Gastric hyperplasia is a benign disease characterized by pathological proliferation of stomach cells. Due to the increase in the number of cells, the mucous membrane of the organ thickens and polyps appear. Pathology can occur not only in the stomach: enlargement can occur in any internal organ. The disease manifests itself in any person, regardless of gender and age.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications and prognosis
- Prevention
Etiology
Gastric hyperplasia develops due to unfinished treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, active cell growth begins and polyps appear.
The main causes of hyperplasia:
- changes in hormonal balance, especially when the amount of estrogen is increased;
- genetic predisposition, in particular adenomatous polyposis (characteristic of polyps in the stomach) - if the pathology is diagnosed in a woman, the disease can be inherited by a daughter or granddaughter;
- long-term use of medications that can affect changes in the structure of the gastric mucosa;
- unfavorable environment - a pathological increase in the number of cells may begin.
The cause is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and other infectious diseases.
Clinical manifestations
The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that in the early stages there are no expressive signs that are alarming. Most often, it is discovered accidentally during a diagnostic examination using fibrogastroduodenoscopy due to patient complaints of stomach pain.
The most striking symptoms that appear during the progression of the pathological process:
- painful sensations in the upper abdomen, occurring with varying intensity;
- a feeling of sour taste in the mouth;
- disruption of the digestive process;
- decrease in hemoglobin;
- possibility of bleeding.
Pain syndrome typically occurs at night or during a long break between meals. It may occur in the form of minor discomfort.
In the absence of timely treatment, symptoms increase, the following signs appear:
- hiccups, vomiting, nausea;
- bloating;
- loss of appetite;
- pale skin;
- decreased blood pressure;
- diarrhea;
- belching.
Most of the listed symptoms are characteristic of many diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract. To avoid misdiagnosis, you should undergo a thorough examination and start treatment on time.
The effectiveness of the treatment course depends on this. It is much more difficult to cope with a disease in an advanced stage, when the pathological process becomes chronic.
Classification
In medicine, experts distinguish between many different types of hyperplasia:
- Focal developing hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa. The first stage of development of the anomaly, when certain polyps begin to appear. Focal diagnosed hyperplasia of the stomach covers only some areas (“foci”), which is why it got its name. The lesions look like growths of various shapes and sizes, painted in a different color, so they are clearly visible during examination. Formations arise at the site of previously received damage or erosion.
- Follicular identified gastric hyperplasia. This type of pathology is often diagnosed. Lymphatic cells begin to grow. The reasons for the development of the anomaly are different: the influence of carcinogens, hormonal imbalance, the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, stressful situations and much more. A distinctive feature of this type of disease is the formation of follicles in the stomach.
- Hyperplasia of the integumentary pitted epithelium of the stomach. A dangerous type of pathology that can contribute to the appearance of a malignant tumor in the intestine. The structure of the epithelium changes under the influence of unfavorable factors: cells grow and become larger.
- Hyperplasia involving the antrum of the stomach. The antrum is the last part of the organ before it exits into the intestine. In this place, with the development of hyperplasia, multiple small growths, pits and ridges begin to form.
- Foveal hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa. This type of pathology is characterized by an increase in the length of the folds of the mucous membrane and an increase in their curvature. Pathology occurs due to prolonged inflammation or self-administration of anti-inflammatory drugs.
There are also other types of pathology: glandular, polypoid, lymphoid.
Hyperplasia of the antrum of the stomach
Possible complications
Since hyperplasia is a pathological growth of tissue, there is always a danger of malignancy, that is, the appearance of altered cells. And the growth of atypical cells means the appearance of a malignant tumor.
The polypous form of hyperplasia often causes complications, since polyps can be damaged, which leads to the development of gastric bleeding. Cell proliferation can be observed not only in the stomach, but also in other digestive organs that have a mucous layer.
Hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa is not a separate disease, but a consequence of other pathological processes. Often the cause of its development is gastritis. Therefore, there is little point in trying to get rid of hyperplasia without curing the underlying pathology. Diet and a healthy daily routine play a big role in recovery.
Symptoms
In the first stages of the development of the disease, it is very difficult to identify the pathology, because there are practically no symptoms: an increase in the number of cells does not cause discomfort to a person, there is no pain even when small polyps appear. When they increase, difficulties begin with the passage of food, which can cause severe bleeding or pain.
As the disease progresses, disruptions in the functioning of the stomach begin, and these are problems with digestion. The following symptoms begin to appear:
- constant or short-term pain that occurs after eating, sometimes during prolonged fasting;
- heartburn;
- flatulence and constipation;
- sour belching;
- nausea and vomiting;
- refusal to eat;
- general weakness, body aches, dizziness;
- anemia.
If such symptoms occur, you should consult your doctor so that the doctor can prescribe an examination.
Symptoms
In the early stages of epithelial tissue proliferation, a person does not feel any discomfort, so the disease can only be detected by chance. Small polyps also do not cause concern to the patient. But when polyps grow to impressive sizes, they can interfere with the normal passage of food.
Significant thickening of the epithelial layer also leads to disruption of the organ; symptoms depend on the size of the lesion. The main manifestations of the pathological process:
- the pain is constant or appears periodically in connection with eating. Some patients feel pain when abstaining from food for a long time, and for some, discomfort occurs immediately after eating;
- heartburn, bloating;
- disruption of intestinal function, the patient suffers from constipation;
- belching with a sour taste;
- nausea, loss of appetite;
- General symptoms often occur - weakness, dizziness.
Advice! It is impossible to make a diagnosis based solely on symptoms. If discomfort appears in the abdomen, it is necessary to undergo an examination.
Diagnostics
During the examination, the medical officer collects the patient’s medical history and clarifies the complaints. It is impossible to establish a correct diagnosis using these data alone. Other studies are prescribed:
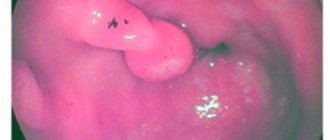
- gastroscopy - using an endoscope tube inserted into the stomach, the walls of the organ and polyps are examined;
- biopsy - a histological examination will establish an accurate diagnosis; using the procedure, the type of pathology and the main cause of the development of the anomaly are determined.
Gastroscopy
After an accurate diagnosis is made, effective treatment is prescribed.
Treatment
Gastric hyperplasia is treated by a gastroenterologist. If necessary, the patient may be scheduled for a consultation with an oncologist or surgeon. Surgery is performed only in extreme cases; usually the treatment regimen is limited to taking medications.
Treatment options:
- Drug therapy. Treatment of gastric hyperplasia is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the pathology. If the anomaly has developed due to a bacterial infection in the body, the person is prescribed antibacterial drugs. To protect the mucous membrane, the doctor prescribes gastroprotectors. A gastroenterologist may prescribe medications to reduce acidity if the patient's test results show an elevated pH. The doctor prescribes hormonal medications when the disease is associated with hormonal imbalances.
- Carrying out surgery. If too many polyps of a significant size appear, the growths may need to be removed. Usually limited to endoscopic polypectomy. In severe cases, open gastric surgery is performed or part of the stomach is removed.
- Diet. The patient must adhere to dietary nutrition. You can only eat food that does not harm the mucous membrane. The menu will depend on the primary disease that caused the pathology. Fractional nutrition is suitable for any patient with such a deviation, regardless of the cause of the development of the anomaly. There should be up to 5 meals per day, small portions. List of products whose consumption is not recommended: alcohol, strong tea, coffee, carbonated drinks. Lean fish and meat, cereals are useful. It is better to cook if the food is steamed, stewed or boiled. Fried and spicy foods should be excluded from the diet. Hot dishes cannot be eaten. A strict diet will help you recover faster.
- Traditional medicine recipes. Can only be used in combination with traditional medicine after consultation with a doctor.
The method of treatment is selected individually. You should not self-medicate, because this can lead to irreversible consequences and serious complications.
Gastric hyperplasia: what it is, symptoms and types, how to treat it
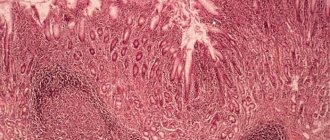
Gastric hyperplasia is the rapid growth of the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the organ without the formation of a cancerous tumor. This phenomenon leads to thickening of its inner surface with the possible occurrence of polyposis.
The pathological condition indicates existing disturbances in the tissue structure. A focal or diffuse process is distinguished.
Gastric hyperplasia
Hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa in general is a rather dangerous phenomenon. Any pronounced increase in the number of epithelial cells indicates a sharp disadvantage. The internal cavity of the organ thickens significantly, which disrupts the digestion process and can lead to the formation of a tumor.
Most often, gastric hyperplasia develops due to the lack of adequate treatment for any gastrointestinal disease. As a rule, it is an ulcerative process, gastritis or inflammation. Often the cause of the disease is Helicobacter pillory.
The concept of pathology and causes
According to ICD-10, the disease is classified as polyposis and is included in the section under code D13.1.
Explaining the essence of the concept of “hyperplasia of the gastric mucosa”, what it is, is complicated by the lack of accurate information about the factors leading to its development. As a rule, the main impetus for it is a whole set of various reasons.
The main ones are always:
- genetic predisposition;
- influence of carcinogens;
- various pathologies of the stomach;
- bad habits;
- side effects of certain medications;
- hormonal imbalance.
Symptoms and types of disease
The clinical picture of the pathology is characterized by a pronounced disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
Typically, the patient complains of noticeable epigastric pain, prolonged discomfort after eating, constant belching or heartburn. Very often he suffers from a sour taste in the mouth, excess gas in the abdominal cavity, and chronic constipation. The person feels sick and sometimes vomits. He loses his appetite, experiences severe malaise, and is prone to dizziness.
There are the following forms of the disease.
- Hyperplasia of the antrum, manifested by the appearance of numerous outgrowths in the mucous membrane. Sometimes there are also bulges or depressions in it.
- Glandular , in which the endocrine glands undergo the greatest changes with the appearance of polyps.
- Lymphoid hyperplasia of the stomach is characterized by the rapid proliferation of the corresponding tissue.
- Follicular is the most common. It develops as a result of unbalanced nutrition or the penetration of various carcinogenic compounds into the organ cavity.
- Lymphofollicular affects the antrum of the stomach. It is considered a combination of the two previous forms with rapid proliferation of lymphatic cells.
- Polypoid is no less dangerous, as it most often leads to a tumor process.
- Focal foveal hyperplasia of the stomach has a clear localization and usually affects the antrum. It usually provokes the appearance of polypous growths.
- Hyperplasia of the integumentary pitted epithelium of the stomach poses the greatest threat to the patient. With this form of pathology, altered cells rapidly develop in the organ.
- Foveal hyperplasia of the stomach, what is it, patients ask when they see the conclusion of a gastroenterologist. It is a type of disease in which a folded structure appears in the mucous membrane with changes throughout the tissue. Develops as a result of a chronic inflammatory process.
Diagnosis of gastric hyperplasia
To establish the exact cause and form of the disease, a number of measures are necessary.
It is necessary to conduct histology and cytology of the biomaterial obtained from the inner surface of the stomach.
It is imperative to do a test for the presence of H. Pylori, as well as antibodies to it in the patient’s blood. Stool is examined to detect antigen.
A breath test using urea is often performed to identify traces of the bacteria.
It is mandatory to undergo ultrasound, CT and MRI,
To determine the exact cause and essence of the process, gastroscopy and other endoscopic studies are required. It is also necessary to carry out radiography using a contrast agent.
Treatment methods for gastric hyperplasia
After the doctor examines the test results and photographs taken during instrumental studies, he determines the direction of combating the pathology.
Small non-glandular formations do not require urgent medical attention. If there is no risk of progression or threat of malignancy, then only constant monitoring by a specialist is required.
Therapy is often also used with:
- antibiotics;
- enveloping drugs;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- substances that reduce stomach acidity;
- gastroprotectors;
- steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- enzymes;
- sedatives.
If conservative treatment is not effective, the doctor decides on surgical intervention. If the disease progresses too rapidly, especially with the rapid growth of the integumentary pitted epithelium, complete removal of the tumors is required.
Large polypous areas require excision
Glandular growths tend to turn into malignant tumors, so they require mandatory resection.
The adenomatous process requires removal, as it threatens to transform into cancer.
If there is a threat of malignant degeneration, complete resection of the affected area of the stomach is necessary.
Diet and lifestyle changes
The patient's nutrition is of great importance in the treatment of hyperplasia.
It is completely prohibited to use:
- canned food;
- spicy seasonings;
- overheated dishes;
- foods with a predominance of fats;
- any spices;
- roast;
- alcohol;
- lemonade.
It is recommended to constantly include lean meat or fish, cereals, vegetables, and fruits in your daily diet. All dishes must be served chopped. Food should be steamed, boiled, stewed. It is advisable to adhere to the principle of fractional nutrition. Don't overload your stomach.
Lifestyle adjustments are also necessary. It is necessary to take vitamins, and use medications required for treatment only as directed and under the strict supervision of the attending physician.
You need to drink at least two liters of liquid per day. Before meals, you should take a glass of still mineral water. Smoking, drinking alcohol or other carcinogenic substances is strictly prohibited.
Forecast and some recommendations
The most favorable prognosis occurs when the disease is detected in a timely manner and urgent measures are taken to prevent further growth of the gastric mucosa.
No less important is the type of disease and the degree of its intensity.
If you strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, it is usually possible to bring the pathological process under control.
In addition, the following instructions from specialists in diseases of the digestive system must be observed:
- Diagnose any disorders in the gastrointestinal tract in a timely manner.
- Get tested regularly for H. Pylori.
- Monitor prescribed therapy.
- Stabilize the pH level of gastric juice.
- Follow the diet strictly.
- Give up bad habits forever.
- Chew food thoroughly.
- Watch the chair.
- Normalize the activity of the nervous system.
You can find out what signals the stomach gives from this video.
Prevention
Prevention of pathology is aimed at preventing its occurrence. For those who have already been diagnosed with it, it is aimed at eliminating the causes of its progression, as well as relieving the main symptoms.
It is imperative to follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle, avoiding stress.
It is required to adhere to the diet prescribed by the doctor, eliminating dietary irregularities. It is worth carefully studying the composition of products before purchasing them in the store. At the slightest suspicion that they contain carcinogens, they must be discarded.
You need to do physical therapy and take walks.
You should not take pharmacological substances uncontrollably, especially steroids or anti-inflammatory medications.
You should contact a specialist with a request to make individual prescriptions and recommendations for correcting the patient’s lifestyle. The specialist will suggest effective measures to prevent hyperplasia and other pathologies of the digestive system.
If there are any signs of trouble, you should immediately consult a doctor. It is prohibited to independently diagnose yourself and begin treatment.
Source: https://GastrituNet.online/bolezni-zheludka/onco/opuholy/giperplaziya-zheludka.html
Prevention
Basic preventive measures for hyperplasia:
- healthy and balanced diet;
- active lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits;
- use of medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- regular preventive examinations;
- urgent treatment of gastric diseases.
Depending on the area of intestinal damage, the gastroenterologist will recommend individual methods of prevention to the person. Self-medication is excluded - you need to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of pathology.