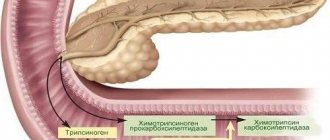
Pancreatic lipomatosis (PG) is the replacement of normal glandular tissue with fat cells. It is not a separate disease - it reflects pathological processes in parenchymal organs. When examined by ultrasound, these changes are described as fatty degeneration of the pancreas. Lipomatosis is rare, tends to be progressive and is accompanied by severe disorders in the body due to a decrease or loss of functions of the affected organ. The nature of fatty tissue changes can be both local and diffuse. Any part of the pancreas is affected: head, body or tail.
Fundamental Factors
The main causes of the disease include the following:
- hereditary tendency to obesity;
- physical injury to the organ;
- toxic poisoning, including alcohol;
- diabetes mellitus (accounts for 70% of cases);
What percentage of humanity suffers from obesity? This is due to the popularity of fast food and other dishes high in harmful substances. The benefits of such products are not only questionable, but also unproven. The risk group also includes those who abuse alcohol and fatty foods, as well as people with gastrointestinal diseases.
Important. Therefore, such individuals are recommended to undergo at least one ultrasound examination annually.
Fatty hepatosis and pancreatic lipomatosis
Pancreatic lipomatosis is a sluggish, progressive and in most cases asymptomatic disease. The pathology consists of a pathological accumulation of fat around the organ. Over time, fat cells penetrate inside and lead to complete fatty infiltration of the pancreas. This pathology has a similar development mechanism to liver hepatosis, since it is caused by the same reasons - obesity, consumption of fatty foods in large quantities, endocrine diseases.
Stages and forms of pancreatic dystrophy
For ease of perception of existing types of diseases, it is better to present the data in a table.
| Stages of dystrophic changes in the pancreas | |
| first | Obesity has occupied up to 30% of the organ, functionality is moderately impaired, and symptoms are not expressed in any way. |
| second | Obesity has occupied up to 60% of the organ, and there are malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) and pancreas (pancreas). |
| third | Obesity has occupied over 60% of the organ, the clinical picture is pronounced, and in some cases endocrine insufficiency is observed. |
| Forms of dystrophic changes in the pancreas | |
| Diffuse | Muscle lipoma - lipid cells grow together with muscle tissue. The line between normal and pathological tissue is not identified. |
| Knotty | The formation of symmetrically localized nodes, surrounded by a unique capsule, occurs. |
| Mixed | It is a duet of the first two forms with corresponding complications, and the symptoms are often confused with one of the forms. Only a specialist can determine the mixed form. |
We also recommend viewing: Where does the pancreas hurt and how does it hurt: we know more, we get sick less
Clinical picture
Unfortunately, fatty degeneration in the first stages is determined only after a complete examination of the body. In other cases, there are no external manifestations. Symptoms begin to appear towards the end of the second stage of the disease, and even then the person feels tightness and discomfort after eating. This is followed by attacks of nausea, “out of nowhere.” Increased gas formation and vomiting are possible. Lethargy and malaise experienced by patients cannot be ruled out.
The advanced stage will be marked by a sharp increase in blood sugar levels, because the gland stops working normally, provoking diabetic changes in the body. Lipomatosis is a consequence of diabetes mellitus and, together with elevated blood sugar levels, a person becomes extremely overweight.
Symptoms are divided into groups, depending on the manifestations:
- pain syndrome - pain in the left hypochondrium along with heaviness in the abdomen (a feeling of heaviness is felt after eating);
- dyspeptic syndrome - nausea, vomiting, excessive gas formation, constipation or diarrhea;
- asthenic syndrome - lethargy, fatigue, weakness.
Symptoms of fatty infiltration
The process by which healthy, perfectly functioning cells are replaced by fat cells is irreversible, i.e. changed tissues are not subject to involution - reverse transformation. In most cases, the disease develops latently, i.e. without obvious signs, and its diagnosis occurs during an ultrasound examination, often unrelated to this disease. Fatty degeneration develops very slowly; the first symptoms of the pathology can appear either after 2 years or after decades.
Primary symptoms occur when 1/3 of the pancreas has already changed. After this, the symptoms become more intense and are accompanied by a variety of manifestations.
But regardless of the variety of symptoms, their causes may be associated with 2 significant disorders:
- Failure of functions of the damaged organ.
- Compression of healthy tissue of the pancreas and neighboring organs.
During the development of pathology, there are fewer and fewer healthy tissues that fully perform their functions, and more and more damaged tissues that have turned into fibrous tissue. Fatty hepatosis of the pancreas negatively affects the functioning of the digestive system.
First of all, the patient’s condition worsens when he eats protein and fatty foods. The following signs of pathology occur:
- nausea;
- pain in the peritoneum;
- excess gases in the intestines (bloating);
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- frequent bowel movements;
- Fatty impurities and other inclusions appear in the stool.
Obesity of the pancreas leads to a failure in the production of hormones, which results in disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system. Most often, carbohydrate metabolism suffers from such changes, accompanied by a sharp increase in glucose levels. If these processes are not corrected, then over time the patient is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus.
Fatty type of hepatosis of the pancreas is a disease that directly or indirectly affects the functioning of the entire body.
Most often, the disease is accompanied by fatty infiltration of the liver, since everything in the body is interconnected, and pathological processes do not develop locally.
For example, when a person has pancreatitis, the risk of developing diabetes is high. In diabetics, degenerative changes affect the pancreas, which negatively affects the liver, causing changes in its tissues.
Preventive measures against lipomatosis
The diagnosis of lipomatosis is unpleasant because the disease is difficult to cure. Therefore, in order not only to protect yourself from excessive therapy, but also to insure the body, it is worth taking preventive measures in order to reduce the likelihood of the disease occurring. The only positive news for patients is the fact that lipomatosis is a benign and slow growth. The disease progresses slowly, but does not show any symptoms. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo an annual examination to detect such diseases. By identifying the disease in time, you can achieve a positive result in the shortest possible time.
This is achieved by excluding all risks and underlying factors. This means you should give up fatty and unhealthy foods, adjust your body weight, do not abuse alcoholic beverages, and eliminate stress.
Important. Most doctors also recommend stopping smoking and undergoing an annual ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
The main cause is considered to be chronic and acute pancreatitis. As a rule, it is as a result of this disease that fatty infiltration of the liver and pancreas develops. But besides this, the disease develops:
- in people over 40-50 years old. From this age, the production of enzymes in the body decreases, its resources are depleted, which leads to disruption of lipid metabolism and the disease described above;
- diabetes;
- hereditary predisposition to metabolic diseases or congenital abnormalities of the liver, pancreas and other organs involved in lipid metabolism;
- alcoholics (regardless of “experience”);
- persons who have suffered complex liver diseases;
- obesity. In this case, fatty degeneration can develop even at a young age if body weight is significantly higher than normal and the person does not take action.
In addition, the disease can become a complication in people who do not follow the prescribed diet due to obesity or after experiencing pancreatitis.
As for symptoms, the disease is asymptomatic for a long time. Only with an increase in fat cells do the following “signals” begin to appear:
- a feeling of pressing pain in the hypochondrium, girdle pain in the right or left side, reminiscent of an attack of pancreatitis;
- persistent nausea, with the urge to vomit (mainly in the morning);
- bowel dysfunction (diarrhea);
- flatulence;
- weight loss in the absence of other reasons;
- increased body fatigue;
- feeling of dry mouth;
- the formation of small ulcers on the oral mucosa.
All this indicates the need to urgently contact a medical facility.
Important! Fatty liver and pancreas cannot be cured, but the pathological process can be slowed down and symptoms can be eliminated with proper timely treatment.
Diagnosis of lipomatosis
You can obtain clear information about the presence of the disease after a complete examination of the body, laboratory tests and ultrasound of the abdominal organs. After the patient undergoes an ultrasound, the doctor will determine the visual characteristics of the organs and assess the general condition of the body. If the equipment detects fatty patches, an echo signal is sent, signaling an uneven structure of the organ.
We also recommend viewing: Medicines for a sick pancreas: what, why, for how long?
The verdicts are as follows:
- no deviations from the norm;
- there are minor changes;
- changes in internal organs are significant.
Important. Based on the verdict, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
ethnoscience
Fatty degeneration of the pancreas can also be treated with folk remedies, although one should not forget about drug treatment so that time is not wasted. There are dozens of folk remedies on the Internet, but it should be understood that for a specific case, only the attending physician recommends a folk remedy. It is based on the patient’s condition, the form and stage of development of the disease and, of course, contraindications. The individuality of the organism plays an important role here, as in principle for all medications and therapies.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The development of the disease is based on processes that cause inflammatory changes in the organ or lead to toxic damage.
First of all, the occurrence of fatty degeneration is associated with diseases such as acute or chronic pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus.
Fatty degeneration of an organ can be caused by certain medications or other toxic substances that can have a destructive effect on the cells of the organ.
A certain role belongs to heredity, injuries of the pancreas and other pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract (diseases of the liver, stomach and duodenum and other structures).
The effect is caused by dysfunction of pituitary control or decreased levels of thyroid hormones.
Dead cells are replaced by a connective tissue component or adipose tissue. This is necessary so that the organ maintains its shape and integrity. At the same time, the replaced structures do not perform the necessary functions, so the functioning of the organ is gradually disrupted.
If the volume of the lesion is small, then the process goes unnoticed by the patient for a long time. But when the “degeneration” progresses and covers a certain volume of the organ, the patient develops symptoms associated with disruption of the gland.
Drug treatment
Given the nature of the disease, it is not surprising that treatment consists of several stages:
- Diet – aimed at reducing overall body weight and improving well-being. The risk of spreading fatty deposits in the pancreas is eliminated. The patient must follow a strict diet with a minimum percentage of fat. You should eat five times a day, excluding smoked meats, pickles, sweets and baked goods. Dishes for the menu are steamed; the diet is based on vegetables, fermented milk products, and lean meat.
- Conservative therapy is necessary only when fatty patches located on the surface of the organ are identified. Fat deposits can also compress the pancreatic ducts, and drug therapy is used to normalize digestive and hormonal levels. Mezim and Festal have proven themselves to be effective means. An alternative to the latter remedy is Pangrol, which is affordable and effective in therapy.
- Surgical intervention is allowed only if the organ is damaged by 60% or more, along with the fusion of fat cells. A notable feature of lipomatosis is that healthy pancreatic tissue, after damage, is replaced by fatty tissue, which impairs the functionality of the organ. The operation is aimed at removing fatty tissue and areas that have occupied the pancreas.
We also recommend viewing: Is it possible to treat pancreatitis at home?
Fatty hepatosis of the pancreas - treatment
Treatment of pancreatic hepatosis must begin with changing your usual diet. Not only the composition of the diet is subject to correction, but also the meal schedule and portion size. Note that diet is the main part of therapy.
The second part of treatment is taking medications. As a rule, treatment is symptomatic. Antispasmodics (No-shpa and Papaverine) are prescribed for pain and spasms, and enzyme preparations (Mezim, Pancreatitn) are prescribed to improve food digestion. To maintain liver function, hepatoprotectors are additionally prescribed - Heptpral, Essentiale, Karsil. If the disease is caused by pancreatic insufficiency, the endocrinologist may prescribe prescription insulin drugs.
In rare cases, when the pancreas is firmly enclosed in a fatty “cocoon”, surgery may be required. This operation is complex and can be life-threatening for the patient.
Considering the complexity of the disease and the high cost of treatment, it is better to practice prevention. Proper nutrition, maintaining a normal weight, a positive emotional background and exercise prevent fatty infiltration of the pancreas.
What can you eat?
The key point of nutrition is the complete exclusion or minimal consumption of fat. The percentage of fat in food should be gentle, it is advisable to regularly consume non-carbonated mineral water, and fruits should be completely excluded from the daily diet.
Not eating meat for an adult is a real sentence, but the menu for fatty degeneration of the pancreas includes meat, namely fish, chicken, and rabbit. Potatoes, zucchini, and pumpkin are allowed as vegetables. The majority of the diet should be cereals, because they are rich in minerals necessary for the functioning of the body. Among dairy products, it is recommended to pay attention to cottage cheese, sour cream, and kefir. The daily allowance for an adult is 2000-2500 kcal, but in this case you can treat yourself to 2800 kcal.
Diet for pathology
The main goal of the diet for pancreatic lipomatosis is to rid the body of excess fat and excess weight. Its main principles:
- frequent split meals (4-6 times a day in small portions),
- cooking method - steaming, boiling, stewing,
- maintaining energy balance and completeness of the diet.
A prerequisite is the exclusion of alcohol and smoking, high-calorie and fatty foods, a significant reduction in the diet of coffee, cocoa, chocolate, and strong tea.
A temporary refusal to eat is recommended: therapeutic fasting has good results for pancreatitis, so experts consider this an effective method for lipomatous changes in the pancreas. In the future, food should contain an increased amount of protein and a reduced amount of fat and carbohydrates. Prohibited foods include fatty, fried, smoked, sweet and salty foods. Preference should be given to plant foods. Particularly healthy are pumpkin, Jerusalem artichoke, zucchini, as well as buckwheat, rice and oatmeal, green tea, lean meats and dairy products.
The daily calorie intake is 2,800 kcal.
In case of violation of the endocrine function of the pancreas, an additional dietary table No. 9 according to Pevzner with carbohydrate restriction is prescribed. In such cases, the basic diet must be strictly observed, since any deviation leads to life-threatening conditions and irreversible changes in the vessels of the retina, kidneys, lower extremities, and peripheral vessels of the legs.
To create a menu, there are special tables listing prohibited and permitted foods and their calorie value.