What is erosive bulbite?
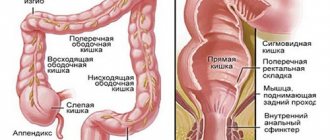
Inflammation of the part of the duodenum adjacent to the stomach causes dysfunction of the “bulb” through which acid from the stomach flows daily to be neutralized. The pathological process negatively affects the functioning of the excretory ducts of the gallbladder and pancreas, as well as metabolic processes and the synthesis of important digestive enzymes.
Erosive bulbitis is quite common and is diagnosed in 2 - 3% of the population through gastroscopy, due to complaints of abdominal pain. The disease does not select according to gender type and can be identified in patients of different age groups, but the peak of activity is recorded after the age of 40 years.
It is worth noting that the disease is relevant in surgery and gastroenterology. Of all the possible negative factors that provoke gastrointestinal bleeding, up to 4% of the causes are provoked by erosive bulbitis.
Symptoms
At the initial stage, symptoms may be absent or occur in a latent form, which quite often leads to delayed diagnosis.
In general, the symptomatic complex is characterized as follows:
- deterioration or complete loss of appetite;
- pain in the epigastric region, which can intensify when the stomach is empty (so-called hunger pain);
- lower abdominal pain;
- discomfort during the act of defecation;
- nausea and vomiting - vomit may contain blood, which will indicate erosive or ulcerative gastrobulbitis;
- in the chronic form, instead of diarrhea there will be prolonged constipation;
- pale skin, increased sweating at night;
- increasing weakness and general malaise;
- dizziness;
- heartburn, belching with an unpleasant odor;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- increased salivation;
- bloating and increased flatulence.
In addition, general clinical signs may be present - drowsiness, apathetic mood, irritability.
Causes of the disease
Acute erosive bulbitis is predominantly a consequence of the negative effect of pathogenic microflora, suppressed immunity, and also tends to be idiopathic in nature.
Studies often determine the presence of Helicobacter pylori in apparently healthy people, therefore, there are maximum acceptable standards.
The likelihood of developing secondary acute erosive bulbitis increases if:
- The patient undergoes long-term treatment with the following drugs:
- indomethacin;
- corticosteroids;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- aspirin.
- After suffering burns and injuries.
- As a consequence of surgical interventions.
- Due to abuse of alcohol and other toxic substances.
- If there is a history of pathologies of the kidneys, liver, heart and blood vessels.
In addition to the above factors, you should pay attention to:
- nutritional culture, adherence to the regime and balanced diet;
- eliminating prolonged periods of stress, normalizing the psycho-emotional state;
- genetic predisposition;
- timely relief of infectious processes in the digestive system;
- the state of the body's barrier functions, their strengthening, recovery after illnesses.
Abuse of sweet, salty, fatty foods can cause the development of superficial erosive bulbitis, against the background of the following pathologies:
- gastritis (antral erosive bulbitis);
- Crohn's disease;
- giardiasis;
- diseases of the duodenum with the formation of defects on the surface.
Signs of pathology cannot be ignored. At the first symptoms, it is necessary to find out the cause of erosive bulbitis and eliminate it without giving it the opportunity to worsen.
Causes
The factors contributing to the development of bulbitis are diverse. However, they have a nature similar to gastritis. Quite often, the reasons that provoke bulbitis are associated with the inappropriate lifestyle that a person leads.
The main causes of bulbitis include:
- microbe Helicobacter pylori - damage to the mucous membrane occurs against the background of existing gastritis, which was provoked by the appearance of this particular bacterium.
- Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, characterized by the absence of normal activity of the stomach and its constant dysfunction.
- infection by helminths - helminthic infestations can easily provoke an inflammatory process in any part, from the esophagus to where the rectum is located.
- excessive alcohol consumption - ethyl alcohol and other additives contained in alcohol not only have a toxic effect, but also contribute to a negative effect on mucosal tissue.
- serious poisoning - disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and leads to the development of an inflammatory process due to the rapid proliferation of bacteria or the penetration of toxic substances.
- taking certain medications can cause disruption of the stomach and lead to an inflammatory process.
- foreign body in the gastrointestinal tract - a foreign object that gets inside the stomach can injure the walls of the mucous membrane, which will undoubtedly cause an inflammatory process.
Important: Not only an unhealthy lifestyle and infection can disrupt the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. In rare cases, bulbitis may be genetic in nature. You can find out if this is true by contacting your doctor for a detailed diagnosis.
Forms of the disease
Since the causes of the formation of erosive bulbitis are different, the course of the disease is not clear and has some differences in the clinical picture.
For ease of diagnosis, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- erosive focal;
- catarrhal-erosive;
- erosive-ulcerative;
- drain gurgling.
To prescribe adequate treatment for erosive bulbitis of the duodenum 12, it is important to determine exactly what form you are dealing with. Having correctly diagnosed the disease, the doctor can develop the most effective therapeutic regimen.
Erosive focal bulbitis
This type of bulbite tends to form pockets of limited location. During the development of the disease, the bulbous fragment is affected, without involving nearby areas of the digestive tract in the process. It is worth noting that the disease is not selective. Focal bulbitis is diagnosed in people of different genders, ages and social backgrounds. This form can be differentiated from gastrobulbitis or bulbopathy by the following characteristics:
- pain under the “spoon” - in the form of spasms or constant;
- bitterness in the mouth, heartburn, belching;
- attacks of nausea, urge to vomit;
- bad breath;
- diarrhea;
- white residue on the tongue.
Having discovered one of the listed signs, it is unacceptable to independently diagnose and prescribe treatment. For the patient, this is a signal to visit a doctor.
Catarrhal-erosive bulbitis
In the international classification of diseases, such a diagnosis does not exist, but practitioners often use the term when filling out prescriptions and cards. The form develops due to a long-lasting inflammatory process in the bulb. Symptoms appear at intervals, with large intervals, and are characterized by the following symptoms:
- “hungry” stomach pain, aching pain in the navel area;
- urge to vomit, nausea, cramps;
- halitosis, bitterness, heartburn;
- constipation;
- loss of strength, dizziness;
- swelling, local rupture of capillaries.
Carrying out diagnostic laboratory tests often reveals large accumulations of bacteria with aggressive effects (Helicobacter pylori).
Erosive-ulcerative bulbitis
When the inflammatory process affects not only the superficial layers of the mucous membranes of the duodenum, but penetrates into the deep tissues, then we are talking about a diagnosis - ulcerative bulbitis. In this case, not only the epithelium is affected, but also the muscular plate. The disease is difficult to diagnose in the early stages, since the symptoms are hidden for a long time. Annoying signs make themselves felt when ulcers with inflamed edges form on hyperemic areas.
Symptoms indicating illness:
- weakness, dizziness;
- constipation, flatulence, bloating;
- nausea, vomiting with bile;
- pain in the epigastric region after eating food.
Erosive-ulcerative bulbitis progresses due to pathological changes in the structure of the glands that produce secretions that inhibit the activity of gastric juice.
Erosive-hemorrhagic bulbitis
The form of pathology develops due to an abnormal release of acid from the stomach into the duodenum. If the patient has not undergone a long course of treatment with certain drugs and does not abuse alcohol, then there is a high probability that the disease is a consequence of giardiasis, Crohn's disease, parasitic infestation, or failure to comply with banal rules of personal hygiene. Also, the cause for the development of erosive-hemorrhagic bulbitis can be the action of toxins of any nature.
Clinical picture:
- pain of varying intensity in the pit of the stomach, under the ribs, at the location of the navel;
- distension of the stomach, feeling of heaviness;
- bad breath, belching, sour taste, coating on the tongue, nausea;
- constipation, diarrhea;
- inclusions of blood in the vomit;
- migraine, weakness;
- trembling in the body.
The intensity of symptoms may differ in different patients, since the course of the disease depends on the state of immunity and the presence of concomitant pathologies. Erosive bulbitis in a child requires emergency hospitalization, as it is fraught with dehydration and serious consequences.
Drain erosive bulbite
There is another type of classification, which involves dividing bulbitis into focal and draining. If the first indicates the presence of local foci on limited tissue fragments, then confluent is a severe form of pathology in which all individual foci are combined into a common conglomerate.
Causes and forms of the disease
Bulbitis occurs in the duodenum according to a certain algorithm. Initially, catarrhal changes occur in the mucosa, which, as they progress, lead to the development of erosions on the surface of the intestinal lining. After this, the eroded surfaces deepen, and in their place deeper lesions - ulcers - form.
Therefore, we can consider that the erosive type of pathology is an intermediate stage between superficial and ulcerative bulbitis.
Acute erosive bulbitis in most cases is associated with the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the duodenum. The greatest role in the appearance of the focal form of the disease is played by Helicobacter pylori infection - invasion of a special pathogen that leads to damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
The occurrence of manifestations of the disease, including focal erosive-hemorrhagic bulbitis, can also be provoked by chemical damage to the mucous membrane. Intestinal trauma occurs when certain toxic substances, including alcohol, enter it. The development of erosive-ulcerative bulbitis can be caused by medications that are part of the group of anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, aspirin, ibuprofen).
Chronic erosive bulbitis often occurs in the absence of proper treatment for the acute form. If a person does not undergo eradication therapy with antibacterial drugs or does not fully comply with the doctor's recommendations, bacteria in his intestines may persist even after symptoms have disappeared.
Due to the persistence of microorganisms in the digestive system, a person develops a chronic disease, which is characterized by constant alternation of periods of exacerbations and remissions. It is much more difficult to treat a pathology with a protracted course, so patients are advised to promptly contact a gastroenterologist when the first symptoms of an acute form of the disease appear.
Symptoms of erosive bulbitis
The therapeutic approach is usually determined by the symptoms, which differ somewhat depending on the form of the disease. If the disease manifests itself in an acute form, the clinical picture is clearly expressed, but it is worth knowing what symptoms of erosive bulbitis accompany the onset of the disease:
- epigastric pain (upper abdomen), after eating;
- belching, sour taste, bad breath, nausea;
- heartburn, bloating, flatulence;
- constipation followed by diarrhea – lack of stability.
If you ignore the first signs of the disease, they will be joined by symptoms indicating a pronounced bulbitis:
- intestinal bleeding;
- black feces due to inclusions of dried blood;
- vomiting like “coffee grounds”;
- increasing pain in the upper abdomen.
Bloody diarrhea and vomiting occur simultaneously and indicate that intestinal bleeding is increasing.
General symptoms from the body:
- hyperthermia;
- dizziness, loss of strength;
- oppression, depression.
The fact that the pathology occurs in a chronic form is evidenced by mild signs, without intestinal bleeding. The patient experiences minor discomfort and usually does not take active measures to eliminate the disease.
Prevention
Preventive measures will prevent the occurrence of any kind of inflammation of the duodenum and stomach. You should follow simple rules.
- timely treat diseases that provoke secondary bulbitis (cholecystitis, pancreatitis, gastritis);
- eat right (avoid too hot foods, smoked foods, canned food);
- get enough sleep;
- do not abuse alcohol or tobacco products;
- avoid stress;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- control the intake of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Aspirin);
- move more (walking, running, hiking).
Bulbit is not a fatal disease, but it causes inconvenience to a person, especially if it occurs in an acute form. A timely visit to a doctor and adequate treatment will allow you to forget about this problem forever.
Diagnostics
In order to establish a diagnosis, the doctor must listen to the patient’s complaints and review the medical history. The clinical picture suggests what is causing the discomfort.
The further algorithm of the doctor’s actions is as follows:
- FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy).
- Laboratory blood test.
- Coprogram.
- Detection of Helicobacter pylori:
- breath analysis;
- invasive techniques;
- enzyme immunoassays.
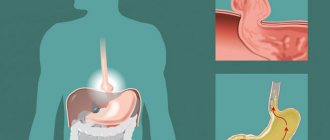
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
The most informative way to examine the digestive organs is endoscopy. The device is used to examine the mucous tissue and identify the signs and form of the disease.
Stomach examination, video
Treatment of erosive bulbitis
The approach to treating bulbitis must be comprehensive to achieve a quick, positive result. In addition to medication therapy, doctors strongly recommend adhering to a diet. Also, after consultation with the doctor, the use of alternative methods is acceptable. Therapeutic regimens are developed by a gastroenterologist after receiving the results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
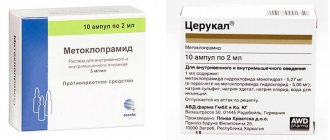
Drug treatment of bulbitis
Treatment of erosive bulbitis is predominantly antibacterial. If tests indicate aggressive life processes of Helicobacter, then treatment with several antibiotics is most effective.
The patient is also advised to use proton pump inhibitors, which tend to protect the intestinal mucosa from excessive, unnatural action of gastric juice and mechanical disorders. The duration of treatment depends on the complexity of the case and is determined by the doctor. The most effective therapy for erosive bulbitis in the stomach is carried out in a hospital setting.
For the entire period of therapeutic action, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are canceled. Prescribed medications for the treatment of bulbitis that help get rid of symptoms:
- antispasmodics;
- prokinetics;
- probiotics;
- sedatives.
If the disease develops due to invasive diseases, anthelmintics are added to the drug therapy for treating bulbitis with tablets.
Treatment of bulbitis with folk remedies
Before you begin treating bulbitis at home, you should consult with a leading specialist about the advisability of action. The approach to unconventional methods should be balanced, since by treating one disease, you can aggravate the course of the concomitant one. As an adjuvant in complex therapy, the following is used:
- Decoctions of licorice, marshmallow, St. John's wort: combine all components in equal proportions, take 2 tbsp. l. The dry mixture is poured with boiled water (400 ml). Leave for an hour, after which take 100 ml, three times a day, before meals.[ads_hr hr_style=»hr-fade»]
- Chamomile tea, brewed in the usual way.[ads_hr hr_style=»hr-fade»]
- Honey with plantain juice: fresh leaves are crushed, the juice is strained. From the total mass of liquid, take 3 tbsp. l., combine with honey (1 tbsp.). To make the medicine more liquid, add a little water. Take 50 ml of the substance before meals.[ads_hr hr_style=»hr-fade»]
- Vegetable juices.[ads_hr hr_style=”hr-fade”]
- Propolis tincture: bee product (60 g), combined with alcohol (250 ml), kept for a week without access to light. Use 7 ml, after mixing with 150 ml of boiled water.
Alternative treatment for erosive bulbitis undoubtedly gives excellent results, but since the effect of medicinal preparations is often cumulative, one should not count on a quick recovery. The best results are achieved by combining traditional and alternative methods.
Diet for erosive bulbitis
Prescribing a diet for erosive bulbitis is the primary task of a gastroenterologist. Proper nutrition, taking into account doctor’s recommendations, improves digestion and promotes rapid tissue regeneration. In combination with drug treatment, changing food habits contributes to complete recovery.
The menu for erosive bulbitis, which occurs in a chronic form, requires the exclusion of salty, spicy, and fatty foods. It is also strongly recommended to give up alcohol and smoking.
If the course is acute, food requirements become more stringent and compliance with the recommendations is mandatory:
- fractional meals (up to 7 times);
- food is not cold, not hot - warm;
- sharply limited amount of salt and sugar;
- exclusion of bread and bakery products;
- drinking up to a liter of milk per day;
- variety of diet with porridges.
It is especially important to follow a diet in the first week of an exacerbation. Further expansion of the list of acceptable products occurs gradually. Cooking methods should be gentle. Steamed or boiled food is welcome.
What foods should you exclude?
- vegetables with irritating effects (garlic, onions);
- drinks containing caffeine;
- foods that cause gas accumulation (cabbage, legumes);
- excessively fatty and fried foods.
Indicative menu for the day
| EATING | ACCEPTABLE PRODUCTS |
| Breakfast #1 | Boiled egg or steamed omelet, crackers, milk |
| Breakfast No. 2 | Carrot puree, any juice except grape juice |
| Lunch | Hercules with milk, tea with milk |
| Dinner | Boiled fish, mashed potatoes, jelly, compote |
| Afternoon snack | Crackers with milk |
| Dinner No. 1 | Lazy dumplings with moderate fat sour cream, tea with milk |
| Dinner No. 2 | Milk or kefir |
Diet
There are several important aspects in the treatment of bulbitis:
- strict adherence to the diet;
- giving up alcohol;
- to give up smoking;
- eliminating the cause of the disease;
- normalization of nutrition and adherence to the regime.
Therefore, therapy should begin with giving up inappropriate habits and maintaining a healthy diet. The diet for bulbitis must be followed with particular strictness during the period of exacerbation of the disease. This diet includes:
- slimy porridge;
- dairy products;
- chicken bouillon;
- jelly;
- oat cookies;
- crackers and refusal of fresh bread.
It is necessary to completely eliminate yeast products, hard fruits and vegetables, smoked foods and overly salty foods. You can eat meat, but only steamed or boiled. It is worth completely eliminating carbonated drinks, as they are incredibly harmful to the condition of the duodenal mucosa.
There are also a number of rules, following which you can improve the general condition of the body and get rid of symptoms related to peristalsis:
- you need to eat at least 5 times a day;
- portions should be of moderate size and not exceed 150 grams;
- food must be chewed thoroughly;
- it is important to eat slowly and in a cozy atmosphere;
- Under no circumstances should you eat on the go;
- you should not eat immediately before bedtime;
- The gaps between meals should be no more than 3-3.5 hours.
It is much easier to prevent the appearance of bulbitis than to waste nerves and energy fighting it. Preventive measures are an excellent alternative method to prevent many gastrointestinal diseases, in addition, this will improve the digestive system and reduce weight if you have extra pounds.
Prevention and prognosis
If you seek help from specialists in a timely manner, the prognosis for acute and chronic bulbitis is favorable. If the cause of the pathology is eliminated, in most cases, the chronic form proceeds with stable remissions. An adequate approach to treatment gradually leads to epithelization of erosion.
When acute erosive bulbitis transitions into a chronic form, the patient is registered and under dispensary observation. Every year, an endoscopic examination is required to monitor the course of the disease.
Prevention measures also include:
- Compliance with the diet for erosive bulbitis is a healthy, balanced diet.
- Quitting addictions (alcohol, nicotine, caffeine).
- Preventive annual examinations and timely treatment:
- ulcers;
- pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- infectious, invasive diseases.
- Strengthening the body's barrier functions.
- Compliance with diet No. 1.
- For chronic erosive bulbitis, examination by a gastroenterologist is carried out twice a year.
You cannot self-medicate. All medications, for any disease, must be prescribed by a doctor. It is important to follow the dosage and recommendations. You should be extremely careful when using ulcerogenic drugs.
Treatment
After diagnosing bulbitis, long-term and complex treatment begins. Therapy for duodenitis bulbitis involves not only resorting to medications, but also changing a person’s lifestyle in general.
So. to achieve a sustainable effect it is necessary:
- adjust your lifestyle;
- stop using tobacco and alcohol products;
- review your diet;
- eliminate possible emotional swings;
- Set aside at least an hour a day for physical activity.
Drug therapy directly depends on the diagnosis. So, depending on the type of bulbitis and the degree of its neglect, the doctor selects a list of necessary medications. Often, their action is aimed at actively healing the mucous membrane and suppressing bacteria that can interfere with this process.
The basis of drug treatment for bulbitis is antacids. They normalize the functioning of the stomach. normalize the level of hydrochloric acid and also enhance the regeneration of mucosal cells. Additionally, painkillers, enveloping and astringent drugs are prescribed.
If there is a pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the patient’s body, it is necessary to undergo a course of antibiotics. In the future, restorative therapy is prescribed. For erosive bulbitis, a starvation diet and mandatory bed rest are indicated, which will include gastric lavage and a one-time injection of magnesium sulfate.