Deformation of the gallbladder in a child is a serious pathology that can cause significant harm to health. As a rule, parents learn about the presence of such a pathology and what it is only at an appointment with a specialist.
Deformation of the gallbladder in a child
In most cases, this anomaly has a congenital form, the development of which is caused by genetics. But there is already evidence that such a disease can also be acquired.
Causes of manifestation
Among the factors that provoke the development of deformity, severe pregnancy is primarily distinguished. Problems often begin to arise in the first trimester. It is this period that is marked by the formation of the digestive systems, which includes the gallbladder.
The reasons influencing the development of congenital deformity are:
- taking medications prohibited during pregnancy;
- the expectant mother has chronic diseases that cannot be corrected through treatment;
- infections in the body;
- smoking or passive consumption of nicotine during pregnancy.
Acquired abnormal forms of the gallbladder are possible under the following circumstances:
- Excessive physical activity of the child.
- Poor nutrition.
- Lifting weights beyond your age.
- Exposure to severe emotional stress.
- Obesity.
A congenital disease usually makes itself felt at the age of three, when the child is already actively consuming regular food. The manifestation of the acquired form is possible at any age.
Causes of gall bladder deformation in children
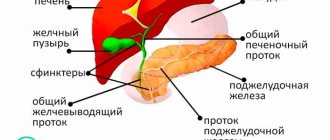
The gallbladder consists of a body, neck and fundus. The organ may become deformed. The components of the bubble change their location relative to each other.
Doctors identify several reasons why gallbladder deformation develops:
- In a newborn, such changes are often caused by harmful factors affecting the mother’s body during pregnancy. The digestive system develops in the first two weeks of pregnancy. It is then that the risk of deformation of the fetal gallbladder is high. Doctors include infectious diseases, consumption of alcoholic beverages, and smoking, both active and passive, as harmful factors. Also, taking certain medications by a pregnant woman often leads to pathology.
- Acquired factors also lead to deformation of the gallbladder. Most often, the pathology becomes a consequence of previous inflammation of the organ itself or its ducts. Infections of the gastrointestinal tract also lead to deformities.
Inflammatory processes and infections prevent the flow of bile. By filling the bubble, it “forces” it to change.
The list of acquired causes of deformity is not limited to inflammatory processes.
This includes weakening of the diaphragm, excessive physical activity, and neoplasms of a benign and malignant nature. In addition, overeating leads to anomaly. Why the reasons listed above lead to deformation of a child’s gallbladder is a question that has not been fully studied. There are often cases when none of these factors affects the organ.
Characteristic symptoms
In medical practice, there are two forms of the disease:
We recommend reading:
Types of gallbladder deformation
- Hypotonic - hypokinetic. It is characterized by prolonged attacks of pain in the area of the right hypochondrium, due to which appetite is impaired, after sleep a bitter taste is felt in the mouth, nausea and belching are possible.
- Hypertonic - hyperkinetic. With this type of development of pathology, severe paroxysmal pain is observed, the location of which becomes the right hypochondrium. The reasons for their appearance are improper eating patterns, non-compliance with diet and excessive physical activity.
Regardless of the form of the disease, at the time of exacerbation, general symptoms will be observed that describe intoxication of the body: fever, nausea, weakness, a feeling that the body is aching, and vomiting can rarely occur. If any of the signs of gallbladder deformation occur, you must promptly seek medical help.
Danger of developing pathology
One of the consequences of an inflection in the body of the organ is stagnation of bile coming from the liver. This condition means the development of a number of diseases.
Bending of the biliary organ and congestion cause the following conditions:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | failure of the digestive process, since bile is one of the most important participants in the process of fat breakdown |
| 2 | Diabetes mellitus leads to partial breakdown of fats, which is not enough for proper enzyme metabolism. The level of fat in the blood plasma increases, glucose is processed too slowly. The body loses tolerance to carbohydrates |
| 3 | weight gain, as unprocessed fats are deposited in problem parts of the body |
| 4 | diseases of the eyes and cardiovascular system. Their development is caused by a lack of fat-soluble vitamins. These substances are needed for the proper operation of all systems. |
| 5 | Chronic cholecystitis is characterized by inflamed walls. The infection is caused by pathogenic bacteria that multiply in stagnant fluid. The stronger the inflammation, the worse the movement of bile |
| 6 | calculous cholecystitis causes inflammation of the walls of the organ and stones in the cavity of the biliary bladder |
| 7 | cholelithiasis, in which the bile becomes viscous, causes stagnation. Dense substances in the liquid precipitate, called biliary sludge. Crystals combine to form stones, even after gallbladder removal |
| 8 | obstructive jaundice leads to blocking of the lumen in the common bile duct, partial or complete. The patient's skin and eyes become yellow due to the accumulation of bile secretions |
Read also: How to take Duspatalin after gallbladder removal?
The patient can prevent the development of pathologies by contacting a doctor with complaints about manifestations of excesses in the bile storage tank.
Diagnosis of pathology
In the case where the gallbladder undergoes any type of deformation, it should be examined and monitored by a specialist.
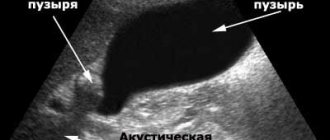
The safest diagnostic method is ultrasound
Ultrasound is considered the safest method for examining pathology in young children. This study allows us to determine the presence of changes, as well as the degree of compaction in the area of the walls of the organ in question.
In a healthy state, the gallbladder will measure 60–90 millimeters in length and from 30 to 40 in width. If the bladder is deformed, echo signs will show kinks and outlines of the organ that do not correspond to the normal state. In addition, when an amplified sound signal appears, we can talk about the presence of stones inside the bubble.
The gallbladder is normal in children
The organ is located in the upper right part of the abdominal cavity, behind the liver. It is pear-shaped, resembling a small pouch with a muscular outer layer. The liver produces digestive juice, which passes into the gallbladder, where fat is stored, emulsified, and bile is transported into the lumen of the small intestine for complete digestion.
Normally, the digestive organ in children should not exceed 3.5 cm in diameter and 7.5 cm in length. Bile storage capacity is up to 100 ml. in children, up to 200 ml. in older children. The gallbladder is normal when it corresponds to age indicators, does not have sand or stones on ultrasound examination, and the outflow of bile is optimal.
Treatment
The choice of treatment method for gallbladder deformation in children depends primarily on the results of a diagnostic examination. Complex therapy must be used, the main task of which is to: relieve pain, relieve the inflammatory process, and restore the outflow of bile.
Many cases of the disease cannot be completely cured, however, despite this, quite positive dynamics are observed.
We recommend reading:
Treatment of a bent gallbladder with folk remedies
It should also be remembered that treatment of pathology takes a lot of time. The course of therapy is carried out 3-4 times during the year. The duration of one course is about two weeks.
The disease precludes independent treatment, and even this is simply impossible, since such a case requires a multi-level technique, the correct selection of which can only be made for a child by an experienced specialist. In this case, the following indicators must be taken into account:
- form of pathology;
- age category of the patient;
- general state;
- presence of concomitant diseases.
When diagnosing gallbladder deformity, the first step is to prescribe bed rest. You also need to ensure that the child drinks a large amount of liquid (less than one and a half liters). A strict diet is required. At the same time, the doctor prescribes drugs from various groups:
- broad-spectrum antibacterial;
- antispasmodic – helps eliminate pain;
- analgesics;
- probiotics – to normalize the gastrointestinal tract;
- choleretic;
- immunomodulatory;
- vitamin complexes.
If the disease becomes chronic, then it is necessary to undergo physical procedures - electrophoresis or ultrasound. It is also permissible to use folk remedies in the form of decoctions, but this is permitted only during the period of remission of the disease.
Classification of pathology
According to the international classification ICD-10, the disease is labeled under code Q44.1 - other congenital anomalies of the gallbladder.
Sub-items include:
- Q00-Q99 – abnormal structure and development of the gallbladder, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities.
- Q38-Q45 – other defects, anomalies in the development of organs of the hepatobiliary system.
- Q44 – congenital anomalies and malformations of the gastrointestinal tract.
It should also be understood that developmental defects can be acquired, as well as deformations that arise during the intensive growth and development of the child.
Special diet
Consumption of vegetables and fruits
The patient's therapeutic nutrition is as follows:
- refusal of sour, salty, spicy and fatty foods, as well as potatoes, since they contain a large amount of nitrogen;
- minimal consumption of cereals and soups;
- Chilled and chopped meat is allowed;
- fermented milk products – no more than 250 grams per day;
- including more fruits, vegetables and freshly squeezed juices in the diet.
Eating food should be done in small portions in 5-6 meals. Overeating should not be allowed.
In order for all actions aimed at treating gallbladder deformation in a child to bring a positive result, it is necessary to follow all the prescribed recommendations of a specialist and be under his supervision at all times. This will protect the little patient from possible dangerous exacerbations.
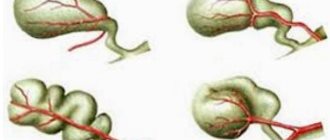
Types of gallbladder deformation
Depending on the course of the pathological process and the nature of the anomaly, doctors distinguish a conditional classification. All existing types of gallbladder deformation have pronounced symptoms, distinctive therapeutic and preventive measures. If the diagnosis is made correctly, this significantly speeds up the recovery process of the clinical patient. The clinical outcome depends on the types of the disease, so accurate diagnosis should be taken with special responsibility, and you must undergo an ultrasound scan.
With an inflection
The pathology is expressed by signs of dyspepsia and does not have a standard focus. The characteristic kinks of the gallbladder provoke constriction of the body with a subsequent risk of rupture. The pain is of uncertain localization; an ultrasound is necessary to determine the affected area. If a healthy organ has the appearance of a bag, then the affected one takes on the outlines of a boomerang, hourglass, or pear shape. At first, the pain syndrome is mild, but over time it becomes intense, and the effect of analgesics is no longer able to prolong the period of remission.
Padding
This is another form of deformation, no less dangerous in its consequences. A constriction in the gallbladder completely changes the shape of the organ and leads to disruption of its functioning. The anomaly appears at birth, but can also affect adult organisms, for example, in the first trimester of pregnancy. It stays with a person for life, but if detected early in childhood, it can be successfully treated. Adults can only maintain general well-being.
Torsion
In this clinical picture, ties appear on the organ, and this is preceded by a number of pathogenic factors. Among them are poor nutrition and internal diseases of the body. A twisted gallbladder is dangerous if the compression occurs directly in the fundus and body. In this case, separation may occur with further leakage of bile into the abdominal cavity, large-scale blood poisoning, and death cannot be ruled out.
S-shaped
If this is a congenital disease, it will go away over time without additional treatment. More often, the characteristic deformity is associated with emotional stress, obesity, cholecystitis, and prolonged physical activity. If the disease is acquired, it is caused by a disturbed position of the internal organs, chronic diseases of the body. S-deformation of the gallbladder is dangerous when localized in the fundus and body.
With a bend in the neck
This is a consequence of progressive cholecystitis, when the inflammatory process spreads to the walls of the gallbladder. Over time, adhesions form at the inflection points in the neck of the gallbladder, significantly complicating the course of the disease. The composition of the bile secretion is pathologically disrupted, resulting in complications in the functioning of the digestive organs.
Labile bend
An attack occurs against the background of physical or emotional stress on the body and is temporary. Severe signs of impaired digestion disappear on their own during the resting stage. Labile deformation of the gallbladder is common, but does not cause any significant cause for concern on the part of doctors. The danger lies in the fact that the inflection point is characterized by its instability - it can periodically change its position.
Contour deformation
In such a picture, a change in the outlines of the indicated organ is observed. Contour deformation of the gallbladder in a child can distort the pear-shaped shape of the organ, which is complemented by acute attacks of pain after eating or exercising. The normal outflow of bile is slowed down, and the risk of developing dangerous stagnation in the digestive organs with a potential risk of rupture of the biliary tract increases.