03/31/2019 Alena Masheva Health
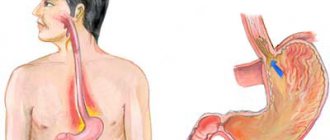
Belching is a completely normal and natural process in the body that occurs after eating. It involves the release of gases from the stomach resulting from the digestion of food. However, if this leaves an unpleasant aftertaste in your mouth, then there is cause for concern. A feeling of bile or bitterness may indicate the presence of some health problems.
We will look at the causes of bile belching, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods in this article. They can be very different. Therefore, you should not turn a blind eye to this problem. Some people try to cope with it on their own at home, but self-medication can be dangerous as it often only makes the situation worse and leads to the development of many serious complications. The best way out is to see a doctor to undergo a full examination and begin complex therapy.
Bitterness in the mouth: what is the problem?
Let's look at this in more detail. As mentioned above, the causes of bile belching can be very different. Most often, the problem is associated with the development of duodeno-gastric reflux. In simple terms: aspiration of stomach contents into the esophagus occurs due to pyloric dysfunction or duodenal hypertension. With these disorders, a person constantly feels an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth. They can develop due to many serious diseases of various etiologies, so doctors advise not to hesitate, but to immediately go to the hospital to receive qualified medical care.
If the digestive system is working correctly, the esophageal sphincters open only when swallowing, preventing the release of digested food from the stomach into the esophagus. But with the development of certain diseases, its normal functioning is disrupted.
According to qualified specialists, the causes of bile belching can be the following:
- pregnancy - as the fetus develops, the uterus gradually increases in size, as a result of which it begins to put pressure on the duodenum, causing liver secretions to enter the stomach;
- congenital developmental defects;
- mechanical injury to the abdominal area;
- hernia and cancerous tumors;
- inflammatory damage to the initial part of the intestine, accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane;
- consequences of long-term use of certain medications;
- duodenogastric reflux;
- various pathologies of the biliary tract, occurring in a chronic form;
- inflammation of the gallbladder of infectious origin;
- consequences of the surgery;
- stones in the kidneys;
- alcohol abuse;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hepatitis;
- liver diseases.
With minor damage to internal organs, clinical manifestations make themselves felt periodically, but if the pathology progresses, then the symptoms become more intense and pronounced, and the patient’s well-being gradually worsens. To select the most effective treatment program, you must first determine the causes of bile belching at night or in the morning. When exactly it manifests itself is of no fundamental importance.
What will help make bile belching less frequent?
Even with well-chosen therapy, bile belching will not go away immediately. It takes time for the inflammation and the resulting swelling of the valves to go away, but you want relief as quickly as possible. This will help by following the rules that will help reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract.
The last meal should occur no later than 4 hours before bedtime. Dinner should be as light as possible, but enough to fill you up. If you have an appetite before going to bed, you should drink a glass of fresh kefir, or better yet, plain warm water, this will dull the feeling of hunger and allow you to fall asleep.
It is better to eat slowly, chewing food thoroughly: this way less air enters the stomach, and, consequently, the pressure inside this hollow organ will be lower. If you have a runny nose, you should empty your nose before eating: disturbances in nasal breathing also lead to the stomach overflowing with air. When breathing through the nose, the pharynx copes with the separation of flows, but when breathing through the mouth, more air enters the esophagus than usual.
After any meal, a light walk of 15-20 minutes is beneficial. If you can’t walk, you should maintain as vertical a position as possible: if you can’t stand, sit down, but the back of the chair or stool should be vertical. You should not lean back on it so that the contents of your stomach, when trying to splash out, are interfered with as much as possible by gravity.
It is good to combat physical inactivity, which often leads to stagnation of bile and, as a result, bilious belching, with the help of physical therapy or any other gymnastics. The exercises should be performed on an empty stomach or 2-3 hours after eating. There is no need to go to the table immediately after class: after physical activity, 20-30 minutes should pass before eating.
It is necessary to establish a water regime: at least drink 1 glass of warm water every 2-3 hours, and ideally do this more often and drink at least one and a half liters of water per day. If it is difficult to drink a glass of water at a time, you can also drink in small portions.
General symptoms
If you belch bile in the morning (the reasons may be of different etiologies), then the clinical manifestations manifest differently in all people. Now let's look at this in more detail. They can be either barely noticeable or pronounced. It is important to understand that in many cases, an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth rarely appears in the initial stages of the disease. As a rule, they make themselves felt at later stages. The following symptoms may be a serious reason to think about going to the hospital:
A serious cause for concern is the simultaneous manifestation of several symptoms. This is most often associated with a disruption in the normal functioning of the body. At the same time, a person’s lifestyle is of no small importance. For example, those who abuse alcohol often experience belching of bile at night during their sleep. It can be associated not only with liver dysfunction, but also with many dangerous pathologies.
How to eat when belching with bile
Meals during treatment for bilious belching and the diseases that led to it should be fractional. You need to take food 5-6 times a day (or every 2.5-3 hours), in portions of about 300 grams.
Among the drinks, those that irritate the gastric mucosa are prohibited: coffee, strong tea (it doesn’t matter whether it’s black or green, it’s the strength that matters), sour fruit drinks. In addition, the drink should not be too hot or cold; a combination of two different temperatures is especially harmful. For example, if you wash down ice cream with hot coffee or a hot cutlet with ice-cold juice, this can provoke not only bitter or sour belching, but also an attack of gastritis and even biliary colic. The temperature requirement applies not only to drinks, but also to food.
All foods that are harmful for any disease of the digestive system are prohibited. This includes cabbage, legumes, rye bread, grapes, as well as everything fatty, spicy, salty, spicy and fried. You will have to forget about fast food for a long time: even when the diet allows cutlets, it is better to make a burger at home from natural ingredients.
Since almost all snacks from nearby stores are not allowed during a diet, and the principle of fractional meals is extremely important for the treatment of bile belching, it is necessary to creatively approach the problem of snacking. It can be fruits, sandwiches, homemade unsweetened soufflés. If your health does not allow you to consume even such foods, baby food, which can be lightly salted, will help out at the beginning of the diet. The main thing is that meals should be complete: at the dining table, and not at the monitor, leisurely, in a pleasant company or, conversely, alone.
Home cooking will also have to change. At first, dishes prepared by boiling or steaming are preferred. At the beginning of the diet, puree soups and minced meat dishes are desirable - first steamed meatballs, then stewed cutlets. Eggs are necessary in the diet, but not fried. You can eat hard-boiled or soft-boiled eggs, but it is preferable, especially at first, to have an omelet, and better yet, a steam one.
As your general condition improves, the diet can be expanded to gradually include fruits, vegetables, stews, chopped rather than pureed foods, harder cereals, and so on. At the last stage, nightshades (for example, tomatoes), citrus fruits and mint are introduced into the diet: these products have a relaxing effect on the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, including sphincters, and can be consumed only when the disease has subsided.
Although the diet for gastroenterological diseases has been tested for decades on millions of patients, we must not forget about the individual reactions of the body. It is rare, but it happens that an approved product causes an adverse reaction in the patient: abdominal pain, heartburn, stool disorders. Of course, such a product should be abandoned during illness. Most often, a healthy digestive system will react normally to such a product, although if the cause of an individual reaction is an allergy, it may remain.
Manifestation of the problem during a night's rest
What do you need to know about this? As medical statistics show, belching bile at night during sleep signals the presence of diseases of the gallbladder and its ducts. In a horizontal position of the body, the sphincter muscles relax, as a result of which liver secretions enter through the esophagus from the stomach into the oral cavity. This does not happen in a completely healthy person, but with the development of any pathologies, muscle tone is disturbed. There are a lot of diseases that provoke the development of such a problem.
But they all share common symptoms:
The main danger of these diseases is that very often they occur in a latent form, without any symptoms. Therefore, if you belch bile at night in your sleep (what to do will be described in detail below), then you should consult a doctor, since then it may be too late.
Symptoms - something to think about
Normal belching appears after eating. The presence of bile and bitterness at the initial stage of disorders may be rare. The more serious the problem, the more often a person feels discomfort and belching with bile begins to be a consequence of any snack. At first, the amount of bile in the stomach may be minimal. But if the problem is not eliminated, changes will appear in the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus. Sometimes a person does not attach importance to belching because he does not connect this symptom with disorders in the internal organs. Additional symptoms may be cause for concern and a visit to the doctor:
- Constant desire to drink. Drinking one or two glasses of water does not leave a person feeling thirsty. This sensation occurs not only after eating salty, spicy food, it haunts you constantly.
- The manifestation of heartburn is not isolated cases, but regular ones. Bile from the stomach flows freely into the esophagus, irritates it, and can cause serious burns.
- Stinging, pain, heaviness in the stomach, right side, lower hypochondrium.
- Sudden nausea leading to vomiting. Relief occurs only after the stomach has completely emptied. There is a bitter taste in the mouth.
- Belching bile is the most obvious symptom of dysfunction of the digestive system.
Recommendation! If one or two signs from the list above are observed, you should consult a doctor.
The listed signs of disorders in the body can manifest themselves complexly or individually. It all depends on the person’s lifestyle and the presence of other diseases that accompany the appearance of belching with bile (gastritis, ulcers, pancreatitis, oncology).
After meals
An unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth is not always associated with dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. Belching bile after eating can be caused by liver dysfunction. This internal organ plays an important role in digestion, so even minor disturbances cause a certain reaction. Eating food is a huge challenge for the liver, as it puts a lot of stress on it. Ongoing diseases can lead to disruption of its normal functioning, so it ceases to normally perform the tasks assigned to it.
A person may experience the following symptoms:
Any liver disease is very serious, so if these clinical manifestations occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. In an advanced form, they are much more difficult to treat and can lead to the development of many complications.
Causes and types of belching after eating
The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Content:
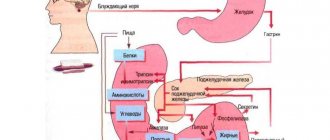
A burp is the sudden (often loud) release of air from the mouth that has accumulated in the esophagus or stomach, sometimes along with a small amount of gastric contents. Belching occurs due to contraction of the stomach muscles when the cardiac sphincter is open.
Everyone, both healthy and sick, faces this unpleasant phenomenon. Belching has haunted us since birth, since almost all babies, without exception, swallow excess air during the sucking process. But with full development and growth, this problem goes away.
With proper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, belching practically does not happen, and if it does happen, it is extremely rare and mostly empty (with air). We regularly swallow small amounts of air, which allows the body to regulate gastric pressure, but then it comes out in such tiny portions that we do not notice it.
Hence the conclusion: belching can have a physiological and pathological origin.
Causes of belching
Let's consider the reasons for the appearance of physiological belching.
Belching periodically appears in people with a normally functioning gastrointestinal tract. As a rule, this is a burp of air, or with the smell of what was eaten or drunk the day before. It occurs when a person:
- has a heated conversation while eating;
- is in a hurry and, practically without chewing, swallows food;
- eats in a state of emotional stress;
- overeats;
- suffers from aerophagia (excessive swallowing of air during and outside of meals).
Remember Professor Preobrazhensky’s remark from the film “Heart of a Dog” about reading newspapers at lunch? Any gastroenterologist will completely agree with him.
However, people face this problem not only because of how they eat, but also because of what they eat.
It's no secret that some foods and drinks increase gas formation. The gas accumulated in the stomach will certainly exit through the esophagus.
These include:
- carbonated drinks;
- popular oxygen cocktails today;
- onion;
- milk;
- ice cream;
- Legumes and cabbage can also cause belching, but the main consequence of their excessive consumption is flatulence.
But you should not take persistent air belching too lightly, as it can be a harbinger of stomach cancer.
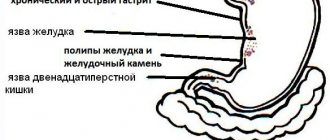
The causes of pathological belching are diseases of the digestive system:
- pancreatitis,
- gastritis,
- gallbladder diseases,
- gastroduodenitis,
- hiatal hernia,
- peptic ulcer.
Persistent belching of air with a feeling of fullness in the stomach, which later acquires a rotten smell, may be a symptom of stomach cancer.
Belching after eating
The causes of belching after eating can be due to both physiological, which were already mentioned above, and pathological processes that disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. These are diseases such as:
- chronic or acute pancreatitis,
- gurgles,
- biliary dyskinesia,
- gastritis with high acidity,
- esophagitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus).
Let us note that frequently repeated belching after eating in an adult can be a symptom of health problems, and not only those affecting the gastrointestinal tract, so do not neglect professional advice.
Frequent (constant) belching
The human body can react in a similar way to:
- for regular errors in diet;
- to improper organization of food intake;
- aerophagia, including neurotic nature;
- to various pathological processes.
Constant burping may indicate:
- for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- for cardiovascular diseases.
In addition, excessive and frequent belching can be observed:
- for problems with the lower alimentary sphincter caused by a hiatal hernia;
- for stomach/duodenal ulcers;
- for non-ulcer dyspepsia;
- with gastroesophageal reflux;
- with pathology of the pancreas and bile ducts.
Types of belching
Types of belching:
- Sour belching after eating
- Belching with bitterness
- Belching with acetone
- Burps without odor
Depending on what causes the belching, it may be:
- sour, which indicates increased acidity of gastric juice;
- bitter - when bile is thrown into the stomach;
- putrefactive or give off acetone - with stagnation and fermentation of undigested food in the stomach and with diabetes;
- air – for aerophagia, dietary disorders and early stages of various gastrointestinal diseases.
Let's take a closer look at the causes of various types of pathological belching.
Sour belching after eating
Sour belching after eating can be a symptom of:
- Inflammatory disease of the gastric mucosa - gastritis;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- Peptic ulcer;
- More serious diseases, including stomach cancer.
Sour regurgitation always accompanies pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract, and it is impossible to get rid of this problem without starting treatment of the causative diseases.
If a man:
- regularly burps sour, later belching may taste rotten;
- loses appetite;
- suffers from heartburn, accompanied by excessive salivation;
- experiences bouts of nausea, even consuming a portion of the most benign food, slightly exceeding the norm;
- experiences heaviness in the epigastric region after eating, sometimes developing into severe pain.
This means that he needs to seek help from a gastroenterologist, since all these signs may indicate gastritis or peptic ulcer disease.
Usually, belching occurs regularly after eating; sometimes gastric contents enter the oral cavity along with gases.
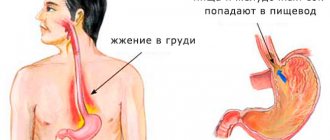
“Sour burps” indicate that the stomach contains more acid than is needed to digest food.
With gastrodigestive reflux, the muscular valve that separates the esophagus from the stomach does not work properly, and acidic stomach juice regularly flows into the esophagus, and from there into the oral cavity.
This condition in 10% of cases can cause the development of Barrett's syndrome, in which, due to frequent irritation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus by the acidic gastric nipple, its structure changes. It becomes similar to the intestinal mucosa.
Constant companions of this disease are:
- very frequent sour belching;
- heartburn;
- sharp or dull pain in the upper stomach.
According to recent studies, the risk of developing esophageal cancer is especially high in people with reflux, since they take medications that reduce symptoms and do not promptly consult specialists to monitor their health condition.
Belching with bitterness
Belching with bitterness is also a sign of certain diseases or disorders and occurs when:
- Gastroduodenal reflux. Bile from the liver should enter the duodenum and then into the lower intestines. When the function of the pylorus is impaired and pressure in the duodenum increases, which can be caused by certain diseases, bile moves in the wrong direction and enters the stomach;
- Injuries, hernias, tumor diseases of the abdominal organs. With mechanical compression of the duodenum, bile, which is under pressure, overcomes the pyloric sphincter and again enters the stomach;
- Taking certain medications. Muscle relaxants and antispasmodics reduce the muscle tone of the sphincter, which causes a gap to form between the duodenum and the stomach;
- Surgical interventions. If during the operation part of the sphincter muscles was cut, then bile will constantly enter the stomach;
- Chronic duodenitis. Inflammation and swelling of the duodenal mucosa increases pressure, due to which duodenal contents are thrown into the stomach;
- Pregnancy. The reason is the same pressure on the duodenum.
From time to time, bile enters the stomach in healthy people. If this happens rarely, there are no symptoms.
Belching with acetone
Belching with acetone can be caused by diabetes.
Digestive disorders, the faithful companion of which is belching, are characteristic of late complications of diabetes mellitus:
- prolonged hyperglycemia;
- diabetic neuropathy;
- violations of carbohydrate metabolism compensation.
Reasons for belching with acetone in diabetes:
- an autonomous form of neuropathy that affects the nerves responsible for the functioning of the digestive tract. Food moves through the esophagus, stomach and intestines with disruptions due to disturbances in the normal rhythm of muscle contractions. There is a delay in the evacuation of contents, and reflux develops.
- decreased tone (paresis) and paralysis (atony) of the stomach. These conditions cause stagnation of food masses in the stomach cavity and create favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
People suffering from diabetes, complicated by disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, are bothered by belching, heartburn and nausea, which worsen after eating.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (impaired carbohydrate metabolism) causes acute atony of the stomach and intestines, the mucous membrane of which can be irritated by ketatic acids and acetone.
All described conditions require contacting an endocrinologist, with subsequent treatment and observation.
Burps without odor
The causes of odorless belching may be:
- physiological,
- pathological.
Physiological belching can be caused by:
- aerophagia - swallowing excess air during eating, which then comes out through the oral cavity;
- diseases of the oral and nasal cavity;
- drinking carbonated drinks or beer;
- hot or cold drink;
- whipped, “airy” drinks – cocktails;
- some products (milk, ice cream, onions);
- binge eating;
- second phase of pregnancy;
- abuse of chewing gum;
- snacks on the go;
- poor chewing of food;
- playing sports and other physical activities after meals;
- sleep after eating;
- eating in a state of strong emotional stress;
- other nutritional disorders.
Constant and frequent “empty” belching is a concomitant symptom of certain diseases. Pathological reasons:
- Neurotic aerophagia. In this case, a person swallows air not only while eating, but at any other time;
- Disorders of gastric motility and tone;
- Chronic gastritis;
- Peptic ulcer;
- Pyloroduodenal stenosis;
- Narrowing of the esophagus.
In addition, “empty” belching can be a sign of cardiovascular disease:
- cardiovascular failure;
- cardiospasm;
- aneurysm of the descending aorta.
The body of a healthy person can be compared to an orchestra in which all the instruments are well-tuned and always play on time.
Belching, even if odorless, may indicate that pathological changes are occurring in the gastrointestinal tract, which should not be ignored in order to prevent the development of the disease.
Belching in a child
For infants, belching is considered a normal reaction of the body.
Swallowing small amounts of air during feeding is necessary to regulate intragastric pressure.
Due to the imperfection of the baby's gastrointestinal tract, the gas bubble lingers in the stomach or passes into the intestines. In this case, the child experiences severe bloating, which can provoke intestinal spasms. The baby will worry and cry until he burps air. Therefore, pediatricians recommend not putting the baby down immediately after feeding, but holding him in an upright position until he burps. But with full development and growth, this problem goes away.
Highly excitable children who worry and cry during feeding should be observed by a neurologist, and breaks during feeding should be taken to hold them in an upright position to regurgitate excess air. Such babies should be prepared for eating. Carry in your arms, calm down.
If frequent belching is observed in a child after one year, you need to consult a doctor, and start with a consultation with a pediatrician.
At this age, the state of the child’s nervous system is also of great importance. If the baby is easily excitable, then he is more prone to gastrointestinal diseases.
Belching of food or air can be caused by:
- improper organization of the child’s nutrition;
- exciting games while eating;
- watching cartoons that cause an emotional outburst;
- adenoids;
- chronic tonsillitis and runny nose;
- increased salivation.
The reasons for constant belching in preschoolers and schoolchildren may be the same as for adults. These are diseases:
- Gastrointestinal tract,
- liver,
- biliary tract.
How to get rid of belching?
With episodic belching, treatment, as a rule, is not required, since it occurs due to eating disorders and errors in diet.
The reason to visit a doctor is constant belching, repeating for an hour for five days. It may indicate pathology and requires identification of the cause and a thorough examination.
A specialist will diagnose and prescribe treatment for the disease that causes constant belching.
What medications should I take? List of medications for belching
As for physiological belching, in order to get rid of it, you need to:
Correctly organize the process of eating, that is:
- eat without haste, chewing food thoroughly;
- do not have emotional conversations while eating, and in general, do not start eating when nervous;
- do not expose yourself to heavy physical activity.
- Avoid soda, beer, and oxygen cocktails;
- Do not eat foods that cause belching. By the way, belching can be an individual reaction of a person to some product that can be identified and stopped consuming;
- Eat nutritiously, high-quality foods that satisfy the body’s need for microelements and vitamins;
- Observe moderation in food, the golden rule is very relevant here: “It’s better not to... than to over...”, you can eat less, but more often;
- Do not drink too hot tea or coffee;
- When drinking, do not use a straw;
- Stop chewing gum; there are many other ways to freshen your breath;
- Stop smoking;
- Walking after eating is enough even for half an hour.
If belching with or without odor is accompanied by pain in different areas of the abdomen, then you should not delay seeking help from a gastroenterologist; self-medication is unacceptable. They can be harbingers of very serious diseases, the timely diagnosis of which becomes the key to successful treatment.
[Video] Dr. Berg - What to do if you have bloating, constipation, acid belching?
Author of the article:
Gorshenina Elena Ivanovna |
Gastroenterologist Education: Diploma in General Medicine received from the Russian State Medical University named after. N. I. Pirogova (2005). Postgraduate course in the specialty "Gastroenterology" - educational and scientific medical ]Our authors[/anchor]
Who should I contact for help?
So what do you need to know about this? To deal with a problem, you must first determine what caused it. Belching of bile, the causes and treatment of which are discussed in our review, is evidence of a disorder in the gastrointestinal tract.
Therefore, you should contact the following doctors for help:
- The therapist conducts an oral interview with the patient and, based on the collected data, writes a referral for consultation with the right specialist.
- Gastroenterologist - deals with problems related to the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. You can make an appointment with him without first visiting a therapist.
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor decides to prescribe additional laboratory tests to assess the patient’s condition and draw up a detailed clinical picture. As soon as the examination results are in hand, the most effective treatment is selected, which, as a rule, is based on taking medications.
Diagnostic methods
What are they and what are their features? So, you are belching bile, what should you do? The first thing you need to do is make an appointment with a therapist or gastroenterologist. It is especially not recommended to hesitate if there is a white or yellowish coating on the tongue, and there is also a bitter taste in the mouth. Patients are examined according to the following scheme:
A number of specialized laboratory tests may be required to obtain more detailed information. The most commonly prescribed are:
- EGDS or esophagogastroduodenoscopy is the study of the inner walls of the esophagus using a flexible hose with a video camera installed at the end. It is highly informative and provides the opportunity to visually assess the degree of damage to internal organs.
- Ultrasound - it can be used to detect tumors and neoplasms in the early stages. It can be carried out both detailed and complex.
- Colonoscopy is a visual examination and assessment of the condition of the intestines.
- Probing the stomach - taking juice for analysis to determine acidity and the presence of certain enzymes. The essence of the study is that a long tube with a probe is inserted into the patient’s stomach and liquid is taken with its help. The procedure is carried out over several days on an empty stomach in a hospital setting.
- Liver examination is mandatory. This is due to the fact that belching of bile is most often associated with a disruption in the normal functioning of this internal organ, so at the examination stage it is important to make sure that there are no pathologies.
The doctor decides which laboratory test methods will be prescribed based on the information received from the patient and the symptoms present. After receiving the results and making an accurate diagnosis, the most effective and safe treatment program is selected. As a rule, a course of medication is prescribed in combination with a special diet. This will be discussed in more detail below.
How is therapy carried out?
Let's look at this aspect in more detail. To date, there is no universal treatment for bile belching, the causes of which cannot always be accurately established. Complex methods are used, aimed not only at eliminating clinical manifestations and normalizing the patient’s well-being, but also getting rid of the cause, as well as preventing future relapses. A prerequisite before starting treatment is a complete examination. According to the doctors themselves, each case has its own specifics and therefore requires an individual approach.
It is immediately worth noting that people with problems with the gastrointestinal tract go to the hospital too late, since most diseases proceed in a latent form for a long time and manage to develop into a chronic form. Therefore, they cannot be completely cured. The only exception is short-term dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and liver caused by poor diet, abuse of tobacco and alcohol products, as well as long-term drug treatment. This pathology is often accompanied by belching of bile and heartburn, as well as a feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
For problems with the gallbladder, symptomatic treatment is carried out, and in the case of pathology of infectious etiology and inflammatory damage to internal organs, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. To make you feel better, the patient is also prescribed analgesics. One of the key requirements is proper nutrition and giving up bad habits, especially drinking alcohol.
If a patient's examination reveals stones in the kidneys or stomach, then drug therapy is useless. In this case, surgical intervention is prescribed to remove them. However, even if it is successful, the person may still periodically suffer from belching bile in the morning or at night. Even after rehabilitation and full recovery, you must adhere to a special diet and try to lead a healthy lifestyle.
For viral hepatitis, patients are placed on inpatient treatment with the use of antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs. The most severe case is cirrhosis of the liver. Painkillers are prescribed.
Most often, treatment of bile belching is carried out according to the standard regimen. It looks like this:
- Taking antacids intended for the treatment of acid-related gastrointestinal diseases. The drugs are available in tablet form and are quickly absorbed by the intestines, creating a protective barrier on its walls. They relieve pain and normalize acidity.
- Taking medications aimed at strengthening and relieving sphincter muscle spasms.
- Taking medications that reduce the level of acidity in the stomach.
- Taking medications that stimulate the production of bile and normalize liver function.
Medicines are selected for each patient individually depending on the diagnosis, the characteristics of the individual patient’s body and his clinical picture. According to many experts, the most effective for belching bile at night and during the day are the following:
- "Almagel", "Rennie" and "Maalox": available in the form of tablets and suspensions. They normalize acidity, and also protect the stomach and esophagus and cleanse them of toxins. In addition, it neutralizes hydrochloric acid.
- "Phosphalugel": considered one of the best drugs for bile belching, as it reduces its secretion.
- “Pancreatin”, “Pangrol” and “Creon”: improves digestion, eliminates atony, reduces the volume of gastric juice and bile produced.
- "Omeprazole": normalizes the acidic environment, eliminates heartburn and a feeling of heaviness, and also relieves general symptoms of certain gastrointestinal diseases.
- "Omez": available in the form of capsules in a quickly dissolving shell. Helps strengthen sphincter muscles and reduce the amount of hydrochloric acid produced.
- “Gasten”: is produced on the basis of natural ingredients of origin, therefore it has practically no contraindications or side effects. Prescribed to support the liver and normalize its functioning.
When belching bile, it is not recommended to start treatment on your own or take any medications. All pathologies that exist today have certain characteristics, so their treatment will be different. If you do not like hospitals, but a week after starting treatment the symptoms have not disappeared, then in this case it is better to consult with a qualified specialist. Further self-medication can significantly aggravate the course of the disease and lead to irreparable consequences.
Why treat belching with bile?
The simplest argument in favor of treatment is bad breath. It often occurs due to inflammation in the esophagus and stomach, and the reflux of bile into the upper gastrointestinal tract prevents the mucous membrane from healing.
But there are also more serious arguments: belching bile, which seems harmless at first glance, leads to serious consequences. These are complications of gastritis and inflammatory diseases of the esophagus, which can lead to ulcers, bleeding and even cancer, which are especially dangerous in the gastrointestinal tract. They quickly metastasize and spread throughout the gastrointestinal tract and the body as a whole.
Traditional medicine
Many people suffer from belching bile. What to do to get rid of it if you don’t have time to go to hospitals? In this case, you can turn to traditional medicine, which our ancestors used for many centuries. There are quite a few recipes that will help get rid of the unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth. These can be various herbal decoctions and infusions, as well as the juices of some fruits and vegetables.
Here are some good recipes:
- Mix equal amounts of freshly squeezed carrot and potato juice. Drink it three times a day shortly before meals for 2 weeks.
- Take 100 milliliters of fresh cranberry and aloe juice, add a tablespoon of honey. Mix all ingredients thoroughly and dilute with 200 ml of clean drinking water. The product is drunk for 7 days 3 times a day before meals. If the symptoms are intense and pronounced, then the course should be repeated after a month.
- Take one tablespoon each of dried fennel flowers, lemon balm leaves and chicory root powder, pour 1/2 liters of boiling water over the raw materials. Leave for 2 hours, then pass through a fine sieve or gauze folded in several layers. The decoction is drunk three times a day after meals.
It is worth noting that traditional medicine is not a panacea for all ills. Therefore, if after some time no results are observed, then you should go to the hospital, since some diseases require complex therapy, the absence of which can lead not only to the development of serious health complications, but also to death.
Why does bile belching occur?
For the appearance of bile belching, a combination of several factors is necessary:
- weakness of the sphincters - valves that prevent the contents of the duodenum from entering the stomach, and gastric juice and semi-digested food from entering the esophagus;
- violation of the outflow of bile due to diseases of the gallbladder: bile may constantly leak or be released in portions, but untimely, which can also cause vomiting of bile;
- the presence of a provoking factor - overeating, especially at night, eating food that provokes excessive secretion of bile - fatty, hot, spicy, drinking alcohol or physical activity in a position that involves a prolonged position with your head down, for example, washing your hair in an inclined position.
The first factor occurs most often due to exacerbation of banal gastroduodenitis - the most common gastroenterological disease. Other causes of weakened sphincters include tumor diseases and sphincter hernias. In modern people, bilious belching often occurs as a result of stress and overwork, but to get rid of it, simple rest is not enough.
A few words about proper nutrition
Let's look at this aspect in more detail. As has been mentioned many times before, treatment cannot be effective without a special diet. This is due to the fact that belching can be a consequence of poor nutrition. If you experience an unpleasant aftertaste and bitterness in the mouth or other more serious symptoms, the first step is to completely reconsider your diet. The following should be excluded from it:
It is recommended to steam, boil or bake food in the oven. The menu must include eggs, dairy products, cabbage, carrots, apples, strawberries and cucumbers. They stimulate the removal of bile from the body, which has a positive effect on overall well-being. In this case, the serving size should not exceed 250 grams. It's better to stay a little hungry, but eat more often.
Preventive actions
This aspect needs to be given special importance. In order to never encounter bile belching (what to do with it was described in detail above), you need to completely reconsider your daily lifestyle. In addition, doctors recommend adhering to the following preventive measures:
These simple tips will help significantly reduce the risk of belching with a bitter taste in the mouth.
Folk remedies
To alleviate the patient’s condition and eliminate unpleasant symptoms such as bitterness in the mouth and belching with air, the use of alternative medicine methods is allowed:
- If the passage of air through the esophagus was caused by gastritis with increased gastric secretion, then it is recommended to drink teas made from mint, lemon balm and raspberry branches daily.
- Flax and fennel seeds help normalize stomach acidity, which should be consumed every morning, a tablespoon on an empty stomach.
- You can eliminate increased gas formation using the following remedy: 120 ml of cranberry juice, 120 ml of aloe juice, 15 ml of honey, 250 ml of warm water. All ingredients must be mixed thoroughly. Drink 50 ml of the drink daily for six months.
- It is beneficial to drink a drink made from linden blossom, fennel and mint. The course of treatment is 3 months, after which it is necessary to take a break for a month and resume treatment.
- For frequent belching with an unpleasant aftertaste, it is recommended to consume 300 ml of natural goat milk daily.
In case of severe heartburn, which often accompanies belching, you need to take calamus root powder on the tip of a knife, then drink plenty of water.
Despite the fact that traditional medicine recipes are based on natural ingredients, it is necessary to consult your doctor before starting therapy.