Diarrhea with cholecystitis has a chronic course and haunts the patient throughout the underlying disease. They cause great damage to health. Digestion, metabolism, water, vitamins and ions are disrupted. Such diarrhea requires qualified and quick help.
Diarrhea with cholecystitis is a common occurrence. Mostly people over 40 years old experience this pathology.
Also at risk are patients who are overweight. Feces during cholecystitis are one of the main indicators of the course of the disease.
Some doctors believe that diarrhea due to cholecystitis is not a completely correct interpretation of a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is believed that inflammation of the gallbladder is more often accompanied by constipation than diarrhea. Despite the disagreement among gastroenterologists, loose stools due to cholecystitis cannot be ignored.
Chronic diarrhea
The disease develops gradually; in the first stages there are no symptoms, including diarrhea. The longer the illness lasts, the worse the gallbladder works. There are either too many bile acids or too little, which leads to intestinal dysfunction. Loose stools with cholecystitis are combined with periodic constipation - this is a characteristic sign of the chronic form. Feces in chronic cholecystitis are accompanied by a foul odor. May include mucus and fat.
Chronic cholecystitis is a less dangerous condition, since pain brings less discomfort and stones do not form. However, even in this case, the gallbladder suffers, diarrhea will also be present. In the chronic course of this disease, exacerbations occur against the background of various previous provoking factors, often related to diet (poor nutrition, alcohol, lack of vitamins, etc.). Diarrhea with cholecystitis, like the disease itself, is most often observed in women, this is due to the following reasons:
During pregnancy, the gallbladder is compressed, which entails consequences that manifest themselves over time;
Loose stools are a sign not only of a poor diet, but also of its imbalance. Girls more often use diets without consulting a specialist; strict restrictions and lack of any microelements greatly affect the body and the functioning of the gallbladder;
Chronic cholecystitis itself, diarrhea, which is a common occurrence, can be provoked by the hormonal background of the female body (progesterone and other elements).
If you ignore the disease, all symptoms may intensify (exacerbation).
Proper diet is the main preventative measure
The only way to prevent unpleasant attacks of diarrhea due to cholecystitis is to review your diet and adhere to basic nutritional rules. It is not recommended to organize the menu on your own - it is better to go to a nutritionist who will help you create a list of dishes that will prevent intestinal upset. It is recommended to exclude the following products or dishes from the menu:
- fatty meats;
- smoked meats, pickles, marinades;
- carbonated sweet drinks;
- conservation;
- chocolate, sweets;
- sweet products, baked goods with cocoa.
Fractional nutrition in small portions will allow the digestive organs to normalize metabolic processes, which will partially prevent intestinal disorders. Be sure to take food warm - hot or cold foods will cause additional problems. Drink up to 2 liters of liquid throughout the day. Prolonged diarrhea can cause dehydration, which can lead to dangerous health complications.
It is quite possible to cope with loose stools that occur due to cholecystitis, but doctors warn that without prior consultation with a specialist, there is a risk of causing health-threatening complications. Diarrhea is usually a consequence of an advanced disease, so experiments, independent use of aggressive pharmaceutical drugs or herbal decoctions are a sure way to problems that will require lengthy and not always effective treatment to eliminate.
Diarrhea with cholecystitis is a common occurrence. Mostly people over 40 years old experience this pathology.
Also at risk are patients who are overweight. Feces during cholecystitis are one of the main indicators of the course of the disease.
Some doctors believe that diarrhea due to cholecystitis is not a completely correct interpretation of a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is believed that inflammation of the gallbladder is more often accompanied by constipation than diarrhea. Despite the disagreement among gastroenterologists, loose stools due to cholecystitis cannot be ignored.
In this material, we will not only introduce you to the causes of diarrhea in this dangerous disease, we will also consider the specifics of cholecystitis and the forms of its course.
Acute diarrhea
The appearance of loose stools during acute inflammation of the gallbladder is explained by the formation of stones. They not only disrupt the secretion of bile, but also cause severe, unbearable pain. The pain symptom is associated with the movement of stones or clots of mucus through the ducts. Diarrhea is the first symptom of gallstone disease. Pain occurs when stones reach a certain size and block the ducts. After 2-3 days, yellowing of the sclera of the eyes and skin is observed, which is due to stagnation of bile.
Most often, this condition is observed in older people, but diarrhea due to the gallbladder in this case will not be considered the main symptom. The first two places will be taken by specific pain and cholelithiasis. Appears after eating (fatty, fried and similar foods), it can also develop against the background of not only the appearance of stones, but also with biliary dyskinesia (BD).
Ignoring this problem will lead to the following complications:
- Bubble rupture (perforation);
- Peritonitis;
- Mechanical (obturacin) jaundice;
- Acute pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas);
- The following will also appear:
- Chills;
- Sweating;
- Increased pain;
- Diarrhea with cholecystitis.
Treatment will involve not only eliminating symptoms, but also therapy aimed at eliminating the underlying cause.
Causes of diarrhea
They, of course, can be completely different, but in most cases the provoking factor is the formation of stones in the cystic duct and other places of the gallbladder, which create an insurmountable obstacle to the release of bile. In addition, the causes of the disease can be various types of injuries or infections, as well as serious diseases such as diabetes. But in this case, cholecystitis is already a complicated consequence of the pathology that exists, and not in the form of an independent disease.
Everything that was listed above can result in an acute form of the disease with the development of inflammatory processes in the gallbladder. As for the chronic course of the disease, this form of the disease, as a rule, manifests itself in situations where the irritating factor, remaining, takes on a protracted nature, ultimately leading to thickening of the walls of the organ. Experts do not have a consensus on how characteristic diarrhea syndrome is of cholecystitis. Many doctors note the presence of constipation in the symptoms of cholecystitis; the clinical experience of others convinces that the disease is more characterized by alternating states of constipation and diarrhea.
In the practice of gastroenterologists, there is also such a sign of acute cholecystitis as repeated stools with a liquid consistency and inclusions of mucus. When the symptom of diarrhea is pronounced, doctors often make a diagnosis corresponding to foodborne toxic infection. Diarrhea due to cholecystitis causes many medical errors when making a diagnosis. But intoxication phenomena in the body can be associated with inflammation in the gallbladder.
In addition to the presence of diarrhea in various forms of cholecystitis, errors in diagnosis are also caused by the presence of other symptoms, for example, the presence of severe chest pain. This situation can be observed in the cardiac form of cholecystitis, which is considered an atypical type of disease, described by S. P. Botkin and called cholecystocoronary syndrome. A feature of this disease is the absence of stones. It is accompanied by hepatitis, inflammation of the pancreas and bile ducts.
Bilious loose stools and diarrhea are liquid bowel movements in which feces contain bile, which makes them yellow in color. In young children who have not even reached the age of one, diarrhea with bile is the norm. Its appearance is explained by the peculiarities of the digestive system adapting to the external environment.
At the same time, in adults, the appearance of bilious diarrhea is a sign of pathological processes in the body. Liquid stool containing bile inclusions is observed in adults due to problems with the liver, gallbladder or its ducts, and the digestive system as a whole. Infections and viral diseases can cause severe water diarrhea.
The liver of a healthy person produces bile, which then moves into the gallbladder, and from it, during meals, into the duodenum. When the above organ is removed, the natural process is disrupted, and bile is released directly and continuously from the liver, which causes diarrhea. The presence of problems in the body can be diagnosed by the appearance of human excrement, its consistency and composition. The stool of an absolutely healthy person may only be yellowish-brown in color. If the yellow color predominates, this is a sure sign of the presence of bile in the biological mass, which may indicate serious disturbances in the functioning of some internal organs.
When a healthy person experiences pain in the abdomen or anus for no apparent reason, it can be rightfully noted that these are the first symptoms of a serious illness. Any inflammation, especially of the colon, begins and develops gradually.
As a rule, diagnosis and treatment begin from the moment when the manifestation of pathology does not allow one to lead a normal lifestyle. Only then does the sick person begin to be active in order to correct the situation. Prolonged neglect of colon inflammation always leads to serious consequences. This kind of behavior is explained by the sensitivity of the problem. Many people, especially men, prefer not to see a doctor, but to carry out treatment with folk remedies. Symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever are considered insignificant and can be easily eliminated. In fact, the situation is more serious.
The gallbladder is an organ that stores bile produced by the liver for release into the intestines at the right time. For normal digestion, it is necessary that bile enters the small intestine during food intake, and not when it is synthesized in the liver.
With cholecystitis, the process of supplying bile to the intestines is disrupted. The outflow of bile slows down, it enters the thin section either in insufficient quantities or between meals. In this case, most of the food turns out to be undigested and in this form enters the large intestine. This is what causes diarrhea.
Diarrhea with cholecystitis has the following causes:
With insufficient activity of the biliary tract, bile is supplied to the small intestine at the wrong time. Food in the intestines is only partially absorbed and enters the large intestine undigested. Here it begins to decompose under the influence of putrefactive bacteria. The result is diarrhea with a strong foul odor.
With cholelithiasis, putty-like bile is formed. The main components of bile turn into stones in the cavity of the gallbladder. They usually have a mixed composition, but predominantly contain cholesterol. Stones are most often accompanied by diarrhea that is unnaturally light in color and has a strong odor.
Diarrhea due to inflammation of the gallbladder is observed when the acute form transitions to chronic. In this case, diarrhea periodically gives way to constipation, since the gallbladder is unstable and secretes either too little or too much bile.
Diarrhea due to cholecystitis is difficult to wash off the walls of the toilet. This phenomenon is due to the fact that the feces contain too much fat, which is not absorbed in the intestines.
Secondary causes of diarrhea
The appearance of cholecystitis and accompanying diarrhea may be associated with other ailments or special conditions:
- Pregnancy. A growing fetus in the uterus leads to organ dysfunction. The gallbladder becomes compressed, cannot function normally, and diarrhea appears.
- Unbalanced diet. Insufficient amounts of proteins, fats or carbohydrates lead to disruption of the outflow of mucus and bile.
- Dysbacteriosis. Changes in intestinal microflora as a result of an infectious disease or its treatment can also stimulate the inflammatory process. In such cases, diarrhea disappears after the underlying disease is cured.
Types and symptoms of acute and chronic cholecystitis
Description of the disease
Cholecystitis is an inflammatory process in the gallbladder, most often provoked by infection of the organ with intestinal microflora against the background of a violation of the outflow of bile through a clogged cystic duct. Typically, cholecystitis is a complication of gallstone disease. The gallbladder is located next to the liver and is actively involved in the digestion process. The exit of bile occurs through the small intestine, but sometimes problems arise with evacuation, and the bile collects in the gallbladder, resulting in severe pain and an increased risk of infection.
As a rule, the disease occurs in combination with cholangitis - inflammation of the bile ducts. Cholecystitis is a common surgical pathology, especially among middle-aged and older women - they get sick three to eight times more often than their male peers.
The main reasons for gender predisposition to cholecystitis:
Chronic compression of the gallbladder during pregnancy provokes long-term consequences - an imbalance of cholesterol and bile acids, and, as a result, stagnation of bile;
Features of hormonal metabolism in women - it has been proven that progesterone, produced in large quantities during pregnancy and menopause, and other female sex hormones negatively affect the functioning of the gallbladder;
Women are prone to dieting, and strict dietary restrictions disrupt the motility (contractility) of the gallbladder.
The risk group, regardless of gender and age, includes people who have previously been ill:
Intestinal and/or liver infections;
Parasitic diseases (helminthic and protozoal infestations localized permanently or at one of the stages of development in the intestines and/or liver);
Gallstone disease (GSD) with obstruction (blockage) of the cervix and/or damage to the mucous membranes of the gallbladder;
Diseases that impair the blood supply to the walls of the gallbladder.
A reflex connection between pathologies of the gallbladder and anatomically unrelated abdominal organs has been proven - these are the so-called viscero-visceral reflexes. All of the above causes of cholecystitis are due to either a violation of the patency (obstruction) of the gallbladder, or a violation of its motility (dyskinesia).
Based on etiology, there are two large nosological groups of cholecystitis:
Calculous (lat. Calculus - stone);
According to the course, cholecystitis is divided into:
According to the nature of inflammation, they are:
Gangrenous and phlegmonous forms of the disease belong to the group of destructive cholecystitis.
The gallbladder is anatomically and physiologically close to the liver. The functions of the liver are varied, one of them is the continuous production of bile and its release into the duodenum. Excess bile accumulates in the gallbladder and is consumed in portions.
The role of bile in the physiology of digestion:
Dilutes food processed with gastric juice, changes gastric digestion to intestinal;
Stimulates peristalsis of the small intestine;
Activates the production of physiological mucus, which performs a protective function in the intestines;
Neutralizes bilirubin, cholesterol and a number of other substances;
Triggers digestive enzymes.
Symptoms of cholecystitis
The initial symptoms of cholecystitis, as a rule, are sharp pains in the right side below the ribs that occur unexpectedly. The reason for this is a stone that blocks the cystic duct. As a result, irritation and inflammation of the gallbladder develops.
The pain goes away after some time on its own or after taking a painkiller, but then it gradually increases, and then it becomes regular. The disease develops, which is accompanied by high fever, vomiting and nausea. The patient's condition continues to deteriorate.
The normal flow of bile into the intestines stops, a sign of which is the icteric coloration of the skin and eye sclera. The prerequisites for jaundice are precisely the presence of stones that block the bile ducts. The severity of the pathogenesis is characterized by the patient’s pulse: usually the heart rate ranges from eighty to one hundred and twenty to one hundred and thirty beats per minute (or even higher), which is a serious sign, meaning that dangerous changes have occurred in the body.
As for the chronic form of cholecystitis, the signs may not particularly manifest themselves; in the future, the disease may make itself known in a more advanced form or take an acute form. In this case, only treatment in a special medical institution will avoid worsening the condition.
Symptoms of cholecystitis are identified by taking anamnesis, physical examinations (inspection and palpation), laboratory and instrumental studies:
Symptoms identified during history taking. Based on the patient’s complaints, previous diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and other organs, the nature of pain in the abdomen and digestive disorders (nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, bloating) are established;
Symptoms determined by physical methods. A coated tongue is a sign of stagnation in the gallbladder. The leading symptom of cholecystitis is pain, determined by palpation, manifested in different projections of the body;
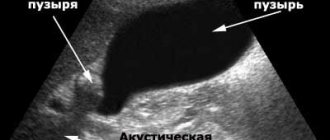
Differential diagnosis based on laboratory and instrumental research methods. The instrumental diagnosis of cholecystitis is based on probing of the duodenum and various modifications of X-ray and ultrasound examinations. With their help, the peristalsis of the bladder, the passage of bile into the lumen of the duodenum and other important functional and morphological indicators are determined.
Nausea with cholecystitis is a common symptom. Nausea is a condition that usually precedes the gag reflex. In some cases, nausea and vomiting is the body's protective reaction to intoxication. With cholecystitis, nausea and vomiting are always part of the pathogenesis of the disease.
Nausea with cholecystitis should be differentiated from similar symptoms with other diseases and pathologies:
Source
Symptoms associated with diarrhea
Before you learn how to treat diarrhea with cholecystitis, you need to accurately recognize it. Acute and chronic forms differ in this regard:
Acute form:
- Severe pain in the right side of the abdomen. They radiate to the back and do not go away for quite a long time; they are observed closer to night and morning;
- Flatulence;
- Mild fever;
Chronic form:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Lack of appetite;
- Bitter belching.
Common to both forms:
- Yellow skin tone;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Bitter taste in the mouth.
Calculous and non-calculous cholecystitis
The main symptoms of non-calculous cholecystitis are the following manifestations of the disease:
- periodically occurring dull or nagging pain in the right hypochondrium;
- irritability;
- bitterness in the mouth, flatulence, belching of air;
- the occurrence of pain in the right hypochondrium and epigastrium after eating fatty, spicy and sweet foods;
- insomnia;
- in rare cases, nausea.
Calculous cholecystitis can also occur in the same way; stones can only be detected during instrumental examination.
Calculous and non-calculous cholecystitis may not manifest itself for a significant amount of time, and will manifest itself in the development of complications. Exacerbation of non-calculous cholecystitis can manifest itself:
- bowel dysfunction;
- fever;
- excessive gas formation;
- bitter taste in the mouth.
Exacerbation of calculous chronic cholecystitis is usually accompanied by darkening of urine and lightening of stool; severe vomiting; steatorrhea; intoxication processes; acute paroxysmal pain in the right hypochondrium and epigastric region, radiating to the neck, forearm, lower back, and scapula; tachycardia and high temperature.
Treatment of diarrhea with cholecystitis
If you suspect diarrhea due to cholecystitis, a gastroenterologist will tell you what to do. Without consultation with a treating specialist, drastic measures should not be taken. All you can do yourself is to provide first aid:
- Take a horizontal position;
- Apply a cold compress to the sore spot;
- Call emergency medical assistance;
- You can use an adsorbent drug that will help reduce symptoms such as diarrhea (Smecta, Atoxil, Enterosgel). It is important that the interval between taking drugs of this group and any other medication should be at least 2 hours.
Take an antispasmodic (No-Shpa) and an anesthetic (Analgin, Baralgin, Ibuprofen, Nimid).
If you have diarrhea due to biliary dyskinesia, only a specialist can tell you how to treat it correctly, but antispasmodics are used for such purposes.
Once a diagnosis has been made, treatment can take two forms:
- Surgical (the bladder is completely removed);
- Conservative.
Appointed:
- Antispasmodics: No-Shpa, Papaverine;
- Choleretic: Allohol, Hologon, Decholin;
- Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory depending on the underlying cause.
In addition, the following are excluded from the diet:
- Fatty, smoked, heavy foods;
- Canned food;
- Cocoa;
- Chocolate;
- Alcohol;
- Sweet carbonated drinks.
You need to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions and drink at least 2 liters of water.
It is possible to cure diarrhea in cholecystitis, however, in 20% of cases it is a very advanced form of the disease. Do not delay in contacting a doctor and this problem will be solved much easier and faster, without the intervention of a surgeon.
If the patient is diagnosed with acute or confirmed symptoms of chronic cholecystitis in the acute stage, then treatment in the surgical department of the hospital is recommended. The treatment method is selected according to the form of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. In some cases, conservative treatment is resorted to, which includes:
- the use of antibiotics, which are selected according to the indications and effectiveness of the drug;
- taking antispasmodics in order to normalize the process of excretion of bile into the small intestine;
- prescribing choleretic drugs if the patient has hypotension and the patency of the bile duct is impaired;
- hepatoprotectors if there is liver dysfunction.
Surgical intervention may involve the use of cholecystectomy - this is when the gallbladder is completely removed. Immediate surgery should be performed if the patient has developed diffuse peritonitis and acute bile obstruction; in other situations, operations are carried out as planned.
1 put the patient to bed and provide him with complete rest;
2 apply a cold compress to the area of the right hypochondrium;
3 call an ambulance.
As for medications, you can give the patient some sorbent, for example, Smecta or Atoxil. This will reduce the occurrence of diarrhea. Make sure that taking this drug does not coincide with taking other medications, otherwise the effectiveness of the latter will be significantly reduced. In case of severe pain, you can take No-shpa, Analgin or Ibuprofen.
In the modern world, there is an increase in gastrointestinal morbidity, which greatly reduces a person’s quality of life. More and more doctors are diagnosing gastritis, which affects people of all ages. Depending on the type of illness, specialists select special treatment and a special diet.
Treatment and prevention of the disease
Loose stools with cholecystitis are only a small part of the problem. Severe pain and digestive tract upset require immediate and effective treatment.
- To improve the secretion of bile, choleretic drugs are prescribed: Allohol, Decholin, Hologon.
- To relieve painful symptoms, the course includes antispasmodics: Papaverine, No-shpu. For the same purposes, painkillers are prescribed: Ibuprofen, Nimid.
- Depending on the causes of the illness, anti-inflammatory or antibacterial drugs are used.
- Diarrhea due to stones in the inflamed gall bladder is treated by prescribing sorbents: Smecta, Enterosgel.
Read more about medications that eliminate diarrhea due to cholecystitis
Not all antidiarrheal drugs can stop diarrhea in diseases of the gallbladder and other gastrointestinal organs. If diarrhea occurs that does not go away, you need to contact a gastroenterologist to find out the cause of the disease. Depending on the results of the examination, you can begin to choose a medicine:
Sorbents. Allows the body to remove toxins produced by microbes or from food. Medicines absorb unwanted substances and are excreted from the body in feces. Sorbents have a binding effect. The use of products in this category is undesirable for inflammation of the mucous membranes of the digestive tract. Accordingly, we refuse Enterosgel, activated carbon, silicon dioxide, Atoxil.
Drugs that suppress intestinal motility, for example, the drugs Loperamide, Imodium. They act on the nerve endings of the intestinal walls, reducing peristalsis. As a result, feces pass through the lumen more slowly, and diarrhea stops.
Antimicrobial agents, for example, Nifuroxazide and Levomycetin tablets. They will act on diarrhea caused by uncontrolled proliferation of microbes. Pathogenic bacteria include Protea, Klebsiella, rotavirus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Salmonella.
Enzymes. Doctors recommend Mezim, Creon, and Festal tablets. They will help if the cause of loose stools due to cholecystitis lies in parallel insufficiency of pancreatic function. The group's preparations contain enzymes extracted from the glands of pigs and cattle. The drugs are prescribed temporarily or for life.
Drugs for restoring motor skills. Affects the enkephalinergic system of the digestive tract. Normalize peristalsis, eliminating diarrhea, constipation, flatulence. Trimedat, Meteospasmil are recommended.
Probiotics such as powders “Linex”, “Bifiform”, “Lactiale”. They contain strains of beneficial microorganisms.
Prebiotics, for example, Hilak-Forte drops. Create favorable conditions for the growth of bacteria from probiotics.
The use of drugs normalizes the composition of intestinal microflora and eliminates diarrhea. However, you should not expect quick results. Only a doctor can select effective medications for the treatment of disorders associated with inflammation of the gallbladder.
If the complex does not help, you need to undergo examination to identify other health problems. First, the patient undergoes an ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the abdominal organs, which will show visual deviations in the structure of the digestive tract and the presence of pathological formations.
Detailed and biochemical blood tests will reveal the inflammatory process and anemia. The level of eosinophils is needed to diagnose allergies or parasitic diseases. Increased levels of ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase) indicate liver disease. High cholesterol levels are often a sign of gallbladder problems.
Elevated values of ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and leukocytes in combination with low hemoglobin indicate the likelihood of internal bleeding and often indicate oncology.
If the cause of diarrhea cannot be determined, the diagnosis is supplemented with:
- CT (computed tomography).
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
- By fluoroscopy.
- Colonoscopy.
- Ultrasound of the intestines.
Depending on concomitant pathologies, the therapeutic regimen includes:
- antacids;
- enzymes;
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antimycotics.
If there are mechanical barriers that disrupt the flow of bile and lead to inflammation, surgical intervention is performed. Preference is given to minimally invasive laparoscopic methods.
Cancer is eliminated with:
- operations;
- chemical and radiation therapy;
- embolization (disruption of blood supply to the tumor).
Most often, stool disorder due to gallbladder inflammation is associated with errors in nutrition, so in parallel with treatment, it is necessary to normalize the menu.