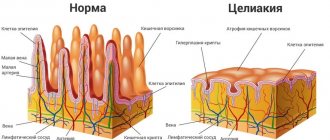
Sore throat due to reflux occurs in most patients suffering from the backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is formed when the process constantly appears.
Loading …
Consult a doctor!
The site provides reference information . Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious doctor . Any medications have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist and detailed study of the instructions is necessary! Be sure to make an appointment with your doctor .
What causes sore throat with reflux esophagitis?
Causes and damaging factors leading to pathology:
- impaired motility of the muscle wall;
- increased gastric secretion of hydrochloric acid (hyperacidosis);
- decreased barrier function of the mucous membrane;
- reduced sphincter functionality.
Conditions that form a risk group:
- smoking, frequent drinking of alcohol;
- stress, excitement, nervous experience, nervousness;
- high body weight, obesity;
- pregnancy due to compression of the internal organs of the abdominal and thoracic cavity by the fetus;
- hiatal hernia;
- frequent heartburn;
- use of certain medications (nitrates, beta-blockers).
These patients often acquire other gastrointestinal diseases. For example, ulcers, colitis, esophagitis, gastritis.
Mechanisms by which pathology develops:
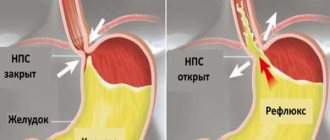
- Initially, insufficient activity of the sphincter occurs; normally, it should always be closed so that the food bolus passes only in one direction;
- through the resulting hole, the food bolus passes in the opposite direction;
- gastric juice enters the esophageal mucosa, for which it is overly aggressive, causing an inflammatory process, up to the formation of an ulcer;
- Gradually, a lump with sour contents spreads up to the throat, causing damage and pain.
The condition can develop in a healthy person. For example, if you bend over too much immediately after eating food, a small hole appears in the sphincter. But when the body is raised to its normal position, it closes again.
If symptoms appear, contact a gastroenterologist or otolaryngologist. Thanks to laboratory and instrumental diagnostics (gastroscopy, laryngoscopy), the diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux is revealed. That is, GERD spreads throughout the gastrointestinal tract, causing complications in the form of damage to the larynx and pharynx (laryngopharyngeal pathology).
These are typical consequences.
Let's summarize:
Diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux is not easy; it cannot be solved 100% by the methods familiar to a gastroenterologist; the efforts of other specialists are required to exclude other conditions with similar complaints.
Each case is discussed individually with patients or their families.
Often the solution may be to evaluate the effect of a trial treatment (more on therapy later...)
Treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux
16, total, today
How does a throat hurt with reflux?
The disease is characterized by classic symptoms. The patient experiences nausea, heartburn, and vomiting. He constantly feels a bitter or sour taste. Belching often occurs. This affects the organs.
Gradually, the acidic environment leads to the following discomfort in the throat:
- a constant burning sensation, due to which appetite worsens;
- pain when swallowing;
- urge to gag reflex;
- taste of bile after eating food;
- bitterness during active movements, bending, during night sleep.
The respiratory system is also affected. Since there is a connection between the gastrointestinal tract and the respiratory tract, acidic contents sometimes penetrate into the trachea. Therefore, the patient develops an active cough and tracheitis.
The frequency of its manifestation depends on the attacks of heartburn. Then a therapist or pulmonologist helps with treatment. He assesses the extent of the damage. It spreads to the lower parts of the trachea and bronchi.
What predisposes to reflux?
- periodic relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter. They should be normal, as they help the stomach get rid of excess swallowed air, but if they are prolonged and frequent, they lead to GERD
- persistently low tone of the lower esophageal sphincter in some people. This factor can be influenced by smoking, a distended stomach, certain medications and foods. To warn you of a frequent question - no, it is impossible to pump up this sphincter like biceps or abs.
- anatomical features of the stomach and esophagus. This is usually a hiatal hernia
What does a dull, drawing, pinpoint or cutting pain in the throat indicate?
Damaging factors causing dull pain:
- chronic tonsillitis is a pathology of the tonsils in which a small amount of an infectious agent is present (staphylococci, streptococci, Klebsiella, pneumococci, Moraxella, Neisseria, enterococci);
- adenoiditis - pathological hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil, making breathing difficult;
- the primary stage of pharyngitis - the throat becomes red, swollen, painful at rest and when swallowing, and malaise is felt.
Pulling feelings develop under the following conditions:
- cervical osteochondrosis – degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the spine, leading to compression and damage to nerve fibers;
- intervertebral hernia of the neck - protrusion of the nucleus of the intervertebral disc into the canal with damage to the fibrous ring up to rupture;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland, benign or malignant growth;
- mediastinitis – inflammation of the lymph nodes of the mediastinum.
Point discomfort occurs when there are violations:
- burn of the mucous membrane as a result of the action of a chemical substance, high temperatures, radiation;
- focal proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, staphylococcal, streptococcal, pneumococcal infections are common;
- mechanical damage, trauma, wounds, bruises of soft tissues with damage to the surface layers.
Cutting syndrome appears with dysfunctions:
- acute stage of viral infection - ARVI, colds, laryngitis, influenza, parainfluenza, coronavirus, adenovirus;
- purulent tonsillitis - accumulation of bacteria in the lacunae of the tonsils, the appearance of a large volume of pus in the process of their metabolism, causing intoxication;
- fungal infection, accompanied by a white coating and swelling.
Often an examination is enough to determine the diagnosis. Some diseases will require laboratory and instrumental tests; the symptoms may be similar to each other. For example, the initial stage of viral and bacterial infection.
When do you need to see a doctor urgently, and which doctor will help?
Some abnormalities are treated at home. You will need antiseptics to make you feel better.
In case of the following changes, it is necessary to consult a doctor; without it, treatment will be difficult or will lead to complications:
- The development of a bacterial infection when an antibiotic needs to be determined. Each drug has its own indications for use, side effects, contraindications, and dose selection. Without a recommendation, the patient will not take the factors into account. The doctor will prescribe a bacteriological culture and determine how you feel. Only then will he prescribe the correct medicine.
- Body temperature more than 38 degrees for 3 days. Therapists advise using antiviral medicine in the first three days. If your health does not improve, tests and re-examination will be required.
- Spread of infection. It is localized in one area of the nasopharynx. If there is no treatment or it is incorrect, the pathology spreads deeper. For example, tracheitis, bronchitis, and pneumonia are formed.
- Risk of sepsis. Bacteria move into neighboring tissues. But they should not enter the systemic circulation. Otherwise, severe reactions develop - myocarditis, pericarditis, meningitis, shock, vascular collapse. All of them lead to gradual death without help.
- Body temperature rises to 40 degrees. The condition is especially dangerous for young children. Fever with dehydration causes attacks accompanied by convulsions. This is dangerous for the nervous system, fraught with damage to neurons in the cerebral cortex.
The choice of doctor depends on the area of damage to the body, accompanying symptoms, age:
- pediatrician – examines children if their health worsens;
- therapist – prescribes treatment for patients who have reached the age of majority;
- neurologist – deals with the identification of neurological disorders, elimination of damage to the central and peripheral nervous system;
- cardiologist – provides therapy for complications of the cardiovascular system;
- otolaryngologist - determines therapy for damage to the nasopharynx and hearing organs;
- endocrinologist – diagnoses dysfunction of the endocrine glands (thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary gland, pineal gland, adrenal glands);
- traumatologist – examines the patient when injuries occur and associated complications occur;
- immunologist – corrects the functional state of the immune system in case of frequently developing diseases and low production of lymphocytes;
- infectious disease specialist – prescribes treatment for infections;
- surgeon - prescribes surgery if conservative methods do not help.
Initially, contact a therapist. He prescribes laboratory and instrumental examinations to help assess your well-being. Sends the patient to doctors of other specialties to further study the problem and prescribe medications.
Treatment
Patients wonder if GERD can be cured.
To get rid of the pathology or alleviate the symptoms, a well-developed treatment regimen for reflux esophagitis is necessary. All unpleasant and painful manifestations warn of possible disorders not only of the functions and tissues of the esophagus, but also of other digestive organs.
Ignoring the initial mild symptoms in most medical histories leads to deepening inflammation of the esophagus, the development of reflux and serious complications that will be difficult and long to cure.
Treatment regimen and medications
In the treatment of GERD with esophagitis, three stages of therapy are provided - independently, with a therapist, with a gastroenterologist.
The first is home self-treatment
It is quite advisable if heartburn or backflow from the stomach occurs no more than once a week. The patient is able to relieve them independently using the following groups of medications in the treatment regimen for reflux esophagitis:
1. Antacids that neutralize the aggressiveness of hydrochloric acid, from which the most effective for a particular patient are selected (Phosphalugel, Gastracid, Daijin, Coalgel, Rutacid, Rennie, Topalcan, Gaviscon).
It is believed that the most effective are non-absorbable antacids of the 2nd generation, which include Maalox, Megalok, Almagel. Approximately prescribed for a course of up to 2 months or used once when heartburn bothers you. For severe pain, use Almagel A, which contains an anesthetic that relieves pain.
2. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), suppressing the production of gastric acid and pepsin and providing mucosal protection - five generations according to the active substance:
- Omez, Losek - omeprazole (1 or 2 times 20 mg);
- Lanzap – lansoprazole;
- Zipanthol - pantoprazole (40 mg once or twice a day);
- Pariet - rabeprazole;
- Nexium - esomeprazole.
The choice of drug is individual.
For example, the third generation drug Pantoprazole, when compared with esomeprazole (V generation), more quickly relieves the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease. In addition, the medicine has shown its effectiveness even during an attack of bronchial asthma, which is provoked by gastroesophageal reflux. Practical studies have shown that Pantoprazole for erosive esophagitis eliminates painful symptoms and inflammatory-erosive lesions detected by endoscopy.
3. Histamine H2 receptor blockers that inhibit acid secretion - Cimetidine 0.3 grams up to 4 times a day, Ranitidine 0.15 - 0.3 grams twice a day (in a smaller dose) or once before bedtime, Famotidine 2 times a day 20 mg.
4. Prokinetics, which strengthen the muscle tone of the lower esophageal sphincter, improve motility (movement of food), reduce the number of esophageal refluxes and the time of contact of the esophageal mucosa with acid flowing from the stomach. Coordinax and Prepulsid are considered one of the most effective prokinetics, however, they can provoke unwanted side effects from blood vessels and the heart. In contrast, Motilium (domperidone) has virtually no side effects, showing good results in esophagitis.
Course of treatment with Motilium: a month - for mild forms of esophagitis, 6 - 8 weeks - for erosive ones. If the therapeutic effect is weak, then therapy is continued for up to 3 months or longer. Adult patients: 20 mg three times a day half an hour before meals. Adolescents and children over 5 years old: 10 mg in a single dose (3 times a day).
Specifics of therapy in children
How to treat reflux esophagitis in children if many medications are contraindicated. But Motilak (Motilium) is allowed even for infants, who are prescribed the drug in suspension at the rate of 0.25 - 0.5 ml per 1 kg of the child’s weight or 3 or 4 times a day.
If the child is in a horizontal position for a long time, the symptoms intensify. Therefore, the sleeping place should have an inclination with the head part rising. This is better than placing a high pillow under the baby's or older child's head, which bends the spine.
Second stage
Consultation with a therapist is required if heartburn and reflux occur 2 times a week or more often. The attending physician will prescribe basic clinical tests, without specialized instrumental studies, and if erosive esophagitis is suspected, he will adjust the treatment regimen.
Third stage
If a patient begins to experience severe manifestations of reflux esophagitis, atypical symptoms, signs of pulmonary symptoms (shortness of breath, bronchospasm attacks, cough), severe pain, a mandatory visit to a gastroenterologist is necessary. It is recommended not to wait for serious manifestations of the disease.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of GERD with esophagitis involves four methods:
- Open surgery.
- Laparoscopy.
- Intraluminal endoscopy.
- Fundoplication, which is performed when laparoscopy is not possible.
The fundoplication technique for reflux esophagitis is aimed at completely restoring the function of the lower esophageal sphincter, which allows you to cure esophagitis forever if you follow special recommendations after the procedure. A healthy patient leaves the hospital after two days.
Top medications to relieve sore throat, painkillers
After examination and diagnostic tests, the diagnosis is determined. The list of medications required to improve well-being depends on it.
The top commonly prescribed medications are:
- Antiseptic sprays. Tantum Verde, Strepsils, Panavir, Miramistin, Octenisept, Septolete, Cameton. The products contain antiseptic and antibacterial substances that destroy bacterial flora and relieve inflammation. If the feeling is unbearable, use medications containing an anesthetic component (lidocaine, novocaine, procaine).
- Antiseptic rinse solutions. Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Septomirin, Orasept, Hexoral, Rotocan, Malavit, Stomatidin. The products wash away pathogenic microflora from the mucous membrane and prevent it from multiplying for a long time. If there are no microbes, inflammation stops and discomfort disappears.
- Herbal rinse. Brew chamomile, calendula, string, viburnum bark, sage, coltsfoot, St. John's wort. Oak bark, which has tanning properties, helps. Make the solution strong.
- Lollipops. Grammidin, Faringosept, Agisept, Doctor Mom, Suprima-ENT, Lizobakt, Larry-plus. Soften the irritated area, destroy the pathogen. Used when rinsing cannot be used. For example, while sleeping, at work.
- Antibiotics. Use cephalosporin, tetracycline, penicillin group, aminoglycosides, chloramphenicol, macrolides, carbapenems. The most common are Amoxiclav with clavulanic acid, Sumamed, Cefazolin, Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Lincomycin, Imepenem, Cefpir. They are prescribed when the nature of bacterial colonization has been proven. Bacteriological culture of sputum discharge from the nasopharynx is carried out. The exact type of microorganism and the antibiotic to which it is highly sensitive are identified.
- Analgesics in tablets. They drink Analgin, Baralgin, Pentalgin. The action is based on reducing the pain impulse transmitted to the main part of the nervous system. The drugs have fewer side effects than other painkillers.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Nurofen, Ketorol, Ketoprofen, Nise, Nimesil, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac. The action is based on blocking the inflammatory process. The activity of cyclooxygenase, arachidonic acid, and prostaglandins is inhibited. Heat and inflammation are eliminated. In mild cases, tablets are used, in severe cases, injections are used. The intake is carried out for no more than 7 days, otherwise side effects will form for the gastrointestinal tract with the risk of an inflammatory process, including ulcers.
All medications are used in a limited course. If the effect does not occur for 3-4 days, make an appointment for the next appointment.
Pain due to GERD behind the sternum
A person suffering from GERD often complains of pain in the esophagus. Here, too, we can note some specificity in the manifestations of the symptom.
- The pain is of a squeezing or pressing nature.
- They appear in the area of the esophagus, and can radiate upward and to the left.
- Chest pain occurs during meals or immediately after a heavy meal, when bending over.
- They disappear a few minutes after taking antacids.
This symptom is caused by spasm of the esophageal muscles.
As already noted, burning chest pain radiating up and to the left is one of the specific symptoms of GERD. With such a complaint, a patient often comes to a cardiologist, not realizing that he does not have heart problems. However, this symptom is also characteristic of a disease such as angina pectoris (the appearance of squeezing pain in the heart area due to a lack of oxygen supply to the heart muscle). Unlike GERD, pain in angina pectoris is relieved by drugs from the nitrate group. In elderly patients, it is possible that two diseases may occur simultaneously, which often confuses doctors. Chest pain due to GERD
People with GERD often report chest pain. People who have had a myocardial infarction (heart attack) or who have other heart problems also often experience chest pain. Chest pain that occurs in the area of the heart may indicate a disease called angina pectoris.
Before you see a gastroenterologist, it is important to make sure that your chest pain is not caused by a heart problem.
Burning, pain behind the sternum with GERD
are present in 46% of patients. They arise, just like heartburn, due to prolonged acidification (pH <4) of the distal part of the esophagus. Most often, this is a burning chest pain of an unattackable nature, which intensifies in a horizontal position or tilting the body forward and is eliminated or weakened by changing the body position or taking antacids, including taking alkaline mineral waters and soda (“alkaline test”).
Retrosternal pain radiates to the interscapular region, neck, lower jaw, left half of the chest and can simulate angina. Patients with pain along the esophagus need a thorough examination to determine the nature of the pathology, including questioning, examination, esophagogastroscopy, X-ray examination of the esophagus, daily (or multi-hour) esophageal pH monitoring, tests with antisecretory drugs and trial treatment (see below).
- chest pressure and pain radiating to the arm, neck, jaw or back
- nausea
- cold sweat
- shortness of breath
- dizziness
- faintness
- fatigue
A characteristic sign of heartburn is that it does not get worse at all during physical activity or does not improve during rest.
If you experience severe chest pain, or pain radiates to your left arm or jaw, consult a doctor immediately, as this may indicate a myocardial infarction. If you have chest pain and you are not sure what is causing it, you need to go to the emergency room.
Preventive measures to avoid sore throat
It is easier to carry out prevention than long-term treatment.
The following techniques are used:
- frequent hand washing with bactericidal soap;
- if it is not possible to wash the brushes, use wet wipes, antiseptic gels and sprays;
- surgical removal of overgrown tonsils, which make breathing difficult and often become inflamed;
- lack of interaction with infected people;
- avoiding visiting crowded places during the season of increased spread of diseases (autumn, winter);
- use of warm clothes in accordance with the temperature regime (you cannot overcool or insulate);
- using a mask when visiting a clinic or inpatient medical facility;
- physiotherapy – magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, heating, ultraviolet irradiation;
- use of multivitamins (Alphavit, Aevit, Actimmune, Centrum, Complivit) if there are not enough substances in the body (especially vitamins C, D);
- proper nutrition, food contains vitamins, microelements, minerals required for the normal functioning of internal organs (vegetables, herbs, fruits, meat, milk are required);
- hardening procedures - visiting a bathhouse or sauna, swimming in a pool, contrast shower, eating ice cream;
- preventive examination by a doctor every 6 months;
- periodic laboratory tests - general blood and urine tests, bacteriological culture of a nasopharyngeal smear;
- drinking water at least 2 liters per day – helps remove toxins, pathogens, and their metabolites from the body;
- walks in the open air;
- playing sports in accordance with your health condition (physical therapy, yoga, Pilates, running).
Preventative measures will not completely eliminate the risk of disease. This is especially true for young children. Their body contains a small amount of antibodies that fight antigens. Immunity is acquired gradually, after contact with pathogenic microorganisms. Taking precautions reduces the risk of severe disorders.
It is forbidden to use antibiotics for prevention. Otherwise, bacteria will develop resistance to the active substance. An irreparable superinfection will appear.
What does a sudden sore throat mean?
When an infectious process occurs, the first signs of immunity appear. This indicates the activation of the following mechanisms:
- the antigen penetrates the oral cavity, settles on the mucous membrane of the larynx, pharynx, which leads to increased immunity, penetration of the microorganism into the intercellular substance and bloodstream;
- a large number of leukocytes are released and migrate to the affected area;
- immune cells produce inflammatory mediators (bradykinin, histamine), leading to dilation of the lumen of the vessel, release of exudate, pain, swelling, and redness.
The reaction persists until the pathogen is eliminated, or the immune system ceases to be activated in the affected area.
In most cases, health deteriorates before the disease develops. There is pain, a sharp loss of strength, malaise, and drowsiness.
There are cases when pain develops abruptly. Bacteria are concentrated in the tissues of the tonsils for a long time, so there is no immediate response from the immune system.
It appears when there is a large area of pus affecting the nerve fibers. A person falls asleep healthy, wakes up with severe pain in the nasopharynx and associated symptoms.
If signs are observed in a child, this indicates an exacerbation of adenoiditis. The immune tissue grows, making the normal breathing process difficult. This causes frequent colds. Chronic tonsillitis is observed.
During night sleep, snoring occurs due to the difficulty in the passage of oxygen in a lying position. Physiotherapy and symptomatic treatment will help eliminate the condition. If there is no effect, surgical removal of the adenoids is prescribed.
Symptoms of LPR
A sore throat is probably the most standard and most common symptom that bothers most people with LPR.
Desire to clear throat . If you feel the need to constantly clear your throat, try stopping it. When you do this repeatedly throughout the day, it can further irritate your throat. Instead of trying to clear your throat, try taking a sip of water. This will help your throat heal faster while keeping other treatment tips in mind.
Excess mucus in the throat . Mucus in the throat occurs because the throat is trying to protect itself, and this is completely natural. Try to drink water often when needed to keep your throat clear.
Chronic cough. Just like when you want to clear your throat, you may find yourself coughing frequently. Try not to cough too hard, as this can irritate your throat further. You can take water or tea to moisten your throat.
Other symptoms that may concern you:
- Feeling of a lump in the throat
- Swallowing problems
- It's hard to talk
- Postnasal drip
- Breathing problems/nasal congestion
- Hoarseness
- Dry throat
- Earache
~
Check out the article on symptoms of LPR for detailed information on each symptom.
Tips for treating a throat
As mentioned earlier, simply drinking water is the most convenient option. A few more options that can be recommended are tea, namely 2 options that meet the requirements for patients with LPR are chamomile tea and marshmallow root tea.
Chamomile tea soothes the throat due to its anti-inflammatory properties. Marshmallow root tea is the best choice because it not only has the ability to coat and heal the throat, but it also has the same effect on the entire digestive tract and also helps with digestion. For more information, check out the article on natural remedies for LPR.