Many patients have pain on the right side under the ribs after gallbladder removal. After radical relief from a biliary disease, this complication is a frequent companion for the patient. To quickly get rid of the consequences in the postoperative period, it is recommended to follow all the instructions given by specialists and be sure to adhere to the prescribed diet. This will make the period after surgery much easier.
Rules of behavior during the postoperative period
Pain in the right hypochondrium when the gallbladder is removed is normal in the postoperative period. The first week after gallbladder removal surgery is considered the postoperative week. When the patient comes out of anesthesia, he should remain at rest for at least five hours. After which it is allowed to perform basic movements (stand up, roll over). During the first day after the gallbladder is removed, eating is prohibited. It is allowed to drink drinking water without gas, a decoction based on rose hips without adding sugar.
On the second day after surgery, drink a liter of kefir (necessarily low-fat). Divide this amount of product into several doses. After a day, if there are no complications, you can introduce low-fat cottage cheese, lean meats (boiled or steamed), vegetable broth, fresh non-acidic fruits, and fermented milk products into the diet. Be sure to adhere to the correct diet - drink large amounts of clean, still water between main meals.
Further, the diet gradually expands, it is forbidden to eat only spicy, fatty, smoked, spicy foods, alcoholic drinks, black bread, soda, spicy dishes, sausages, canned food, marinades, chocolate and coffee. For some time after removal of the gallbladder, pain will be felt in the right side in the place where the injections were made. Reviews from many patients and surgery confirm this. Sometimes even sleeping on the right side hurts. This is normal until the injured tissue recovers.
If there is pain on the right after removal of the gallbladder, it is recommended to consult a doctor; he should examine the intervention site and assess the condition of the tissues. After surgical treatment, a tube is inserted into the patient on the right side, which provides drainage. If the discharge stops, it is removed after a day. During this period, physical activity is prohibited. Wearing soft underwear is recommended. The postoperative period ends with the removal of sutures. Another week after discharge, the patient is usually on sick leave until all the wounds have completely healed.
In some cases, complications may occur - compaction, redness or discharge in the intervention areas. In such cases, conservative therapy is extended. If the patient does not follow a gentle regimen for his body, hernias may form at the puncture sites, they are painful, and if they are pinched, constipation occurs. You cannot shower for five days after the operation; the wounds are lubricated with iodine, fucorcin or cutasept. If your back hurts in your side when the gallbladder is removed, this is normal in the postoperative period. To relieve pain, doctors prescribe painkillers and antispasmodics.
Laparoscopy is not an abdominal operation. After 6 months, complete rehabilitation of the patient was completed. The main goal of the postoperative period is to reconstruct the functions of the organs of the digestive system so that they can perform their work in the absence of the gallbladder. Digestion will gradually improve, but only if the person strictly follows all medical prescriptions. Doctor's recommendations after cholecystectomy:
- Limiting the consumption of fats, spicy and fried foods.
- You cannot have sex for three weeks.
- Make sure there is no constipation in the first days after surgery.
- Limit physical activity for a month and a half.
- Adhere to proper nutrition - avoid heavy foods that cause disturbances in the functions of the digestive system.
- Take vitamin complexes prescribed by your doctor.
The specified diet is observed for at least two years if the gallstone is removed. In the absence of an organ, you should avoid eating heavy foods for life.
Thanks to this, you can completely restore the process of food digestion and bile secretion. Do not consume cold or hot foods. If alarming signs appear, especially if the organ has already been removed a long time ago, it is imperative to visit a doctor, who, based on examination, symptoms and other diagnostic measures, can draw conclusions about the patient’s condition. Visit your doctor from time to time for consultation.
Diagnostics
To find out why, after removal of the gallbladder, the right side under the ribs continues to hurt, they resort to instrumental research methods. Among them:
- Ultrasound. Against the background of DSO, an ECHO picture of dilatation of the common bile and pancreatic ducts is possible.
- MRI. Helps in searching for anatomical defects that interfere with the outflow of bile. Option of choice for suspected tumors that are not always clearly visible on ultrasound.
- FGDS. Allows you to exclude or establish gastritis, peptic ulcer, inflammation of the duodenal papilla and other pathologies of the digestive tube.
- ERCP. Represents an X-ray examination of the bile and main pancreatic ducts by introducing a contrast agent into them.
- Laparoscopy or laparotomy. A necessary measure in case of suspected serious complications requiring surgical intervention (for example, internal bleeding, peritonitis).
Causes of pain
Why does my side hurt after cholecystectomy? Radical treatment is carried out for gallstones and cholecystitis. But if the bladder is removed after the disease, it is impossible to immediately remove the heaviness and pain in the right side; after the operation, it is impossible to establish metabolic processes and changes in the chemical composition of bile. After diagnosis and treatment of gallstone disease, loss of an organ occurs, which plays one of the most important roles in the digestive process. As a result, other organs are now forced to completely rebuild their functions.
Since the accumulation and synthesis of secretion previously occurred in the gallbladder, the process of its entry into the intestine when food was consumed was controlled. The functioning of the abdominal organs is destabilized, resulting in pain in the liver, pain in the back, and in the abdomen. Biliary fluid is not able to circulate fully, which causes the following symptoms:
- circulation and secretion synthesis are disrupted,
- the concentration of positive microorganisms in the intestinal tract decreases,
- possible exacerbation of gastritis, duodenitis,
- chronic diseases worsen (ulcers, acute pancreatitis),
- pain in the right hypochondrium or pain in the left hypochondrium in front,
- liver enzymes in the blood fluid increase in volume.
The localization of the pain syndrome is determined by the type of disorder of the sphincter of Oddi. On average, the duration of such symptoms is about half an hour. Symptoms are most often felt after dinner and may be accompanied by bouts of nausea.
Increased tone of the sphincter of Oddi
Pain in the hypochondrium after removal of stones along with gallstones is caused by an increase in the tone of the sphincter of Oddi. When the gallbladder is filled with secretion, a reflex relaxation of this area occurs. If the gallbladder is absent, dysfunction of this part of the biliary system occurs. The liquid stops its accumulation, as a result of which its concentration decreases, while it is periodically thrown into the cavity of the small intestine, regardless of the main meal of food, when they enter the intestine, bile begins to become infected with pathogens in the bile ducts, causing the development of an inflammatory process.
The main clinical manifestations of dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi include:
- Painful sensations in the right hypochondrium.
- Various dysfunctions in the digestive system - increased gas formation, attacks of nausea or vomiting, heaviness, bitter or sour belching, intestinal disorder.
Traditionally, such signs occur after the main meal, at night, and their location varies. A nagging pain can radiate to the heart, and pain is felt in the lumbar region.
In most situations, the amount of food consumed does not affect the appearance of unpleasant clinical signs. How long ago the operation was performed also affects.
Inflammation in the bile ducts
If the right side hurts after removal, this is the first sign of postcholecystectomy syndrome. This symptom develops as a result of the inflammatory process in the bile ducts. This pathology develops if the bile ducts become inflamed (with the development of cholecystitis in the patient’s body). Most often, this condition can be caused by cholelithiasis - the formation of stones in the bile ducts.
This pathological condition can be provoked by inflammatory processes in the channels that remove secretion. This also negatively affects the functioning of an organ called the liver.
Basic functions of the gallbladder and bile
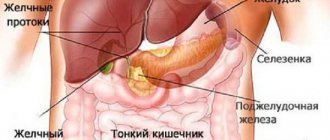
Hepatocytes (the so-called liver cells) constantly produce bile, which, through the bile duct system, enters the gallbladder and accumulates in this reservoir, which is located just below the liver. Its shape is similar to a pear, the capacity of which ranges from 40 to 70 milliliters. The muscles of the walls of this tank are very elastic and can stretch greatly.
The main functions of the gallbladder are:
- accumulation of bile produced by the liver;
- bringing this liver secretion to the required concentration;
- delivery of bile to the duodenum when food enters the gastrointestinal tract.
The gallbladder and intestine are connected to each other by a common bile duct, at the end of which there is the so-called sphincter of Oddi, which ensures a portioned flow of bile into the digestive system.
Bile, which accumulates in the gallbladder, is a complex mixture of various components, such as:
- special bile acids;
- fatty acid;
- set of enzymes;
- complex of minerals;
- cholesterol;
- products produced during hormonal metabolism, and so on.
The main component of this liver secretion is water, which ensures its fluidity. Bile is involved in the breakdown of food (especially heavy fats), as well as in the process of removing harmful substances from the body. The liver of a healthy person produces more than one liter of this secretion during the day.
The main functions of bile:
- emulsification of fats for their subsequent absorption;
- strengthening and activation of the action of enzymes produced by the pancreas (lipase, amylase and trypsin);
- neutralization of pepsin (the environment in the intestines is alkaline, and in the stomach it is acidic; it is with the help of bile that gastric digestion changes to intestinal);
- stimulation of intestinal peristalsis, which ensures better movement of food and its effective digestion;
- removal from the body of products of hormonal and drug metabolism, as well as various toxins and other harmful substances;
- participation in the breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates;
- improved absorption of minerals and vitamins;
- maintaining the normal state of intestinal microflora by preventing the appearance and further spread of pathogenic bacteria.
Read also: How to take Hofitol for stones and after removal of the gallbladder?
Treatment of pain in the right side
If pain occurs when the gallbladder is removed, how to treat such a symptom, how to reduce the severity of pain, what to do? If pain occurs after cholecystectomy, this may be a reaction of the liver to changes in the body.
Therefore, treatment is aimed not only at restoring biliary outflow, but also at protecting liver cells to eliminate bile secretion.
Drug therapy
To sanitize the intestinal tract, doctors prescribe antibacterial drugs. To eliminate pain, painkillers and antispasmodics are used.
To protect the liver, hepatoprotectors and choleretic drugs are necessarily prescribed.
Postoperative complications
If pain persists for a long time after removal of the gallbladder, a detailed search for the cause begins. Cholecystectomy is a fairly safe operation, but it can also have complications. First of all, possible errors (iatrogenesis) during the operation are excluded. Among them:
- Infection of a surgical wound;
- Incorrect suturing;
- Damage to the biliary tract and surrounding organs;
- Leaving a section of the cystic duct that is too long, in which bile begins to accumulate (0.1-1.9% of cases of pain after surgery).
- Persistence of pathologies that interfere with the outflow of bile (for example, bile duct cysts).
Pain after gallbladder removal is rarely associated with iatrogenicity, but you should be aware of symptoms that may indicate it. Infection is indicated by redness and swelling of the tissue in the suture area, and the formation of purulent masses. There may be a persistent increase in body temperature and widespread pain throughout the abdomen. A dangerous sign is a “board-shaped” stomach, or the expression of muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall.
Important! Cholecystectomy carries some risk of bleeding. It may indirectly be indicated by the progression of general weakness and pallor of the skin. The addition of shortness of breath and dizziness to the pain syndrome serves as the basis for an emergency visit to the doctor.
Pain prevention and diet
As a preventative measure, you should follow the rules of conduct described above during the postoperative period.
The diet is followed for life. Periodic consultations with the attending physician are required. Physical exercises can be started no earlier than six months after cholecystectomy.
Choleretic products
The diet should contain foods rich in fiber. Among them are: dill and parsley, sour fruits and berries, bran from corn or oats, tomatoes, carrots, olives, cabbage. Food should be consumed according to a schedule - at least five times a day, at intervals of two to three hours, in small portions.
Cholecystectomy
The absolute indications for cholecystectomy are diseases that lead to serious disruptions in the functioning of the biliary system organs:
- acute cholecystitis;
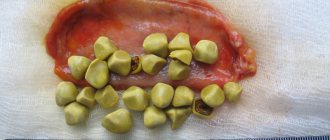
- cholelithiasis;
- formation of polyps in the gallbladder.
If there are appropriate indications, the surgeon decides to remove the gallbladder. There are two main ways to perform the operation:
- laparoscopy;
- open abdominal surgery.
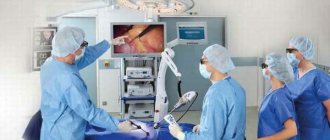
Laparoscopic or endoscopic cholecystectomy of the gallbladder is a surgical procedure that allows you to remove the organ without incisions. This method is low-traumatic and shows good results. The procedure involves making small punctures using instruments, after which no scars remain on the human body. After the operation, the patient does not require a long stay in the hospital, since he can return to normal life quickly enough.
The operation is performed in the traditional way extremely rarely. It is prescribed only in case of acute inflammation of the gallbladder or if there is a risk of injury to its walls. Open abdominal surgery involves making a large incision followed by removal of the organ. The recovery period after surgery lasts about a month.
Main pathologies of the biliary system
Why does my gallbladder hurt and have to be removed? Experts divide the most common gallbladder diseases into the following groups:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | dyskinesia (disturbances in normal functioning) |
| 2 | inflammation (cholangitis and cholecystitis) |
| 3 | pathologies caused by metabolic disorders (cholelithiasis, polyposis) and so on |
The course of all of these groups of pathologies is accompanied by pain, heartburn, loose stools and other symptoms that are extremely unpleasant for a person appear, causing him serious discomfort. In many cases, drug therapy does not give the desired result, and the bladder has to be removed.
However, even after the removal of this organ, in many cases the patient continues to be bothered by pain and digestive disorders (colitis, pancreatitis, and so on). This is due to the fact that surgery often eliminates the consequences and not the cause of the pathology (for example, with calculous cholecystitis, the root cause is a violation of normal metabolism, and surgery does not eliminate this problem).