
These medications should be taken 4-5 times a day, thirty minutes before meals, until acute heartburn and pain in the esophagus stop. As a rule, the duration of such treatment should be at least ten days.
For severe pain in the esophagus, hospitalization of the patient is recommended. He will be prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as analgesics (to reduce pain).
In addition to the above groups of drugs, in case of severe esophagitis, the attending physician may prescribe H2-histamine blockers, vitamins and drugs that improve the regeneration of the damaged mucous membrane of the esophagus.
If the inflammation was caused by poisoning, then the patient is prescribed sorbents. He is also advised to rinse his stomach.
If esophagitis is caused by infection, the patient is prescribed antibiotics.
In addition, during treatment of inflammation of the esophagus, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Don't overeat.
- Do not eat three hours before bedtime.
- Perform physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Follow a strict diet (table No. 1).
Completely eliminate the following foods from your diet:
- carbonated drinks;
- sweets, cakes, pastries and other sweets;
- smoked meats;
- sausages;
- tea;
- coffee;
- onion;
- garlic;
- tomatoes;
- margarine and butter;
- semi-finished products;
- fried food;
- fried food;
- pepper;
- fatty meats and fish;
- milk;
- salty food;
- conservation;
- jam;
- salo.
The basis of the diet should be the following products:
- porridge with water;
- jelly;
- yogurt and low-fat kefir;
- vegetable stew;
- steamed meat and fish;
- vegetable soups.
Preparing for surgery
Before the operation, the entire range of diagnostic measures is performed - fibroendoscopy of the esophagus and stomach, radiography, manometry of the esophageal sphincter, daily pH monitoring. General clinical and biochemical blood tests, coagulogram, tests for viral infections, and ECG are prescribed. Having studied the anamnesis, the doctor at the Medicine 24/7 clinic must exclude contraindications to surgical treatment.
During the day, food should be limited to a minimum; only the lightest foods are allowed. It is recommended not to drink 8 hours before surgery. Before the operation, a cleansing enema is given or a laxative is prescribed.
The essence of surgical treatment of reflux esophagitis
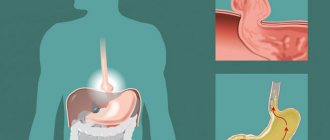
The essence of surgical treatment of reflux esophagitis is to strengthen the esophageal sphincter. To do this, the walls of the stomach are wrapped around its lower part and sutured. This creates an additional muscle cuff.
This type of surgery is called a Rudolf Nissen fundoplication. The operation is performed open or laparoscopically.
In the first case, access is created by cutting the abdominal wall, in the second case - using several punctures. At the Medicine 24/7 clinic, preference is given to minimally invasive, laparoscopic surgeries, which have a number of advantages.
First of all, there is significantly less tissue trauma and almost complete absence of postoperative traces; there is no need to remove sutures. Rehabilitation after laparoscopic surgery is faster and easier.
Laparoscopic operations require a particularly highly qualified surgeon. The specialists of the Medicine 24/7 clinic have this qualification, which is the key to successful treatment results and minimal risk of complications.
Distal esophagitis
What is distal esophagitis? In this case, damage occurs to the distal part of the esophagus - the one that is directly adjacent to the stomach. Distal catarrhal esophagitis is characterized by the following manifestations:
- sharp discomfort in the esophagus, stomach;
- choking cough;
- vomit;
- severe burning behind the sternum;
- decreased mood, irritability;
- general weakness.
Note! In a significant proportion of cases, chronic distal esophagitis occurs in an asymptomatic form. Only as it progresses does distal reflux esophagitis cause substernal tenderness, dysphagia, belching and heartburn.
Such signs of distal catarrhal reflux esophagitis worsen when the patient assumes a supine position.
Sometimes distal esophagitis occurs with repeated insufficiency of the cardia due to the reflux of acidic gastric contents.
How the operation is performed
Small incisions are made on the abdominal wall, through which a laparoscope with a video camera and surgical instruments are inserted. The abdominal cavity is inflated with compressed air.
The muscular wall of the stomach is cut, pulled to the bottom of the esophagus and wrapped around it. This creates a coupling that is secured with seams.
During an open operation, the sequence of actions of the surgeon is the same. The only difference is in creating access by cutting the abdominal wall and then placing a suture on it. Open surgery takes on average half an hour less time. There are cases when this method of performing the Nissen operation is considered preferable. The decision is made individually.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
After operation
The first day after the operation, the patient eats liquid food through a tube. On the second day you can get up and drink. A control x-ray is taken to evaluate the results of the operation, the patency and function of the esophagus and sphincter.
On the third day, you can take liquid food on your own. If the patient feels normal, the patient is discharged from the hospital.
Further, the diet can be gradually expanded and diversified, but you will have to follow the diet for at least a week. You can't take baths these days. High physical activity should be avoided for 3 to 4 weeks after surgery.
The material was prepared by oncologist, endoscopist, chief surgeon of the Medicine 24/7 clinic, Konstantin Yuryevich Ryabov.