GastrituNet.ru » Stomach diseases » Syndromes » Motility disorders
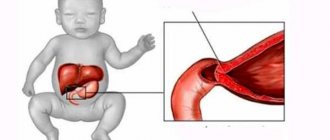
Peristalsis of the stomach is a wave-like contraction of the muscular wall of the organ, which contributes to the grinding of food, its uniform mixing with digestive juices and the movement of the food bolus from the cardiac (initial) part of the stomach to the pyloric part, which ends with the transition to the duodenum.
- 1 The mechanism of gastric peristalsis
- 2 Causes of impaired motor function of the stomach
- 3 Symptoms of impaired peristalsis and signs of disease
- 4 Diagnostics
- 5 Treatment of motor disorders
- 6 Useful video
- 7 Advice from a gastroenterologist
Mechanism of gastric peristalsis
The motor function of the stomach is carried out due to the contractile activity of the muscular lining of the organ, consisting of three layers of smooth muscle tissue:
- external longitudinal;
- middle circular;
- internal longitudinal.
The main property of smooth muscle cells is their automatism - the ability to spontaneously excite and contract in the absence of external stimuli.
In a full stomach, the elastic muscle wall tightly wraps around the food bolus, while the normal physiology of the process involves three types of contractile activity of the stomach:
Tonic waves arise as a result of redistribution of muscle tone. The contractions are prolonged, slowly spreading throughout the entire volume of the organ. They help grind food coming from the oral cavity and compact it into a food bolus.
Peristalsis is carried out due to the action of circulatory muscle fibers. The lumen of the stomach narrows behind the food bolus and the space in front expands. The pressure difference is the way chyme moves to the final part of the stomach.
Systolic contractions in the antrum and the opening of the pyloric sphincter contribute to the entry of the next portion of acidic gastric contents into the duodenum for further processing.
Gastric motility
The term motility is used to describe muscle contractions in the gastrointestinal tract. Although the gastrointestinal tract is a round tube, when its muscles contract, they block this tube or make its internal lumen smaller. These muscles can contract synchronously, moving food in a certain direction - usually downwards, but sometimes up short distances. This is called peristalsis. Some contractions may push the contents of the digestive tube forward. In other cases, the muscles contract more or less independently of each other, mixing the contents but not moving them up or down the digestive tract. Both types of contractions are called motility.
The term motility is used to describe muscle contractions in the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract is divided into four sections: the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine. They are separated from each other by special muscles called sphincters, which regulate the flow of food from one section to another and which are tightly closed most of the time. Each section of the gastrointestinal tract performs different functions in the overall digestive process and therefore each section has its own types of contractions and sensitivities. Contractions and sensitivity that do not correspond to the functions performed by this department can cause various unpleasant symptoms in the patient. This article describes the normal contractions and sensitivity of the esophagus and stomach, and the symptoms that may occur as a result of abnormalities.
Causes of impaired motor function of the stomach
Changes in the tone of the muscular lining of the organ:
- increase – hypertonicity ;
- decrease – hypotonicity;
- complete lack of tone - atony .
This leads to a failure in the forward movement of chyme through the sections of the stomach to the duodenum. Violation of gastric motility in the form of hyperkinesis (increased) or hypokinesis (slowed down) of the process.
The causes of impaired gastric motility are various pathological processes: gastritis, erosion, ulcers, scars, tumors, polyps. Depending on the location of painful foci and their prevalence, peristalsis weakens or intensifies.
Gastric motility also suffers when there is a disorder in the humoral and nervous regulation of the motor activity of the organ. An increased concentration of hydrochloric acid, as well as the hormones secretin and cholecystokinin, slow down motility, and the secretion of gastrin and motilin, on the contrary, enhance peristalsis.
With the predominant influence on the smooth muscles of the stomach of the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system (vagus nerve), motility increases, and activation of sympathetic fibers suppresses motor activity.
Poor gastric motility causes
The main reasons for weakening motor function are:
- poor nutrition, consumption of large amounts of simple carbohydrates, high-calorie foods;
- eating disorders: long intervals between meals, overeating;
- insufficient amount of fluid consumed; dehydration;
- low level of physical activity;
- chronic diseases of the liver, gall bladder, pancreas;
- infection of the body;
- malignant neoplasms in the intestines;
- complications after surgical intervention on the abdominal organs;
- chronic fatigue syndrome, constant stress, depression;
- side effects of medications;
- heredity and characteristics of old age;
- bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction.
Weak peristalsis, most often a consequence of poor nutrition, leads to constipation. Snacks on the go, junk food (fast food, sweets, flour products, coffee, carbonated drinks) cause digestive disorders.
Constant fermentation and rotting of undigested and unremoved food leads to intoxication: the destructive effect is first on nearby organs - kidneys, liver - then other systems are affected by harmful substances. A high level of slagging and the formation of fecal stones negatively affect the condition of the mucous membrane. Persistent constipation contributes to the development of hemorrhoids, the formation of polyps in the intestines, which can develop into cancerous tumors.
Another less common variant of peristalsis dysfunction is increased muscle contractions. The following factors can enhance the motor activity of the digestive organs:
- consumption of foods that irritate the mucous membrane: sour, spicy foods;
- oncology;
- dysbacteriosis;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- taking certain medications (for example, antibiotics).
In this case, the patient suffers from severe pain and diarrhea: the stool is very liquid and has a foamy consistency. Frequent diarrhea leads to dehydration. Therefore, if motor skills increase, especially in children, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor.
Symptoms of impaired peristalsis and signs of disease
Symptoms of motor function disorder are manifested by early satiety syndrome, nausea, heartburn, vomiting, and dumping syndrome.
When the tone of the muscular wall of the stomach weakens - hypotonicity - the organ increases in size, stretches, and is not able to tightly enclose the bolus of food. The clinical picture consists of symptoms:
- the appearance of discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region after eating;
- belching;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- vomiting.
Food stagnates in the stomach for a long time, its evacuation into the intestines is disrupted, processes of rotting and fermentation occur, and infectious and toxic lesions of the food tract, similar to poisoning, develop.
Signs of accelerated evacuation of food from the organ are:
- paroxysmal abdominal pain after eating;
- nausea;
- weight loss;
- dyspepsia in the form of periodic diarrhea.
Increased levels of the hormone progesterone during pregnancy reduce the tone of the smooth muscle fibers of the stomach. There is a feeling of discomfort and fullness in the stomach even with a small amount of food consumed.
Dumping syndrome develops after removal of part of the stomach, which is manifested by persistent inhibition of the contractile activity of muscle fibers.
For gastric motility tablets
Drugs to improve gastric and intestinal motility stimulate smooth muscles and activate the transit of food through the digestive tract. Let's take a closer look at each of these drugs.
Metoclopramide
This drug is a non-selective dopamine receptor antagonist that stimulates gastric smooth muscle cells. Its main features include:
- increased motility and peristalsis of the stomach;
- improvement of anthro-duodenal consistency;
- reduces the urge to vomit;
- eliminates nausea.
Many studies have proven its effectiveness.
Despite these positive qualities, there is a fly in the ointment, namely frequent side effects that occur in almost a third of patients taking metaclopramide:
- extrapyramidal disorders;
- depression;
- drowsiness;
- hyperprolactinemia.
All of these side effects are caused by the drug's ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier into the brain. That is why its widespread use was suspended at one time.
Experts do not recommend prescribing this drug to relieve symptoms of MEF disorder. It should only be used in cancer patients who are vomiting due to chemotherapy.
Domperidone
This drug does not cross the blood-brain barrier.
This drug does not cross the blood-brain barrier. Among its positive properties we note:
- improving the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter;
- activation of peristalsis of the esophagus and gastric outlet;
- antiemetic effect.
Domperidone has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration because it has been associated with an increased risk of sudden death. Despite this, the drug is successfully used in many European countries.
Itopride
This drug is a prokinetic agent with a combined effect. Itopride leads to increased gastric motility and also accelerates the excretion of food masses further into the small intestine.
No serious side effects were found with the use of itopride.
Diagnostics
Modern modifications of X-ray examination with contrast make it possible to accurately determine the types of motor activity of the stomach: tone, peristalsis, evacuation rate, the presence or absence of esophagogastric or duodenogastric reflux.
A method for recording biopotentials or electrogastromyography , based on recording signals that can be used to judge the motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract.
Balloonographic method . A balloon with a probe and an electromanometer is inserted into the stomach. The device records the vibrations that the gastric wall causes when it contracts to the medium (water or air) inside the balloon.
The open catheter method is recognized as the simplest, physiological and at the same time informational way to study disorders of motor activity of the stomach and intestines. A catheter filled with a special solution is inserted into the gastric cavity. A column of fluid senses and transmits changes in pressure in the stomach. These fluctuations are displayed graphically. The method makes it possible to evaluate the muscle tone of the organ, the frequency, amplitude and rhythm of contractions.
How is the treatment carried out?
Timely diagnosis and treatment will help avoid complications.
To bring gastric motility back to normal, it is necessary to accurately determine the type of pathology. To do this, you should contact a gastroenterologist. Based on the presence or absence of certain symptoms, the doctor may suspect the type of pathology. After examination and making an accurate diagnosis, the gastroenterologist will be able to decide on the direction of therapy. For treatment, medications are used that increase or slow down gastric motility, folk herbal remedies, and physiotherapy. A prerequisite for the treatment of any digestive disease is diet.
Necessary drugs
There are special drugs that affect the motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract. Medicines affect the muscles of the stomach or the receptors of the nervous system that regulates the tone of the organ, in order to stimulate or inhibit contractility. Only a doctor can prescribe medicine, determine the dosage and duration of use. Common drugs for the treatment of pathology:
The drug will quickly eliminate stomach discomfort.
- Prokinetics - tablets that will help improve peristalsis and increase the rate of evacuation of food from the stomach: "Motilium";
- "Passengers";
- "Ganaton";
- "Cerucal";
- "Itomed."
- "Atropine sulfate";
- antacids;
Light exercise and abdominal massage will also help restore peristalsis.
Natural Medicines
Drug therapy can be supplemented with properly selected folk remedies. To regulate peristalsis, there are recipes made from natural ingredients. By consuming ginger, infusion of the herb wormwood, buckthorn decoction, vegetable oils on an empty stomach, dried fruits, plantain seeds, wheat bran, we stimulate the contractile activity of the stomach. Peppermint, chamomile, lemon balm, fennel seeds, centaury, lavender tea, oregano inhibit excess peristalsis. To improve motor skills, it is useful to drink berry and vegetable juices and include fermented milk products in your diet.
Treatment of motor disorders
Therapeutic tactics depend on the diseases leading to this pathology, the nature of the disorders (hypertonicity, hypotonicity, increased or sluggish peristalsis) and consists of drug treatment, diet therapy and prevention of exacerbations.
Drug treatment
With gastroparesis - with a decrease in muscle tone and suppressed gastric emptying, accompanied by profuse vomiting, electrolyte disturbances and ketoacidosis, treatment of the underlying disease is required.
A group of antiemetic drugs based on domperidone is prescribed: Motilium , Motilak , Passazhix .
You can improve gastric motility with the help of prokinetic drugs: Ganaton , Itomed , Trimedat .
Drugs to improve gastric and intestinal motility stimulate smooth muscles and activate the transit of food through the digestive tract.
Proper nutrition
In addition to drug treatment, diet therapy plays a large role in alleviating the patient’s condition.
With sluggish gastric peristalsis, food lingers in the cavity for too long, and the normal digestion process is disrupted. The basic principle of a diet for this pathology is to eat in small portions, no more than two dishes at a time; it is not recommended to drink liquids while eating. Products that cause increased gas formation are prohibited: sweet, salty, carbonated drinks. Increase the amount of protein in the diet by consuming lean meat, cottage cheese, and lactic acid products.
Physiotherapy
Therapeutic exercises are aimed at strengthening the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
A set of exercises that restore muscle tone:
- Starting position (IP) lying on your back: alternately press your leg bent at the knee to your stomach.
- Lying on your back, perform the movements performed when riding a bicycle with your legs.
- From a lying position on your back, try to lift your legs up, supporting your lower back with your hands.
- While standing, bend your torso to the sides.
- Standing on your knees and leaning on your hands, stretch your legs back one by one.
Improving gastric motility
Prokinetic drugs are used among drugs.
In addition to improving and normalizing gastric peristalsis, these drugs increase the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter, which reduces the manifestations of GERD. Prokinetic agents are used among drugs. In addition to improving and normalizing gastric motility, these drugs increase the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter, which reduces the manifestations of GERD. These drugs include type 2 dopamine receptor blockers (metaclopramide), a prokinetic agent with a combined effect (itopride), and second-generation selective dopamine receptor blockers (domperidone).
With gastroparesis - with a decrease in muscle tone and suppressed gastric emptying, accompanied by profuse vomiting, electrolyte disturbances and ketoacidosis, treatment of the underlying disease is required. A group of antiemetic drugs based on domperidone is prescribed: Motilium, Motilak, Passazhiks. You can improve gastric motility with the help of prokinetic drugs: Ganaton, Itomed, Trimedat.
Useful video
What food improves peristalsis is voiced in this video.
Folk remedies
Traditional healers offer decoctions and infusions of plants as additional supportive treatment.
- yarrow herb;
- chamomile inflorescences;
- dandelion root;
- dog-rose fruit;
- plantain grass;
- oregano
Medicinal plants are used in the form of infusions. Dose calculation: 30 g of crushed dried raw materials are poured into a glass of boiling water. After 30 minutes, filter and consume 100 ml between meals for at least a month.
Prevention
- treatment of major diseases that lead to disruption of the motor activity of the digestive system.
- fractional diet: eating at the same time in small portions.
- Avoid overeating, especially before bed.
- prevention of obesity.
- engaging in vigorous physical exercise.
- rehabilitation of patients in a sanatorium.
Treatment methods
In the process of treating intestinal motility disorders, highly specialized specialists, as a rule, use an integrated approach. This category of patients is prescribed medications, physical exercise is recommended, and nutrition is adjusted. Also, many doctors practice the parallel use of time-tested folk recipes, herbal infusions, and decoctions that can enhance intestinal motility.
Medicines:
Today, many specialists very successfully use medications in the treatment of impaired intestinal motility, the components of which stimulate and enhance the motility of the organ. They also increase the tone of muscle tissue. For example, tablets “Vasopressin”, “Aceclidine”, “Proserina”.
This category of patients is prescribed medications that have a stool laxative effect, through which it will be possible to enhance the contractile functions of the organ. Thanks to the use of such medications, patients are able to empty their intestines by increasing peristalsis.
Three groups of drugs can be used during therapy:
- Affecting only the intestines . The most fast-acting and powerful laxatives in this group include Glauber's salt and Epsom salt. After a person takes this laxative, his osmotic pressure in the intestinal lumen will almost instantly begin to increase. At the same time, there will be an obstacle to the absorption of chyme, namely its liquid part, which will result in increased peristalsis. Stool removal will begin in about an hour.
- Affecting only the small intestine . The most effective remedy from this group is the well-known castor oil. After taking it, the patient will find it easier to move feces through the intestines, increase the motility of the organ, and significantly speed up the process of bowel movements. The elimination of stool will occur in the range from 2 to 6 hours. It is worth noting that the act of defecation can be accompanied by fairly moderate spastic pain, localized in the stomach.
- Affecting only the large intestine . This group includes medications that are either synthetic or herbal in origin. This category of patients is often prescribed synthetic medications, for example, Guttalax, Bisacodyl, and Phenolphthalein tablets. All these medications are presented in pharmacy chains in the form of suspensions, suppositories, and tablets. The components present in them enhance intestinal peristalsis, effectively cope with prolonged constipation, and also help with organ atony that occurs after surgical treatment. It is worth noting that the human body quickly gets used to such medications, and intestinal colic and allergic reactions may occur while taking them. As for herbal medicines, in their production manufacturers use the following components: rhizomes of licorice, buckthorn, rhubarb, and hay leaves. In pharmacy chains they are presented in various pharmacological forms.
Also, in the course of drug therapy, specialists include medications that normalize the functioning of the central nervous system. For example, the condition is stabilized with the help of antidepressants, tranquilizers, and antipsychotics.
Nutrition rules
Patients need to adjust their diet and adhere to the following recommendations that will help restore intestinal motility:
- Vegetables are best consumed unprocessed.
- The diet should include freshly squeezed juices.
- There should not be long gaps between meals.
- It is necessary to exclude all junk food from the diet.
- Before your morning meal you should drink a glass of water.
- The daily volume of liquid should not be less than 1.5 liters.
- Patients need to consume fermented milk products.
- Before going to bed, it is recommended to drink a glass of low-fat kefir.
The modern dynamics of life forces a person to often eat on the go or eat fast food. As a result, a phenomenon occurs such as gastric peristalsis, which is one of the stages of digestion and processing of incoming products. Many people face this problem due to gastrointestinal diseases, and this process is observed in people of different ages. This is especially acute for patients with disorders of the digestive system.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Even “advanced” ulcers or gastritis can be cured at home, without surgery or hospitals. Just read what Galina Savina says and read the recommendation.
Advice from a gastroenterologist
Disturbances in the motor activity of the stomach and the entire digestive system as a whole can be both functional and pathological in nature.
The doctor has all the tools at his disposal for timely detection of the disease and prescribing adequate treatment. Therefore, at the first signs of discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract, you should seek advice from a medical institution, and not try to cope with the problem with painkillers or traditional medicine.
Improving intestinal motility
Diet
If you have intestinal atony, eat regularly, at least 4 times a day. Drink at least 2 liters of fluid per day. Include foods with a laxative effect in your diet.
Grocery list
- vegetables rich in plant fiber: carrots, white cabbage, zucchini, beets;
- fruits: figs, plums, apricots, apples, pears;
- berries except blueberries and chokeberries;
- vegetable, berry and fruit juices;
- bread made from a mixture of rye and wheat flour: “Darnitsky”, “Orlovsky”, “Borodinsky”, varieties with added bran;
- cereals: oatmeal, millet, buckwheat, pearl barley;
- nuts, seeds;
- one- and two-day kefir;
- vegetable oil.
Set of exercises
Do morning exercises, do exercises to stimulate intestinal function:
- Walk in place with high knees for 2-3 minutes.
- Lie on your back, stretch your arms along your torso, slowly raise your legs, hold them at a 45° angle to the floor, and perform crossing movements. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Lie on your back, arms along your body, bend your legs at the knees and hip joints, pull them towards your stomach, clasping them with your arms, slowly return to the starting position. Repeat 10-15 times.
Drugs
- Prokinetics. Only one drug from this group is registered in Russia - Prucalopride. It acts on serotonin receptors in the intestinal wall and stimulates motor activity.
- Anticholinesterase drugs . Prozerin improves neuromuscular conduction and stimulates motor skills. The drug is prescribed to patients in surgical hospitals to combat intestinal atony after surgery.
- Laxatives with osmotic action. Duphalac (lactulose), Forlax (polyethylene glycol) attract water into the intestinal lumen, soften the stool, and increase its volume.
- Prebiotics are preparations containing ballast substances. Dietary fiber stimulates intestinal function. Popular products: wheat bran, Mucofalk (psyllium seed hulls), Fitomucil (plum and psyllium seed hulls).
- Contact laxatives – irritate receptors in the colon wall and activate smooth muscle contractions. Main drugs: Senade, Guttalax, Bisacodyl.
Be sure to read:
Intestinal flu: symptoms and treatment in adults