04/15/2019 Alena Masheva Health
Gastrointestinal diseases are gradually becoming the most common in the modern world. And this is not surprising - fast food and snacks on the go are popular, and unhealthy food is sold in supermarkets. Diseases such as gastritis or ulcers are popular today. But symptoms of reflux esophagitis are no less common. According to statistics, millions of people in the Russian Federation suffer from it.
This is the name given to the release of bile into the oral cavity, esophagus, and stomach. The disease progresses quite quickly and leads to dangerous complications if it is not treated in time. Therefore, it is necessary to know the symptoms of this disease, its causes, and treatment methods.
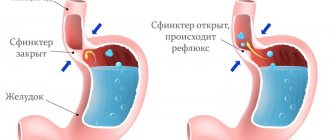
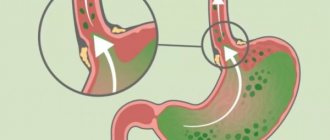
Movement of bile in the body
The release of bile into the oral cavity is a physiologically abnormal phenomenon. But why is this happening?
Bile is produced by the liver. Then it rises into the gallbladder with the help of the sphincter of this organ due to contraction of the bile ducts. Accordingly, bile accumulates in this bladder. As soon as a person begins to eat, it enters the stomach through the sphincter of Oddi. Juices and bile mix in the stomach, and the digestion process begins.
But as a result of certain factors, the sphincter of Oddi relaxes. They can cause the following: removal of the gallbladder, liver dysfunction, dyskinesia of the bile ducts. As a result of this, the discharge of bile into the stomach no longer depends on impulses emanating from the brain. The sphincter begins to contract voluntarily. Then the release of bile into the stomach and further into the esophagus and oral cavity occurs. Injuring the mucous membranes of these organs, which are not intended for contact with bile.
Symptoms of bile reflux into the esophagus
In the early stages, the disease is not noticeable to a person and does not manifest itself in any way; it can only be detected during a routine examination. As this condition progresses, clinical signs will become noticeable.
If you detect even mild and intermittent signs, it is better not to wait for self-cure (of course, if bile reflux is not associated with pregnancy), but to seek medical help. With early diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe treatment that will be more effective than in advanced cases.
Possible signs that may indicate bile reflux into the esophagus:
- heartburn - a strong burning sensation is felt in the stomach and behind the sternum. Most often occurs after meals or at night;
- Incessant hiccups are another common symptom. Most often appears when the stomach is full;
- the pain is moderate, similar to heart pain, but occurs after eating. Severe pain occurs with serious changes in the gastric mucosa - ulcers, erosions and atrophies;
- belching with a bitter or sour taste, which happens even with little physical activity, overeating or stress;
- vomiting with bile occurs already in the later stages and indicates serious pathological disorders in the digestive tract;
- also in the later stages, a narrowing of the food tube appears, which is expressed by the sensation of a foreign body;
- tooth enamel deteriorates;
- persistent cough.
If signs appear, there is no need to postpone a visit to the doctor; inaction in this case can lead to attacks of angina and tachycardia, and to the formation of adhesions in the esophagus. These adhesions can subsequently lead to cancer of the esophagus or stomach.
What is reflux?
The release of bile into the oral cavity is a pathological condition. But reflux in itself is not such. This is the name for the processes of moving the contents of one hollow organ to another, but in the direction opposite to the normal physiological one. Hence, reflux can be observed not only in the digestive system, but also, for example, in the genitourinary system.
However, most often people experience symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. What does it mean? The contents of the stomach are thrown back into the esophagus and then into the oral cavity. During normal functioning of the body, this should not happen: food passes along the reverse path - from the oral cavity through the esophagus to the stomach.
To prevent gastroesophageal reflux from occurring, our body has a special organ - the lower esophageal sphincter. It contracts after food passes into the stomach and prevents it from returning.
Folk remedies
Folk recipes will help reduce bile formation, restore the esophageal mucosa, and eliminate signs of gastrointestinal dysfunction:
- To reduce acidity, you should take 300 ml of a mixture of cream, tomato juice and milk in equal proportions with meals.
- In order to improve the flow of bile from the stomach and restore the walls of the organ, you need to eat flaxseed porridge in the morning. To prepare it, you need to pour half a glass of seeds with 300 ml of water and wait for swelling.
- Herbal medicine should be supplemented by following dietary table No. 1. Proper nutrition eliminates negative symptoms and facilitates the course of the disease.
Pathological and non-pathological reflux
Reflux will not be pathological if some of the stomach contents flow back into the esophagus. Here it is called belching. A person may encounter this phenomenon, for example, after a hearty lunch. But if the release of bile or stomach contents into the oral cavity occurs regularly, this is a reason to be wary.
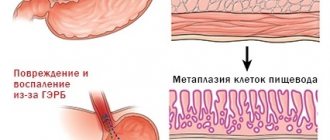
The delicate mucous membranes of the esophagus and oral cavity are damaged from contact with bile and gastric juice. Systemically repeated reflux causes inflammatory processes in them. This syndrome, in which damage to the esophagus is observed due to the regular reflux of stomach and duodenal contents into it, is called reflux esophagitis. Or GERD - gastroesophageal reflux disease, when bile and gastric juices cause ulcerative, erosive damage to the mucous membranes, and the development of their inflammation.
Calling this disease simply reflux is incorrect. After all, it can also be non-pathological - in the form of rare belching. According to statistics, GERD most often affects adults. Moreover, men suffer from reflux esophagitis 2 times more often than women.
If treatment is not started on time, then as a result of such an aggressive effect on the esophagus, its functional epithelium begins to be replaced by a cylindrical analogue. The patient is diagnosed with Barrett's esophagus. And this is already a dangerous precancerous condition.
Symptoms of the disease
The initial stages of the disease are mostly asymptomatic. The patient feels minor discomfort, but does not associate it with the occurrence of a serious illness. Due to the structural features of a person, such a symptom as the release of bile usually occurs with cholecystitis, pancreatitis, and duodenitis.
Symptoms of the disease are:
- Bitter taste in the mouth. When the bile ducts are blocked, their contents do not enter the duodenum and begin to penetrate the walls of the organ. Accumulated bile causes a bitter taste in the mouth, which is felt in the morning, before eating. This sensation is a sign of bile reflux.
- Vomiting bile. Abuse of fatty foods and alcohol leads to negative consequences in the form of nausea and vomiting, especially in people with gastrointestinal diseases. The appearance of nausea, vomiting mixed with bile, and diarrhea after a feast should make the patient think about why there is a malfunction in the body and begin an examination.
- Stomach pain. The walls of the stomach have many nerve endings, so when any gastrointestinal disease occurs, the patient feels pain in the abdomen.
- An alarming symptom is stomach pain, hyperthermia and belching, which can occur even from a small amount of food and indicates an inflammatory process.
- Bitter belching. Bile can back up into the esophagus during sleep, when the ducts and gallbladder are relaxed. Bitter belching indicates stones in the gall bladder, and this requires urgent medical attention to avoid complications.
- Heartburn. A burning sensation occurs as a result of gastric juice entering the esophagus. This symptom can easily be confused with heart disease, so if it occurs, you should promptly seek help from a specialist. In addition, thirst is a common symptom of bile release.
- Bile leakage can occur even in completely healthy people. Most often after alcohol abuse and overeating. However, in a calm state this rarely happens, and if heartburn occurs repeatedly, this indicates a pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
When the first symptoms occur, you must consult a specialist, undergo diagnostic tests and determine the cause of the disease. An accurately established diagnosis will allow you to prescribe adequate treatment.
Why is this harmful?
The release of bile into the oral cavity at night or during the day is a physiologically abnormal phenomenon. After all, the mouth and esophagus are intended only for eating food, and not the contents of the duodenum or stomach.
The only exception here is vomiting. They are not reflux in nature. This is an emergency measure when the stomach needs to be cleansed of toxic contents. Thus, it saves the entire body, preventing the intestines from absorbing harmful substances from this mass into the blood.
Hydrochloric acid, bile, and pancreatic secretions are aggressive in nature. They need to break down food. Accordingly, only the mucous membranes of certain organs of the gastrointestinal tract can withstand their effects. To avoid damaging other tissues of the body, the lower digestive sphincter works. It prevents the stomach contents from rising back up. But for a number of reasons it cannot always fulfill its functions.
Non-pathological causes
As gastroenterologists who give advice to patients say, the reflux of bile into the stomach is not always pathological. Let's consider the most common causes of this process that do not require treatment:
- Violation of the usual diet. Eating large amounts of foods that stimulate increased bile secretion - fatty or smoked foods, strong tea or coffee.
- Abuse of highly carbonated drinks.
- A side effect from taking certain medications. In particular, relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter.
- Addiction to tobacco.
- Alcohol consumption.
- Severe stressful situation.
- Involvement in vigorous physical activity immediately after a heavy snack.
- Overeating before bed.
- Pregnancy.
- Adopting an uncomfortable sleeping position when you squeeze the organs of the digestive tract. Therefore, reflux of bile into the esophagus often occurs at night.
Causes
Before we look at the causes of bile reflux into the stomach, let's dive a little into biology and talk about how food moves through the esophagus. Once food enters the human body, it always moves downward. The exception is the body's defense mechanism, called vomiting, which allows you to urgently get rid of toxic substances.
In the digestive tract there are special muscle valves - sphincters, which are responsible for ensuring that food moves only in one direction - down. However, in certain disorders of the body, these muscles can relax under pressure and the contents of the intestines can move in the opposite direction. At each stage, food is exposed to certain chemicals that, once in earlier parts of the digestive system, can cause irritation and even damage to the mucous membrane.
Possible reasons:
- Pregnancy. The embryo located in the mother’s body begins to put pressure on the internal organs as it grows. Under such pressure, the sphincter muscles can relax.
- Congenital pathologies and defects.
- Acquired defects (hernias, injuries, neoplasms).
- Complications after surgery, during which the sphincter muscles could be affected.
All of the above reasons are in one way or another related to damage to the sphincter, but bile reflux does not always occur because of this. There are other risk factors that can provoke this phenomenon:
- obstruction in the digestive tract;
- lack of diet (irregular meals, dinner before bed, etc.);
- binge eating;
- physical activity immediately after eating;
- inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- drinking large amounts of liquid during meals;
- regular consumption of foods that reduce sphincter contractility (tomatoes, chocolate, coffee drinks).
Pathological causes
What to do if bile is released into the oral cavity? If you suffer from this systematically, then you need to urgently contact a gastroenterologist. After all, this phenomenon causes quite serious pathological reasons:
- Obesity of the second or third degree.
- Enterocolitis of various origins, causing bloating.
- Dyskinesia of the bile ducts.
- Pyloric insufficiency.
- A hiatal hernia in the lower esophagus.
- Ascites with damage to the respiratory organs or cardiovascular system.
- Pathological processes affecting the duodenum.
- Diseases of the intestines, stomach, and other organs of the digestive tract. Common causes here are gastritis and peptic ulcers (for example, small intestinal ulcers).
- Chronic constipation.
- Duodenal obstruction.
- Pathologies of the vagus nerve.
- Benign and malignant tumors.
- Infectious diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
- Chronic pancreatitis or cholecystitis.
- Hereditary predisposition.
Diagnosis of pathology
Like almost any examination, it all begins with collecting an anamnesis, carried out during communication with the patient. The doctor listens to complaints, determines how long the problems bothering the patient last, and how pronounced the symptoms are.
Video - History
Then, to determine the cause of bile entering the upper parts of the stomach and esophagus, a series of instrumental and hardware studies are carried out.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy shows the presence of bile in the lower esophagus.
- Ultrasound of the stomach helps to detect the presence of bile in it.
Ultrasound of the stomach
- An ultrasound of the abdominal cavity can show abnormalities of the internal organs that caused the formation of reflux.
- Analyzes of biological substances secreted by the body will help determine the presence of inflammatory and other pathological processes.
- Choledochoscintigraphy shows how normally the muscle valves contract.
- Additionally, the tone of the gallbladder can be examined.
To detect bile reflux esophagitis, the tone of the gallbladder can be examined.
Based on all the data, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed, which is necessarily accompanied by a diet.
Symptoms
The fact that inflammatory processes in the esophagus have begun, caused by bile reflux, can be recognized by the following characteristic symptoms:
- Heartburn. You have a feeling that there is something baking and burning behind your sternum, “in the pit of your stomach.” An unpleasant sensation rises from bottom to top. Most often it appears at night, after sudden movement.
- Bitterness in the mouth paralleled by a burning sensation in the larynx. Again, the feeling increases after a sudden movement, tilt, when moving the body to a horizontal position from a vertical one and vice versa.
- Vomiting after eating. Bitter taste of vomit.
- Feeling of severe pain in the diaphragm area.
- Hiccups after eating.
Reinforcement of therapy - proper nutrition
Proper nutrition - prevention of gastrointestinal diseases
To consolidate the positive effect after treatment, the patient must carefully monitor his diet and lifestyle. In other words, to prevent a recurrence of the disease, it is necessary to follow a diet, eat small meals (eating small portions throughout the day - 5-7 times a day) and give up bad habits. Excessively spicy and fatty foods must be completely excluded from the diet.
You should also avoid fried and smoked foods. Today, there are a lot of recipes for delicious and healthy food that is steamed or boiled. Nutritionists have developed dozens of diets that can prevent the reflux of bile into the esophagus.
Tips for proper nutrition from a gastroenterologist
Doctors recommend that people who suffer from this disease change their diet as follows:
- Vegetable proteins should be present in large quantities in the daily diet
- reduce the amount of animal proteins as much as possible
- add vegetable fats to food - olive, sunflower or corn oils (preference should be given to unrefined virgin oils)
- It is advisable to reduce the consumption of sweets to a minimum; the lack of sweets can be replaced with juices and fruits
- fermented milk products are excluded from the diet, as they significantly increase acidity in the stomach
- refusal of semi-finished products
- Avoid eating dry food and visiting fast foods
By following these tips, there is a high probability that you will never have bile reflux into the esophagus.
Read along with this article:
- Why does bile reflux into the stomach?
- How to treat gastroduodenal reflux? What are the treatments?
- Acid in the mouth: causes, how to eliminate
- What can cause bitterness in the mouth? Possible reasons,…
- How to treat reflux esophagitis: drug treatment and…
- What gastroscopy shows: everything about the procedure
- Stool analysis for Helicobacter pylori: features of the procedure
- What does an ultrasound of the esophagus determine and how to prepare for it?
- Gastroscopy: how to prepare for the stomach examination procedure correctly
Possible complications
According to the advice of gastroenterologists, when bile is thrown into the stomach, you should under no circumstances wait for this condition to worsen. The disease that caused it will not go away on its own, but will only continue to progress. This is fraught with the following:
- Attacks of angina and tachycardia.
- The appearance of adhesions on the walls of the esophagus due to its constant irritation by bile.
- Replacement of the normal mucous lining of an organ with scar tissue.
- All changes in the lining of the esophagus can provoke the development of cancer of both it and the stomach.
Therapy scheme
The reflux of bile into the esophagus cannot be ignored!
There is no point in ignoring such a problem as the reflux of bile into the esophagus. In addition to the fact that a person experiences discomfort, this disease can also become a springboard for the development of other diseases. Considering these facts, it is necessary to undergo a full diagnosis, identify the causes and decide on a treatment regimen. In modern realities, treatment can be carried out either conservatively or through surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
This type of treatment involves the complete neutralization of bile, as an irritant to the mucous organs. The following medications may be prescribed for this:
- Maalox
- Domperidone
- Papaverine
- Metoclopramide
- Drotaverine
The purpose of a particular drug, as well as the dosage, is determined exclusively by a medical specialist.
Surgical intervention
Considering that the reflux of bile into the esophagus can occur due to a hernia or tumor that compresses the duodenum, the doctor may decide on surgical intervention. During the operation, the cause that contributes to the reflux of bile is surgically removed. The decision for surgical intervention is made by the endocrinologist based on the diagnostic examinations and tests performed.
Diagnostics
If you constantly notice the reflux of bile into your esophagus, you should make an appointment with a therapist or gastroenterologist. To confirm the diagnosis of reflux esophagitis, the patient is prescribed FGS. With this diagnostic procedure, you can immediately determine the presence of bile in the stomach and take a fragment of the mucous lining of the organ for examination for a biopsy.
In some cases, an additional endoscopic examination is prescribed. The following diagnostic procedures may also be needed:
- Echography.
- Ultrasound examination.
- Ultrasonography.
- Carrying out radiography with a dye.
Causes of the disease
The factors causing the constant reflux of bile into the esophagus are internal (physiological) and external (nutritional) reasons.
Internal:
- stomach pathologies: reflux esophagitis, gastritis, ulcer;
- chronic inflammation of the duodenal mucosa;
- gallbladder disease;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- structural features of the sphincter between the stomach and duodenum;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- oncological neoplasms in the abdominal cavity;
- obesity;
- pregnancy.
External:
- unbalanced diet;
- drinking water at the same time as eating;
- dry food, snacks;
- binge eating;
- tobacco and alcohol abuse;
- long course of taking painkillers and analgesics;
- playing sports after eating;
- lifting heavy objects;
- uncomfortable posture during sleep;
- stress;
- passive lifestyle.
Directions of treatment
In most cases, therapy is medicinal and conservative. The goals of reflux treatment are as follows:
- Protection of the mucous membranes of the esophagus from aggressive influences.
- Neutralization of aggressive components of gastric juice and bile.
- Increased speed of passage of a bolus of food through the esophagus.
- Increased tone of the pylorus (lower esophageal sphincter).
- Increased activity of the cardiac gastric zone.
Surgical treatment is used only in difficult cases:
- Correction of complex complications causing bile reflux. For example, hiatal hernia.
- Cases when the disease has reached its final stage. When diagnosing Barrett's esophagus.
Causes of pathology
Normally, digestive processes occur in the human body only from top to bottom. The exception is the gag reflex, which allows you to clear the stomach of toxins. The sphincter allows you to avoid the reverse movement of masses along the esophagus. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract may occur.
Reasons for the reflux of bile into the stomach, which do not cause serious consequences requiring therapy:
- poor nutrition, abuse of smoked meats, canned and fatty foods, tea and coffee, carbonated drinks;
- smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- uncomfortable body position during sleep;
- long-term use of pharmacological agents;
- bending over and lifting heavy objects after eating;
- overeating, especially during pregnancy.
Conditions that require specialist help:
- dysfunction of the pylorus of the stomach;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- pathological changes in the duodenum;
- moderate and severe obesity;
- hiatal hernia;
- enterocolitis of various origins with intestinal bloating;
- ascites in diseases of the heart and respiratory system;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pharmacotherapy for such pathologies does not always help; in many cases, surgical intervention is necessary. Before treating a pathology, it is necessary to eliminate, if possible, the causes that caused it. Sometimes the reflux of bile into the stomach occurs in practically healthy people.
Drug therapy
In most cases, the conservative treatment regimen consists of taking the following drugs:
- Proton pump inhibitors. These are drugs such as Omez, Gastrozol, Ranitidine, Pepticum.
- Antacids (protect mucous membranes from damage, reduce the secretion of secretions by the gastrointestinal tract). "Almagel", "Maalox", "Gastrofarm".
- Selective drugs that enhance evacuation functions and accelerate the flow of bile. These are Cisapride and Motilium.
- To eliminate bitter belching and normalize bile secretion, use Ursosan, Ursofalk, Ursoliv.
- To relieve the patient of pain, doctors prescribe well-known antispasmodics (painkillers). These are “Baralgin”, “No-shpa”, “Spazmalgon”. In particular, they are prescribed as injections to reduce stress on the stomach.