Psychotherapist
Krashkina
Irina Ivanovna
30 years of experience
Psychotherapist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, member of the Russian Professional Psychotherapeutic League
Make an appointment
Therapists are most often approached with complaints that are characteristic of disorders of the digestive system. Everyone should know what the symptoms of dyspepsia are in an adult. Diagnosis requires a serious differential approach, since this group includes all nonspecific signs of symptom complexes of the gastrointestinal tract. Treatment of dyspepsia directly depends on the causes of the disease, and in most cases this is a deficiency of digestive enzymes or poor nutrition.
Symptoms and signs of dyspepsia
Dyspepsia syndrome is a digestive disorder and symptoms that are characteristic of various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and their borderline phases.
When digestion is disturbed, symptoms appear that are united by a common name - gastric dyspepsia, this includes:
- problems with swallowing;
- nausea and vomiting attacks;
- belching;
- pain in the stomach;
- heartburn;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- bloating;
- constipation, diarrhea.
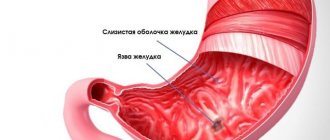
Dyspepsia of the stomach and intestines causes pain in the epigastric region. They can be either quite intense or in the form of mild discomfort. There is a feeling of rapid satiety and fullness, and as a result, nausea, belching, and heartburn. Another alarming sign is loss of appetite, quickly and sharply. After this, the person begins to lose weight for no reason. Intestinal dyspepsia is accompanied by rumbling in the stomach, flatulence, diarrhea or constipation.
Disruption of the process of digesting food in the intestines may indicate pathologies such as dysbiosis, diverticulitis, enzymopathy, enteritis, colitis, tumors in the intestines, irritable bowel syndrome, pancreatic diseases, and metabolic pathologies. Also, intestinal dyspepsia may indicate that an infection is developing in it (dysentery, cholera, intestinal tuberculosis, salmonellosis, etc.).
There are 2 main groups of dyspeptic disorders - functional dyspepsia and organic. In the first case, only disturbances in the functioning of the organ are detected, that is, functional lesions, while in the second they are exclusively organic in nature. In the latter case, the symptoms will be more pronounced, and the disorders will continue for a long time.
How to treat indigestion?
Some people may experience relief from upset stomach symptoms as a result of:
- leisurely consumption of food in small quantities containing a small amount of fat (during the day);
- abstinence from smoking;
- abstaining from drinking coffee, carbonated drinks and alcohol;
- stopping the use of drugs that can irritate the stomach lining, such as aspirin or anti-inflammatory drugs;
- sufficient rest;
- reducing emotional and physical stress, for example through relaxation therapy or yoga.
You can learn more about foods and natural remedies that relieve an upset stomach on this page - What to eat and take when you have an upset stomach.
Your doctor may recommend taking antacids or medications that reduce acid production or help your stomach empty more quickly. Many of these drugs can be purchased without a prescription. Over-the-counter medications should be used only in the dosages indicated and should not exceed the duration of use stated on the label. If you are seeing a doctor, always inform him or her about this before starting to use a new drug, because this is important.
The following antacids are generally recommended to relieve stomach upset:
- Alka-Seltzer
- Maalox
- Milanta
- Rolaids
- Riopan
Many brands on the market use various combinations of the three main salts - magnesium, calcium and aluminum with hydroxide ions or bicarbonate ions to neutralize stomach acid. However, side effects may occur when taking antacids. Magnesium salts can cause diarrhea, and aluminum salts can cause constipation. Magnesium and aluminum salts are often present in the same product to balance these effects.
Antacids with calcium carbonate, such as Tums, Titralac and Alka-2, can also provide an additional source of calcium, although they can cause constipation.
H2-receptor blockers (H2RAs) include the following drugs:
- Ranitidine (Zantac)
- Cimetidine (Tagamet)
- Famotidine (Pepcid)
- Nizatidine (Axid)
H2RAs relieve symptoms of indigestion by reducing the production of hydrochloric acid. They work longer but do not work as quickly as antacids. Side effects of H2 blockers may include headache, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, and unusual bleeding or bruising.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) include the following drugs:
- Omeprazole (Omez, Prilosec, Zegeride)
- Lansoprazole (Prevacid)
- Pantoprazole (Protonix)
- Rabeprazole (Aciphex)
- Esomeprazole (Nexium)
PPIs are more powerful drugs than H2 blockers, although they also relieve symptoms of indigestion by reducing stomach acid production. Proton pump inhibitors are most effective in treating symptoms of indigestion in people who also have GERD. Side effects of PPI use may include back pain, aching, cough, headache, dizziness, abdominal pain, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, constipation and diarrhea.
Prokinetic drugs such as Metoclopramide (Reglan) may be helpful for people who have difficulty emptying their stomach. Metoclopramide also improves muscle activity in the gastrointestinal tract. Common side effects of prokinetic drugs include fatigue, drowsiness, depression, anxiety, and involuntary muscle spasms.
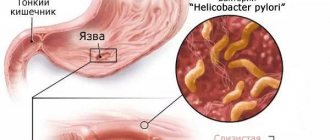
If test results show that there is bacteria in the stomach that causes peptic ulcers, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to suppress the infection.
Causes
There are several forms depending on the reasons that cause the development of the syndrome:
- simple dyspepsia. It is also called nutritional. Caused by nutritional problems. In turn, there is fatty (soapy), fermentative and putrefactive dyspepsia. In the latter case, it develops if the food is dominated by protein products or stale meat is used. Fermentation develops from excessive consumption of carbohydrates (bread, cabbage, legumes, sugar) and drinks that cause fermentation (beer and kvass). Fatty dyspepsia develops with excessive consumption of fatty foods, especially pork and lamb;
- dyspepsia associated with a deficiency of secreted enzymes for digesting food in the intestines and stomach. In turn, it can be gastrogenic (lack of enzymes in the stomach), pancreatogenic (deficiency of pancreatic substances), enterogenic (lack of intestinal juices), hepatogenic (insufficient secretion of bile from the liver);
- dyspepsia, which is associated with problems with the absorption of food in the intestines with malabsorption syndrome. As a result, nutritional components do not flow from the intestines into the blood;
- dyspepsia, which is associated with intestinal infections. In this case, it could be either dysentery or salmonellosis.
- intoxication. It manifests itself due to poisoning in various diseases, including influenza, acute surgical pathologies, and also when consuming poisons.
All of these factors can contribute to the onset of the disease. Symptoms and treatment of dyspepsia of the stomach and intestines directly depend on the causes.
Risk factors
These include:
- frequent and severe stress, emotional tension. In this case, the pathology will have a neurotic origin;
- some medication use. This applies to antibiotics, hormonal or antitumor and other agents;
- poor nutrition. Most often this concerns overeating;
- intoxication. In this case, there may be either a disease of viral or bacterial origin, or household poisoning;
- excessive release of hydrochloric acid;
- problems with gastrointestinal motility.
These are the main factors that contribute to the occurrence of dyspepsia.
Complications
Gastric dyspepsia occurs in diseases such as esophagitis, GERD, cancer, stenosis or ulcer of the esophagus, cancer or the presence of benign tumors, periesophagitis, scleroderma, diverticulum. Also, the presence of dyspepsia of the stomach and intestines may indicate diseases of the muscles, central and peripheral nervous systems, pathologies of internal organs, for example, narrowing of the esophagus can be caused by cysts and tumors that oppress it from the outside. This also applies to aortic aneurysm, vascular anomalies, and thyroid hyperplasia.
Complications of dyspepsia are most often associated with the underlying illness that causes the appearance of this syndrome. The patient may suddenly lose weight and lose appetite for a long time. One of the severe consequences is Mallory-Weiss syndrome. In this case, the mucous layers of the lower part of the esophagus, where it passes into the stomach, rupture. Because of this, gastric bleeding begins. It can be quite intense and even lead to death. Most often, the occurrence of Mallory-Weiss syndrome is associated with repeated bouts of vomiting.
When to see a doctor
For treatment of stomach or intestinal dyspepsia, you should contact a gastroenterologist. Don't delay going to the doctor. Particular attention should be paid to such symptoms as abdominal pain at night, sudden weight loss for no reason, nausea, vomiting, frequent belching, and heartburn attacks. Diagnostics can be carried out at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg), which is located in the center of Moscow.
Treatment: what to do about the disease?
A prolapsed organ should be treated comprehensively. Prescribed:
- diet;
- physical therapy complex;
- traditional methods of therapy.
Synthetic medications are prescribed by a gastroenterologist, based on the diagnostic results and the general condition of the patient. The doctor prescribes the drug, dosage and regimen. The method of getting rid of pathology is based on the reasons for its occurrence. It is not the symptom of the disease that should be eliminated, but the factors that provoke it. Comprehensive therapy with proper nutrition and exercise is used. Treatment with recipes “from your grandmother” will help reduce symptoms and speed up the recovery process, but they cannot overcome the decrease in muscle tone on their own.
Principles of nutrition
With this pathology, it is recommended to exclude white bread from the diet.
There is no special diet for this pathology. It is important to eat food in small portions, but at least 5 times a day, avoiding overeating. The maximum interval between meals is 4 hours. It is necessary to exclude spicy dishes, white bread, semolina porridge, fatty and fried foods. You should avoid cocoa, baked goods and rice. The menu is enriched with fruits and vegetables to give the body the necessary amount of vitamins and easily digestible minerals. The first hour after eating, physical activity is contraindicated. It is recommended to eat bran bread, cereal porridge and lactic acid dishes.
Physiotherapy
Bed rest and lack of exercise can only make the situation worse. All loads should be moderate, correctly distributed and agreed upon with the doctor. Exercises are performed in a supine position, with limbs extended. Take deep exhalations and inhalations, while the air must be pushed out by the abdominal muscles - 10 repetitions. It is recommended to alternately raise the outstretched legs 5 times each. You can imitate riding a bicycle and do arm raises. Useful exercise: take a deep breath, exhale, press the right leg to the chest, exhale - lower it. This is done 5 approaches for each leg. All movements should be smooth, avoiding jerking and pain.
Traditional methods of therapy
With the help of tinctures of wormwood, chicory, yarrow, calamus or centaury, appetite is regulated. To do this, pour 25 g of dry herbs into a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour. You need to drink 25 ml of the tincture every 30 minutes. before meals. Secretory function is normalized with plantain decoction. 75 g of medicinal plant are poured into 0.5 liters of water and boiled over low heat. Drink 100 ml half an hour before eating. You can make clay compresses. Mix the clay with water and apply the cake to the stomach for 3 hours.
Diagnosis of dyspepsia
Before starting treatment for dyspepsia, it is necessary to undergo an examination, which includes not only a description of complaints, an external examination, but also the following:
- laboratory tests - general and biochemical blood tests, examination of stool for the presence of blood, coprogram;
- instrumental studies - a test for gastric acid secretion, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, examination of gastric materials for the presence of Helicobacter pylori, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, colonoscopy, radiography, computed tomography, esophageal and antroduodenal manometry.
You can undergo diagnostics at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg), which is located in the central district of Moscow, near the Tverskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Belorusskaya, Chekhovskaya metro stations. If you have a disease, you may need to consult not only a gastroenterologist, but also other specialists: a psychiatrist, neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment depends on the severity of the pathology and the type of injury. If a person exhibits symptoms that he has torn his stomach, then consultation with a surgeon is necessary. If the muscle damage is minor, then treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis (at home).
If a hernia occurs, it is strangulated, or muscle tissue ruptures, surgical treatment is indicated.
Conservative treatment of abdominal tear:
- Using a bandage to fix muscles and reduce pain, it is also a preventive measure for prolapse of internal organs. The bandage must be worn while lying on a flat surface,
- Use of painkillers for severe pain
- Anti-inflammatory therapy,
- Compliance with the protective regime : refrain from lifting heavy objects, do not make sudden movements or bends, smooth, gradual rise from a horizontal position,
- The food is correct and complete.
Surgery:
- Restoring the integrity of muscle tissue,
- Plastic surgery for hernial protrusion.
In the postoperative period, it is necessary to wear a bandage, avoid increased intra-abdominal pressure (strong laughter, carrying heavy objects, constipation), and follow the recommendations given by the attending surgeon.
Spool (navel) in the abdomen
If the spool is displaced, it must be replaced. However, this is not so easy to do. This procedure must be performed by a trained person.
You cannot put the spool in place on your own, as this can lead to displacement and prolapse of the abdominal and pelvic organs.
You can put the spool in place using a massage or a jar:
- Treatment with massage. At the same time, the skin of the abdomen and the massage therapist’s hands are soaped. Circular movements are performed throughout the abdomen. At first the circles are large (under the ribs and above the pubis), but gradually the circle becomes smaller and forms around the navel. This method is painless,
- Treatment with a cup. The abdomen is lubricated with vegetable oil and with massage movements they try to put the navel in place. After that, a circle of potatoes is placed on the navel, wrapped in a cloth, the ends of which stick out (they must be moistened with alcohol). The ends are set on fire and a jar is placed on the navel. Keep the jar for 10 minutes, after which it is carefully removed. Check that the spool is in the correct place.
Belly edit
Editing is carried out with the patient lying on his back in a relaxed state.
Reduction of hernias and tears should only be performed with the appropriate knowledge and skills.
The masseur lubricates his hands with cream to improve gliding. Reduction is carried out using gentle massage movements. You cannot press or pull down too hard, as this can lead to strangulation of the hernia, as well as prolapse of organs.
An air hernia (air in the hernial sac) is reduced using a spiral motion.
Traditional methods
What to do if your stomach is torn or torn? You can use folk recipes. But this can only be done with slight damage to the muscle fibers.
Traditional methods of treatment:
- Warming up with clay. It is necessary to make a cake from red clay, which is heated, wrapped in cloth and applied to the sore spot until it cools and dries,
- In the first days, cooled cabbage leaves are applied to the affected area,
- Wrap the salt in a cloth. Moisten the resulting bag and apply it to the sore spot.
Treatment
To treat dyspepsia, drug therapy is necessary. Separately, you need to get rid of diarrhea or constipation, and for this purpose special means are prescribed. Other drugs are also prescribed to treat dyspepsia and alleviate the patient’s condition:
- painkillers (antispasmodics);
- drugs that reduce the level of acidity in the stomach;
- enzyme agents to improve digestion processes.
Treatment must be comprehensive and systemic. It is necessary to treat the disease that caused dyspepsia, that is, gastritis, duodenitis, GERD, cholecystitis, gastric or intestinal ulcers, pancreatic diseases.
It should be remembered
- The term "indigestion" is used to describe one or more symptoms, which include a feeling of fullness in the stomach while eating, discomfort associated with a feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating, and a burning or pain in the upper abdomen.
- Indigestion can be caused by a disease in the digestive tract, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, cancer, or abnormalities of the pancreas or bile ducts.
- Sometimes a person may have symptoms of an upset stomach, the cause of which may not be identified. This type of stomach upset is called functional dyspepsia.
- Indigestion and heartburn are different conditions, but a person can suffer from both at the same time.
- To diagnose an upset stomach, your doctor may order x-rays of your stomach and small intestine; for blood and stool tests; for endoscopy with biopsy in order to correctly diagnose and identify the cause necessary for successful treatment.
- Some people may find relief by making some lifestyle changes to reduce their stress levels (see How to Relieve Stress - Top 10 Tips).
- To treat stomach upset, your doctor may prescribe antacids, histamine H2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs), proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), prokinetics, or antibiotics.
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of dyspepsia
Main misconceptions:
- nausea, heaviness and bloating will go away on their own. They are temporary, so you don't have to go to the hospital;
- antispasmodics or enzyme agents remove heaviness in the stomach and discomfort in the intestines;
- If you eat something sour or spicy, the discomfort will disappear.
All of the above opinions are completely wrong. You should not rely on myths that were previously believed. If alarming symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist.