Causes of biliary colic
The main reason for the phenomenon is the presence of stones in the gall bladder. Stones are retained in the ducts of the bladder, and the outflow of bile is disrupted. Most often, the provoking factor for stone shifting is fatty, dense foods.
This stimulates the production of bile and its outflow into the duodenum from the gallbladder, this leads to the displacement of stones that can get stuck in the duct at the exit of the organ in the area of the junction of the bile and main ducts of the pancreas (papilla of Vater).
Other causes of pain include:
- various disorders in the functioning of the biliary tract;
- artificial nutrition for a long time;
- an infection in the ducts and bladder that disrupts the outflow.
Risk groups include:
- female gender (twice as often);
- age over 45 years;
- overweight;
- high cholesterol in the blood;
- Nordic type of people (with fair skin, hair).
The muscles of the walls of the ducts begin to contract frequently, trying to squeeze the stone into the duodenum and overcome the obstacle to the normal outflow of bile. This intense work leads to sharp pain in the right hypochondrium. Often such efforts are justified and the stone ends up in the intestines, but there are cases when this does not happen and it has to be removed in other ways, including medical intervention.
If the cause is not a stone, but, for example, a tumor of the bladder or its ducts, then the pain may not leave the patient for a very long time. When moving through the ducts, the stone can damage the mucous membrane and therefore, even after the stone has passed, the patient may feel an unpleasant sensation on the right side.
But only 15% of patients with stones in the bladder complain of colic. This means that not every person suffering from various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract develops them.
Methods of treatment using psychosomatics
The choice of treatment and the search for a psychological cause depends not only on the affected organ, but also on the specifics of the disease. One of the common problems is polyps in the gallbladder, benign and malignant neoplasms. But besides this, there are other ailments:
- Biliary dyskinesia is a weakening of the motility of the gallbladder, which leads to suppression of bile production and weakening of its release into the intestines. In turn, this inhibits the functioning of the digestive system.
- Cholecystitis is inflammation of the bladder walls. Often occurs without infection, but is complicated by the development of neoplasms. Without treatment it becomes chronic. And growing formations can burst and lead to blood poisoning.
- Gallstone disease is the formation of stones due to stagnation of bile. Stones cause pain and blockage, preventing organs from functioning properly.
All of these diseases require both psychotherapeutic intervention and medical treatment. It is necessary to select drugs to restore tissue and eliminate symptoms. Sometimes surgical removal of stones is indicated. But it is even more important to achieve harmony in the emotional sphere, change your lifestyle, and get rid of bad habits.
It is important! Only a doctor has the right to prescribe medical treatment! Self-medication can aggravate the situation or provoke the disease to become chronic.
Signs and symptoms
The clinical picture of the condition is the same. Let us note the main symptoms of biliary colic:
- Pain in the right side, which is often spasmodic in nature, and can also be burning and intolerable. Their duration ranges from 10 minutes to 6 hours. In this case, they can radiate to the shoulder blade, right shoulder, back;
- The onset of pain is sudden, often in the evening or at night after a heavy dinner, the menu of which included fatty foods, as well as after severe emotional or physical fatigue;
- The pain may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting, first with food, then with a mixture of gastric juice and bile;
- A possible temperature increase of no more than 39 degrees, but such a symptom can quickly disappear, since it is more of a reflex nature;
- If colic continues throughout the day, then there is a possibility of inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis);
- Due to the fact that during colic, the outflow of bile is delayed, its pigments enter the blood and the patient’s skin and eye membranes may turn yellow, the urine will become dark, and the feces, on the contrary, will become discolored;
- Against the background of other symptoms, weakness, anxiety, bitter taste in the mouth, lack of appetite, bloating, belching, diarrhea may occur;
- Your heart rate and blood pressure may increase and your skin may become pale.
Most often, biliary colic goes away on its own, but sometimes it can serve as a signal of disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract and the need to consult a doctor.
Symptoms of reflex spasm
The spasm occurs suddenly, more often in the evening or in the middle of the night, usually after a late, hearty dinner. A sharp, unbearable pain is localized under the right rib, where the gallbladder is located (if you draw an invisible line from the lower ribs located on the right to the nipple of the right breast exactly vertically, then we will get the exact location of the organ).
With gall bladder colic, the pain radiates to the right scapula and collarbone, and with choledocheal colic, the pain covers the area of two subcostal zones to the level of the shoulder blades (girdles). In this case, the abdomen swells, and upon palpation, unpleasant pain is noted in the area of the gallbladder. The doctor can feel a dense, painful ball (the size of the compaction can reach a decent size - sometimes the size of a goose egg) under the arch of the rib on the right.
In this case, the person feels discomfort - distension in the painful area (usually in the liver area). Patients describe their condition as if they were tied with a tight belt, which they immediately want to unfasten, take a deep breath and at the same time lean forward. Such symptoms are characteristic of cholelithiasis.
As for dyskinesia or giardiasis, the symptoms are not clearly defined, the pain is moderate, which, in principle, can be tolerated.
Worst of all, when the patient has a concomitant disease, namely angina pectoris or other diseases of the cardiac system, then the pain can radiate to the cardiac region and thereby worsen the condition of the heart muscle (exacerbate the disease) and the person’s well-being.
Other symptoms characteristic of spasm:
- attacks of nausea;
- profuse salivation (pronounced in the presence of Giardia in the liver);
- vomiting with or without bile (typical of cholelithiasis);
- the temperature rises sharply, accompanied by severe chills (a direct symptom of stagnation of bile and inflammation in the bladder);
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
You should also consider the different types of pain and symptoms that occur against the background of various diseases. So, for example, with choledocheal colic against the background of cholelithiasis, pain syndrome that does not go away for a long time (6 hours or more), jaundice occurs.
If we consider the pain that occurs with acalculous cholecystitis, it can be characterized as follows. The spasm begins suddenly. After some time, the pain subsides a little, but at the same time becomes permanent.
Symptoms:
- A slightly elevated temperature (37.2 or slightly higher) may be normal;
- The muscles in the area of the right hypochondrium are tense;
- With palpation (light tapping), the pain intensifies;
- ESR levels and leukocytes in the blood increase.
With inflammation of the bile ducts, there is a so-called triad of symptoms:
- pain under the rib on the right;
- the temperature rises;
- a yellowish tint appears on the skin, sclera of the eyes and mucous membranes.
In severe cases of the disease, the following symptoms may be added to this list: bloating, confusion and short-term loss of consciousness (during an attack, when a sharp stone begins to move along the passage, a person may lose consciousness from pain). In addition, there is a decrease in blood pressure, stool becomes discolored (takes on the color of gray clay), urine takes on an unnatural shade (resembles the color of beer).
The acute form of cholecystitis and cholangitis requires immediate medical attention. You may have to urgently operate the organ (cholecystectomy - removal of the gallbladder along with its contents, namely stones). Also, during surgery, the ducts are carefully examined; if conglomerates are found in them, they are naturally removed.
Emergency care for biliary colic
It is not advisable to get rid of an attack of biliary colic on your own; it is better if professional emergency assistance is provided.
What you can do to help yourself before the ambulance arrives:
- Unbutton tight clothes, lie on your right side and try to relax;
- Avoid eating at this time. If you are thirsty, it is better to quench it with plain water rather than coffee or tea, since these drinks provoke the production of bile, and this increases the pain syndrome;
- Do not take strong painkillers without the advice of a doctor; in extreme cases, you can take no more than one tablet of no-shpa;
- Do not use a heating pad, as this will increase the pain due to the contraction of the ducts.
Diagnostic methods
Regardless of the severity of the symptoms of gallbladder inflammation, treatment cannot be delayed. Any delay threatens the development of serious complications not only physically, but also emotionally.
Currently, the following methods for examining the gallbladder are most often prescribed:
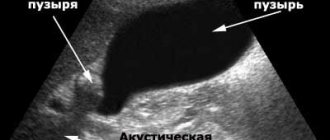
- Ultrasound. During its implementation, it is possible to detect an increase in the size of the organ, as well as identify the cause of this pathological condition.
- Analysis of duodenal contents. The biomaterial is collected with a probe, which is inserted to a depth of no more than 60 cm. Normally, there should be no pathogenic microorganisms in the bile. If there are any pathologies, pus, microbes or atypical cells may be found in the secretion.
- X-ray examination. It can be performed either with or without the use of a contrast agent.
- Oral cholecystocholangiography. This method involves taking a contrast agent orally. 12 hours later, a series of x-rays are taken. This method allows us to identify morphological changes in the organ.
- Intravenous choleography. In this case, a contrast agent in an amount of 30-40 ml is injected into any blood vessel.
- Infusion cholegraphy. It involves intravenous drip administration of a contrast agent, after which X-rays are taken.
- Laparoscopic cholecystocholangiography. In other words, this is a puncture of gallbladder tissue. Cells can be collected through the liver or directly from the organ being studied.
- Relaxation duodenography. Involves the intravenous administration of antihypertensive substances and barium suspension. After this, a series of x-rays are taken.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
The appropriateness of prescribing a particular method is determined by the doctor based on the results of the examination and medical history.
Treatment methods
After a series of diagnostic measures, the following treatment is prescribed:
- Compliance with dietary table 5A, on the first day complete refusal to eat;
- Taking antispasmodics that relieve spasm of the muscles of the ducts: no-spa intramuscularly or intravenously (2% 4 ml), then in tablets 4 times a day, 80 mg. As an option, platiphylline is also prescribed intramuscularly or intravenously (0.2%, 2 ml), papaverine (2%, 2 ml), then in tablets of 50 g 3-4 times a day, atropine sulfate solution intramuscularly (0.1% - 1);
- Pain relief: take analgin intramuscularly (50% - 2), ketorol or ketorolac intramuscularly 2 times a day, baralgin 5 ml. If painful spasms do not go away, then stronger painkillers are prescribed;
- For increased acidity in the body, omeprazole is prescribed 2 times a day, 20 mg;
- If the accompanying symptoms of biliary colic are nausea and vomiting, then the doctor prescribes treatment with metoclopramide 2 times a day, first intramuscularly 2 ml, then in tablets 10 mg. Alternatively, you can use cerucal according to the same scheme;
- Motilium 40 mg 2 times a day is often prescribed to improve motility of the gastrointestinal system;
- To improve protective functions, hepatoprotectors are used mainly in the form of Essentiale 3 times a day, 2 tablets.
After pain has been relieved, further treatment depends on the cause.
You can relieve symptoms for a short time using folk remedies.
Symptoms of the disease
The gallbladder can become ill when there is a predisposition to cholelithiasis or other diseases of the digestive or biliary system.
We recommend reading:
Adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder
Symptoms of biliary colic occur mainly in the evening or at night, after the cause appears. The pain is localized in the right hypochondrium. With choledocheal colic, pain occurs in the abdominal area, slightly above the navel.
Angina pectoris
Painful sensations can radiate to the area of the scapula or collarbone, and also surround the hypochondrium, depending on the cause of their formation. Unpleasant sensations are transmitted to the liver. There is a feeling of fullness. Patients feel the desire to loosen the belt, lean to the sides or forward.
Symptoms of gallbladder spasms caused by giardiasis or dyskinesia are mildly painful. In the event of an attack of gallstone disease, the pain is sharp, wave-like, unbearable. In some cases, colic may have signs of heart disease: pain in the left side of the chest, angina.
In biliary colic caused by dyskinesia and giardiasis, symptoms include excessive drooling and nausea. Vomiting occurs in case of an attack of cholelithiasis. In such a situation, after vomiting with bile inclusions, sharp relief occurs.
Choledocheal colic has characteristic symptoms:
- bitter taste;
- elevated temperature;
- dark color of urine;
- discoloration of feces;
- yellowness of the skin and whites of the eyes.
In addition to the listed symptoms, biliary colic is characterized by bloating and painful sensations on palpation. The pain is localized at the locations of the gallbladder and ducts. Tapping the costal arches, especially on the right side, also causes pain.
An attack of biliary colic has 3 possible outcomes:
We recommend reading:
Gallbladder dyscholia
Painkillers
- The pain went away without any visible health consequences. In such a situation, it is customary to talk about biliary dyskinesia or temporary blockage of the ducts. The exact cause can be diagnosed through an ultrasound examination and a contrast X-ray. Depending on the results, the specialist prescribes treatment.
- Biliary colic does not go away. In case of acute pain syndrome, it is necessary to provide first aid: give antispasmodics, painkillers, temporarily refuse to eat and drink, call an ambulance.
- The pain syndrome went away, but the general health did not improve. This situation indicates the development of inflammatory processes in the gallbladder. The patient is advised to urgently consult a surgeon.
Folk remedies against biliary colic
- At the first signs, you should dissolve a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar in 200 ml of apple juice. After this, the attack will subside, but not for long - for about a quarter of an hour;
- For a week, in the morning on an empty stomach you need to drink the juice of 4 lemons diluted with a glass of water. This will help remove the stones;
- Terpenes, substances found in large quantities in peppermint, dissolve the stones. A tablespoon of raw material is steamed with a glass of boiling water and left for 5 minutes. The infusion is filtered and mixed with a tablespoon of honey. Drink this remedy twice a day between meals for 4-6 weeks;
- Taraxacin, contained in dandelion, improves the flow of bile from the liver, which helps normalize the functionality of the gallbladder. Mix a teaspoon of holly mahonia with 2 teaspoons of marshmallow roots. Steam with 4 cups of boiling water and continue heating for 15 minutes. Remove from heat and add a teaspoon of mint and 2 teaspoons of dandelion to the broth. Leave for another quarter of an hour and filter. Drink during the day instead of tea;
- Pears contain pectin, which softens stones. The peel is cut off from the fruit, the pulp is cut into small slices and boiled for 20 minutes. It is recommended to eat a plate of still warm boiled pears twice a day for 2 weeks.
Gall Bladder: Brief Description
It is an auxiliary organ that is hollow. Located in the right hypochondrium. The gallbladder is a kind of reservoir for secretions produced by the liver. Its shape can be pear-shaped, spherical or conical. The color of the organ is dark green. The capacity of the gallbladder is about 60 ml in adults and about 25 ml in children. It cannot be felt by palpation and can easily stretch.
Functions of the organ:
- accumulation of bile produced by the liver;
- participation in the process of formation of intra-articular fluid;
- lipid breakdown;
- activation of lipase (digestive enzyme);
- cleansing the body of harmful compounds;
- regulation of water-salt balance;
- neutralization of the negative effects of hydrochloric acid;
- preventing the occurrence of putrefactive fermentation;
- assistance in the absorption of vitamins and microelements.
Despite the impressive list of what the gallbladder does, it is not necessary. This means that after its resection a person can live a full life.
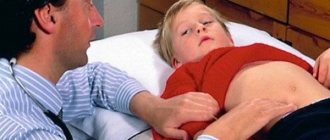
Spasm in a child
Dyskinetic disorders of the bile ducts and bladder are one of the most common diseases of the digestive system in children. The main symptom is abdominal pain under the right rib of varying intensity. Spasm occurs due to hormonal and autonomic disorders. In other words, if there are problems with blood circulation, metabolic processes, and hormonal levels. Under the influence of the sympathetic nervous system, sphincter motility is disrupted and spasm occurs.
Provoking factors are:
- Binge eating;
- Excess weight;
- Eating fatty, fried foods, large amounts of sweets;
- Previous alcohol use;
- Smoking;
- Stress;
- Dry food;
- Poor quality products with chemical additives;
- Dietary disorder;
- Physical, emotional exhaustion;
- Lifting weights;
- Hereditary diseases;
- Abnormal structure of organs;
- Chronic inflammatory processes in the digestive system.
Spasm of the gallbladder can occur against the background of difficulty in the outflow of bile and during its normal movement. But the clinical picture is changing. In the first case, the pain is intense, sharp, and passing. In the second - encircling, dull, long-lasting. Accompanied by nausea, bitterness in the mouth, vomiting, and stool disturbances. If there is frequent or prolonged colic, the child should be shown to a specialist and undergo an ultrasound.
Treatment according to psychosomatics
The gallbladder is an organ that is affected when a person has an abundance of negative thoughts. Less often - with a heightened sense of self-sacrifice. And dyskinesia, and cholecystitis, and neoplasms, and stones - all these diseases are psychological in nature. There are many conservative and surgical methods for treating pathologies, but it is possible to forget about illnesses forever only after a radical change in your own behavior.
According to psychosomatics, the gallbladder will function normally if you follow the following recommendations:
- Forgive other people for their grievances and insults. It is necessary to understand why they slandered or committed some action against a person. It is important to let go of all grievances without keeping them to yourself and without constantly remembering them.
- Control the degree of anger and irritability. It is recommended to meditate a little and try to relax, at least count to 10 or more. After this, you need to express your accumulated dissatisfaction, but also not stoop to insults.
- Don't consider yourself right in everything.
- Avoid getting into conflict and stressful situations.
- Periodically make every effort to fulfill your own desires, and not to satisfy the needs of others.
To improve the atmosphere, it is recommended to concentrate on positive emotions. In addition, sleep should be complete. Quality rest, moderate physical activity, and regular walks are the key to health and longevity.
Treatment with medications
Qualified therapy is prescribed by a doctor after identifying the root cause. To relieve painful symptoms in a hospital setting, antispasmodics and painkillers are administered intravenously, and tablets are taken at home.
Antispasmodics:
- No-Shpa;
- Drotaverine;
- Meverin;
- Papaverine;
- Spazmolgon.
Painkillers, combination drugs:
- Analgin;
- Baralgin;
- Combispasm;
- Nurofen;
- Ibuprofen;
- Solpadeine;
- Ketanov;
- Ketolong;
- Diclofenac;
- Dicloberl;
- Nise.
Sometimes taking pills for biliary colic causes an immediate gag reflex. The chosen medicine should be turned into powder, or Nitroglycerin should be placed under the tongue. Holagol, produced in the form of red drops, has a rapid analgesic effect. Place 5 drops on a piece of sugar, put it in your mouth, and slowly dissolve.
Additional medications:
To normalize the outflow of bile, Ursosan is prescribed. To support liver function, milk thistle powder, Galstena, Karsil, Gepabene are recommended. To improve digestion, Pancreatin and Mezim are prescribed. If biliary colic is associated with diseases of the stomach or intestines, treatment is prescribed with drugs whose action is aimed at restoring acidity and eliminating the inflammatory process - antacids, prokinetics, proton pump inhibitors. For spasms of the gallbladder associated with stress, sedatives are prescribed - Nova-Passit, Afobazol, tincture of valerian, motherwort, gloda. The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor.
In severe cases, surgery is indicated. For stones larger than 3 cm, the entire gallbladder is removed. The operation is also performed for some types of cancer.
Traditional treatment
The drugs Validol, Barboval, Volocardin, as well as mints and chewing gum will help temporarily relieve pain and improve the patient’s condition. You should also serve the patient tea based on medicinal herbs with a sedative, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antispasmodic effect. Mix lemon balm, mint, chamomile, and valerian root in equal proportions. Pour boiling water over and leave for 15 minutes. Give it to drink like regular tea.
Folk and homeopathic remedies help cure cancer. This method of therapy is used if there is no point in carrying out chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery will not give the desired effect. Under the guidance of experienced homeopaths, people are cured. Therefore, it is worth paying tribute to medicinal herbs and not neglecting them even when prescribed medication.
After relief of painful symptoms, the main task is to improve the functioning of the diseased organ and its condition. The main efforts are aimed at normalizing the outflow of bile and eliminating the inflammatory process.
- Collection of dandelion, yarrow, calendula. Removes spasms, normalizes muscle function, stimulates the flow of bile, reduces gas formation, and relieves pain. Calendula is a powerful bactericidal and anti-inflammatory agent. Mix in equal proportions, pour boiling water, leave for half an hour. Take 150 ml 20 minutes before meals 4 times a day. The minimum course of therapy is 10 days.
- Cucumber juice. Dilutes bile, stimulates its movement, facilitates the functioning of the digestive tract. Drink 100 ml of fresh juice up to 4 times a day.
- Dried apricots. Rinse, pour boiling water for a few minutes. Every day you need to eat at least half a glass. Restores the functioning of the intestines and cardiovascular system, eliminates stagnant processes.
- Viburnum with honey. An effective remedy for inflammation of the gallbladder and blocked ducts. Mix the juice with fresh honey. Take every morning on an empty stomach for a month. Take a short break. I repeat if necessary.
- Milk thistle. A natural gastroprotector that restores liver cells, removes toxins from the body, strengthens the immune system, and normalizes digestion. The plant is included in many homeopathic preparations. Take 1 teaspoon 3 times 20 minutes before meals or half an hour after meals.
Traditional medicine also offers remedies that help destroy stones and remove them from the body. In this case, treatment should not be carried out without the supervision of a specialist.
Causes
The occurrence of biliary colic may be associated with temporary exposure to unfavorable factors or pathologies of internal organs and systems.
The most common causes of discomfort are:
- Cholelithiasis;
- Moving stones along channels;
- Impaired flow of bile;
- Inflammation of the organ;
- Congenital anomalies;
- Sphincter dysfunction, pathological weakening of muscles;
- Cholecystitis;
- Giardiasis;
- Neoplasms;
- Diseases of the pancreas, intestines, liver, heart;
- Disturbed diet;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Smoking, drugs;
- Lifting weights;
- Binge eating;
- Excess weight;
- Taking medications;
- Damage to the body by helminths;
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach, duodenum;
- Oncology;
- Intestinal inflammation;
- Appendicitis in the acute stage;
- Stress.
Biliary colic can be short-term, long-term, appear once or make itself felt constantly. In any case, you need to seek help from specialists and undergo an examination.
Nutrition
It should be balanced and easily digestible. You should eat in small portions to avoid overeating and not to burden the digestive system. Prolonged fasting is not allowed, as the body begins to eat itself. Limit the consumption of spicy, fried, sweet foods, and during an exacerbation, avoid them altogether. To normalize the functions of the gallbladder, it is recommended to eat dried fruits, fermented milk products, stewed vegetables, first courses, cereals, and eggs. The meat should be twisted and chopped. Chicken, turkey, and lean pork are allowed. In the absence of gastrointestinal diseases, it is not necessary to follow a strict diet, you just need to monitor your diet and eat healthy products.