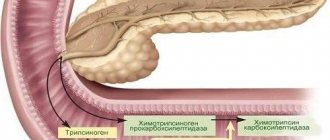
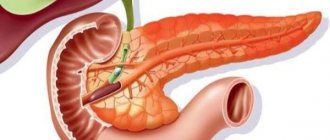
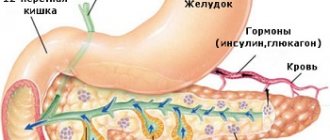
Topographically, the organ is located in the center of the abdomen, retroperitoneal, adjacent to the posterior wall of the stomach - they are separated only by the omentum (fat layer), its head is in contact with the duodenum, the tail is located close to the spleen, you can see in the photo. The gland performs a dual function in the body: it synthesizes digestive enzymes that take part in the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and produces endocrine hormones (insulin, glucagon, kallikrein), which are responsible for carbohydrate metabolism. Therefore, any anatomical and functional disorders lead to the development of pathology of digestive or endocrine function.
An exception is a strong bend of the organ, when the pancreas covers the duodenal bulb, and it becomes sandwiched by the tissue of the gland. This pathology is rare and is a temporary phenomenon. Obstruction may develop, which requires urgent medical intervention.
Form
The pancreas consists of 3 main parts: head, body and tail. It has an elongated, curved shape. It is located on the posterior wall of the peritoneum, partially located in the left hypochondrium. Most of the gland is exocrine. The smaller part is represented by pancreatic islets - endocrine glands.
The shape of the pancreas can change throughout a person's life. The child is characterized by a natural curve and even has a wedge-shaped appearance. In an adult, it takes on a more elongated shape, maintaining a slight natural curvature. Pathological is the enlargement of the organ and the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms. In this case, a diagnosis is carried out and the cause of the manifestation is determined.
It is important to know! When the pancreas is damaged, pain and poor digestion often occur. Having noticed such symptoms, a person should consult a doctor for a full examination.
Organ deformation
Diagnosing a bend in the pancreas in a child is often only a reason for parents to worry. The organ tends to change its shape as children grow, the position in which the examination was done. So, in a lying position, it has one appearance. In a vertical position, the shape changes.
The shape of the organ is individual for each child’s body. This depends on the shape of nearby organs and their location. Features of embryogenesis distinguish:
- elongated shape. The organ is more straightforward. All its parts are approximately at the same level;
- curved shape in the form of a comma, an angle, the letter “L”. This design is formed by its parts of the structure: body, head, tail.
When viewed in cross-section, they have a different shape: the head is oval, the body is prismatic, and the tail is ellipsoidal.
As a child develops, the external form does not change; its parts can change shape and location. Therefore, the bend of the pancreas should be observed and not panic. If there is no disruption in nutrition or other pathologies of the child’s gastrointestinal tract, then the bend is a temporary phenomenon.
The ring-shaped shape of the gland is dangerous. It wraps around the initial part of the small intestine and can compress it, which contributes to the obstruction of digested food into the intestine. And this already borders on gastrointestinal pathology and the development of pancreatic disease. Ring-shaped pathology is rare.
Deformation
A bend is not a pathology if there are no symptoms. If only a bend was detected through hardware examination, the doctor will advise you to adhere to preventive standards and undergo the examination again after a certain period of time.
The most accessible and informative research method is ultrasound.
It will be necessary to treat the pathology if a hidden disease is detected. Based on the research carried out, a diagnosis is made, then a scheme for influencing the disease is drawn up.
Why is the pancreas deformed in adults and children?
Among the reasons for deformation are:
- inflammatory process (pancreatitis);
- cystic formation;
- tumor formation.
If, along with the deformation, there are characteristic changes and symptoms of the disease, an in-depth study is required. Pancreatitis can lead to severe modification of the pancreas due to inflammation and insufficient outflow of enzymes. The formation of a cancerous tumor leads to tissue degeneration. The cyst leads to uncharacteristic deformation.
Note! Sometimes the doctor prescribes several additional examinations.
The appearance of pancreatic deformation in adults and children may be normal. In some cases, the curvature appears and later disappears on its own. This often happens in childhood, so don’t start panicking right away.
Bend or bend of an organ - what's the difference?
In medicine, the term bending of the pancreas is practically not used, because it can change its shape while remaining fully functional. In most cases, symptoms of bending in a child are completely absent. If the doctor speaks of a bend, this may mean that the organ has taken an unnatural position. If the deformed pancreas affects neighboring organs, preventing it from working, it is necessary to prevent the development of complications.
Causes of deformities
Bending of the gland, unlike deformation, does not lead to anatomical and functional disorders. Most often, the cause of curvature is the position of the body and the mobility of the gland due to its continuous growth.
The head of the pancreas encloses the pyloric part of the duodenum in a ring
Deformation is associated with structural disorders in the organ, which, in turn, cause functional deviations. Among the reasons that provoke changes in the shape of the pancreas are:
- pancreatitis (acute, chronic);
- adhesive process in the area where the organ is located;
- diabetes;
- infections (mumps, adenovirus, herpesvirus, rubella, ECHO and Coxsackie, influenza);
- injury;
- obesity;
- cystic process;
- disruption of the outflow of pancreatic juice in diseases of the duodenum and biliary tract;
- cystic fibrosis;
- tumor formations;
- congenital developmental anomalies (hypoplasia, hyperplasia, ring-shaped head);
- toxic damage.
These processes lead to tissue damage, replacement of areas of necrosis (death) with connective tissue, deformation and disruption of the digestive and endocrine functions of the organ. The pancreas increases in volume, loses its usual shape, becomes lumpy, and acquires curves that do not disappear over time or when changing body position.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
You can understand the state of the pancreas using hardware methods. The most common:
- ultrasonography;
- radiography;
- computed tomography.
The doctor selects specific diagnostic methods.
To obtain a complete picture, you will need to take a number of laboratory tests: blood, feces, urine. A general biochemical blood test will reveal the inflammatory process and estimate the amount of enzymes in the blood. Using a coprogram, the state of digestion is assessed. The presence of fats and fatty acids in the stool indicates that a small amount of pancreatic enzymes enter the intestines.
Helpful information! Using ultrasound and CT, you can understand whether there are deviations in the size and shape of the gland, and identify diffuse tissue changes.
Symptoms of the disease
As a rule, changes in the shape of the pancreas are not accompanied by any discomfort. Unpleasant sensations appear only at a severe stage of the disease, when the organ bends around the duodenum.
Doctors identify the following symptoms of a bent pancreas:
- Acute pain in the abdominal area;
- Vomiting and diarrhea;
- Rejection of bile into the stomach;
- Increased amount of saliva produced;
- Rapid breathing.
We also recommend viewing: Where does the pancreas hurt and how does it hurt: we know more, we get sick less
These signs indicate the need to undergo a medical examination as soon as possible, but the final diagnosis is made by a qualified specialist.
Treatment of the disease
Symptoms and treatment are closely related to each other. Therapy begins after a person consults a doctor with complaints or a pathology is accidentally discovered during a routine examination. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the disease. After normalization of the condition, the pancreas will take its usual shape. For treatment, medications, proper diet, and food enzymes are used.
Medicines
Drug treatment is used for acute and chronic lesions. If a doctor has diagnosed a person with pancreatitis, the following classes of medications may be needed:
- painkillers;
- enzyme agents;
- inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes.
Your doctor will be able to draw up a specific treatment regimen. The specific medicine, dosage, and duration of use are selected individually. If pancreatitis is not treated in time, it can seriously deform the pancreas.
Phytotherapy
The use of herbal medicine is advisable if the pathology is not serious. It can improve digestion and relieve inflammation of the gland. This way you can treat the identified bend. The following herbal remedies are used:
- Rosehip infusion. Pour 20 g of rose hips into 150 ml of boiling water. Drink the resulting infusion throughout the day, dividing it into 3-4 doses. Rose hips reduce the severity of inflammation, strengthen the immune system, and supply the body with vitamins.
- St. John's wort decoction. Pour a tablespoon of dry St. John's wort into 300 ml of boiling water. Then continue boiling for 5 minutes. St. John's wort is taken 1-2 times a day before meals in small quantities. Helps relieve inflammation and pain.
The ingredients are purchased at the pharmacy.
Before using herbal medicine, consult with the treating gastroenterologist.
Therapy of the disease
Therapeutic treatment is necessary only in case of acute inflammatory process. Tumors are observed from the first days and treated by oncologists. In case of injury, tumor, compression of the duodenal bulb by the parenchyma of the gland and the development of intestinal obstruction in this place, treatment is surgical.
Medicines
Pancreatitis is a common cause of the appearance of an angular bend, which appears with an acute onset. With timely and adequate treatment, the iron returns to its normal position. Therefore, it is necessary to begin therapy as early as possible using:
- antispasmodics,
- painkillers,
- antibacterial,
- anti-enzyme,
- enzymatic agents.
According to the famous pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky: treatment of pancreatitis necessarily includes therapeutic nutrition.
Phytotherapy
Herbal medicine is not suitable as a method of treating pathology that has caused bending or deformation of the pancreas. In acute pancreatitis or during exacerbation of a chronic process, it is contraindicated: it can worsen the course by adding an allergic component. The disease is too serious and can cause severe complications, often leading to death, so the use of medicinal plants for its treatment is not recommended. Similarly - when a gland tumor is detected.
In other cases (in case of injuries, congenital anomalies, cysts), the method is ineffective.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment are used only for pancreatitis: in the acute phase, when the child cannot eat, warm mineral alkaline water without gas is used. The frequency and volume of fluid you drink is determined by your doctor. After 2–3 weeks, in the phase of unstable remission, symptomatic physiotherapy is used to:
- relieving spasms,
- improving the outflow of pancreatic juice,
- anti-inflammatory action,
- restoration of blood circulation in the affected organ,
- improving motility of the stomach and duodenum.
An effective method is:
- electrophoresis with novocaine, antispasmodics (papaverine, platiphylline, No-Shpa), liquid mud preparations (medicinal mud, peloidin, humisol),
- Ultrasound in pulsed mode relieves pain well and normalizes gastric secretion.
Diet during illness
To achieve a pronounced result, you need to adhere to a special diet, which includes:
- exclusion of alcohol, fatty, fried, salted, smoked foods;
- fractional meals 5-6 times a day;
- eating steamed food.
The diet should be as light as possible.
To quickly normalize digestion, you need to start using specialized enzymes.
Treatment of bended pancreas
After a thorough examination, the attending physician will select a treatment regimen in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient. Treatment includes medication, physical therapy, and a special diet. The course of treatment and its duration are determined after a detailed diagnosis.
Most often, doctors prescribe diet number 5, which is low in fat.
To maintain normal digestion, after consultation with a specialist, you can drink herbal teas based on St. John's wort and motherwort. Sometimes the tea includes chamomile and immortelle flowers. These herbs reduce inflammation and promote the timely production of digestive enzymes. The same teas are used for prevention of chronic pancreatitis.
Important. If any unpleasant sensations appear or changes in the state of the digestive and excretory system, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will identify the reasons for the deterioration of the condition and adjust the treatment regimen.
Reactive pancreatitis
Reactive pancreatitis is caused by spasms of the pancreatic ducts, as a result of which enzymes cannot enter the gastrointestinal tract and accumulate in the gland, beginning to “digest” it. The child begins to experience pain, which usually manifests itself sharply and sharply, is clearly localized above the navel and is girdling in nature. Nausea and vomiting of undigested stomach contents are possible. The attack of pain can last up to several hours.
An attack of reactive pancreatitis can be caused by:
- inflammatory processes in the child’s body (with acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, sore throat, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract);
- excessive consumption of food that the child’s body is not able to cope with. First of all, these are fried foods, dry foods (chips, crackers with seasonings), carbonated drinks;
- food with a large number of preservatives, flavor enhancers and other food additives;
- change of diet (for example, when a child enters school or kindergarten). This is how the body reacts to unusual food;
- taking certain medications (antibiotics or antiviral drugs).
Chronic pancreatitis in children
As a child grows up, he or she may develop bad eating habits. Addiction to sweets and carbonated drinks contribute to the development of chronic pancreatitis. An uneven diet, which, unfortunately, is typical for most schoolchildren, also has an effect. Among the causes of chronic pancreatitis in children are also intestinal parasites (worms), poisoning, trauma and infectious diseases.
Chronic pancreatitis is detected only at the time of exacerbation; between exacerbations there are no manifestations of the disease. An exacerbation can be triggered by the intake of junk food, medications (especially when self-medicating), or illness.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis during exacerbation:
- pain. In young children, the pain spreads throughout the abdomen or is concentrated near the navel. In older children, the pain is concentrated in the upper abdomen and can radiate to the back;
- nausea and vomiting (more common in older children);
- decreased appetite;
- stool disorders (diarrhea and constipation may alternate);
- general poor health, tearfulness, fatigue, drowsiness.
Causes of changes in the shape of the pancreas in childhood
Children of different ages often encounter this problem. The cause may be genetic predisposition, irrational or irregular nutrition.
The main cause of bending of the pancreas in a child is acute pancreatitis. Symptoms of the pathological process appear clearly. If the parents contact the doctor in time and begin treatment, the organ will return to its previous shape.
If the deformation of the pancreas is accompanied by a disturbance in its location, this does not indicate a disease. But in such cases, a full examination is required to make an accurate diagnosis and prevent the development of possible complications.
Deformation of the organ may be accompanied by displacement to the side. Often this phenomenon is characterized by an enlargement of the pancreas. Then the child needs treatment.
Video: SDK: Pancreas. Routes of drug administration - Dr. Komarovsky
Bend gallbladder in a child
One of the diseases that modern parents often have to deal with is the bending of the gallbladder in children. When symptoms appear, this disease causes a lot of inconvenience, primarily to the child himself. Its essence is that due to the deformed shape of the gallbladder, it does not work fully. The outflow of bile, necessary for the breakdown of fats, is disrupted, which interferes with the normal digestion process.
Gallbladder bends - causes and symptoms
Normally, the gallbladder is pear-shaped and consists of three sections: the body, the fundus and the neck. Deformation can be found anywhere.