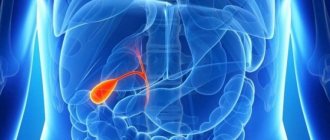
The gallbladder is an internal organ important for the digestion process and has a pear-shaped shape. It is located on the right side directly under the liver. Conventionally, the gallbladder is divided into three components. The widest part is called the bottom, the place where the bladder narrows is called the body, and the narrowest part is the neck, from which the duct extends. Bubble sizes range from 60 to 120 mm.
The main function performed by the gallbladder is the processing, accumulation and storage of secretions produced by the liver. The organ is important for digestion: the bile stored in it is excreted into the intestines to break down fats received with food. Another of its functions is to protect other internal organs from the harmful effects of hypotoxic acids.
What is gallbladder constriction?
Constriction of the gallbladder is a negative change in the shape of the organ.
A congenital constriction is formed in a child as a result of development in the womb. This occurs in the fifth or sixth week during the development of the digestive tract organs. The congenital disease does not cause any special sensations or complications. There is a possibility that the pathology will disappear as you grow older. However, for certain reasons, cholelithiasis or pericholecystitis may occur.
Acquired constriction of an organ occurs in a person in adulthood or old age. The disease is dangerous because it causes stagnation of secretions and occasionally leads to the death of cells on the walls of the internal organ.
Therapy methods
The doctor selects a treatment method depending on the cause that caused the pathological disorder. If it is not detected, the disease will reappear. There is pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy. The first is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. Symptomatic treatment alleviates the patient's condition during the acute stage of the disease.
The dosage of drugs is selected individually for each patient. It depends on the condition of the internal organs and the cause of the disease.
Pathogenetic therapy includes radical and organ-preserving methods.
- Diet. To avoid a process in which increased bile formation occurs, you should adhere to proper nutrition. Fatty, spicy, fried, salty foods are excluded from the diet. Food should be consumed in small portions, 5-6 portions per day. A person should not remain for a long time with an empty stomach.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. They help reduce the immune system response in the organ. There is a decrease in the flow of interstitial fluid, so the swelling goes away.
- Choleretic agents. Promote increased secretion production and its further outflow. The method is used if the exit route of biological fluid is not obstructed by excessive narrowing of the lumen or concretions.
- Surgical intervention. The method is used if, due to pathology, the lumen is excessively narrowed, stones have appeared that prevent the release of bile. Surgery can be performed in early childhood to eliminate the risk of inflammatory processes.
If the constriction of the gallbladder does not cause a disturbance in the patient’s body, does not affect his well-being, or does not threaten his life, therapy may not be carried out. You can live with this condition for the rest of your life.
Therapy begins if the process worsens, inflammation and the formation of adhesions begin. Therefore, if a patient belongs to a risk group, he must constantly undergo laboratory tests and undergo instrumental examination methods. If the inflammatory process begins, it is possible to eliminate it with the help of medications without resorting to surgery.
Additionally, symptomatic methods of therapy are prescribed that eliminate the negative impact of the disease on the body:
- Painkillers. It is used only according to doctor's indications, for acute pain syndrome. It is recommended not to use analgesic therapy for more than 7 days, since after the passage of time, addiction to the active substance of the drug is possible.
- Antipyretics. During an acute inflammatory process, body temperature may rise to critical values, above 38.5 degrees. In this case, it is necessary to use antipyretics, which should additionally eliminate inflammation and reduce the pain effect.
Etiology of the disease
The acquired constriction appears during the life cycle. Its formation is provoked by the following reasons:
- the presence of adhesions on the walls of the organ resulting from the inflammatory process;
- omission of other internal organs that produce compression;
- stone formation;
- an increase in the size of the liver that occurs due to various pathologies;
- constant intense physical activity, including lifting heavy objects;
- prolonged fasting followed by overeating;
- sudden weight gain;
- unbalanced diet, strict diets and long-term consumption of junk food;
- frequent nervous tension, stress, accompanied by eating a large amount of food.
Sometimes doctors associate the occurrence of organ constriction with pathologies of other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pregnant women are at risk, since during pregnancy there is a possibility of compression and displacement of internal organs.
People who are often in a sitting position are more susceptible to the disease. Sedentary work increases the risk of constriction.
Watch the video to see how fasting affects the gallbladder:
Features of the diet and menu for constriction or kinking of the gallbladder
An important point in the treatment of this disease is diet .
If the pathology can be eliminated and is not accompanied by stone formation, a diet is indicated at the time of therapy.
In chronic forms of constriction/kinking of the gallbladder, as well as when diagnosing cholelithiasis, patients must adhere to certain nutritional rules throughout their lives:
- The amount of fried, sour, spicy foods should be kept to a minimum. An ideal alternative would be food that is steamed, boiled or baked in the oven/over a fire.
- During the day you should drink at least 2 liters of purified water. It is useful to drink mineral water, but without gases. Alcohol should be excluded.
- The daily menu should include 5-6 meals, but you should not overload your stomach. Preference in the diet should be given to fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and seafood. You should forget about fast food.
- Sweet foods (including honey, chocolate, jam), baked goods, and some dried fruits (raisins, dried apricots) negatively affect the quality of bile. But parsley, pumpkin juice, rose hip decoction, and olives have the opposite properties.
- Consuming corn oil daily will protect the mucous membrane of the gallbladder from inflammation.
Recommended menu for the treatment period:
- Fresh vegetables (carrots, celery), sauerkraut : no more than 150 gr. before every meal.
- Boiled egg with weak tea. You can make an omelet from eggs. Tea can be replaced with coffee, juice, or rosehip decoction.
- Borscht without meat, soups with milk/vegetable broth.
- Lean meat. It can be boiled, then baked in the oven, and cut into pieces before eating. It is better to use chicken or beef. Alternative option: sea fish (perch, hake), boiled milk sausages.
- Vegetable salads can be seasoned with vegetable/corn oil. Adding parsley or dill to these dishes will have a good effect.
- Crumbly porridges are alternated with pasta made from durum wheat. It is useful to consume bran every day: it prevents the process of stone formation. For the same reasons, doctors advise eating bread with bran. Patients can treat themselves once a week to fresh buns or cheesecakes with cottage cheese.
Food should not be cold or hot : it should be heated before consumption, or allowed to cool slightly.
After finishing your meal, you should not go to bed for 2 hours: problems with the outflow of bile can cause intestinal ulcers.
Rate
—
Clinical picture of gallbladder constriction
The congenital disease often goes away without symptoms. The problem is discovered accidentally during an ultrasound examination. If the constriction is strong, then when transferring the baby to solid food, the following may occur:
- nausea;
- periodic pain in the peritoneum;
- gagging.
Often such symptoms are mistaken for a gastrointestinal disorder.
A disease acquired during life sometimes also occurs without symptoms, but more often it still has a certain clinical picture. With prolonged stagnation of bile or the onset of the inflammatory process, the following signs will make themselves felt:
- vomiting attacks, accompanied by the release of a certain amount of bile;
- yellowness of the skin and sometimes mucous membranes;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- severe pain on the right side under the ribs;
- change in the color of stool, becoming colorless;
- the presence of dark-colored urine;
- loss of appetite and weight loss;
- profuse sweating;
- bowel disorder, most often characterized by diarrhea;
- yellow or white coating on the tongue;
- heaviness and unusual sensations in the stomach.
Rare symptoms are:
- loss of consciousness;
- transfer of pain from the peritoneum to the back;
- elevated temperature.
Symptoms
Often, a congenital kink of the bladder does not “give signals”, and a person learns about its presence by chance. An ultrasound or other study needed to diagnose a disease not related to the bend can tell about the deformation.
The symptoms that appear are subtle, so people often ignore them. The patient should be alerted to:
- nausea that appears immediately after waking up,
- feeling of discomfort after eating unhealthy food,
- bloating,
- frequent vomiting.
Obviously, the symptoms listed are characteristic of many disorders.
Acquired constriction in the gallbladder in most cases has a more pronounced clinical picture (however, it can also be asymptomatic). There are quite a lot of symptoms:
- Pain (often aching) in the area of the right hypochondrium.
- Paroxysmal nausea and vomiting.
- Yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes.
- A bitter taste appears in the mouth.
- Profuse sweating.
- Loss of body weight for no apparent reason.
- Loss of appetite, aversion to food.
- Loose stools, in rare cases constipation.
- The pain radiates to the collarbone and back.
- In very rare cases, loss of consciousness.
- Belching, heartburn.
- Darkening of urine and discoloration of stool.
- Discomfort in the stomach, heaviness in the abdomen.
Symptoms depend on which part of the gallbladder was marked by the constriction. Congenital pathology is treated during exacerbations, and acquired deformity requires treatment immediately after diagnosis. It is necessary to eliminate pain, cope with inflammation and normalize the flow of bile.
Diagnosis of the disease
The following actions help to diagnose gallbladder constriction:
| Initial examination by a gastroenterologist | During the examination, the doctor interviews the patient, identifying the symptoms of the disease. |
| Examination of the patient's body | The doctor palpates the patient's abdominal area and assesses the condition of the mucous membranes and skin. |
| Laboratory examinations | Specialists conduct an analysis of the patient’s blood, urine, and stool to determine the degree of development of the disease and the presence of complications. |
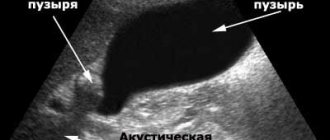
| Ultrasound examination | Using an ultrasound, a specialist determines the thickness of the walls of the internal organ, its size, and the presence of pathology. This study includes several steps. First of all, an ultrasound is performed on an empty stomach after a special three-day diet. The gastroenterologist gives the patient dietary recommendations in advance, and the patient prepares for the ultrasound at home. The second study is carried out half an hour after taking the choleretic medication. |
Diagnostics
The main way to detect gallbladder deformation is to perform an ultrasound. In some cases, it allows you to evaluate not only the shape and size, but also the performance of the gallbladder. However, finding out the actual causes of deformation is not so easy. Even comprehensive diagnostic measures do not guarantee that difficulties can be avoided.
To determine the congenital or acquired nature of the deformity, a test with choleretic agents can be performed: for example, with egg yolks. If the constriction is congenital, the shape of the bladder on ultrasound will not change after taking choleretic drugs.
Sonographic signs of deformation reveal the presence of linear formations with different localizations. They can be determined by performing a transverse scan. The constriction is often fixed at the junction of the body and the neck. The bile located in the bladder has the appearance of an echo-negative formation. The study reveals the degree of dyskinesia, which is present in 80% of cases.
Treatment
Drug therapy
When prescribing treatment by a gastroenterologist, the following may be used:
- choleretic agents (Gepabene, Flamin, Allochol, Odeston), which help get rid of bile stagnation and avoid stone formation;
- antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Baralgin), which help cope with severe pain;
- antibiotics that help get rid of the inflammatory process.
Surgery
Treatment through surgery is prescribed if the outflow of bile is completely blocked, which leads to rupture of the organ. To prevent such a situation, the surgeon completely removes the damaged organ.
The operation is carried out as follows:
- The patient is under general anesthesia.
- An incision in the skin and tissue is made in the navel area, and a cannula is inserted into the incision.
- To inspect the internal cavity, a special instrument attached to the camera is inserted.
- Using fixed cannulas, the gallbladder is separated from the walls and the affected internal organ is removed.
- The incisions made are sutured by the surgeon.
Traditional medicine
Traditional methods of treating the disease are prescribed by a gastroenterologist in combination with medications. They help cope with the symptoms of the disease.
| Collection of choleretic herbs | The medicine is purchased at the pharmacy. It consists of a set of several herbs: chamomile flowers, calendula, yarrow leaves, mint and tansy. To prepare the medicine, 2 tbsp. l. herbs are poured with 1 tbsp. boiled water, the resulting solution is prepared in a water bath for 10-15 minutes. 1 tbsp. The decoction is taken for one month. |
| Corn silk | Dry collection in the amount of 1 tbsp. l. mixed with 1 tbsp. boiled water and leave for 2-3 hours. The decoction is taken three times a day, 50 g each. This decoction helps to cope with bile stagnation. |
| Mint and chamomile | The herbs are mixed in equal proportions and 250 ml is added. boiled water. Insist for one hour. Take 100 ml 3 times a day. |
| Gentian | 1 tbsp. l. 500 ml of dry grass is poured. water, infused for eight hours. Accepted 1 tbsp. before eating. |
It must be remembered that without consulting a doctor, taking the above remedies is not only harmful, but also life-threatening. Only a specialist can prescribe medications to avoid complications and aggravation of the disease.
Diet
One of the main ways to get rid of the disease is to review your diet and create a special diet. The gallbladder is an organ of the gastrointestinal tract, so it is very important to follow special nutritional rules to get rid of the disease.
When re-tying you should:
- consume low-fat dairy products;
- include stewed, boiled meat and seafood in the diet;
- eat chicken and turkey meat, as it is dietary;
- limit the consumption of vegetable oils;
- eat vegetable dietary soups, fish soup made from lean fish;
- exclude sweet, fatty, smoked foods, salty and peppery foods, carbonated drinks, fast food, spicy foods, canned food;
- eat warm food, avoiding cold and hot;
- eat more fresh vegetables and fruits;
- drink 2 liters of clean drinking water every day, since water is the main assistant in removing toxins and harmful substances from the body;
- Chew food thoroughly.
If you follow a special diet, the symptoms of the disease will quickly go away, and the internal organ will soon return to normal.
Indications for surgical treatment - stages of surgery for constrictions and bends of the gallbladder
Surgical treatment of the disease in question is carried out when the outflow of bile is completely blocked, which can cause rupture of the gallbladder.
To prevent this phenomenon, the surgeon removes the gallbladder through laparoscopic surgery.
The algorithm for this manipulation is as follows:
- The patient is given general anesthesia, so he sleeps during the procedure.
- The operator performs skin resection in the navel area. A cannula is inserted into the formed hole.
- For a qualitative examination of the internal organs, a telescope is inserted into the abdominal cavity, which is connected to a camera.
- The separation of the gallbladder from its walls and its removal is carried out by fixing additional cannulas.
- At the end of the laparoscopy, the surgeon sutures the incisions made.
The open surgical technique is used in the following situations:
- The patient was found to have scars/adhesions that were the result of previous manipulations.
- The doctor is not able to perform the necessary inspection of internal organs.
- During laparoscopy, bleeding began.
Complications associated with improper treatment
If due to stagnation of bile or the development of gallstone disease, which is caused by pathology, inflammation begins, this can provoke cholecystitis. Timely treatment can prevent disease of the biliary system.
A person is able to lead a full life if he follows the diet prescribed to him, takes anti-inflammatory drugs and other drugs that improve the formation of bile and its secretion after surgery.
Patients need to know that bile, necessary for complete digestion, is produced not in the gallbladder, but in the liver. The bubble is used as a storage vessel. After the bladder is removed, bile accumulates in the bile duct - common bile duct.
In the subacute course of cholecystitis (when the symptoms are unclear), the disease in question can become chronic. The main risk with chronic cholecystitis is the possibility of exacerbation of inflammation at any time, and the symptoms of the disease worsen your health.
Forecast
When pathology is detected in children, the prognosis is favorable. A complete recovery of the child is possible without medical manipulation. If the condition does not return to normal by a certain age, the gastroenterologist uses methods of drug and surgical correction. Surgery is performed only in extreme cases, when the patient is worried about acute relapses.
For adult patients, the prognosis is also considered not burdened, but only if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. The danger of such a disease manifests itself when treatment is delayed, due to the risk of dangerous complications, which are then difficult to eliminate. The constriction of the gallbladder itself is not considered dangerous.
Diagnosed constriction of the gallbladder is not a disease, especially if it occurs congenitally. It can be present for a long time and not make itself known; it is most often discovered during a routine examination of the abdominal organs. Treatment is required when symptoms appear; their intense occurrence becomes an indication for surgery.
Methods of treating pathology
Laparoscopy procedure
You can radically get rid of the constriction only through surgery, completely removing the organ (cholecystectomy).
Drug therapy is necessary to get rid of uncomfortable symptoms and eliminate relapses, but the pathology can only be completely eliminated through surgery. Surgery is prescribed only if there is no result from traditional treatment, there are several constrictions, stones have formed, or the disease is severe. Surgery can be performed using 2 methods: open surgery or laparoscopy.
The first method is classic, it is used in the presence of large stones and severe inflammation. The incision is made in the abdominal cavity. The recovery period is difficult and takes up to 3 months. Complications are possible.
Laparoscopy is a modern technique performed through small punctures in the peritoneal cavity. The patient can be free within 24 hours. The risk of inflammation and side effects is minimal. A few days are enough for rehabilitation.
At the same time, one cannot ignore the risks and discomfort of patients. Because of this, it is not advisable to remove the organ surgically if there is no inflammation. In such a situation, there is a chance to use only traditional therapy and traditional methods of treatment.
Treatment of pathology in the traditional way means the use of medications that are necessary to relieve inflammation and reduce congestion:
- Choleretics are drugs that increase the production and secretion of bile.
- Cholekinetics are drugs that increase the passage of bile into the duodenum.
- Anti-inflammatory medications are necessary to reduce inflammation that may occur due to bladder constriction.
Choleretic drugs
It is possible to use folk remedies in parallel in the form of herbal decoctions that provide a choleretic effect.
Features of therapy
For traditional treatment of acquired constrictions in adult patients, medication is required:
- painkillers (“Nurofen”, “Ibuprofen”) and antispasmodics (“Drotaverine”, “No-shpa”);
- choleretic drugs (“Flamin”, “Gepabene”, “Hofitol”), but provided that there are no stones in the organ;
- if there are stones in the lumen of the gallbladder, hepatoprotectors (Ursosan, Ursohol) are prescribed that can protect the liver, dissolve stones, and normalize the excretion of bile;
- To relieve inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed (Cefolasporin, Ampiox), and after them probiotics (Bifiform, Linex).
Probiotics to relieve inflammation
Therapy with the prescription of medications is supplemented with physiotherapy. If the patient suffers from colic or spasms, they are relieved using ultrasound or electrophoresis.
Removal of stagnant bile from the bladder and ducts is done using a mineral water tube. This procedure, like exercise therapy, promotes the proper functioning of the organ.
For complex therapy, traditional medicine methods are recommended - for example, drinking decoctions of plants that have a choleretic effect (dandelion inflorescences, corn silk, immortelle, yellow gentian).
Raw pumpkin seeds and its juice, and pollen can help relieve congestion in the gallbladder.
To eliminate inflammation, use anti-inflammatory herbal decoctions based on chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort and nettle. Some of these herbs help the flow of bile.
Diet is an integral part of treatment. Experts advise eating small portions. The dishes must be warm.
Salted, smoked, fatty and fried foods, marinated foods, as well as bone broths and semi-finished products are prohibited.
It is prohibited to consume chocolate, sweets, high-fat dairy products, sour apples, and coffee. Fatty meats and fish, beans and mushrooms can cause harm.
In some situations, children may show signs of congenital constriction. They need to be put on a diet. On the advice of specialists, you can give your child various remedies.
If necessary, use painkillers and choleretic agents, as well as antispasmodics in small doses, if they have no contraindications for children.
Treatment of congenital pathology
In cases where the congenital anomaly does not cause discomfort to the patient, no treatment is required. If such a pathology causes concern, then the same therapy is necessary that is prescribed for acquired constriction.
How to cure a child from gallbladder constriction
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky believes that therapy for such pathologies should be carried out individually. In this case, it is necessary to influence not the pathology itself, but those factors that contribute to its appearance.
Since in most cases this pathology appears due to errors in nutrition and poor lifestyle, parents should obtain information from their pediatrician about their child’s diet, daily routine and other points.
Dr. Komarovsky recommends adhering to the following recommendations:
- You should not allow your child to overeat; the best option is portion feeding;
- the child should eat only when he has an appetite;
- You should not allow your child to eat a lot of fatty foods and sweets;
- Do not give your child spicy or salty foods;
- In order for the baby to have a good appetite, he must actively walk and play;
- He must drink the required amount of clean water per day.
Komarovsky claims that bending, constriction of the gallbladder and dyskinesia do not pose a danger to the child, which means that drug therapy is not required. The child will grow, and the shape of his gallbladder will also change. Therefore, the problem may resolve itself.
Drug therapy may be prescribed for a child with hypomotor dyskinesia to stimulate motor skills and thus get rid of uncomfortable symptoms. Most often, choleretic drugs made from plants are prescribed, for example, “Hofitol”, “Flamin”, “Allohol”, “Holosas”.
Choleretic herbal remedies
For hypermotor dyskinesia, antispasmodics are required to help relax the gallbladder and relieve pain.
For complex treatment, medications to improve liver function and vitamins may be prescribed.
If the disease was caused by bacteria or helminths, antibiotics and antiparasitic drugs are prescribed.
If we talk about homeopathic remedies that are recommended for diseases of the gallbladder, Dr. Komarovsky calls them ineffective, but at the same time emphasizes that they will not cause harm.
Of the auxiliary methods of treating dyskinesia, Komarovsky prescribes physical therapy and physiotherapy. All this increases blood supply to the biliary tract, increases the activity of muscle tissue in the liver area, promotes the outflow of bile, which helps restore the functioning of the gallbladder.
Constriction in children
Bladder constriction for children is less dangerous for children than for adult patients, and this is confirmed by the famous pediatrician from Ukraine Komarovsky. The doctor says that the child’s condition should be monitored, examined regularly and drug treatment should be used in extreme cases. Most often, the clinical picture normalizes on its own; the child will simply outgrow the disease. It will be difficult for parents to identify a disorder of this nature in an infant without the participation of a professional. If there is the slightest suspicion of constriction, the child should be shown to a gastroenterologist and undergo an ultrasound of the gallbladder.
Disease prevention
The gallbladder can become deformed under the influence of various factors, which to some extent depend on the patient, so the basis of prevention is a healthy lifestyle. A sedentary lifestyle can provoke bending, so it is important to completely eliminate physical inactivity. The problem often occurs in men whose work involves lifting heavy objects. Risks can be reduced by strengthening the muscle frame.
The need for periodic examinations for problems in the gastrointestinal tract should not be ignored. To get a complete picture, it is enough to undergo an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity once a year, for patients in the risk group once every 6 months.
Since the pathology is common not only among adults, but also in children, the first examination, if there are no complaints, should be done at 1-2 years. A gastroenterologist should interpret the ultrasound results; he will notice the slightest disturbances and select a method for their effective correction.