Field of activity
So, let's figure out what a gastroenterologist does? What does it cure? It should be noted that the doctor observes all organs that take part in the digestive process.
Unfortunately, today a gastroenterologist is one of the most sought-after doctors. Because many reasons can bring a patient to the doctor’s office. Let's look at them:
- Stomach diseases. A gastroenterologist treats peptic ulcers, gastritis, polyps, and cancer.
- Gallbladder diseases. People consult a doctor with cholecystitis. This is a large-scale inflammation of the bladder. As a result, digestive functions are significantly impaired. The doctor also treats biliary dyskinesia. The disease is characterized by decreased patency and mobility of the ducts. In this case, dyskinesia is not an inflammatory, but a somatic phenomenon. As a result, the patient’s digestive processes in the body may become difficult and even stop completely. The patient experiences a significant deterioration in health.
- Diseases of the pancreas. As a rule, in most cases the doctor is faced with pancreatitis. This disease is an inflammation of the pancreas. It is characterized by a delay in the production of digestive enzymes in the gland. Subsequently, these processes lead to the destruction of the pancreas. Often such a disease goes from an acute form to a chronic one.
- Diseases of the spleen. The doctor treats cysts and tumors of this organ. And other pathological conditions of the spleen are included in the specificity of the doctor.
- Intestinal ailments. Patients with various inflammatory processes in this area are referred to a gastroenterologist. These are colitis, duodenitis. A gastroenterologist also treats dysbiosis. This is a disease that provokes a change in the composition of the intestinal flora. They also consult a doctor if they have enterocolitis or parasitic infestations.
Gastroenterologist – who is he and what does he treat?
A therapist (pediatrician), gynecologist or nutritionist can refer you to a doctor of this specialty for advice on a matter in which they are not competent. But patients still have an open question: who is a gastroenterologist and what does he treat? Today this profession is in demand. According to statistics, the prevalence of digestive diseases is increasing, up to 95% of the world's population needs medical supervision, both children and adults from young to old. What does a gastroenterologist treat? These are diseases associated with:
- stomach (polyps, gastritis, peptic ulcer, etc.);
- gallbladder, including cholecystitis;
- spleen (tumors and cysts);
- intestines (dysbacteriosis, colitis, invasions, etc.);
- pancreas (pancreatitis).
When should you visit a gastroenterologist?
Unfortunately, gastrointestinal diseases are quite common today. Therefore, gastroenterology is one of the most widespread areas of medicine. At the same time, patients of doctors in this area are people of all ages. Indeed, often even infants need consultation from a doctor such as a gastroenterologist. What does the doctor treat for babies? Of course, dysbiosis is relevant for infants.
When should you seek help from this specialist? As a rule, a patient’s visit depends on many reasons, the main one of which is the patient’s well-being. While the symptoms are not very pronounced, a visit to the gastroenterologist is postponed. And only when there are obvious signs of illness that affect the overall well-being and quality of life, the patient comes to the doctor.
Any discomfort associated with the gastrointestinal tract requires attention. This may be heaviness, pain in the stomach or intestines, frequent constipation, bloating and other similar circumstances.
Who is a gastroenterologist
A gastroenterologist is a doctor who specializes in the problems of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and belongs to the specialization of gastroenterology. Specialists of this profile see patients in clinics for adults and children, and work in hospitals and clinics.
Patients often shorten the name of the specialization to the short word “gastrologist,” meaning an expert on gastritis, although the doctor’s competence includes problems and diseases of many digestive organs. In gastroenterology, narrow areas are distinguished.
When a visit to the doctor should not be postponed
If we talk about symptoms, then there are a number of signs, the occurrence of which requires contacting a gastroenterologist.
These reasons include:
- frequent occurrence of heartburn after eating;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- unpleasant belching (often occurs after eating);
- odor from the mouth;
- pain, heaviness in the stomach, nausea (appears before eating and disappears after it);
- bowel dysfunction;
- frequent occurrence of pain in the hypochondrium, intestines, stomach;
- diabetes;
- non-infectious skin rashes, peeling, eczema, causeless deterioration in the condition of hair, nails, skin;
- unusual color of feces, vomiting (this symptom requires immediate medical attention).
People who have been treated with medication for a long time should not neglect consulting a doctor. It is recommended that patients undergoing radiotherapy or chemotherapy see a doctor.
Appointment with a gastroenterologist
Gastrointestinal diseases are common among people of all ages, so a gastroenterologist can be both an adult (general specialist) and a pediatrician - he helps to cope with dysbiosis and spasms in infants, and digestive pathologies in older children. You do not need to undergo any tests in advance; a specialist will find out everything you need and issue a referral for the necessary examinations. The doctor approaches each patient individually. A standard gastroenterologist appointment consists of:
- oral questioning of the patient (collecting anamnesis);
- inspection;
- subsequent diagnostics.
Appointment with a gastroenterologist - preparation
As a rule, there is no need to prepare for your initial appointment with a gastroenterologist. But some clinics require you to follow some recommendations: if possible, refrain from eating and drinking water, and do not clean off the white coating from your tongue, as it may be taken by the doctor for analysis. If you plan to conduct an examination of the stomach, colon or duodenum, doctors will personally and in advance tell you how to prepare for the examination: whether to go on a diet beforehand, take a laxative or do an enema. Otherwise, the gastroenterologist accepts clients according to the general rules.
How is an examination by a gastroenterologist performed?
At the first meeting, the doctor listens to the main complaints, finds out the causes of the ailment and tries to find out the provocateurs of the phenomenon. To diagnose pathologies, physical examination methods are used, the main of which is palpation, palpation of the abdomen in order to find the source of pain. When localization is found, the doctor may prescribe a set of additional studies that will either confirm or refute the diagnosis. Other methods included in the examination by a gastroenterologist: percussion (tapping) and auscultation (using a stethoscope).
What tests does a gastroenterologist prescribe during an examination?
Diseases diagnosed and treated by a gastroenterologist may require additional research. To identify various pathologies they are used
What tests does a gastroenterologist prescribe besides this? The most common, prescribed to both adults and children: urine and stool tests, general and biochemical blood tests. In addition, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent blood test (to detect Helicobacter pylori) may be required.
Diseases treated by a gastroenterologist
The list of ailments that fall under the competence of this doctor is quite extensive. It should be remembered that a gastroenterologist deals with all diseases related to the digestive system. What does the doctor treat?
We will try to provide the most complete list of ailments included in the specifics of this specialist:
- antibiotic-dependent colitis;
- achalasia;
- Whipple's disease;
- botulism;
- Crohn's disease;
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (gastrinoma);
- bloating;
- gastroenteritis;
- hemorrhagic colitis;
- gastroduodenitis;
- glucagonoma;
- intestinal obstruction (dynamic);
- dysphagia;
- dyspepsia;
- dysphagia lusoria;
- diarrhea, constipation;
- spasm (diffuse) of the esophagus;
- jaundice;
- insulinoma;
- intestinal lymphangiectasia;
- lump in the throat;
- acid reflux;
- sugar intolerance;
- ulcerative colitis (nonspecific);
- foodborne toxic infection caused by bacteria Clostridium perfringens and staphylococcus;
- regurgitation;
- membranous esophagitis;
- lazy bowel (colon) syndrome;
- liver steatosis;
- malabsorption syndrome;
- nausea, vomiting;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- tropical sprue;
- food poisoning (chemical);
- liver enlargement;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- peptic ulcer;
- celiac disease;
- excess vitamin A in the body;
- illnesses caused by salmonella, enterobacteria;
- esophagitis;
- enterobiasis;
- gastritis;
- Barrett's esophagus.
Who is a gastroenterologist and what is his type of activity?
A gastroenterologist is a specialist who diagnoses and treats pathologies of the digestive system and develops methods for the prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Typically, the initial appointment with patients of this kind is carried out by a therapist or pediatrician, who then decides which specialist to refer the patient to.
Today, a gastroenterologist is one of the most sought-after specialists, as the number of pathologies associated with disruption of the digestive glands and dysfunction of the digestive tube organs is growing. The reasons for this are low-quality food products, urbanization, poor ecology, dry food, semi-finished products and fast food dishes. Of considerable importance for the development and further normal functioning of the stomach and glands of the digestive system in children is high-quality food prepared from fresh products.
A gastroenterologist may have a narrower specialization.
- Surgeon-gastroenterologist. Treats diseases of the digestive system using surgical methods. Such diseases include umbilical and linea alba hernias, including the use of synthetic materials to prevent relapse. A surgical gastroenterologist also performs removal of the gallbladder, stopping gastrointestinal bleeding, and resection of the walls of the digestive tube.
- Pediatric gastroenterologist. Engaged in diagnostics and selection of treatment methods for young patients (from birth to 18 years). Most often these are diseases associated with gallbladder dysfunction, gastritis and ulcerative defects of the walls of the stomach and duodenum, congenital developmental anomalies (esophageal atresia, megacolon, anal atresia, congenital polyposis of the large intestine, and so on).
There are branches of gastroenterology that specialize in diseases of a more specific part of the digestive system.
- Hepatologist. Treats and diagnoses pathologies of the liver, biliary tract and gallbladder.
- Coloproctologist. Deals with the study of the normal structure, functions and pathological changes of the entire large intestine and rectum. After a detailed analysis of the patient’s condition, he prescribes the most suitable and effective treatment.
- Proctologist. A narrower specialty appeared not so long ago, as it used to be called coloproctology. A doctor of this profile treats diseases of the rectum (hemorrhoids, rectal prolapse, cancer, anal fissure, polyps, paraproctitis, congenital coccygeal cysts, and so on).
Specialists of this profile are constantly engaged in improving their specialization, gaining new knowledge on diagnostic methods, treatment of the most common diseases of the digestive system, therefore the science of gastroenterology has a strictly defined list of studies that are most valuable for science and practice:
- epidemiology of all diseases of the digestive system;
- study of the morphology of the relevant organs during the patient’s lifetime and at autopsy;
- causes of diseases (toxins, viruses, bacteria, protozoa, parasites, exposure to iatrogenic and mental factors);
- violation of other organs and systems due to pathology of the digestive tract;
- mechanisms for regulating the functioning of the digestive organs, their dysfunction in pathologies;
- methods of therapy and prevention of diseases;
- modern methods of diagnosing the digestive system;
- secretion of glands involved in the digestion of food, motor function of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of different parts (esophagus, duodenum and stomach, parts of the small and large intestines, rectum and perianal area).
The doctor's consultation
Having analyzed what diseases a gastroenterologist treats, we will consider modern diagnostic methods.
Doctor's consultation includes:
- Preliminary survey of the patient, detailed anamnesis collection.
- Examination of the patient with palpation of the abdominal wall.
- Diagnostics (ultrasound, FGDS).
- Taking tests (blood, stool, urine).
- Selection of effective treatment.
- Adjusting your diet. Selecting an appropriate diet.
- Constant monitoring and control over the progress of treatment.
Stages of medical consultation
Initial consultation with a gastroenterologist includes:
- studying the patient's history and complaints;
- examination and palpation of the organs that the patient complains about;
- referral for tests and necessary research.
The final diagnosis and selection of treatment methods are carried out after receiving examination data (second appointment with a gastroenterologist).
Since in most cases the gastroenterologist prescribes endoscopic examinations, before making an appointment with a gastroenterologist, you should clarify whether the examination can be carried out on the same day (the examination can be carried out by the same gastroenterologist, and this speeds up the diagnostic process).
It is also possible to have a preliminary consultation with a gastroenterologist online, during which you can find out what the disturbing symptoms may be associated with and what examinations are needed.
Diseases of the esophagus
Some of the common ailments with which patients come to see a gastroenterologist are:
- Hiatal hernia. With this disease, the natural valve located between the esophagus and the stomach does not function. The patient experiences pain in the hypochondrium. Often the symptoms are accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the mouth and belching.
- Dysphagia. Inflammatory and other pathological processes in the pharynx, larynx, oral cavity, and esophagus lead to difficulty swallowing.
- Esophageal ulcer.
How to prepare for an appointment with a gastroenterologist
All gastroenterologists must have an excellent knowledge of anatomy, understand the intricacies of the physiology of the digestive process, the symptoms of diseases, and understand modern methods of treatment and prevention. No special preparation is needed to see a gastroenterologist. Previously, before visiting a specialist, the patient was asked not to drink or eat, and also not to clean off the white coating from the tongue, which the doctor could take for analysis.
Before examining the stomach and intestines, you should follow a diet, take a laxative and do enemas. Doctors will inform you about all requirements separately.
Stomach diseases and duodenal diseases
The doctor's specialty includes many pathologies of the above organs. The following ailments are most often diagnosed:
- Duodenitis. A disease characterized by an inflammatory process in the duodenum.
- Gastritis. A disease in which the stomach lining becomes inflamed. This pathology seriously disrupts digestion. And this even affects the general well-being of the patient.
- Stomach or duodenal ulcer.
Quite often, various ailments are accompanied by an unpleasant aftertaste, belching, rumbling in the stomach, and abnormal bowel movements. It should be understood that all such signs signal a pathological process in the body. Therefore, it is imperative to tell your doctor about them.
Along with serious pathological processes, a gastroenterologist treats constipation and diarrhea. Consequently, it will allow you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms much faster and easier. Postponing the problem for later is fraught with serious consequences.
Ignoring frequent constipation causes very serious complications. In most cases, such patients are diagnosed with hemorrhoids. The fight against illnesses with such consequences becomes significantly more complicated. Because now it is not enough to get rid of just problems with stool. In this situation, the gastroenterologist treats hemorrhoids, as well as the main problem, which has been ignored for a long time. That is why you should not put off visiting a doctor, even if it is inconvenient to voice “ugly” symptoms to the doctor.
Types of diagnostic examination of the gastrointestinal tract
Methods for a comprehensive study of all organs and parts of the digestive system make it possible to identify the disease in the shortest possible time. Experts divide research methods into three large groups.
- Physical.
- Laboratory.
- Instrumental.
In the process of working with a patient, the doctor prescribes a particular examination.
Physical studies
Direct initial examination by a doctor, involving the use of various examination methods.
- Palpation, that is, palpation of the abdomen and organs located inside.
- Percussion is tapping to determine the boundaries of the location of organs.
- Auscultation involves listening to sounds made by the organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
An initial examination allows a specialist to identify organic pathologies, but does not allow a complete picture of the disease to be obtained. A more complete examination involves the use of laboratory and instrumental methods.
Laboratory research
What tests does a gastroenterologist prescribe when testing blood? It is important to determine the levels of certain substances and enzymes.
- Bilirubin in the blood indicates gastrointestinal pathologies associated with the outflow of bile.
- Increased concentrations of transaminases AST and ALT are observed in liver diseases.
- The gamma-GT enzyme indicates inflammation of the bile ducts and hepatitis.
- Amylase above normal indicates pancreatic disease.
A coprogram is a detailed examination of feces.
Instrumental diagnostics
Most instrumental diagnostic methods require special preparation from the patient.
Preparation for endoscopic examinations
All types of endoscopy are performed in the morning, on an empty stomach. Before the study, patients should not smoke, drink any types of liquids, or take medications. The endoscopy procedure is not painful, but it is extremely unpleasant. Irritation of the mucous membranes of the esophagus by the endoscope tube provokes vomiting.
We recommend: Endoscopist: who is it, what does it do and what is it for?
To reduce sensitivity, the doctor irrigates the patient’s throat with medications that reduce the sensitivity of the mucous membrane of the esophagus. If the patient is prone to an allergic reaction, then treatment with an antisthetic is not carried out.
After endoscopy, the patient should not drink or eat for 40 minutes. After the biopsy, you can only eat cold foods.
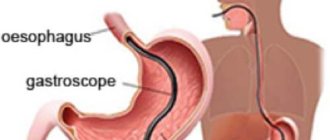
FGDS is a whole complex of studies of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum using a probe. And to study the lining of the rectum, a modern optical device, a sigmoidoscope, is used, which is inserted into the rectum for just a couple of minutes; anesthesia is not required.
When performing gastroscopy, the color, density, structure of the gastric mucosa is assessed, the presence of erosive defects is identified, the degree of swelling is established, and individual areas of the organ are examined for hemorrhages.
Capsule endoscopy is the most modern and advanced method of examination, in which the patient swallows a capsule with a miniature camera. As it moves through the gastrointestinal tract, the camera will transmit images through the computer. The capsule comes out naturally.
Laparoscopy combines the research process with therapeutic measures.
Radiation techniques
Study of the abdominal organs using x-rays and more informative fluoroscopy. Before the procedure, patients consume barium porridge, which is opaque to X-rays.
Liver diseases
The importance of this organ for humans is enormous. The liver performs more than 500 diverse functions in the body. And, unfortunately, to this day it has not yet been possible to reproduce its activity artificially.
Therefore, any pathology is a serious reason to consult a doctor. You can start visiting the clinic with a therapist. However, you should know that it is the gastroenterologist who treats the liver.
The most common are:
- Different types of hepatitis. This is inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis can be chronic or acute. As a rule, these ailments are characterized by a viral nature. Today, there are six types: hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, G. The disease becomes chronic if liver inflammation continues for six months.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
Diseases of the gallbladder and ducts
This organ performs an important function in the digestive process. The bladder maintains and regulates the pressure of bile in the ducts, promotes the digestion and absorption of fats, and takes part in the absorption of vitamins by the body. Its role in suppressing putrefactive microflora in the intestinal cavity is invaluable.
Timely contact with a gastroenterologist for various pathologies of the gallbladder and ducts allows for successful treatment using a conservative method. This makes it possible to avoid surgical intervention.
What diseases does a gastroenterologist treat? The following ailments often bring you to the doctor:
- Biliary dyskinesia.
- Cholecystitis.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Cholangitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Gallbladder polyps.
What diseases do gastroenterology specialists treat?
Specialists in this category treat the digestive tract. A person may have problems ranging from the esophagus, where chewed food ends up, to diseases in the rectum. The patient should contact this specialist if problems such as:
- pathology in the work of the sphincters, which are located between the border of the stomach and esophagus;
- diseases of the esophagus: the presence of polyps, achalasia, dilated veins in the esophagus, diverticula;
- diseases in the stomach: ulcers, gastritis, papillitis, erosion, tumors, polyps;
- diseases of the pancreas: pancreatic necrosis, pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, diabetes mellitus, cyst, oncology;
- pathology in the duodenum;
- diseases occurring in the spleen: cyst, abscess, malignant neoplasms;
- pathology of the rectum and anus;
- intestinal diseases: colitis, duodenitis, adhesions, enteritis, obstruction, ulcers, flatulence, tumors, worms, dysbacteriosis;
- various liver diseases, pathologies in the gallbladder and biliary tract: cholecystitis, hepatitis, Gilbert's syndrome, oncology, cirrhosis of the liver, curvature of the biliary tract.
Skin rashes
The inflammatory process occurring in the sebaceous gland and hair follicle is a common pathology. However, not every patient who is faced with this problem knows that it is often the gastroenterologist who treats acne.
After all, diseases of the digestive system lead to incomplete digestion of food and its stagnation. As a result, large quantities of toxins accumulate in the gastrointestinal tract. They enter the blood. It is known that the skin performs an excretory function in the body. Therefore, accumulated toxins, coming out through its cover, provoke the occurrence of acne.
Rashes can be a symptom of the following ailments and conditions:
- dysbacteriosis;
- constipation;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- stones in the bile ducts;
- gastritis (acute, chronic).
Giardiasis
An unpleasant disease caused by protozoa. The infection provokes an inflammatory process throughout the intestine. It is most pronounced in the small and duodenal intestines. Much less often, changes affect the large intestine or the appendix.
The degree of inflammation in the disease may vary. Sometimes edematous forms are observed. And sometimes inflammatory changes in the intestinal walls become hemorrhagic. In this case, erosions and ulcers are often diagnosed.
It is very important to identify the disease in time and not to forget that a gastroenterologist treats giardiasis. The following symptoms may suggest the disease:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- bitter belching;
- feeling of pain when palpating the gallbladder;
- bitterness in the mouth.
However, do not forget that all of the above signs can signal another disease. In this case, self-diagnosis and self-medication are quite unsafe.
With a long course of the disease, the above signs may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dirty skin tone;
- the appearance of dark “circles” under the eyes;
- increased skin rashes;
- coated tongue;
- bad breath.
Clinical manifestations of the disease can be neurotic in nature, allergic-dermatic. Due to such a variety of symptoms, the diagnosis is confirmed by a gastroenterologist only after a laboratory examination.
Where does a gastroenterologist see
Gastroenterology rooms are open in clinics that accept adults and children at their place of residence. Gastroenterology departments operate in hospitals and clinics. You can make an appointment with a specialist directly or through a general practitioner. After examining the patient, the general practitioner or pediatrician will, if necessary, refer you to an appointment with a specialist in gastrointestinal diseases.
Diagnosis of the disease is a very important and difficult stage of treatment. In addition to the initial examination of the patient, a set of tests is expected. Only after studying the results of a medical examination can a doctor formulate a diagnosis and begin adequate treatment.
- During the initial examination, the patient's complaints are taken into account.
- The features of the diet and nutrition regime are established.
- The oral cavity is examined.
- The abdomen is palpated.
- A general analysis of blood and other types of fluids is prescribed.
- Various types of endoscopic examinations are prescribed.
- Determine the need for an ultrasound examination.
Currently, doctors have established that stomach and duodenal ulcers are caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Its presence in the body is determined by conducting special blood and stool tests, which are prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
Features of the initial examination
In the oral cavity, the doctor is primarily interested in the plaque and color of the surface of the tongue. A “varnished tongue” with a smooth and shiny surface, devoid of taste buds, occurs when the gastric mucosa is atrophied. A brownish or white coating on the tongue occurs when the gastrointestinal tract is painful.
The doctor palpates the abdomen, paying attention to decreased elasticity of the skin and its roughness, thinness, and pallor. It is important to note the shape and size of the abdomen. Attention is paid to intestinal motility and movements of the abdominal wall during breathing.
A strongly retracted abdomen may indicate acute peritonitis. Protrusion is possible with ascites, that is, accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity or with flatulence and banal obesity.
An increasing asymmetry of the abdomen is observed with problems with the spleen or liver.
If necessary, the doctor performs examinations of the rectum, examining the anus, sacrococcygeal region and perineum. This method is used to diagnose prolapse of the mucous membrane, identify fissures in the anus, formations and hardening of the rectum.
After identifying the disease, the doctor draws up a treatment plan. Therapeutic actions are selected taking into account concomitant diseases, age and general condition of the patient. Treatment with drugs is supplemented by physiotherapy, herbal medicine, and diet. In severe cases, surgical intervention performed by a gastroenterologist-surgeon is chosen.