Home Diseases and treatment Gastroenterology
10 Feb 2021, 20:02 Anna 864 No
Sometimes, when examining the pancreas, you can notice that the organ is deformed. If this happens, then the treating doctor should pay attention to this and find out why the pancreas has changed its shape.
What forms of pancreas are there?
First, let's figure out what shape the pancreas should be normally.
This depends on the individual characteristics of the body, such as: the location of other organs relative to the pancreas, their shape and size. If one of the organs is deformed, this leads to deformation of the pancreas. It may become angular or oblong.
It is worth noting that another difference of the pancreas is that it can change its location depending on the person’s posture.
The pancreas moves downwards if a person is standing and moves towards the back if a person is in a lying position. At the same time, the organ itself does not suffer, since it has the property of collapsing without any consequences.
In children, the pancreas has its own characteristics. It happens that a child experiences diffuse changes in an organ, and there is nothing to worry about. Over time, as the child grows, the pancreas will go through certain stages of deformation, but these are temporary processes. Eventually it will take its shape.
Location
This organ is an elongated formation located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach, next to the duodenum.
The length in adults reaches up to twenty-two centimeters, and the width in the head area is up to nine. The mass of the gland is from seventy to eighty grams.
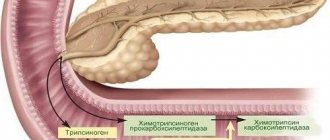
Important. The area of the gland adjacent to the duodenum is called its head. The duodenum goes around it like a horseshoe.
The body of the gland is separated from the head by a specific fold in which the portal vein is located, collecting blood from the intestines, spleen and stomach and directing it to the liver.
Next, after the head, the APPD region (accessory pancreatic duct) begins. This duct in most people connects with the main duct, and only in forty percent of cases with the duodenum through the MDS (small duodenal papilla).
However, it is still impossible to say unambiguously what shape the iron has. Some deviations from the classical form of this organ are common and are not pathological. It is worth noting that the organ moves slightly when the body position changes. So, if a person is lying down, then the gland will move a little lower, and if he is standing, then the shift will occur towards the back, i.e. deep down.
We also recommend viewing: PSA level for prostate cancer: diagnostic rules and norms of indicators
Sometimes a person is faced with a pathological process such as gland deformation. Like deformation of any organ, such a change can lead to serious consequences for the body. Therefore, it is important to know what kind of condition this is - deformation in the pancreas and how to diagnose it.
The pancreas is capable of not only changing its location, deviating from the initial position when the body moves, but also arching and also slightly shrinking. This change in its shape is physiological and is not a pathology. Therefore, any curvature of this organ of the digestive system should be considered a variant of the norm.
Important. Pancreatic curvature is often diagnosed in children. However, with age, this phenomenon disappears without a trace.
What are the possible causes of deformation of the pancreas?
Experts classify the causes of pancreatic bending as follows:
- Cystosis. The cyst will be visible on ultrasound as a darkening. This process is not a symptom of the disease. This is a reason for the patient to undergo a full examination, because it is necessary to understand what processes are disrupted in the body.
- Pancreatitis of acute and chronic forms. With this disease, it is important to start treatment in a timely manner, since in this case the organ not only stops deformation, but also regains its previous shape.
- With pancreatitis, there is a bend at an angle with an upward displacement. This causes the patient to experience vomiting and nausea, accompanied by high fever and pain in the left hypochondrium.
- Tumor formation. This process can be detected using ultrasound, which shows deformation and an increase in the size of the organ.
- Abdominal trauma. A possible cause of deformation of the pancreas may be a strong blow.
The following diseases can also cause changes in the shape of the pancreas: diabetes mellitus, obesity, cystic fibrosis, diseases of the gallbladder and duodenum and various infectious lesions.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the gland is a rather complex process, because... it is located deep in the area behind the peritoneum. The palpation method is not suitable for this organ in most cases. This becomes possible only if it is increased excessively.
If a patient has acute pancreatitis, changes in the gland are identified based on his complaints and a list of laboratory tests. In this case, the following are diagnosed:
- urine,
- blood,
- cal.
For a more in-depth analysis of the tissues of this organ, hardware diagnostics are used:
- fibrocolonoscopy;
- ultrasonography;
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography;
- esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Most often, for this disease, doctors prescribe an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and the area behind the peritoneum. However, research does not always end there. There are cases when the patient’s tests are normal, but no special clinical signs are detected. Then, in addition to ultrasound, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CT (computed tomography) are prescribed. When the doctor believes that there are neoplasms in the tissues of the gland, he prescribes an MRI and histological examination.
Important. In addition, when the lumen of the duodenum is compressed by pancreatic tissue, endoscopy is prescribed.
Symptoms
Typically, pancreatic deformity does not cause any symptoms. If the organ is strongly bent, malaise and discomfort may occur. This may manifest itself as a result of functional disorders in the organ and in the digestive processes in general.
The following symptoms may appear:
- increased body temperature;
- frequent abdominal pain spreading to the back area;
- nausea, vomiting, belching;
- abdominal muscle tension;
- diarrhea, constipation;
- increased gas formation.
Is organ deformation dangerous?
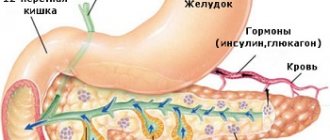
The pancreas plays an important role in the functioning of the body. It performs endocrine and exocrine tasks, is responsible for digesting food and synthesizing enzymes.
Having noticed a pathology on an ultrasound, in particular deformation, you must immediately undergo a full examination in order to exclude, and possibly prevent, serious disorders and complications.
The pancreas is unique. Its size and shape vary from person to person. This is influenced by the position of adjacent organs, due to which it can become angular, elongated or more rounded. No less surprising is the ability of the gland to change its position. If you stand, it moves closer to your back, and if you lie down, the gland will be under the stomach from below, hence its name - pancreas.
Thanks to such skills of stretching and changing position, organ tissues “know how” to bend, straighten and even curl. All this data is normal.
Deformation or bending, as doctors more often call this phenomenon, is mostly temporary and therefore does not cause any particular concern. If you have been diagnosed with a bend, perhaps after some time during a second ultrasound, it will no longer be there. For example, it is quite common in children and adolescents. The bend disappears during the process of growth and development, and the gland acquires a more elongated shape over time.
The only concern is when the pancreas becomes ring-shaped and thus compresses the duodenum. To be fair, we note that this is extremely rare. The pathology is accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system.
Curvature of the pancreas in children
Genetic predisposition, poor nutrition and other reasons can cause deformation of the pancreas in children. If a bend in the organ is detected, then there is no need to be upset. We have already said above that this process may be an age-related feature. But, despite this fact, it is necessary to undergo a full examination of the body. This is necessary in order to exclude the possibility of developing any disease, or, conversely, to diagnose the disease in time and prevent the development of complications. For treatment, first of all, it is necessary to choose the right diet, follow the recommendations of the attending physician and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Forms of indolent pancreatitis
The disease can be primary or secondary. In the first case, the abnormal process begins directly in the pancreas. In the second option, the pathology is diagnosed due to diseases of nearby internal organs - the gallbladder, stomach, etc.
The causes of the primary disease include alcohol dependence, genetic predisposition, drug intoxication, long-term smoking, constant stress and neuroses.
The etiology of the secondary disease is caused by pathologies of the gallbladder (cholecystitis with the formation of stones), cirrhosis of the liver, chronic forms of hepatitis, parasitic diseases, cystic fibrosis (a congenital disease accompanied by damage to the exocrine glands).
According to Loginov, depending on the clinic, chronic pancreatitis can be:
- Recurrent form. This disease is characterized by periods of relapse of the disease, which are followed by periods of remission.
- The painful form is accompanied by constant painful sensations.
- Pseudotumor form. The main clinical sign is obstructive jaundice.
- Painless or latent form. Exocrine insufficiency is most often diagnosed, and intrasecretory insufficiency is somewhat less common.
- Sclerosing pancreatitis. This disease is accompanied by severe failure of the internal organ and develops along with other pathologies.
In accordance with the Marseille-Roman classification, the disease is of the following types:
- Calcifying form. The disease occurs with the development of protein plugs or stones in the gland ducts. It is observed in approximately 50-85% of all clinical pictures. In turn, it is divided into subgroups. In the first case, regular solid crystals are formed, the etiology is due to bad eating habits and alcohol intoxication. In the second option, soft stones, formation is based on heredity.
- Obstructive pancreatitis is accompanied by obstruction of the pancreatic ducts or a tumor.
- Inflammatory form. There is fibrosis of the gland.
- Pseudocysts or true cysts (cystic form).
In accordance with Loginov’s classification, sluggish pancreatitis has several degrees of severity - mild, moderate and severe.
Treatment of the disease
Symptoms and treatment are closely related to each other. Therapy begins after a person consults a doctor with complaints or a pathology is accidentally discovered during a routine examination. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the disease. After normalization of the condition, the pancreas will take its usual shape. For treatment, medications, proper diet, and food enzymes are used.
Medicines
Drug treatment is used for acute and chronic lesions. If a doctor has diagnosed a person with pancreatitis, the following classes of medications may be needed:
- painkillers;
- enzyme agents;
- inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes.
Your doctor will be able to draw up a specific treatment regimen. The specific medicine, dosage, and duration of use are selected individually. If pancreatitis is not treated in time, it can seriously deform the pancreas.
Phytotherapy
The use of herbal medicine is advisable if the pathology is not serious. It can improve digestion and relieve inflammation of the gland. This way you can treat the identified bend. The following herbal remedies are used:
- Rosehip infusion. Pour 20 g of rose hips into 150 ml of boiling water. Drink the resulting infusion throughout the day, dividing it into 3-4 doses. Rose hips reduce the severity of inflammation, strengthen the immune system, and supply the body with vitamins.
- St. John's wort decoction. Pour a tablespoon of dry St. John's wort into 300 ml of boiling water. Then continue boiling for 5 minutes. St. John's wort is taken 1-2 times a day before meals in small quantities. Helps relieve inflammation and pain.
The ingredients are purchased at the pharmacy.
Before using herbal medicine, consult with the treating gastroenterologist.