Tenesmus is a pathological condition characterized by the appearance of the urge to have a bowel movement, but the act of defecation does not occur. Such problems can occur in various diseases. It is extremely important to identify them in a timely manner in order to eliminate the problem and avoid serious complications.
The principle of tenesmus
False urge to defecate occurs with increased innervation of the muscle tissue of the intestine surrounding the muscles. Due to excessive excitability of the autonomic nervous system, smooth muscle spasm develops. The muscles of the intestines, pelvis, and perineum are involved in this process.
Rectal tenesmus is accompanied by severe pain. They intensify with each new attack and decrease after bowel movement.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of development of tenesmus is associated with spastic contraction:
- intestinal smooth muscles (mainly the rectum and sigmoid colon);
- Bladder.
Spastic muscle contraction leads to voluntary contractions of the abdominals, muscles of the pelvic floor and perineum.
As a result of the simultaneous spastic contraction of this muscle group without concomitant relaxation of another muscle group (especially the sphincters), it becomes difficult to remove the contents of the bladder or rectum, or a jerky ejection of small portions of excrement occurs.
The release of mucus, pus or blood during tenesmus depends on the pathological process that caused the tenesmus.
Muscle hypertension underlying tenesmus depends on irritation:
- nerve plexuses of the muscle wall;
- irritation of the hypogastric nerves and pelvic plexus coming from the central nervous system.
Symptoms
The clinical picture largely depends on the cause of the urge to go to the toilet, mostly without bowel movement. At the same time, the lower abdomen hurts. The pain syndrome persists for a long time.
The following negative changes are also possible:
- feeling of a full stomach;
- excessive gas formation;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- rise in temperature;
- migraine;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- gagging;
- sudden change from constipation to diarrhea;
- general increasing malaise;
- loss of appetite;
- feces with pus and blood.
The formation of cracks and erosions in the anal area is also possible. In this case, minor rectal bleeding is noted.
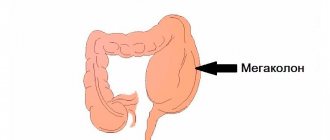
Rectal prolapse
Rectal prolapse is the turning out of all layers of the distal colon. It occurs equally often in children, men and women. In the first case, this is explained by the anatomical features of the child’s body, in the second – by hard work, in the third – by bearing and giving birth to a child. Many diseases of the rectum in women are associated specifically with childbirth.
Sometimes the causes of the disease can be injuries to the buttocks, falls, bruises of the sacrum or spinal cord.
There are three degrees of the disease:
- The intestine falls out during defecation, and then returns to its place on its own.
- The intestine falls out during bowel movements and physical exertion. It can only be returned back by repositioning it.
- Prolapse occurs during coughing, laughter and may be accompanied by fecal and urinary incontinence.
Symptoms of rectal disease in such cases may begin suddenly or appear “increasingly.” This may result in mucus or blood discharge, abdominal pain, and constipation.
Treatment of prolax (intestinal prolapse) is most effective if performed surgically. Drug therapy is used as an additional method.
Causes of pathology
The urge to defecate without feces occurs with increased excitability of the nervous system.
There are many reasons for such problems:
- infectious diseases;
- proctological pathologies;
- inflammatory process in the intestinal area;
- frequent digestive poisoning;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- exposure to stress;
- excessive psycho-emotional stress;
- the presence of neoplasms in the pelvic area;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Pathology in various diseases
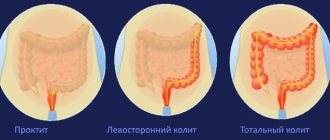
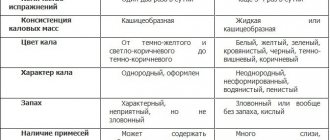
This unpleasant symptom often signals the development of serious diseases. Similar problems are observed with hemorrhoids, dysbiosis, irritable bowel syndrome and a number of other diseases.
Haemorrhoids
With this pathology, the rectum is affected. The development of the problem is caused by varicose veins and their protrusion into the intestinal lumen.
With hemorrhoids, a false urge to go to the toilet is not always observed. Their occurrence is explained by the addition of a secondary infection.
Irritable bowel syndrome
With IBS, pain occurs in the abdominal area. Abnormal bowel movements are also possible. Painful tenesmus is often observed. The appearance of such problems is often provoked by constant stress, poor nutrition, and hormonal imbalance.
Dysbacteriosis
Intestinal tenesmus is often observed with dysbacteriosis. The development of pathology is caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the gastrointestinal tract.
The following changes are noted:
- abdominal pain;
- chronic diarrhea;
- the presence of streaks and blood clots in the stool.
Autoimmune diseases
Among the autoimmune pathologies that can provoke the appearance of tenesmus are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
The inflammatory process develops due to insufficient activity of the immune system .
There is a sharp decrease in weight, a lack of iron, vitamins, and microelements in the body.
Polyps in the rectum: symptoms
Polyps are benign formations on the epithelium of the rectum. There are fibrous and adenomatous, villous and multiple polyps of mixed type.
- Fibrous polyps are formed from connective tissue.
- Adenomatous - from gland tissue (this type of polyp is the most dangerous, as it can degenerate into cancer).
- Villous polyps are epithelial growths that have many papillae-villi.
- Mixed type of polyps - combinations of previous types.
The main causes of the disease are untreated inflammation in the rectum (colitis, hemorrhoids, enteritis).
When polyps appear in the rectum, symptoms may be as follows:
- Blood during bowel movements.
- The stool is painful, sometimes accompanied by bleeding.
- If an infection occurs, fever and chills may increase.
- Constipation (if polyps are large).
- Sensation of a foreign body in the anus.
It should be borne in mind that very often it is difficult for the patient to detect the formation of polyps or simply inflammation of the rectum - symptoms as such may be absent.
Polyps are treated surgically. Other methods are simply ineffective and only provide temporary relief.
Single polyps are removed using electrocoagulation (cauterization). Transanal excision is used to treat large polyps. Treatment of polyps that have begun malignant degeneration is carried out by removing the affected area of the rectum.
Tenesmus in a child
The digestive system in children is not yet fully developed. In the acute course of pathologies of the lower gastrointestinal tract, tenesmus is often observed.
In addition to the imaginary urge to defecate, cramping pain is noted. Stool is often completely absent, but if present, it can change consistency. It contains admixtures of mucus and blood.
At an early age, the child experiences the following changes:
- loud crying;
- redness of the facial skin from straining when trying to empty the intestines.
Diagnostic methods
In order to identify the cause of tenesmus, you should seek help from a gastroenterologist.
You may need consultation with other specialists:
- infectious disease specialist;
- oncologist;
- proctologist
The doctor conducts an examination and finds out the following points:
- when the symptoms appeared, their frequency, duration;
- lifestyle, diet of the patient;
- presence in the anamnesis of gastroenterological, proctological pathologies, disorders in the activity of the central nervous system.
The following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- general tests of stool, urine, blood;
- stool test for occult blood;
- biochemical detailed blood test;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- colonoscopy;
- anoscopy.
Treatment
If a person experiences tenesmus, treatment is prescribed depending on the causes of the pathology, the severity of the condition, etc. It is very important to correctly determine the cause of the phenomenon. If a patient has colorectal cancer, it is better to detect it as early as possible. For this disease, complex treatment is prescribed, which includes a variety of techniques. It is also necessary to begin treatment for inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract as soon as possible. Early diagnosis of these pathologies is the key to successful treatment results.
At the appointment, the doctor will draw up a complete picture of the occurrence of the disease. The survey may include the following activities:
- blood tests;
- colonoscopy;
- bacterial culture of stool;
- CT scan of the abdominal region;
- screening for sexually transmitted diseases.
The treatment regimen will depend on what particular pathology caused intestinal tenesmus. If the cause of tenesmus in adults is an inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract, then the treatment regimen will be the same. For infectious diarrhea, completely different methods are already used, etc.
Therapy methods
Treatment involves taking medications and following a diet. Traditional medicine recipes are effective.
Drug treatment
It is possible to get rid of unpleasant symptoms with the help of medications.
The choice of drug depends on the cause that provoked the appearance of tenesmus:
- Intestinal infections. Medicines that have an antibacterial effect are prescribed. The most commonly used are Nifuroxazide and drugs from the enterosorbent group (Enterosgel, Sorbex).
- Proctitis, colitis. Sulfonamides are used.
- Hemorrhoids, anal fissures. Anti-inflammatory, wound-healing, softening ointments, suppositories (Methyluracil, Ultraproct, Proctosan), and medications that improve blood circulation (Detralex) are used.
- Diarrhea. Loperamide and Imodium are prescribed.
- Flatulence. Espumisan is used.
- Constipation. Mild laxatives help solve the problem: Lactulose, Duphalac.
The sedatives Alora, Novo-Passit, and valerian tincture are used.
The following remedies will help remove the urge and eliminate pain:
- No-Shpa;
- Papaverine;
- Duspatalin;
- Hyoscytamine;
- Dicyclomine.
Warm vegetable oil is used for microenemas.
Diet
To eliminate tenesmus, it is important to properly organize your diet. Pickles, smoked meats, spices, as well as fried, hot, cold, spicy dishes are excluded from the menu. The food is steamed or boiled.
During the treatment period, split meals are recommended. You need to eat in small portions, but often.
You should avoid the following products:
- fatty meats;
- cabbage;
- baking;
- legumes;
- canned food;
- sweets;
- alcoholic drinks.
If you are prone to constipation, preference should be given to:
- pumpkin;
- beets;
- freshly squeezed juices;
- decoctions based on dried fruits;
- bran bread;
- fermented milk products.
It is allowed to include soups, cereals, boiled and stewed lean meats, and fish in the menu.
Traditional medicine
Sitz baths using cool infusions of sage, marigold, and chamomile have a good effect. Microenemas with a decoction of St. John's wort, chamomile, and sea buckthorn oil have a positive effect. With their help, it is possible to eliminate inflammation and irritation.
Herbal teas are recommended to help relieve spasms.
The following plants are used for their preparation:
- chamomile;
- valerian;
- oregano;
- Melissa;
- sweet clover;
- motherwort;
- mint.
Chamomile infusion has a calming tonic effect. To prepare it, 1 tbsp. raw materials are poured with a glass of boiling water and left for an hour. Then filter the liquid and drink 75 ml three times a day.
Preventive actions
Painful symptoms appear due to improper nutrition and unhealthy lifestyle. It is easier to prevent the appearance of tenesmus than to deal with its manifestations.
To this end, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- minimize psycho-emotional shocks;
- avoid overexcitation;
- properly plan your diet;
- introduce a sufficient amount of fiber-rich foods into the menu;
- eat small portions, but more often;
- eat food warm;
- stop drinking alcohol, drugs, and smoking;
- engage in physical exercise, the load should be moderate;
- treat any diseases in a timely manner.