The term used in the title is used in colloquial language to refer to dyspeptic syndrome - a disturbance in the absorption of food, accompanied by abdominal pain, flatulence and other characteristic symptoms. According to ICD 10, the pathology has code K30 (with the exception of the nervous, neurotic and psychogenic varieties). In 90% of cases, digestive disorders are functional in nature.
Causes of indigestion
Factors that cause dyspepsia include:
- Eating too much food or not chewing it enough. Both slow down the breakdown of the product into individual components. The food does not have time to be processed and begins to rot, which leads to the development of pathogenic flora, intoxication, and the appearance of dyspepsia.
- Lack of coarse plant fiber - an insoluble substance involved in the formation and movement of the food bolus through the intestines. Normally, a person should receive 20–45 grams of this component every day. Otherwise, the pushing of food through the gastrointestinal tract slows down, a fermentation process occurs, and pathogenic microorganisms actively develop.
- Prolonged psychological stress. Experiences that do not stop for several days or weeks lead to a weakening of immune processes, which causes the activation of opportunistic bacteria in the intestines.
- Gastritis, ulcers and other inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - toxic substances are released in the affected area, which irritates the intestinal walls. Peristalsis increases, fluid is released into the lumen, diarrhea, flatulence, and pain occur.
- Traumatic or spontaneous damage to the nerve trunks innervating the digestive structures (neurogenic intestine). Due to disruptions in the process of breaking down food, the patient may experience both diarrhea and constipation.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
Intestinal dyspepsia is usually accompanied by symptoms of indigestion:
- aching pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen,
- diarrhea or constipation,
- nausea without vomiting,
- heartburn,
- bloating.
At the same time, each type of intestinal dyspepsia has its own symptoms:
- the fermentative form is characterized by flatulence with specific sounds in the abdomen, pain due to increased gas formation, and frequent bowel movements;
- the putrefactive form is accompanied by severe intoxication of the body and, as a result, headache, loss of strength, and the appearance of loose stools with the smell of rot;
- fermentation dyspepsia is additionally accompanied by flatulence, discomfort in the stomach, the appearance of an unpleasant metallic taste in the mouth, decreased appetite, a feeling of extreme fatigue, and headaches;
- in the fatty form of the pathology, discomfort or pain in the abdomen is observed 0.5-1 hour after eating, as well as diarrhea with the appearance of a whitish coating on the stool.
The reason for urgent contact with specialists are cases when manifestations of dyspepsia are accompanied by:
- shortness of breath,
- chest pain,
- weight loss,
- the appearance of tarry black stools,
- progressive difficulty swallowing,
- increased sweating,
- jaundice.
The presence of dyspepsia is determined by a gastroenterologist.
Differential diagnosis includes taking an anamnesis, during which the specialist determines the presence of specific symptoms, the frequency and intensity of their manifestation.
It is mandatory to palpate the abdomen, listen to intestinal motility and determine the presence of bloating. Laboratory tests are also prescribed: blood, feces, urine.
In some cases, there is a need for additional examination methods:
- endoscopy,
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs,
- radiography,
- analysis of gastric juice,
- manometric studies,
- tests to detect the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Only after this is medication treatment prescribed.
Symptoms of indigestion in adults
Dyspeptic syndrome leads to the appearance of several characteristic signs in the patient. The most striking is bloating. Patients complain of an increase in its volume, a feeling of heaviness, gurgling or rumbling. When gases that have an unpleasant odor escape, the condition improves, but soon becomes the same.
Stomach dyspepsia is accompanied by a feeling of discomfort and heaviness in the epigastric zone - an area located in the upper third of the abdomen. Nausea and vomiting may occur. After this, the adult patient complains of heartburn, which develops when gastric juice enters the mucous membrane of the esophagus.
Vomiting that occurs with dyspepsia brings temporary relief. The complete absence of this effect suggests a cerebral origin for nausea.
If indigestion was caused by an inflammatory process, the complex of symptoms includes the following conditions:
- Hyperthermia.
- Pain in muscles, bones.
- Weakness.
- Atony.
- Fatigue.
Sleep is also disturbed and the psycho-emotional state changes. The person becomes whiny.
Video: What is Dyspepsia
Traditional therapy
Treatment of dyspepsia can be carried out not only with the help of medications, but also with the help of folk recipes. Many doctors allow the combination of traditional methods of therapy with the use of pharmaceutical drugs, provided there are no contraindications.
The following recipes will help cope with the symptoms of dyspepsia:
- Pour 1 tbsp. l. celery seeds 500 ml boiling water, leave for 2 hours, strain. Drink 2 tbsp. l. 4 times a day.
- Mix 2 tbsp. l. dried calendula flowers and 2 tbsp. l. blackberries, add 1 liter of boiling water. Infuse, drink 0.5 cups before each meal.
- Combine cumin and marjoram seeds in equal proportions, take 2 tbsp. l. mixture, pour 1 glass of hot water. Leave for 15 minutes. Healers advise: drink the product 2 times a day, 100 ml.
These simple but effective folk methods help eliminate pain and discomfort in the epigastric region, normalize digestive processes, get rid of nausea, heartburn and increased gas formation, however, before starting treatment, you must consult with a specialist about the possibility of using alternative medicine for stomach indigestion.
Types of dyspepsia
There are two main forms of intestinal disorders:
- organic;
- functional.
In the first case, the clinical picture of the disease is a consequence of real changes in the structure of the intestine caused by injury, an atrophic process, or a tumor. Nerve trunks, muscle layers or the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract may be damaged. This type of dyspepsia is caused by:
- ulcer;
- gastritis;
- pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- cancer.
As well as diseases accompanied by atrophy of nerve trunks.
Functional disorders include disorders that occur in the absence of organic changes. It is often not possible to establish the exact cause of such conditions. Therefore, the type of indigestion in question is considered idiopathic. When the etiological factor is eliminated, the disease goes away without medical intervention.
What to do if you have indigestion
Functional dyspepsia is relatively easy to eliminate. Therefore, on the first day of illness it is permissible to refuse to visit a doctor. In this situation, the following medications are recommended:
- Enterosorbents (Enterosgel, Activated carbon).
- Enzymatic (Creon) and carminative agents.
If the patient’s condition has not improved after 24 hours, it is necessary to visit a general practitioner or gastroenterologist. With a rapid deterioration in health and a bright “clinic” of the disease, refusal to travel to a medical organization is unacceptable. The patient is transported to the hospital as quickly as possible.
Medical nutrition
When starting to treat dyspeptic disorder, you need to pay special attention to your diet. Diet is perhaps the main step in improving the patient’s condition, along with drug therapy. Correcting your diet allows you to quickly get rid of the symptoms of the disorder and maintain normal stomach function for a long time. On the first day of exacerbation of dyspepsia, it is recommended to refuse to eat or significantly reduce the number of foods consumed. In this case, the products can only be eaten in pureed form. Such measures are necessary to eliminate the irritating effects of foods on the gastric mucosa and thereby reduce the symptoms of indigestion.
A diet for dyspepsia involves following certain rules for preparing and eating food. You need to eat in small portions, that is, in small portions 5 times a day, avoiding overeating or feeling hungry, chewing food thoroughly and not being distracted by extraneous activities (watching TV, reading a book). The food temperature must be warm.
Dishes should be steamed; boiling and baking under foil are also allowed. Fried foods are excluded, as they significantly impair the functioning of the stomach and cause severe irritation of the walls of the organ. For the same reason, any fatty foods, spicy, smoked, spicy, or pickled foods are excluded. You should not eat rich pastries, raw vegetables and fruits. And, of course, a therapeutic diet involves a complete abstinence from coffee, strong black tea, carbonated drinks and alcohol.
The basic rules of healthy eating for those suffering from dyspepsia must be observed constantly, and in case of exacerbation of the disorder, it is recommended to adhere to a particularly strict eating regimen. This will allow you to quickly get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of indigestion and significantly improve your well-being.
Accurate diagnosis
Symptoms of indigestion occur in many diseases. Therefore, differential diagnosis for the pathology in question requires a large amount of interventions. First of all, the organic origin of dyspepsia is excluded. For this, the patient is prescribed an FGDS with a biopsy, ultrasound, and x-ray of the stomach. In the latter case, a contrast barium mixture is used to assess the functional state of the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition to the above, a person undergoes four more examinations:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- ECG.
- Pyloric flora test.
- Checking stool for the presence of red blood cells.
At the beginning of the diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude symptoms of anxiety: dysphagia, vomiting “coffee grounds”, palpable tumors in the abdomen, causeless weight loss. The presence of these phenomena is an indication for targeted cancer screening.
The diagnosis of “functional dyspepsia” is made if organic causes have not been established. A true disease is considered when at least six months have passed since its debut, and the symptoms have not disappeared for the last three months.
Why does dyspepsia occur?
What is intestinal and stomach dyspepsia is well known to those who suffer from peptic ulcers , pancreatitis , gastroesophageal reflux disease , cholecystitis , stomach tumors and other ailments of the digestive system.
Intestinal and stomach dyspepsia can develop against the background of disturbances in the nervous regulation of the motor functions of the stomach and duodenum. The manifestation of toxic dyspepsia is often associated with infectious intestinal diseases.
If a person has been diagnosed with “ functional gastric dyspepsia ,” then such phenomena are associated with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, pathological processes in the intestines, dysbiosis, etc. Functional gastric dyspepsia manifests itself under the influence of a number of factors that aggravate these processes. Thus, gastric or intestinal dyspepsia is often observed in those who are used to eating food very hastily. A person chews food very poorly, so it does not mix enough with the digestive enzymes of saliva. Also, food is poorly digested by those who are accustomed to overeating. In some cases, the phenomenon of dyspepsia is observed in those who consume certain foods that are poorly digested by the gastrointestinal tract. In some cases, the consumption of carbonated drinks, alcohol, and drinks containing caffeine also negatively affects the functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Another factor that provokes dyspepsia is stressful situations. During severe emotional shocks, the hormones adrenaline and cortisone , which promotes blood flow to the muscles rather than to the digestive system. In addition, in a state of stress, a person swallows a lot of air in the process of absorbing food, which also worsens the digestion process. You should not engage in physical exercise immediately after eating, as stress causes a redistribution of blood flow.
In addition to these factors, the occurrence of functional dyspepsia is provoked by smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, and infectious diseases that affect the gastric mucosa. Sometimes the condition is aggravated by high air temperature and increased atmospheric pressure.
Manifestations of fermentative dyspepsia are often observed in a person if he has switched to food that is unusual for him, as well as if he has consumed a large amount of plant fiber. Manifestations of putrefactive dyspepsia are sometimes associated with intestinal hypersecretion, which occurs as a consequence of inflammatory-necrotic processes.
of fatty dyspepsia are very rarely observed . This condition develops after eating fatty foods by those who suffer from diseases of the liver, biliary tract or pancreas.
Treatment of dyspepsia
Treatment for indigestion depends on its cause and severity. Organic changes require the elimination of pathological deformations (tumors are removed, the ulcer is put into remission). Good results in the correction of functional disorders can be achieved by combining three types of influence: medications, herbal-based folk remedies and diet.
Drugs
The range of medications used to treat dyspepsia may vary. Their choice depends on the specifics of the pathology. To eliminate episodic short-term disorders, the following drugs are used:
- Enzymes (Creon) - contribute to the complete breakdown of food and its absorption.
- Antiemetics (Metoclopramide) - blocks dopamine receptors, relieves nausea and vomiting.
- Antidiarrheals (Loperamide) - slow down the motility of the digestive tract, reduce the permeability of the intestinal wall, and have a fixing effect.
- Enterosorbents (Activated carbon) - bind and release toxic products formed in the gastrointestinal tract into the external environment.
To accelerate the elimination of toxins and undigested food residues, the patient can undergo gastric lavage and a cleansing enema. The first manipulation is carried out before taking sorbents.
Etiology
The causes of indigestion are as follows:
- lack of a normal diet;
- unbalanced diet;
- too much fast food, processed foods and similar unhealthy foods for the body;
- habit of drinking sweet carbonated drinks with food;
- alcohol abuse;
- drinking strong tea and coffee;
- too many confectionery products;
- following diets that are not justified from a medical point of view;
- physical activity immediately after eating;
- physical inactivity, that is, a sedentary lifestyle;
- taking medications without a doctor’s prescription, including hormonal drugs;
- damage to the body by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- presence of chronic gastroenterological diseases;
- liver diseases;
- infections in the stomach;
- increased stomach acidity;
- malignant or benign formations in the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition, symptomatic indigestion can occur under severe stress, nervous strain, and chronic fatigue.
Indigestion in pregnant women
In the final stages of pregnancy, dyspepsia occurs in 50% of expectant mothers. This is due to the increased pressure of the uterus on the stomach and a change in the hormonal pattern, against which the tone of the cardiac sphincter decreases, which causes reflux of hydrochloric acid into the esophagus, the development of esophagitis, heartburn, chest pain, and dyspepsia. Due to the pressure of the gastrointestinal tract, a woman quickly becomes full when eating food and cannot eat the required portion.
If a pregnant woman tolerates dyspepsia relatively easily, it is better to refuse drug correction of the condition. The patient is advised not to smoke, not to take NSAIDs and antidepressants. In cases of severe distress, antacid medications are indicated.
Drinking a soda solution to neutralize hydrochloric acid during heartburn is unacceptable. When a chemical reaction occurs, a gas is released, which stretches the stomach and intensifies the “clinic” of dyspepsia.
Indigestion in children
Improper intestinal function is often found in newborns, whose microbiological environment in the gastrointestinal tract has not yet formed. Infants who begin to receive complementary foods also suffer. In the latter case, the cause is the incorrect quantitative or qualitative composition of food.
Functional dyspepsia in young children requires minimal therapeutic intervention. Pediatricians prescribe probiotics (Linex), which promote the formation of the correct composition of microflora, and correct the baby’s nutrition. If there is evidence of a spasm, the child is prescribed No-Spa and local exposure to heat (a heating pad on the stomach).
Video: A child has a stomach ache
Possible complications
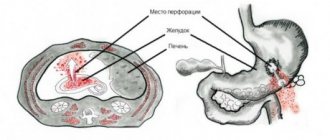
A one-time disorder that is not associated with the presence of organic changes does not entail consequences and goes away within a few days. Chronic processes that occur over 3–6 months cause weight loss and dehydration. Ruptures of the esophageal mucosa may occur, accompanied by bleeding (Malory-Weiss syndrome).
The consequences of organic dyspepsia depend on the disease that led to the intestinal disorder. A stomach ulcer can perforate and bleed, while cancer can destroy surrounding tissue and metastasize. The task of preventing these processes falls on the gastroenterologist treating the patient.