The pancreas and diabetes mellitus are interconnected: with the development of pathological changes, the organ ceases to function normally and produce insulin in sufficient quantities. New-onset diabetes is currently not treatable with medication. Lifelong replacement therapy or surgical methods are used.
What affects the functioning of the pancreas?
The pancreas is an organ with a complex structure that simultaneously belongs to two different systems: digestive and endocrine. The functions of the gland are influenced by various external and internal factors. When the exocrine function of the pancreas is impaired, pancreatitis most often develops. Insufficiency of endocrine activity of the pancreas leads to the development of diabetes.
Severe inflammation of the pancreas leads to a cessation of insulin synthesis and the appearance of type 1 diabetes. In type 2 diabetes, pancreatic function is not impaired, but the body does not respond to the normally produced hormone. Factors that provoke changes in sugar levels have been identified:
- hereditary diseases (cystic fibrosis),
- inflammatory process in the tissues of the pancreas (pancreatitis), its complications in the form of pancreatic necrosis with irreversible changes in the tissues of the pancreas in the form of the development of fibrosis,
- pancreatic tumor or large benign neoplasm compressing the gland tissue,
- injuries and surgical interventions,
- adrenal gland diseases,
- atherosclerosis and, as a consequence of this pathology, decreased blood circulation and impaired nutrition of the organ,
- congenital diseases not associated with genetic defects,
- external influences in the form of poor nutrition and bad habits,
- abuse of carbohydrates, which can lead to hypoglycemic coma - after which insulin secretion may be impaired,
- pregnancy.
In addition, there are common reasons that significantly disrupt the functions of the pancreas and affect its functioning:
- increased body weight,
- diseases of other digestive organs (most often - pathology of the gallbladder and biliary dyskinesia),
- viral infections involving the pancreas,
- helminthic infestations,
- bacterial infections that provoke purulent processes in the pancreas,
- long-term use of chemical drugs - corticosteroids, non-steroidal (even long-term use of indomethacin ointment), estrogens, antibiotics from the tetracycline group,
- side effects of long-term use of contraceptives,
- autoimmune diseases.
Symptoms of manifestation
Diabetes mellitus is a pathology characterized by absolute or relative insulin deficiency. Complications from the blood vessels, nervous system, internal organs, and eyes are possible. Absolute - characterized by reduced production of insulin by pancreatic cells. There is not enough of it in the blood, and the penetration of glucose into the cell is impaired. Type 1 diabetes mellitus develops.
With relative deficiency, the amount of insulin produced is normal, but the sensitivity of tissue receptors to insulin is impaired. This is the so-called type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms characteristic of each type of diabetes are listed in the table:
[wpsm_comparison_table id=”15" class=””]
A characteristic sign of diabetes is the smell of acetone on the breath. This symptom occurs as a result of ketoacidosis (accumulation of ketone bodies in the blood), causing bad breath and urine.
If at least one of these signs appears, you should check your blood sugar level and consult a doctor.
Sometimes symptoms may appear that indicate a malfunction of the pancreas: nausea, vomiting, undigested pieces of food in the stool. In such a situation, many people think about how they can clean the pancreas at home.
Sometimes insufficient substances that promote the breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates may be produced. In this case, enzyme replacement therapy is prescribed. This includes medications: Panzinorm, Festal, Creon. These methods will also prevent the development of type 2 diabetes.
Types of diabetes
In order for a patient to be effectively treated with pancreatic medicine for diabetes, it is necessary to find out what type of disease he has developed. It depends on many factors. The main role is played by age and pathogenesis of the disease.
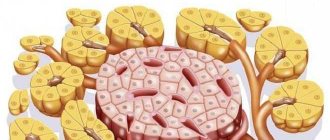
Diabetes mellitus refers to the pathology of the endocrine part of the pancreas. It is represented by the islets of Langerhans and occupies only 2% of the volume of the entire organ. Islets are formed by cells of different structure and functions. They are united by the secretion of hormones - active components that control various types of metabolism, digestion processes, and growth. There are mainly 5 types of endocrine cells that play a significant role in the production of hormones. Among them, the following are associated with carbohydrate metabolism:
- beta cells (60%), producing insulin and a small amount of amylin, also involved in the regulation of sugar levels,
- alpha cells (25%) secrete glucagon, an insulin antagonist (breaks down fats, increasing the amount of glucose in the blood).
According to the mechanism of development and clinical manifestations, the disease is divided:
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus is insulin-dependent and develops in young patients, although in recent years the age limit has risen to 40-45 years. A sharp deterioration in the condition occurs when more than half of the beta cells die. This mainly happens in autoimmune diseases, when the body begins to intensively produce antibodies to the cells of its own tissues. As a result, this can cause the death of cells that produce insulin, and absolute deficiency of the latter develops. Pathological anatomy of the pancreas in type I diabetes in a microslide describes alternating damage to the islets: one is susceptible to atrophy and hyalinosis, the other is compensatory hypertrophied.
- Diabetes mellitus type 2 is non-insulin dependent and is characterized by a relative deficiency of insulin. A patient with this type of diabetes is an elderly person who is overweight. In this type of diabetes, insulin is produced in normal amounts. The mechanism of development of the disease is a sharp decrease or blocking of the volume of structures that ensure contact of insulin with cells to provide them with glucose. The cell lacks carbohydrates - this serves as a signal for even greater insulin synthesis. But since the increase cannot continue indefinitely, its production drops sharply.
- Hidden (latent) diabetes mellitus: the normal amount of insulin produced by a healthy pancreas is no longer perceived by the body as a hormone - insulin resistance is developed.
- Symptomatic (secondary) diabetes - combines diseases that are a consequence of pancreatitis, cancer, hemochromatosis, and removal of the pancreas. These diseases lead to a sharp decrease in insulin production, as in type 1 diabetes, but the pathology itself associated with the manifestations of diabetes mellitus occurs with a clinical picture, as in type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes is pregnancy diabetes that occurs in the second half of pregnancy. It is rare, and the reasons for its occurrence are not fully understood. The approximate mechanism of action is the production of hormones by the fetal placenta that block the absorption of insulin by the mother. Insulin resistance develops - the insensitivity of cells to sufficient insulin available, as a result of which blood sugar rises.
- Diabetes associated with starvation - lack of adequate nutrition. Since 1985, it has been identified as a separate category and classified into pancreatic and pancreatogenic, affecting patients in tropical countries aged 10 to 50 years.
All types of diabetes mellitus, regardless of their etiology and pathogenesis, are characterized by hyperglycemia, sometimes by glucosuria, complications that develop against this background. Fats become a source of energy - the active process of lipolysis begins with the formation of a large number of ketone bodies, which have toxic properties and disrupt the metabolism of fats, proteins, and minerals.
The structure of the pancreas and types of diabetes
The pancreas is a large endocrine and exocrine gland involved in digestion. On the one hand, it secretes pancreatic juice, which contains enzymes involved in digestion.
On the other hand, its internal secretory function is responsible for the production of the hormone insulin. In addition, it has other properties: it controls the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the body.
The structure of the pancreas is divided into three main parts:
- The head of the pancreas is enclosed by the duodenum. It is separated from the body of the organ by a groove and has a duct that flows into this intestine through the duodenal minor papilla.
- The triangular body shape of this organ has 3 edges and 3 surfaces.
- The pear-shaped tail extends towards the spleen.
Iron consists of different types of tissue surface, each responsible for its own function. Exocrine secretion is performed with the help of small components of the external secretory function - acini. They have ducts that connect into one common one, and through the head of the pancreas they exit into the duodenum, through which pancreatic juice enters.
Endocrine function depends on the cells located between the acini. These are the islets of Langergars, which do not have ducts and, thanks to the network of blood vessels connecting them, the hormone insulin enters the blood.
To understand how diabetes mellitus manifests itself, you need to know that it is divided into several types:
- The disease of the first type is manifested by a malfunction of the pancreas and a lack of insulin production by the cells of this organ.
- The second type of disease does not manifest itself as insulin deficiency, because the cells produce it in sufficient quantities. The body stops accepting this hormone and becomes resistant to insulin. The gland can remain completely healthy.
- Symptomatic.
- Hidden form.
- Pregnancy diabetes.
- Caused by insufficient food.
The symptomatic form of diabetes, as stated earlier, is caused by chronic inflammation of the pancreas.
Pain in the pancreas that occurs with diabetes
The greatest likelihood of developing diabetes is a pathology of the pancreas. The most common is pancreatitis - inflammation of organ tissue. Since the entire tissue is damaged, the pathological process involves the acini responsible for the exocrine function and the islets of Langerhans located between them, which produce insulin. This often occurs with alcoholic pancreatitis, cholelithiasis, and after pancreatic surgery. When areas of pancreatic necrosis with cell death are formed, when all functions of the pancreas are disrupted, this is clinically manifested:
There is a primary phase of inflammation, when the stomach begins to ache, and the resulting sensations are characterized by varying intensity and localization. The duration of this phase is up to 10 years.
The next phase is characterized by the appearance of dyspepsia: pain is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, which does not bring relief, diarrhea in the form of repeated fatty, foul-smelling pancreatic diarrhea, bloating, and belching. At this stage, pancreatic cells are destroyed, which cannot be restored - an irreversible process occurs, and addiction to glucose occurs. Hyperglycemia appears after eating, the rest of the time the blood sugar level is normal.
When the pancreas is damaged in type 2 diabetes mellitus, all the signs of chronic pancreatitis are revealed. Long-term inflammation of the gland causes the development of diabetes mellitus in the patient, since these changes are interrelated due to the structure of the pancreas.
With exacerbation of pancreatitis, the localization of the pain symptom in the abdomen can be of different localization. It depends on the prevalence of inflammation in the organ:
- pain may disturb in the right hypochondrium and epigastrium, if the process has more affected the head of the pancreas or has spread to the body,
- localization in the epigastrium and left hypochondrium conditionally indicates damage to the body with possible involvement of the tail,
- with pain in the hypochondrium radiating to the lower back, arm, jaw, as with angina pectoris, or pain of a girdle nature can occur with total damage to all parts of the pancreas involving the peritoneum.
When the pain worsens, it can be intense, paroxysmal, and “dagger-like” in nature.
Mechanism of pain
The occurrence of pain in the pancreas in diabetes mellitus does not occur in the early stages of the disease. This occurs much later when pancreatitis develops. At its first appearance, you can help the patient if you conduct a timely examination and prescribe treatment. In some cases, when it is severe pancreatitis that causes diabetes, pain appears during attacks of pancreatitis and increased sugar.
In addition to pancreatic pain, with diabetes the patient experiences pain as a reaction to food (short-term), and indicating another pathology. For any intensity of pain, even unexpressed, you need to consult a doctor for examination, since with diabetes the pain threshold is reduced - pain can be felt even with significant or critical changes that require immediate medical attention.
In addition to the pain that occurs with significant changes in the pancreas, mainly of an inflammatory nature, ailments can be caused by complications of pancreatitis. Factors that provoke pain in diabetes mellitus include:
- stomach or duodenal ulcer,
- reaction to taking metformin with insufficient nutrition or to the use of biguanides by a diabetic simultaneously with alcoholic beverages,
- ketoacidosis,
- liver diseases,
- lactic acidosis.
Treatment of diabetes mellitus with pancreatitis
The most important condition in the treatment of diabetes mellitus and pancreatitis is the simultaneous treatment of two diseases. To do this you need:
- strictly adhere to the diet on an ongoing basis, and not just during an exacerbation;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- take medications with enzymes for replacement therapy (Creon, Festal);
- use glucose-lowering tablets with mandatory daily monitoring of blood sugar levels (Siofor, Glucophage), it should not be lowered below 4.5 mmol/l.
If an operation is performed for pancreatitis (partial or complete removal of the tail), then a patient with diabetes mellitus must be switched to insulin. Injections are given in small doses before meals. After stabilizing the sugar level, it is possible to prescribe tablets on an ongoing basis.
In extremely severe cases of pancreatitis, surgery may be necessary to transplant the patient's own islet cells that produce insulin. After this, the pancreas is removed. This treatment method is available only in large specialized endocrinology centers.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the pancreas in existing diabetes should be comprehensive and determine not only the pathology in the structure of the organ, but also its functional integrity. This is due to the fact that during the inflammatory process, damage can develop in a small area, and the rest of the organ can compensate for its functions. Clinical manifestations, as well as changes during ultrasound, may be absent, but the laboratory method will determine functional changes.
Therefore, the diagnosis is made on the basis of medical history, complaints, objective status, laboratory and functional studies.
When examining a patient, it is impossible to palpate the pancreas due to its retroperitoneal location. Accessible abdominal organs are examined and tested. The skin, condition of nails and mucous membranes are also carefully examined. The signs that are observed with pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus indicate pathology, but are not characteristic only of these diseases:
- paleness or icterus (yellowness) of the skin,
- dry tongue, coated tongue,
- peeling, brittle nails, hair falling out,
- hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity or pain) of the skin to the left of the navel,
- pain in the epigastrium or hypochondrium upon palpation.
When prescribing any diagnostic method to verify the diagnosis, the characteristics of the gland tissue are taken into account: during a routine x-ray examination it is not visible, but its ducts are visualized when contrast is administered.
It is best and most convenient for the patient and the doctor to clarify the disease using ultrasound - the safest and most accessible method that well determines changes in the structure and density of the organ, as well as accurately determines the size of the gland, its parts, the main duct, and reveals the presence of formations.
Dopplerography determines existing blood flow disorders in the vessels.
Computed tomography (CT) makes it possible to see the layer-by-layer structure of the gland, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) determines the smallest structures. MRI is less dangerous compared to CT.
Laboratory research
Laboratory diagnostics are mandatory when verifying the diagnosis. Analyzes make it possible to assess the degree of functional damage to an organ. Moreover, a violation of the excretory (level of produced digestive enzymes) and endocrine (sugar in the blood and urine) functions of the gland is determined, as well as inflammatory changes in neighboring organs that always accompany pancreatitis (levels of transaminases, bilirubin and its fractions, total protein with its components).
Usually prescribed:
- general blood test - it determines the presence of an inflammatory process at the time of the study (increased ESR, leukocytosis),
- biochemical studies: blood and urine diastasis, blood and urine sugar, coprogram.
In the case of an episodic increase in blood sugar or when its numbers are normal, but there are also complaints about thirst, sometimes dry mouth, it is necessary to determine blood sugar with a carbohydrate breakfast or TSH (glucose tolerance test, when glycemia is determined on an empty stomach and after 2 hours after a carbohydrate breakfast). This way hidden diabetes mellitus is revealed.
Instrumental diagnostics
The most widely used ultrasound is the retroperitoneal space, where the pancreas is located, and the abdominal cavity.
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas and abdominal organs is the safest and most convenient diagnostic method, which does not take much time and does not require special preparation other than fasting before the procedure. Ultrasound makes it possible to monitor conditions in the pancreas and track them over time; it is well tolerated even by a child of any age. Therefore, it is necessary to do an ultrasound once every six months to see how the iron is restored after treatment.
Diabetes mellitus is an endocrine dysfunction of the pancreas. Therefore, with diabetes, organ tissues undergo further changes, which manifest themselves in the form of:
- fibrosis,
- lipomatosis,
- atrophy.
If the process is acute, swelling of the gland is observed, its size increases, and tissue density changes.
With long-term diabetes, areas of compaction are visible on ultrasound, mainly in the head of the pancreas, and the size of the organ itself becomes significantly lower than normal.
Changes in the pancreas that are visualized in diabetes mellitus have a picture characteristic of pancreatitis disorders. Moreover, changes in neighboring organs: the liver and gall bladder are simultaneously determined.
X-ray methods include:
Instrumental diagnostics, in addition to ultrasound, include:
- EGDS (esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy) to study the condition of the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stomach - often this pathology is an indirect sign of inflammation of the pancreas or its complication,
- MRI – magnetic resonance imaging.
Treatment of the pancreas for diabetes
Diabetes mellitus in most cases occurs against the background of pancreatitis. These two diseases are related because insulin, which is involved in carbohydrate metabolism, is produced by beta cells of the islets of Langerhans, which are surrounded by special glandular structures - acini, which produce digestive enzymes. During the inflammatory process in the pancreas, not only the glandular tissue with its exocrine function is affected, but also the islet tissue, with the development of diabetes mellitus.
Therefore, complex treatment is prescribed, including:
- lifestyle modification,
- dietary food,
- drug therapy,
- surgical methods in severe cases.
For low glycemia, an endocrinologist can prescribe traditional medicine recipes using medicinal herbs that affect sugar levels.
Drug therapy
Complex drug therapy for pancreatitis in diabetes mellitus is the main method of treatment. The patient is observed by a gastroenterologist and endocrinologist, receives hypoglycemic medications, as well as a complex of vitamins, vascular, and nootropics due to damage to the nervous and vascular system. The amount of treatment depends on glycemia and developed complications of diabetes mellitus.
In parallel, the following is assigned:
Pancreas transplantation as a method of recovery
If conservative treatment of pancreatic diseases is ineffective, the question of organ transplantation arises. Severe complications or organ rejection may occur after transplantation. But if the operation is successful, the patient’s condition will improve, and he will be spared the constant administration of insulin in case of diabetes.
Pancreatic transplantation is a complex operation. It's connected:
- with retroperitoneal location of the pancreas,
- with proximity to many large vessels and vital organs,
- with the structure of the pancreas tissue, which responds to any influences,
- with possible severe complications in the form of self-digestion of the organ and damage to neighboring organs when the pancreas is damaged.
But such operations are carried out: approximately 200 cases have been described, and, according to statistics, 1 thousand people are subjected to them every year. An organ transplant is an expensive and extremely dangerous treatment, but it helps the patient to exist without being tied to the constant administration of insulin.
With pancreatitis, pancreatic tissue is affected, including the islets of Langerhans: all types of cells that synthesize hormones partially die. First of all, the beta cells that produce insulin are damaged. In severe cases, when diabetes cannot be cured and drug therapy is not enough, an alternative to pancreas transplantation is transplantation of cells of the islets of Langerhans. This makes it possible to treat type I diabetes mellitus in cases where insulin replacement therapy has reached its limits and becomes ineffective.
The method involves injecting the patient with healthy endocrine donor cells into the portal vein of the liver using a catheter. The method is aimed at making the remaining own beta cells work, as well as avoiding further severe complications of diabetes.
The prognosis is favorable; no deaths were recorded during the intervention.
Increased beta cells
An increase in beta cells can also be achieved through therapeutic methods thanks to the development of modern medicine. The scientific method is based on the intramuscular injection of a special protein into the body, which stimulates the transformation of beta cell precursors into fully functioning ones. This treatment method is now being successfully tested for diabetic pancreatic disease.
How to restore an organ through immunomodulation?
In patients with type 1 diabetes, the number of beta cells that produce insulin is significantly reduced. Their body produces antibodies aimed at destroying these cells (autoimmune process). Today, the possibility of creating immunomodulation is being studied: if antibodies are isolated, it will be possible to create a special vaccine that will stimulate the immune system to destroy these antibodies. In this case, the surviving beta cells will begin to multiply and normalize carbohydrate metabolism in the body.
Principles of treatment
I would like to once again draw attention to the fact that everyone who is wondering how to restore the pancreas should take into account that this is a long and complex process. In particular, therapy will be based on the use of various hormonal drugs and enzymes.
However, a significant role in the presented therapy, when diabetes mellitus is present, should be given to proper nutrition. To do this, at a minimum, it will be necessary to exclude from the diabetic’s diet all unacceptable foods, as a result of which the pancreas suffers.
Drug therapy will be successful only if all the specialist’s recommendations are followed. Such treatment will make it possible to avoid certain problems and improve the functioning of the body as a whole.
For example, if there is pain in the abdominal area, the doctor should prescribe painkillers. Speaking about this, they pay attention to the need to use No-shpa, Papaverine.
In order to relieve the pancreas area, some enzymes are used.
For example, Pancreatin, Mezim or Digestal.
A person with an affected pancreas is prescribed not only drug therapy, but also a strict diet, which constitutes the main treatment. The process uses hormonal agents and enzymes.
In order to effectively treat pathologies, it is also necessary to exclude a certain list of products from the menu, which depends on the underlying disease. Helping a person with an inflamed pancreas and diabetes can be extremely difficult; success can only be achieved by following all the doctor’s instructions.
The process of treating the pancreas in diabetes mellitus is quite complex, because the improvement in this case may not be significant. Only comprehensive methods should be used, namely, not only medications, but also a special diet.
In order for the recovery to be complete and diabetes mellitus not to be associated with complications, such therapy can be maintained throughout life.
If a diabetic is diagnosed with pancreatitis, cystosis or pancreatic cancer, it is important to begin therapy immediately.
Treatment principles:
- taking medications that relieve inflammation and resolve cysts;
- the use of medications that restore and support the functioning of the affected organ;
- treatment of complications;
- strict adherence to the diet;
- maintaining sugar within normal limits.
What medications will help restore the organ?
To relieve the inflammatory process in the pancreas, the following groups of drugs are used:
- antibacterial;
- analgesic;
- anti-inflammatory.
To restore secretory function, replacement therapy with medications containing enzymes (Creon, Mezim forte, Panzinorm) is prescribed.
The dosage and duration of the course are selected by the doctor individually, based on the medical history, diagnostic results, and the patient’s age. Diabetics are also prescribed Dibikor, which stimulates metabolic processes and has a beneficial effect on the affected organ.
Restoring gland function with proper nutrition
The main condition for the rapid restoration of pancreatic function is proper nutrition. A person should avoid fried, fatty, spicy foods.
It is necessary to limit the consumption of baked goods and sweets. To unload the organ, three-day fasting is indicated.
Pancreatogenic diabetes is an endocrinological disorder that develops as a result of acute or chronic inflammation of the pancreas, when the organ ceases to produce insulin in the required amount. It is treated with medication and diet.
Doctors prescribe the following groups of medications:
- enzymatic (Pancreatin, Panzinorm, Pangrol);
- painkillers (Duspatalin, Mebeverine);
- sulfonylurea drugs (Glyurenorm, Daonil, Diabeton);
- thiazolidinediones (Avandya, Actos);
- biguanides (Diformin-retard, Silubin);
- combined agents (Glimecomb, Amaryl M).
For this type of diabetes, a high-calorie diet with a low fat content and a predominance of carbohydrates is indicated.
Diabetes mellitus is caused by a malfunction of the human endocrine system, which disrupts the production of insulin. With any type of diabetes, the patient feels constant thirst, he urinates frequently and profusely, and is bothered by muscle weakness.
Type 2 diabetes often occurs against a background of obesity, and methods of compensating for it in this case are associated with a special diet. It is one of the main folk methods of treating this type of disease.
Diet for diabetes
First of all, you need to eat more fruits and vegetables. Bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol are completely excluded. The consumption of foods with a large amount of fats and carbohydrates must be reduced to a minimum, we are talking about fatty meats, baked goods, baked goods, sweets, potatoes, rice, etc. However, you cannot go hungry, you need to eat small meals - 5-6 times a day.
In addition to diet, it is very important to be a physically active person: do exercises in the morning and engage in other sports. It is very important to avoid stress, as a surge of emotions can cause an increase in blood sugar.
Here are some recipes based on foods that are used to treat diabetes:
- take three regular white beans and place them overnight in a glass half filled with cold boiled water. Waking up early in the morning, eat beans and drink water;
- take a horseradish root about 20 cm long and as thick as a man’s finger. There is no need to clean it, just wash it. Then, in a crushed state, place it in a 3-liter jar. Add 9 peeled and chopped garlic cloves there. Fill everything with fresh beer almost up to the neck of the can and leave in a dark place for 10 days. Strain and drink the infusion 1 teaspoon three times a day, the next day 1 tablespoon three times a day. Course of treatment – 1 month;
- grind 2 tablespoons of buckwheat using a coffee grinder and mix them with 1 tbsp. low-fat kefir. Shake well and take 2 times a day in the mornings and evenings half an hour before the main meal.
How beekeeping products can help
Nature comes to the rescue in the fight against illness. There is probably not a single disease that cannot be treated with folk remedies.
And although herbal medicine cannot completely cure severe autoimmune diseases, it can significantly alleviate the patient’s condition. For type 2 diabetes mellitus, it is recommended to take propolis preparations.
They reduce the concentration of glucose in the blood and increase the body's defenses.
Honey can also be beneficial, but since this product is rich in carbohydrates, it must be used with caution, in accordance with the characteristics of the disease.
Herbal medicine: folk remedies
Most traditional medicine recipes are based on the action of medicinal herbs and plants. Any herbal collection should be formulated in such a way as to have a beneficial effect on blood sugar levels, keep metabolism under control and improve the function of all internal organs.
It is customary to treat a disease such as diabetes with white mulberries, rowan berries, raspberries, dandelions, oats, alfalfa, green beans, blackberries and celery.
Here are some recipes:
- when high blood sugar is associated with weakened pancreatic function, you can prepare the following remedy: place 10 bay leaves in a thermos and pour boiling water over them in an amount of slightly more than one glass. After 24 hours, take one glass (50 grams) three times per day half an hour before sitting down at the table. The course of treatment is 14-21 days;
- The pumpkin stalk will help reduce sugar levels to normal. For one part of the stalk you need to take five parts of distilled water. Boil for a few minutes, strain and drink the decoction one glass 1-3 times a day;
- Diabetes can also be treated with wormwood. You need to take dry crushed wormwood herb in the amount of 2 tbsp. l., place in a small glass container and pour in 100 ml of vodka. Close the dish with a lid and put it in a dark place for 8 days. After this time, shake, squeeze out the wormwood herb, and store the infusion itself in a bottle in a dark and cool place, tightly closed. Drink 15-25 drops before meals 3 times a day;
- dry linden flowers in the amount of 2 tablespoons, pour 2 cups of boiling water. Set aside for half an hour, then strain. Drink at any time of the day or night instead of tea;
- take dry crushed knotweed herb in the amount of 20 g, brew with 1 glass of boiling water and leave for a quarter of an hour. Then strain and drink 1 tbsp. l. three to four times a day.
Other traditional methods of treating the disease
Treatment of the pancreas with folk remedies is used to improve the performance of this organ without causing harm to the body. The pancreas is an internal secretion organ that produces insulin and enzymes for the complete digestion of food entering the body.
Most often, disruption of the pancreas is caused by chronic or acute pancreatitis, as well as diabetes mellitus.
Pancreatitis is diagnosed with complete or local inflammation of the pancreas. The causes of the development of the disease can be a variety of factors, including blockage of the bile ducts due to gallbladder disease, severe poisoning with alcohol-containing drinks, trauma to the pancreas, infectious diseases, and connective tissue disorders.
Any dysfunction of the pancreas causes the development of diabetes mellitus. Most often, the disease occurs due to obesity, atherosclerosis of the vascular system of the pancreas, and also due to the presence of a hereditary predisposition. The main symptom of pancreatic disease is a constant dry feeling in the mouth.
How to treat a disease with traditional methods
Well-known folk remedies will help cleanse the pancreas and blood vessels from stagnant cholesterol and accumulated harmful substances. Since ancient times, folk recipes have been used to treat diseases in gentle, effective ways. Such treatment methods in some cases have a much greater effect than traditional medical treatment.
In order for the folk method to be effective, it is necessary to adjust the diet and adhere to the therapeutic diet prescribed by the doctor. If the pancreas is diseased, the menu excludes foods containing sugar, sweet, fatty, fried and spicy foods, and alcoholic drinks.
Meals should be balanced, frequent, but in small doses, since overeating is not allowed. Buckwheat and oatmeal porridge are especially recommended for use in food.
It is also necessary to completely stop smoking.