Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Exocrine insufficiency syndrome develops when there is a lack of gland enzymes or a change in the normal functioning of the intestines.
Digestion is immediately disrupted, since their action causes the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The disease can be congenital (cystic fibrosis, birth defect) and acquired (acute and chronic pancreatitis, cancer, surgical interventions, diseases of the duodenum, cholecystitis). Insufficiency of exocrine pancreatic function can be caused by the following reasons:
Primary develops when the gland itself is damaged and there is a lack of pancreatic enzymes.
Secondary - the organ copes with its job, but there are certain reasons why enzymes cannot work correctly: acceleration of intestinal motility, incomplete mixing of enzymes with the food bolus, their insufficient activity or complete destruction by intestinal microflora, dysbacteriosis.
Symptoms
The symptoms are specific and immediately suggest a disease of the pancreas. Malabsorption syndrome develops - insufficient absorption of nutrients in the intestine. Patients report diarrhea (more than two bowel movements per day) or prolonged constipation.
Often there is rumbling in the stomach, periodic pain in the stomach, bloating and flatulence.
Steatorrhea appears - fatty feces - fetid stools, difficult to wash off, glossy, in large quantities and several times a day. Further, protein absorption is impaired, patients develop edema, anemia, and weight loss sharply. Weakness, apathy, mood changes occur, and there is a tendency to depression.
There are three stages of the disease:
- Stage 1 – latent (hidden) course, there is already a problem in the gland, but the organ copes with the normal load. Changes can only be found after eating a large meal.
- Stage 2 – full clinical picture with steatorrhea, diarrhea, flatulence.
- Stage 3 – dystrophic – irreversible metabolic disorders, weight loss, swelling, massive disorders in organs and tissues.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is complex and requires special studies:
Coprogram is a stool analysis that reveals a large amount of undigested fibers and drops of fat.
The most revealing will be the detection of pancreatic elastase 1 during enzyme immunoassay; the only drawback is that it cannot be detected in the primary stage of the disease.
Study of the contents of the duodenum during duodenal intubation (the probe is inserted through the mouth to the duodenum), after stimulation of the pancreas with the hormones secretin and pancreasimin.
Treatment
The most important role is played in treatment . Spicy, spicy, fatty foods, strong coffee, soda, and alcohol are excluded. The ratio of proteins: fats: carbohydrates is 20%:20%:60%. Mandatory use of multivitamins.
Patients are forced to use appropriate enzyme preparations for life: Wobensin, Pancreatin, Creon, Kadistal, Mezim-Forte. The dose and medicine are selected strictly individually.
If you follow the doctor's instructions, the prognosis is favorable.
Enzyme deficiency in adults
What leads to enzyme deficiency in adults:
- Overeating, in which there are simply not enough enzymes to process excessive amounts of food.
- Any form of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) - not only in the acute stage, but also in the chronic course of the disease.
- Various conditions that interfere with the flow of pancreatic juice into the intestines (tumors, gallstones, parasites).
- Pathologies of the liver and biliary system, due to which pancreatic enzymes are not sufficiently activated by bile.
- Inflammation of the wall of the small intestine (enteritis). This cause of enzyme deficiency may be of infectious origin.
- Gastritis with reduced acidity of gastric juice, which negatively affects the process of enzyme activation in the stomach and small intestine.
- Death of cells of the intestinal mucosa in Crohn's disease, amyloidosis, dysbiosis, systemic autoimmune disorders and a number of other conditions.
- Congenital disorders of the synthesis of digestive enzymes.
- Consequences of surgical treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (removal of part of the stomach or intestines).
- Irrational diets, hypovitaminosis and fasting can also cause a lack of enzymes.
Enzyme deficiency symptoms in adults
Treatment for enzyme deficiency can only be prescribed by a doctor based on the results of a comprehensive examination. Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease as much as possible, reducing existing symptoms and normalizing the digestive process. Facilitating the digestion of food is the most important goal of therapy. After all, intestinal disorders that arise from a lack of enzymes aggravate damage to the intestinal mucosa, which aggravates the course of the disease.
When there is a lack of enzymes, two main interrelated processes occur:
- impaired digestion of food (maldigestion);
- insufficient absorption of nutrients in the intestines (malabsorption).
Typically, the first signs of decreased production of lipase, which is responsible for the digestion of fats, appear. Undigested fats pass through the intestines, irritating its walls and causing symptoms of pancreatic disease such as flatulence, bloating, pain and diarrhea. The excretion of large amounts of fat in the stool is called steatorrhea. This is manifested by copious unformed stools with an oily sheen that is difficult to wash off, the presence of undigested particles in the stool, bloating and non-localized abdominal pain.
Since the breakdown of not only fats, but also proteins and carbohydrates is disrupted, the intestines do not receive enough nutrients. Sometimes a person himself tries to eat less so as not to provoke a painful attack. As a result, so-called trophological insufficiency occurs: the level of necessary substances in the blood decreases. A person loses weight, muscle wasting, loose swelling, and exhaustion begin. Due to a deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K), osteoporosis may develop and problems with skin and hair may occur. The risk of infections and heart problems increases[2].
Due to the large “safety margin”, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency does not immediately appear. Symptoms of the disease occur only when the functioning of the gland is impaired by 90% or more. On average, clinical signs become noticeable ten years after the onset of the disease. This is the danger of chronic pancreatitis: a person may not be aware of the disease, although when certain causes are eliminated, the likelihood of developing complications is significantly reduced. Let's talk about the causes and risk factors for developing pancreatitis.
And secondary nutrient deficiency negatively affects the general condition. Therefore, the treatment regimen necessarily includes enzyme preparations that compensate for the deficiency of basic enzymes. It is also important to adjust your diet and avoid overeating.
Diagnostic measures
Impaired functioning of the pancreas is manifested by all the typical symptoms: pain, nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, diarrhea. In some cases, clinical manifestations may be absent for a long time. But in the future this leads to pronounced changes in the digestive process.
Diagnosis of such conditions presents certain difficulties due to the vagueness of manifestations and minor changes in functional examination methods.
Biochemical blood parameters - enzyme activity (most often amylase). With exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis, the numbers exceed the norm by 3 times. In other cases, this process is so short-lived that it is not possible to determine its increase in the blood.
Treatment of exocrine insufficiency
The main method of treating exocrine insufficiency is nutritional correction. The patient is required to completely stop drinking alcoholic beverages. Doctors also strongly recommend that you stop smoking, as it affects the pathology of the pancreas. A person should not eat before going to bed or at night when the digestive system is not fully functioning. It is worth excluding all fatty meat and fish from your daily diet. It is better to cook dishes by steaming or simply boiling. It is necessary to develop a certain diet. The patient should eat many times a day (from 4 to 6), but the portions of meals are minimal.
Dietary nutrition for the patient is prepared by the attending physician; it is not recommended to do this on your own. The doctor draws up a treatment and nutrition plan based on diagnostic information, and also takes into account the individual characteristics of the patient. Vegetables and fruits are added to the diet, which become substitutes for animal food. The body should largely consume carbohydrates of plant origin. Some patients look for carbohydrate substances in sweets, but such food will not bring benefits, so you should avoid it. With a sudden transition to a dietary diet, some patients experience increased formation of gases in the stomach. This problem can be solved simply - just use bran.
In addition to diet, the complex of therapy for the treatment of exocrine insufficiency includes taking medications. Most often, doctors prescribe Mezim, Pancreatin, Creon. The most effective of these medications is Pancreatin, which has a gentle effect on the walls of the pancreas, promotes the release of enzymes, which effectively improves well-being.
It is possible to determine that the course of treatment has been chosen correctly a few days after the start of therapy. The patient's problems with stool disappear, namely, diarrhea stops. This is also reflected in the clinical examination of stool, the indicators of which gradually return to normal. If there is no improvement after 5-7 days, then you should contact your doctor to review the diagnosis or complex of drug therapy.
Development of exocrine type of insufficiency
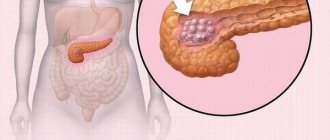
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is one of the types of organ dysfunction, which is manifested by a lack of production of juices by the glandular tissue of the organ for digestion.
The main symptoms of the development of this disorder are:
- poor digestion of food;
- increased level of gas formation in the stomach;
- disruption of the process of feces formation;
- feeling of nausea;
- the appearance of a feeling of heaviness.
Nausea is characteristic of exocrine insufficiency.
An increased level of gas formation in the stomach is characteristic of exocrine insufficiency.
The reasons for the violation may be the following:
- disruption may be caused by irreversible changes;
- stomach problems;
- dysfunction of the duodenum;
- problems with the gallbladder;
- eating disorders;
- alcohol abuse;
- food starvation.
Treatment of this type of pathological disorder begins with determining the causes of its development. If the cause of the disorder is diet or alcohol abuse, then it is necessary to begin adjusting the patient’s diet and eliminating alcohol consumption.
?enablejsapi=1″>
?enablejsapi=1″>
Enzymes with IHERB Enzyme deficiency a possible cause of excess weight
Pancreatic diseases
Disturbances in the pancreas in children are especially dangerous, since malfunctions in such an important organ lead to serious pathological disorders in a child’s developing body. Failures in the pancreas lead to metabolic disorders; such changes can lead to disruptions in the development of the child
Causes and types of exocrine insufficiency
The disease is classified depending on factors, size, and the presence of other disorders in the body. There are two types of exocrine insufficiency:
- acquired – occurs in people who have chronic pancreatitis syndrome;
- congenital - specific anomalies are transmitted according to the genetic code, which block the normal production of nutritional enzymes.
Exocrine insufficiency of pancreatic disease has its own qualifications, depending on the condition and its spread to neighboring organs of the system. A secondary form of the disease is identified, in which enzyme elements are produced. But the peculiarity of the disease is not the synthesis of substances in the small intestine and duodenum. An inactivation process occurs in the pancreas, which complicates the health condition. There is also such a classification as the aerphic form of the disease, in which disorders occur in the pancreas itself, provoked by improper synthesis of enzyme substances.
We also recommend viewing: The appearance of a spasm in the pancreas: symptoms and treatment methods
The causes of the disease are different factors, but they are divided according to the form of the disease. The primary classification group of pathology arises from chronic pancreatin. In addition, the disorder can be caused by:
- pancreatic agenesis;
- hypoplasia;
- Johanson-Blizzard or Shwachman diseases;
- genetic predisposition to enzyme deficiency;
- consequences of surgery;
- exocrine deficiency;
- severe obesity, which provokes changes in the cellular components of the pancreas;
- malignant and benign neoplasms in the pancreas;
- cystic fibrosis - this disease is congenital in nature, in which disturbances occur in the activity of secretion, and is accompanied by improper functioning of the organ.
The causes of disorders of the exocrine activity of the gland organ can be atrophy and fibrosis. Such symptoms are consequences of disorders in the body. The most common of them are:
- stones appear in the ducts of the pankyriatic system;
- pancreatic necrosis - the syndrome manifests itself with the complete or partial death of pancreatic cells;
- diabetes mellitus – the diagnosis is a severe complication of pancreatitis and most often has a second form of development;
- cirrhosis of a pancreatic nature;
- hemosiderosis - in the soft tissues of hemosiderin, an accumulation of iron pigment occurs, which is found in large quantities in the organ;
- poor nutrition, uncontrolled consumption of foods that destroy the walls of the pancreas;
- atherosclerosis;
- alcoholic, obstructive, calculous pancreatitis.
The secondary type of enzyme deficiency is formed due to disorders that occur in the small intestine of the digestive tract. Main pathologies:
- side effects after surgery on the digestive system;
- protein deficiency;
- improper functioning of the hepatobiliary subsystem;
- enterokinase enzymes do not leave the body in full or completely incorrectly;
- excretory insufficiency;
- damage to the mucous membrane;
- gastrinoma is an active neoplasm.
In the pancreas, there are also absolute and relative forms of the disease. With a decrease in the size of the parenchyma in the pancreas, absolute enzymatic deficiency is formed, which manifests itself with poor production of bicarbonates and enzymes. In medical practice, this form is extremely rare in patients with exocrine insufficiency. Most often, this type of disease is diagnosed in children who have congenital anomalies of the structure of the body, for example, with incomplete formation of the gland ducts, hereditary pancreatitis, hypoplasia of the pancreas.
Important! It is quite rare for adult patients to experience such a disorder as an acquired disease. This is possible as a result of self-treatment of pancreatitis of various types.
The relative form manifests itself along with the disease itself. That is, it cannot exist separately. It is caused by poor passage into the lumen of the intestinal tract (the pancreatic substance does not enter its thin walls), which can be caused by its accelerated entry into the organ. With this disorder, the pancreas functions as usual, but due to obstruction it does not deliver enzyme substances to its target. Obstacles to the movement of pancreatic juice can be stones, tumors, or scars.
We also recommend viewing: What functions does the meridian perform in the pancreas and spleen?
It is worth noting that the relative form of deficiency has its own characteristic developmental features. The mechanism of damage goes something like this:
- The intestinal mucosa can be damaged for any reason, which affects the synthesis of cholecystokin or secretin.
- Against this background, the enzymes that enter the gland organ cannot do their job, which is due to a sharp drop in pH, which activates them. In patients, the index of the intraduodenal element varies within 5.5.
- Products entering the digestive tract are not broken down and become one large lump, which provokes the formation and entry of various infections into the body, since the intestinal microflora is disturbed. Also, the development of harmful bacteria occurs in the organ itself due to favorable environmental conditions for them.
Important! Bile juice enters in smaller quantities, as its movement through the system is blocked.
This form of classification is observed in patients who are constantly hungry or on a strict diet. Insufficiency of protein elements affects the development of the disease, which is called “exocrine insufficiency,” as well as pancreatitis, which becomes chronic.
Exocrine type of enzyme deficiency
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency used to be a disease primarily of people over the age of 50, but every year it gets younger. This occurs due to the fact that the number of cells for secretion production is significantly reduced. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency syndrome occurs due to:
- reducing the level of endocrine-type parenchyma mass;
- outflow of secretions into the lumen of the duodenum;
- There is a lack of enzymes in the secretion, and they slowly process nutrients.
The clinical picture is as follows:
- The body rejects fatty and salty foods - it is difficult to digest, the process is extremely difficult and painful.
- A feeling of heaviness in the stomach, which most often occurs due to the fact that a person has eaten a fatty, salty or smoked dish.
- Diarrhea, which is a consequence of the fact that food is not absorbed in the body. Most often, its consistency is similar to porridge.
- The stomach is swollen.
- I suffer from colic and painful sensations in the bones.
- Heart rate increased.
- Convulsions and shortness of breath may occur.
- Blood clots worse.
- The skin becomes dry and itchy.
- I am worried about constant nausea.
All these signs indicate that the body does not have enough fats, which are extremely important for it. That is why it is difficult and painful to bear their lack.
Treatment is based on the following principles:
- you need to eat often and in small portions;
- the diet is based on excluding fatty foods from the diet, including fatty meat and products made from it;
- you need to eat no later than 7 pm and completely avoid snacking at night;
- completely prohibited;
- All permitted food products must be agreed upon with the attending physician, who will monitor this process until complete recovery.
Important! Animal food must be compensated for by plant food, which should make up at least 75% of the total diet. . Due to the fact that the body does not produce the required amount of enzymes and does not receive enough fat, carbohydrates will be rapidly eliminated from it
They need to be taken from healthy foods. Sweets, although rich in carbohydrates, are absolutely not suitable for this. When the amount of plant foods in the diet increases, the body reacts to this with increased gas formation, which decreases if you eat bran. Enzyme deficiency is compensated for by taking Creon, Pancreatin, Mezim. The first sign that the therapy is going correctly is the normalization of stool and the disappearance of other negative symptoms.
Due to the fact that the body does not produce the required amount of enzymes and does not receive enough fat, carbohydrates will be rapidly eliminated from it. They need to be taken from healthy foods. Sweets, although rich in carbohydrates, are absolutely not suitable for this. When the amount of plant foods in the diet increases, the body reacts to this with increased gas formation, which decreases if you eat bran. Enzyme deficiency is compensated for by taking Creon, Pancreatin, Mezim. The first sign that the therapy is going correctly is the normalization of stool and the disappearance of other negative symptoms.
How does exocrine pancreatic insufficiency manifest: symptoms
Pathology may be accompanied by a decrease in the production of all enzymes, or a decrease in the production of only one of them.
The mosaic nature of the clinical picture is determined by the fact that the symptoms of exocrine insufficiency are superimposed on the signs of the associated disease.
Let us highlight the main factors of anxiety.
- Abdominal pain in the upper abdomen (occurs at an early stage of inflammation of the pancreas).
- Symptoms of maldigestion: flatulence, mushy stools, intolerance to smoked foods, fried foods, fatty foods, which can be explained by bicarbonate deficiency, insufficient production, inadequate activation and early destruction of enzymes. Possible: nausea, loss of appetite, repeated vomiting.
- Symptoms of malnutrition: signs of lack of vitamins, folic acid, iron, asthenic syndrome, as a result - loss of body weight.
Other symptoms identified by gastroenterologists: bloating, steatorrhea, impaired stool frequency.
Malfunction of the pancreas
Like any other pathology, pancreatic insufficiency has its own causes.
This organ of the digestive system is the largest gland in the body, which can function “for wear and tear” for a long time, and at the same time not show any signs of overload.
The pancreas is endowed with endocrine and exocrine functions.
With their help, the organ can regulate metabolic processes in the body and produce digestive enzymes that help break down complex food components in the intestines.
If the pancreas for some reason stops secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes, then pancreatic insufficiency occurs.
Insufficiency of exocrine pancreatic function: causes, classification, mechanisms
The pathology can be either congenital or acquired (the latter option is diagnosed more often); primary - occurs against the background of inhibition of enzyme synthesis and damage to organ tissue, secondary - is accompanied by problems with the absorption of enzymes in the intestine.
Chronic pancreatitis leads the list of root cause diseases .
Read and watch the video. A gastroenterologist explains what chronic pancreatitis is.
In addition, enzymatic dysfunctions occur when:
- atherosclerosis;
- cystic fibrosis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- obesity of the last degrees;
- pancreatic head cancer;
- chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis;
- endocrine diseases;
- other diseases of the biliary tract and gastroduodenal zone.
Among other reasons, we note:
- operations on the gastrointestinal tract;
- prolonged fasting;
- poor chewing of food;
- insufficient protein content in the diet.
This problem is more often diagnosed in older patients (60-69 years old).
Intestinal form of cystic fibrosis.
A genetic defect in this hereditary disease disrupts the reabsorption of sodium chloride by all exocrine glands, as a result of which their secretion becomes viscous, thick, and its outflow is difficult. The secretion stagnates in the excretory ducts of the glands, they expand, and cysts form. Glandular cells die. The most common forms of cystic fibrosis are intestinal and pulmonary, in which the glands of the intestine or bronchi are predominantly affected, respectively. Combined forms may occur. Damage to the intestinal glands in cystic fibrosis leads to significantly impaired processes of digestion and absorption of food components (maldigestion and malabsorption syndromes). Fat digestion suffers to a greater extent, which is associated with inhibition of the enzymatic activity of the pancreas, which also suffers in cystic fibrosis.
In newborns, the intestinal form of cystic fibrosis can manifest as meconium ileus - intestinal obstruction as a result of blockage of the intestinal lumen by thick and viscous meconium. Normally, newborns should pass meconium on the first day of life. If this does not happen, suspicion should arise regarding cystic fibrosis, especially if the parents or close relatives of the child have signs of this disease. Complications of meconium ileus are perforation (formation of a hole) in the intestinal wall and the development of a serious condition - meconium peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum).
Types of pancreatic insufficiency and their signs
Pancreatic diseases are classified into 4 main types:
- Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, caused by a decrease in the activity of special secretory substances that break down food into substances that are freely absorbed by the body, or a violation of the secretory outflow of pancreatic juice into the intestine due to narrowing of the flow channels due to tumors or fibrosis. When enzyme activity is disrupted, the secretion becomes thick and viscous and does not break down food well. When the flow channels are narrowed, an insufficient amount of fermenting substances enters the intestines, which do not fully cope with their task. Its main symptoms: intolerance to spicy and fatty foods, heaviness in the stomach, diarrhea, bloating and colic; minor: shortness of breath, tachycardia, pain throughout the body, convulsions. Fats entering the intestines are not processed and are excreted in undissolved form along with feces (pancreatic steatorrhea). Fatty acid deficiency leads to brittle bones, decreased blood clotting, seizures, impaired night vision, and impotence. A decrease in protein fermentation causes shortness of breath, tachycardia, anemia, general weakness, and fatigue.
- Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is a consequence of a decrease in the production of pancreatic (pancreatic) juice, which is responsible for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. It manifests itself as indigestion, nausea and heaviness in the stomach, excess gases in the intestines and disruption of its activity; is the cause of diabetes mellitus. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency can be relative or absolute. The first is reversible, the integrity of the organ in this case is not impaired, the malaise is caused by the immaturity of the pancreas or a violation of secretion, and is more common in children. Absolute deficiency is accompanied by atrophy of the acini and fibrosis of pancreatic tissue, and a decrease in the production of enzymes. It is a consequence of diseases such as chronic or acute pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, Shwachman-Diamond syndrome.
- The lack of enzymes in the gastric juice involved in the digestive process is pancreatic enzymatic insufficiency. Symptoms indicating insufficiency of enzymes for digesting food: flatulence, nausea and vomiting, foul-smelling diarrhea, dehydration, general weakness, etc. The most significant and characteristic sign of enzyme insufficiency is changes in stool: increased frequency of bowel movements, stool with excess fat, which is bad flushed from the toilet, acquiring a gray color and a putrid stench.
- With endocrine insufficiency of the pancreas, the production of the hormones insulin, glucagon, and lipocaine decreases. This form of failure is dangerous because it causes a malfunction of all human organs and has irreversible consequences. The symptoms are similar to those characteristic of a deficiency of pancreatic enzymes. Insulin is responsible for the supply of glucose from the blood to the body's cells and lowers the sugar level, while glucagon increases it. The normal level of glucose in the blood is 3.5-5.5 mmol/l. Changes in the norm lead to the development of diseases - hyperglycemia (increased glucose levels) and hypoglycemia (respectively decreased). Impaired insulin production leads to increased blood glucose levels and the development of a disease such as diabetes. The main signs indicating a lack of insulin hormones: increased blood sugar after meals, thirst, frequent urination; in women - itching in the genitals. With a decrease in glucogan production, the following set of symptoms is characteristic: weakness, dizziness, tremors of the limbs, changes in the psyche (anxiety, depression, causeless restlessness), convulsions, loss of consciousness. If, for insulin deficiency, treatment is prescribed by an endocrinologist, then for glucogen deficiency, the help of a psychotherapist is also necessary.
Diagnosis of pathological changes in the pancreas
First of all, the attending physician conducts a survey of the patient and finds out the symptoms that distinguish pancreatic enzyme deficiency. To diagnose the disease, laboratory blood tests are performed (for the content of hemoglobin and biochemical substances, for sugar levels), studies of the presence of enzymes in the urine, stool analysis and coprogram for fat content (normally no more than 7%), elastase-1 and the state of absorption and processing food by the body.
To identify degenerative changes in organs, abdominal ultrasound, CT and MRI are prescribed. An important diagnostic method is endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (examination of the pancreatic ducts and bile ducts for their patency and the presence of keloid formations). To clarify the diagnosis, a method of direct study of secretions obtained from the pancreas by aspiration of the pancreas is used, which allows one to determine the content and volume of pancreatic juice.
Important information: What is the echogenicity of the pancreas and why is it increased?
Endocrine insufficiency is tested by glucose tolerance testing—blood collected on an empty stomach and blood collected 2 hours after a meal or 75 g of glucose. This test shows the body's ability to produce insulin and process glucose.
The following indicators indicate a disturbance in glucose metabolism: blood glucose level of at least 6.7 mmol/l; 2 hours after taking 75 g of glucose - 7.8-11.1 mmol/l. Normally, the blood glucose level should not exceed 6.4 mmol/l. If the blood glucose level taken on an empty stomach is 7.8 mmol/L or more than this value, then diabetes occurs.
Symptoms of pancreatic enzyme deficiency
Violation of this usually manifests itself with characteristic signs that are largely similar in children and adults. The following symptoms indicate a lack of pancreatic enzymes in early childhood:
- frequent, loose stools (up to 6 times), greenish in color with whitish flakes;
- bloated stomach;
- regurgitation;
- sleep disturbance;
- the child is capricious and eats sluggishly;
- weight below normal.
If pancreatic insufficiency is suspected, the child requires clinical observation and a full range of studies to determine the extent of its damage.
Lack of digestive enzymes in the older group of the population can manifest itself in the form of dyspeptic disorders with the following clinical symptoms:
- the nature of the stool changes (lipase deficiency): it becomes frequent, profuse, grayish in color, oily, difficult to wash off; there is a fetid putrid odor, undigested food remains in the stool;
- exhausting severe flatulence with transfusions in the abdomen and “explosive” release of gases;
- nausea, loss of appetite;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- weight loss and general malaise (no feeling of vigor, fatigue, weakness, insomnia, headaches).
A functional disorder of the digestive system, the cause of which is associated with a lack of pancreatic enzymes, requires treatment.
Treatment of pancreatic enzyme deficiency
If there are indications such as diarrhea, steatorrhea (fatty stool), progressive weight loss against the background of other signs of dyspepsia, enzyme replacement therapy is carried out to correct pancreatic insufficiency. The duration of administration and dose of medications are selected taking into account age, body weight, and the form of digestion and absorption pathology.
Pharmacology has in its arsenal several groups of enzymatic preparations that differ in their components. Each has its own strict indications for use, violation of which will not lead to recovery and may cause unwanted side reactions. Here are some examples:
- Group I – active ingredient pepsin (Abomin, Pepsidil, etc.). Prescribed to restore the activity of the gastric mucosa, for example, with hypoacid gastritis.
- Group II - pancreatic enzymes lipase, amylase, trypsin (Pancreatin, Mezim forte, Creon, Pangrol, Pancitrate, etc.). These light enzyme preparations are often prescribed prophylactically. They mix well with the food bolus and are physiological. Large indivisible Pancreatin tablets are practically unsuitable for children. In children's practice, highly active Creon is successfully used in small capsules, which, if necessary, can be opened and the contents dispensed.
- Group III - complex preparations containing pancreatin, hemicellulose, bile components (Digestal, Festal, Cotazim forte, Enzistal, etc.). Additional intake of these enzymes is justified in order to compensate for disorders of cavity digestion. For liver diseases and nonspecific ulcerative colitis, caution is required.
- Group IV - combined agents (Combitsin, Panzinorm forte, Pankreoflat).
- Group V – active ingredient lactose (Lactrase, Tylactase). Used for better absorption of dairy products.
The selection of treatment forms for pancreatic enzyme insufficiency is strictly individual; medications are not interchangeable. Only a doctor of appropriate qualifications can make a competent prescription and determine the correct method of administration.
Drugs for enzyme deficiency
Enzyme preparations, depending on their composition, can be divided into several groups:
- Pancreatin preparations, mainly obtained from the pancreas of pigs (contain amylase, lipase and trypsin).
- Combined preparations containing bile components in addition to pancreatin.
Plant enzymes containing papain, fungal amylase, protease, lipase, including in combination with simethicone, adsorbents and other substances.
MEZIM® FORTE 10,000 is recommended for persons with diseases of the digestive system accompanied by digestive disorders due to a deficiency of digestive enzymes
Drugs from different groups, despite their similar composition and pharmacological activity, are not interchangeable and have different indications for use. Pancreatin preparations are a universal means of normalizing digestion and are used as part of complex therapy of any etiology.
They contain protease, amylase, lipase in various doses. It should be noted that, as a rule, pancreatin for the production of enzyme preparations is obtained from animal pancreas tissue. However, animal origin does not always guarantee safety for humans.
In particular, protein components of cattle tissues can provoke the development of spongiform encephalopathy and other prion infections. In this regard, the most physiological and safe is pancreatin, obtained from the tissues of the pancreas of pigs, so its use does not carry the risk of developing the diseases mentioned above.
Pancreatin preparations are produced in the form of various dosage forms - tablets, dragees, capsules with microgranules and mini-tablets. The choice of dosage form is also important for the effective elimination of digestive insufficiency and must be justified in each case.
The most common are tableted enzyme preparations coated with an acid-resistant coating. This type of dosage form protects enzymes from destruction under the influence of the acidic environment of the stomach and ensures their action in the intestines.
To better mix enzymes with the food bolus and prevent inactivation of substances under the influence of gastric juice, pancreatin preparations are used in the form of gastrosoluble capsules containing mini-tablets coated with an enteric coating.
When it enters the stomach, the capsule shell is destroyed and its contents quickly and evenly mix with partially digested food, after which it gradually enters the duodenum. And only there the mini-tablets dissolve, as a result of which the enzymes begin to act. These types of enzyme preparations show maximum effectiveness in correcting various types of enzyme deficiency.
One of these drugs is MEZIM® FORTE 10,000, containing a large number of active components (7500 units of amylase, 10,000 of lipase and 375 of protease). MEZIM® FORTE 10,000 is recommended for people with diseases of the digestive system, accompanied by digestive disorders due to a deficiency of digestive enzymes - cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, chronic hepatitis, irritable bowel syndrome and chronic pancreatitis.
Another drug of choice for correcting enzyme deficiency is PANGROL®, which is presented in several doses, which allows you to select the optimal dosage regimen taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease. PANGROL® 25,000 is characterized by lipase activity of 25,000 IU, amylase - 22,500 IU, protease - 1250 IU. In PANGROL® 20,000, the activity of lipase is 20,000 IU, amylase - 12,000 IU, protease - 900 IU. PANGROL® 10,000 is characterized by a reduced content of enzymes (lipase activity - 10,000 IU, amylase - 9000 IU, protease - 500 IU).
Like MEZIM® FORTE 10,000, this drug does not contain bile, which is important when treating patients with viral liver damage. Indications for the use of PANGROL® are insufficiency of exocrine pancreatic function in adults and children, which is caused by various diseases, including: chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, pancreatectomy, gastroectomy, etc. The drug should be taken without chewing and with a non-alkaline liquid (water, fruit juices ).
Indications for use of PANGROL® are insufficiency of the exocrine function of the pancreas in adults and children, which is caused by various diseases