What is a disabled gallbladder?
Any competent doctor will say that as such there is no diagnosis called “disabled gallbladder” in nature or in medicine. This is what people call dysfunction of a given organ, when it does its job only to some extent or does not do it at all. A wrinkled gallbladder is one of the varieties of this pathology. It is detected during an X-ray or ultrasound examination. This also means a non-functioning gallbladder. Only in this case has significant deformation of the organ already occurred. It looks as if some fragment of healed tissue is adjacent to the liver. It is no longer possible to return the function of such an organ to its previous course.
Diagnostics
The specialist collects data on those pathologies of the biliary system and the gastrointestinal tract as a whole that the patient has a history of. Examines the color of the skin and the presence of scratching, indicating itching. Performs palpation of the area of the right hypochondrium. Next, clinical tests of urine and blood, biochemical blood test, coprogram, and coagulogram are prescribed. Of the instrumental diagnostic methods, the presence of a disabled gallbladder can be confirmed by ultrasound.
In a healthy person, the bladder should have a lumen. If it is turned off, the lumen is not visualized on the monitor. The organ resembles an oval formation that casts a shadow. Ultrasound examination makes it possible to differentiate pathology from inflammatory processes, abscess, and empyema. In such cases, the cavity is visible, but the walls of the gallbladder are thickened, it is enlarged in size, sand, stones, and stagnant bile can be visualized inside.
There is also the concept of “wrinkled gallbladder”. The organ can take part in the digestive processes, even a lumen is visible during diagnostics, but the amount of bile it contains is not enough for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. If obstruction of the bile ducts with stones occurs, the organ is clearly visible on the monitor; you can notice stagnation of bile in it or the presence of a suspension like flakes. At the site of obstruction, the expansion of the ducts is noticeable.
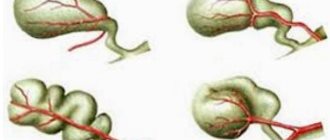
One of the variations of the disabled gallbladder
The next method used for diagnosis is cholecystography. During the procedure, a contrast agent is used, which is injected into the patient's body. It must fill the gallbladder and biliary ducts so that the radiologist can analyze the extent of the pathological process. The disconnected gallbladder will not be visualized, since the contrast agent simply will not get into it. At the same time, the specialist diagnoses the presence of the following conditions:
- adhesive process;
- presence of stones;
- obstruction of the biliary tract;
- the presence of polyps or tumors.
Causes of pathology
The gastrointestinal tract turns off, as a rule, due to various factors that provoke it. Thus, a disabled gallbladder can occur as the final stage of some diseases that were not treated in time, and perhaps not even diagnosed.
So, why is the ZhP not functioning:
- The organ is clogged with stones as a result of cholelithiasis. This happens when a patient develops cholelithiasis, but does not go to a medical facility for treatment. Then more and more solid formations appear in the gallbladder, as a result of which this organ becomes clogged with stones, which displace bile from there and prevent it from entering the bladder. And the gallbladder loses its efficiency.
- Such conditions of an organ, in which it partially or completely ceases to perform its functions, can occur when the outflow of bile is disrupted. Obstruction of the biliary tract provokes cholelithiasis of the organ; for example, a stone stuck in the flow can clog the bile outlet.
- Porcelain gallbladder is another pathology leading to gallbladder shutdown. In this case, it all starts with a metabolic disorder. This, in turn, leads to the formation of calcareous growths on the walls of the gallbladder. At first they look like plaques, then gradually expand and completely cover the entire tissue of the organ. As a result, it becomes first dense, and then extremely hard, as if a stone does not contract or stretch, and loses its everyday functions.
- Collapsed gallbladder or shrinkage of the organ. In this case, the gallbladder seems to be “deflated,” deformed, and pressed against the liver. Accordingly, it is no longer capable of working with such deformation.
Why is pathology dangerous?
A disabled gallbladder can occur as a consequence of a complication of cholecystitis. Accordingly, the consequences of these two pathologies are similar. When the functions of the gall bladder are impaired, a dangerous syndrome develops. It can lead to completely irreversible consequences.
If the shutdown of the gallbladder is not diagnosed in time, microholes appear in the walls of the organ, through which bile penetrates into the abdominal cavity. This leads to inadequate functioning of the neighboring viscera, and if you do not consult a doctor in time, dangerous peritonitis will develop. When the gallbladder subsides, bile can enter the bloodstream and sepsis develops. As in the case of peritonitis, the prognosis here is very, very unfavorable. If there is an incorrect diagnosis, incorrect or untimely treatment, everything can end in death.
It happens that everything does not end so badly, and the patient can live with a disabled gallbladder . In this case, adequate therapy is necessary to restore the functions of the organ. It helps only in simple and not advanced cases. In most examples, doctors show patients with such a diagnosis in their charts to have a gallbladder amputation.
Consequences for humans
If the gallbladder has stopped functioning, this is a sign that the digestive system has been suffering from ongoing inflammatory processes for a long time. Gallstone disease is easily treated in the initial stages, when stones have just begun to form, there are few of them. But when the bladder has already lost the ability to accept and secrete bile, the stage of cholelithiasis is severe.
The fact that the consequences are truly dangerous is due to their irreversibility; most violations cannot be restored.
When the inflammatory process affects the walls of the bladder, their integrity is compromised. They can become hard as stone or, conversely, deplete when the organ shrinks. If pus has already accumulated inside the bladder, then due to the weakness of the walls it leaks outside the organ and enters the abdominal cavity. The consequence of this is often intensively developing peritonitis. Peritonitis can result in death.
If you seek medical help in time, you can return the walls of the bladder to their previous tone. This requires complex treatment, which includes medication and diet therapy. They are often prescribed for life, but this is the only way to resume the functioning of the organ.
Fact. Strong, intense inflammatory and purulent processes that last for a long time can turn off the gallbladder. Therefore, a favorable outcome and complete recovery are unlikely.
Symptoms and diagnosis
What signs indicate a disabled gallbladder, what are the symptoms of this disease? The fact that the gallbladder is disabled will present a complex of symptoms and signs. The person first begins to experience discomfort and pressure in the right side under the ribs. After some time, these sensations intensify, and the patient begins to experience severe pain, which is also accompanied by hepatic colic.
Also, when the gallbladder is not working, increased gas formation, nausea and vomiting, high temperature, weak and liquid stools appear . When gallstones clog the gallbladder, a person begins to feel an unusual and strange taste in the mouth.
With advanced problems with the biliary tract, the patient’s skin acquires a specific pronounced yellow tint, then the whites of the eyes also succumb to yellowing.
It is worth remembering that in this way, similar symptoms and signs can manifest various diseases not only of the gallbladder, but also of the liver. And in order to clarify and confirm this particular diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a complete study of this organ. Be that as it may, if you find all these signs, you should immediately see a gastroenterologist.
Symptoms
A disabled gallbladder is often the result of advanced cholelithiasis and associated pathologies. Therefore, the symptoms are similar to those that appear in advanced stages of cholelithiasis.
The main ones are:
- severe pain syndrome;
- flatulence;
- bloating;
- problems with stool, often diarrhea;
- heartburn;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth after eating and in the morning.
Vomiting after eating is a symptom that requires urgent medical attention; it is usually associated with blockage of the bile ducts due to a large number of stones and concretions.
Symptoms when the gallbladder is turned off may be mild. Sometimes painful sensations can be mistaken for inflammation of appendicitis. And also due to a violation of the outflow of bile, it enters the blood, which causes yellowness of the skin and increased color of urine. Some people perceive such symptoms as signs of jaundice.
Treatment
So, doctors absolutely confirm: the gallbladder is disabled, what should you do about it? Treatment begins with identifying the reason why the gallbladder is not working. If the stone has completely blocked the duct, or the organ is clogged with hard neoplasms, of course, they must be removed and removed. If the stones are small in size, it is sometimes possible to break them up using a special therapy method.
Basically, doctors prescribe a painkiller that relieves spasms to a patient with a gallbladder shutdown. If the attending physician decides that the function of the organ can still be restored, then the patient is prescribed drugs that stimulate bladder contraction. Vitamins, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agents, and warm alkaline mineral water are also prescribed. It must be remembered that depending on the complexity of the pathology, treatment methods for a disabled gallbladder are selected. If an organ does not work at all, and its tissues have already begun to die, doctors decide to amputate the organ.
Possibility of restoring gallbladder function
There is a possibility that the bubble will start again. It will be possible to restore its functions with the help of special medications if the damage to the organ is not serious and its functionality is only partially lost.
Drug treatment aimed at restoring organ function involves adjusting the normal flow of bile. The patient is prescribed drugs that can break down tumors, choleretic, bile-excreting agents. The tone of the organ, its ability to contract in time to release bile during the digestion of food entering the body, is also restored with the help of a targeted drug.
Gallbladder removal
If the shutdown of the gallbladder is caused by the organ being clogged with stones, the patient undergoes surgery to remove the stones. Solid neoplasms are also removed if they block the currents and it is not possible to break them up with medication. However, some doctors are sure: if stones have already begun to form in the gallbladder, then no matter how many times they are removed, they will form again and again. Therefore, it is better to amputate the bladder along with the stones.
Well, and, of course, the gallbladder is cut out without any options, if it is impossible to restore its function, and if the tissues of the organ have already undergone significant death.
If there are no contraindications, amputation is performed using the laparoscopic method, which allows you to return to normal life (albeit with some restrictions) after two to three weeks.
Prevention and diet
Since a disabled gallbladder is, as a rule, a consequence of other common diagnoses associated with this organ, therefore, the prevention that needs to be carried out to prevent gallbladder dysfunction is the same as the prevention of other gallbladder diseases. Firstly, nutrition must be balanced and proper. You shouldn’t get too carried away with unhealthy foods such as fatty, smoked, very salty and very sweet. The diet should include porridge in water, soups in low-fat broth, meat and fish cooked with steamed vegetables, stewed in water (without oil) or in broth. Among the foods consumed, it is necessary to give priority to lean meat and fish, vegetables, and fruits. Secondly, measures to prevent a disabled bladder include giving up bad habits, especially excessive consumption of alcohol-containing drinks.
In addition, you should maintain a necessary and normal level of physical activity - you should not unnecessarily overload your body with rigorous training or very hard physical labor. At the same time, you should not completely immerse yourself in physical inactivity. Moderate activity such as walking and light exercise will be useful not only for the prevention of gallbladder diseases, but also for the body in general. And some doctors also say: in order to avoid diseases of the gallbladder, liver and other internal organs, it is very useful from time to time to arrange fasting days for yourself and cleanse the body of toxins.
If, nevertheless, a gallbladder disease has already been diagnosed, the patient is shown a special diet for a diseased gallbladder. In this case, the same nutritional principles described above apply. Just before eating, food should also be pureed to a puree state, and you should eat in very small portions, increasing the number of meals during the day. You also need to drink more liquid: this can be ordinary purified water, alkaline mineral water, as well as vegetable juices, which help liquefy and remove bile. Doctors recommend increasing the total amount of fluid entering the body per day to three liters.
And you should not neglect folk remedies that dilute, remove bile and maintain the functions of the gallbladder in a normal, efficient state.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis begins with a visit to a gastroenterologist or therapist. During the examination and collection of anamnesis (what the person has been ill with during his life), the doctor will determine a range of diagnoses that need to be confirmed and excluded.
The first appointments when an organ is disconnected, as a rule, will be clinical and biochemical blood tests and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, in particular an examination of the gallbladder. The fact is that the symptoms of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are sometimes similar, a disease of one organ entails disturbances in the functioning of others, and it is impossible to start with examining this organ exclusively. Otherwise, there is a high risk of detecting a problem, but not finding the cause of its occurrence, which means prescribing not the most effective treatment.
Specific examinations of the gall bladder, which are performed to clarify the diagnosis, are contrast radiography, endoscopic cholangiopacnerography (we will discuss this procedure below, in the section on treatment). In addition, to find out the reasons for the shutdown of the bladder, tests can be prescribed for a number of infections, helminths and protozoa, and much more.
In most cases, initial examinations provide a clear picture of the disease and allow us to develop the right treatment tactics. A clinical blood test will answer the question of whether there is inflammation, a biochemical test will answer the question of whether there is dysfunction of individual organs, and an ultrasound will show their anatomical features and can often help establish the exact location of the inflammation. During an ultrasound, you can examine and describe the location of the bladder, its shape, size, the presence of kinks and bridges, flakes, clots and stones, filling, wall thickness and their peristalsis (successive contractions). Large bile ducts are also visible. All this is enough to determine the reason for such a disconnection and deterioration in the patient’s well-being.
The patient himself can help increase the information content of biliary ultrasound by providing the doctor with good acoustic access. Ultrasonic waves propagate well in liquids and poorly in gases. The principle of the method is based on this. The main accumulation of gases in the abdominal cavity is normally located in the intestines. The intestine occupies a large volume of the abdominal cavity and runs next to literally all its other organs.
In order for an ultrasound to be more informative, it is necessary to minimize the amount of gases in it. To do this, the day before the study, they begin to take carminative drugs: simethicone, enterosgel, activated carbon, polyphepan. The patient should check with the doctor which one is best to take before the study.
As a rule, a 12-hour fasting diet is prescribed before the ultrasound. But before the study, the doctor may prescribe to eat a certain product in the right quantity some time before the procedure. This is a mandatory recommendation: gallstones behave differently on an empty stomach and after eating provoking foods. All this is a comprehensive preparation for an ultrasound scan of the liver and gallbladder.
Diet effectively helps reduce gas formation in the intestines. It starts at least three days before the ultrasound. The diet involves fractional meals, 5-6 times a day, in small portions. You should eat boiled food and low-fat foods: lean beef, chicken, turkey, rabbit, lean fish, oatmeal or buckwheat in water without oil, hard low-fat cheeses. Before the study you should exclude:
- Legumes (beans, soybeans, peas, chickpeas and products containing them).
- Carbonated drinks.
- Dairy and fermented milk products, including cottage cheese, sour cream.
- Bread, except dried white bread in small quantities.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits, mushrooms in any form.
- Pickles, including sauerkraut.
- Fatty meats and fish, deli meats, sausages.
- Any alcoholic drinks, including beer.