One of the reasons why a child complains of pain in the abdomen or right side, especially after eating, a bitter taste in the mouth, or loss of appetite, is an increase in the size of the gallbladder as a result of a functional impairment of its motility.
The gallbladder (GB) is filled with a biological fluid - bile, the purpose of which is to break down complex fats, regulate the processes of intestinal digestion, and remove cholesterol and toxic compounds from the body. Due to disorders of the digestive system for various reasons, the outflow of bile becomes more difficult and stagnation occurs. Characteristic symptoms require referral to specialists.
How does the gallbladder work?
The gallbladder (cholecystis) is an organ of the digestive system involved in the accumulation and release of bile into the small intestine. When your child's appetite awakens, the entire digestive system of his body prepares for food intake. The gallbladder accumulates bile, the pancreas accumulates pancreatic juice, and only from the stomach does food enter the intestines, where it is enzymatically processed and further digested. Important! Digestive problems, fatigue, papillomas and warts can be a consequence of infection of the body with parasites. They live for years in our body, sucking all the juices out of us, suppressing the immune system and destroying internal organs.
Bile is secreted by the liver and subsequently stored in the gallbladder. Its role in the body is to participate in the breakdown of complex fats and activation of intestinal digestion processes. The walls of the vomiting intestine are irritated by the action of bile acid, and thereby the body receives a signal about the need to activate intestinal motility.
Dimensions of the gallbladder: norm and deviations
The gallbladder is an organ in which bile produced by the liver accumulates and enters it through the ducts. The bladder contains bile until the first meal. As soon as food enters the lumen of the duodenum, the walls of the organ contract, bile is released into the intestine, where it activates the digestive processes and takes part in the breakdown of complex fats.
On average, the normal sizes of the gallbladder in an adult are:
- 6–10 cm – length;
- 2.5–4 cm – width;
- 3 mm – wall thickness;
- 20–30 ml – volume.
In children, normal gallbladder sizes depend on age
Periodic changes in the size of the gallbladder throughout the day are a normal process caused by the release of bile into the intestines, emptying of the organ and its subsequent filling. However, in some pathological conditions the gallbladder remains enlarged.
Constantly exceeding normal parameters indicates violations. In this case, the organ is filled with bile, its contractile function is impaired. As a result, bile stagnation occurs and digestion processes are disrupted. This condition can occur due to certain pathologies or is a temporary physiological reaction of the body caused by nutritional errors.
When the gallbladder enlarges, bile accumulates and stagnates in the organ, its viscosity increases, and outflow becomes difficult.
Necessary diagnostics
The simplest, but fairly reliable method for diagnosing changes in the gallbladder is ultrasound. If its results are questionable, and also for a more accurate diagnosis of the cause, the following is carried out:
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal cavity;
- ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) – X-ray contrast study of the bile and pancreatic ducts;
- FEGDS (gastroscopy);
- Biochemical blood test (total bilirubin and its fractions, amylase).
With their help, you can determine down to the smallest detail how the gallbladder and ducts, liver and pancreas, duodenum and other structures of the biliary system look and function.
Diagnostic procedures
As a rule, the presence of a problem with the gallbladder can be determined during the initial examination. With the help of palpation, the doctor can easily identify pathology. To clarify the nature of the disease and identify the causes that caused it, additional diagnostic methods will be required. Usually the doctor prescribes:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, the results of this study will allow you to determine the exact size of the gallbladder, as well as examine the bile ducts;
- X-ray examination will provide information about possible congenital pathological features in the structure of the organ;
- duodenal intubation will allow us to study the biochemical composition of bile;
- in some cases, computed tomography data may be required;
- The patient will need a blood test.
Based on the data obtained during the examination, the doctor will develop a treatment regimen for the patient.
We recommend reading:
Parasites in the gallbladder
How to restore the size of the gallbladder
The principles of organ restoration are based on diet. To speed up bile secretion, the child is transferred to food according to table No. 5. Therapeutic nutrition provides for portioned meals at regular intervals. The diet must contain dietary fiber, fruits, herbs, vegetables, and fiber. Vegetable salads with vegetable oil will be beneficial for your baby.
Dr. Komarovsky suggests removing fried, smoked and spicy foods from the children's diet. The pediatrician advises replacing carbonated drinks with uzvar, juices, and herbal teas. Young children love to chew crackers, so children 3 years old are recommended to be given dried crusts of coarsely ground products instead of white soft bread.
Drug therapy
For biliary dyskinesia, appropriate medications are prescribed to relieve spasms from the gallbladder:
How to treat a baby to speed up the secretion of bile? The gastroenterologist prescribes Digestal, Holagol, Magnesium sulfate, Allochol, Sorbitol. Among herbal remedies, the activity of the biliary system is improved by elecampane, immortelle, arnica, oregano, and calamus.
Antibiotics are prescribed for the treatment of acute cholecystitis, before and after surgery. Indications for surgical intervention in the child’s digestive tract are:
Dimensions of the gallbladder of a healthy child
The table shows the dimensions of an organ that does not have pathological abnormalities:
| Age | Length, mm | Width, mm |
| 2–5 years | 50 + 1,5–2 | 17 |
| 6–8 years | 61 + 2,3–2,5 | 18 |
| 9–11 years | 64 + 1,6 | 23 |
| 12–16 years old | 65 + 1,5 | 24 |
The permissible length, which is considered normal, is 75 mm, the average width of the ducts is approximately 8 mm. An enlarged gallbladder will most accurately be indicated by an ultrasound diagnosis.
Prevention
Patients are recommended treatment table No. 5 with the use of Essentuki mineral water No. 2 and No. 4. To prevent the development of diarrhea, doctors advise eliminating fatty, fried and spicy foods from the diet.
It is important to eat small meals, up to 6 times a day, giving preference to water-based cereals, low-fat dairy products, boiled meat and poultry. Strong tea, black coffee, cocoa are removed from the menu.
A timely diagnosis, adequate therapy, and adherence to a diet will allow you to avoid relapses, the appearance of stones, and surgery in the future. It is important for people at risk to change their eating habits and undergo periodic examinations.
The main causes of pathology and how dangerous it is
When the gallbladder enlarges, the bile produced in the liver constantly flows into the duodenum. It irritates its mucous membrane, can be thrown into the stomach and cause inflammatory processes. All this threatens:
- Inflammation of the bladder wall;
- Thickening of bile and formation of stones;
- Digestive and nutrient absorption disorders.
The reasons for an enlarged gallbladder are various diseases of the digestive system. This means that such a disorder should be considered exclusively as one of the symptoms of diseases of the gallbladder and ducts, liver, pancreas and duodenum.
Possible development mechanisms:
- Poor contractility of the organ and thickening of bile - the bladder cannot expel its contents, which is why it gradually overflows and stretches.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Obstruction in the ducts through which bile flows.
The main reasons and their distinctive features are described in the table.
| What diseases can cause the gallbladder to become enlarged? | Other symptoms and changes characteristic of the causative pathology | |
| Ultrasound data | Manifestations | |
| Cholecystitis, gallstones | Thickening, thinning, separation of walls, inclusions in the lumen | Severe pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting |
| Biliary dyskinesia | Decreased organ contractility | Heaviness in the liver area, bitterness in the mouth, bloating |
| Congenital and acquired developmental anomalies | Bend of the neck of the gallbladder, atresia (narrowing) of the ducts | |
| Disabled bladder and its dropsy | A stone driven into the neck | On palpation of the abdomen, a round painless or slightly painful tumor in the right hypochondrium, yellowness of the skin, white feces, dark urine |
| Gallstone disease, stenosing papillitis | Dilated common bile duct (choledochus) | |
| Tumors of the pancreas, bile ducts and gallbladder | Tumor-like formation, thickening, cyst in the head of the pancreas, dilatation of the ducts | |
| Acute and chronic pancreatitis |
Temporary enlargement of the gallbladder often occurs in children with errors in diet and biliary dyskinesia. If disorders are corrected in a timely manner, this will prevent the development of more serious changes.
Reasons for changes in the size of the gallbladder in a child
Pathological changes in the size, shape and condition of the gallbladder are possible with the following diseases and conditions:
- dyscholia , biliary hypertension syndrome - the appearance in the lumen of the organ on an empty stomach of a large amount of thick bile, which stretches it;
- obstructive jaundice , cholelithiasis;
- malformations of the biliary tract;
- biliary dyskinesia – impaired contraction of the gallbladder;
- tumors, polyps, cholesterosis;
- acute cholecystitis, acute hepatitis.
Obstructive jaundice can be the result of surgical treatment, compression of the bile ducts by stones, tumors, or adhesions in the area of the hilum of the liver or pancreas. The normal outflow of bile is disrupted, as a result of which the bladder enlarges significantly.
With dyskinesia, the motility of the organ is impaired, which also contributes to delayed emptying of the bladder. Prolonged stagnation of bile contributes to the deterioration of its physicochemical properties and leads to an increase in the size of the organ.
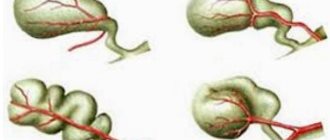
The size of the gallbladder is also often changed when it is deformed. There is an S-shaped deformation, fixed kinks or constrictions, and “Phrygian cap” type deformations.
How to treat?
If an increase in cholecystis is detected in the fetus, no way. It is necessary to see a doctor and look at the condition of the gallbladder over time.
Treatment for an adult child depends on the disease. For example, therapy for biliary dyskinesia consists of choleretic medications and diet, with diet being of paramount importance. Small meals and moderate temperature conditions of food are necessary.
Prohibited foods for gallbladder enlargement:
- strong meat and mushroom broths;
- smoked sausages;
- Hot herbs and spices;
- radish, sorrel;
- canned food;
- chocolate, coffee;
- baked goods;
- carbonated drinks;
- chewing gum.
Treatment can also be carried out using herbal choleretic infusions: decoctions of corn silk, St. John's wort and yarrow. During an exacerbation, they are drunk for one month, then 14 days a month for six months.
Drug treatment can only be carried out by a doctor. He prescribes the appropriate medications and determines the dosage. Treatment with choleretic drugs should last from six months to a year.
Prevention
- Get your teeth treated in a timely manner, as even a minor infection can cause an exacerbation.
- It is very important to protect your child from stress!
- It is useful to give your child vitamins in the spring.
- Excellent prevention is hardening, as well as general strengthening measures for the body.
In this video, the famous children's doctor Evgeniy Komarovsky clearly talks about the causes of problems in the functioning of the gallbladder and pancreas in children.
Causes
A child may have kinks in the gallbladder of a congenital or acquired nature. Often the etiology is combined. For example, when a bend occurs in a child who is initially predisposed to it due to the action of external factors. The patient’s management tactics depend on the reason for the change in organ configuration.
Functional inflections in healthy children
A bent gallbladder in a baby is not always a sign of an abnormality in intrauterine development. This anatomical feature can occur in children during the period of active growth and is even considered a type of normal. It is caused by a change in the location of organs relative to each other, an increase in the workload on the gallbladder. This is especially often observed when switching from breastfeeding to eating rougher food.
Functional bending of the gallbladder in a small child is characterized by lability. It can repeatedly change location depending on the position of the body, and disappear temporarily (for example, if the child stands up). With age, this bend usually disappears completely and does not lead to gallbladder diseases.
Acquired bends of the gallbladder
They are of a secondary nature. They arise under the influence of external factors. Among them:
- Errors in nutrition. Both overeating and fasting have the same negative effects.
- Obesity. The accumulation of fat around the abdominal organs leads to their displacement relative to each other. The position of the gallbladder also changes.
- Physical inactivity. For example, if a child often spends time sitting at the computer. The bend is functional in nature and disappears when the body position changes.
- Excessive physical activity. We are talking about excessive sports training, lifting loads whose weight does not correspond to age.
- Compression by other organs. For example, in pathologies accompanied by a pronounced enlargement of the liver or right kidney.
- Diseases of the biliary system. For example, adhesions during chronic inflammation are one of the causes of constrictions on the gallbladder in a child, narrowing the lumen of the organ.
- Prolapse of internal organs. According to a similar mechanism, functional excesses of the gallbladder occur in children who have suddenly and significantly lost weight.
What is causing the problem? Functional diseases
Is your child's gallbladder enlarged? The reasons may vary, and the list is worth exploring.
- In this case, a very important factor is genetic predisposition, especially if we are talking about some anomalies in anatomical development.
- Risk factors include hormonal disorders, since these biologically active substances control the functioning of all digestive organs.
- Potentially dangerous are constant stress, nervous and emotional overload - this also affects the functioning of the endocrine glands.
- Sometimes an enlargement of the gallbladder occurs against the background of systemic allergic reactions.
- If we talk about physiological prerequisites, then the reasons include the appearance of neoplasms in the ducts or cavity of the gallbladder, as they impede the outflow of fluid.
In children
An enlarged gallbladder in a child is most often a temporary phenomenon, which is caused by the structural and functional immaturity of the organs, active growth of the body, or errors in nutrition.
In an infant, this condition can occur due to improper feeding with artificial formulas, lack of a diet, or too frequent and/or heavy feeding. In older children, problems can be caused by switching to a general diet too early, or by including low-quality or too fatty, fried, or spicy foods in the diet. If unfavorable factors are eliminated, the size and functional state of the organ are normalized.
The most common pathological causes of organ enlargement in a baby include the following diseases:
- bile duct dyskinesia (the most common cause of organ enlargement in children, diagnosed in 80% of cases);
- scarlet fever;
- obstructive jaundice;
- hepatitis (infection of an infant can occur during fetal development or at the time of birth);
- gastroenteritis, gastritis, pancreatitis;
- intestinal infections, helminthiasis;
- structural abnormalities of the gallbladder and ducts, incorrect location of the organ.
Carefully! Stress, emotional stress, hormonal disorders, and allergies can provoke ductal dyskinesia and an increase in bladder size in children and adults.
Congenital structural abnormalities usually appear immediately after birth, much less often as the child grows older
Reasons for the increase
The size of this organ may exceed normal values due to the presence of a disease such as chronic cholecystitis. This term refers to inflammation of the gallbladder, which most often occurs due to microflora entering the body (Escherichia coli, staphylococci, enterococci, streptococci, etc.). The disease is detected in women in most cases.
In adults
One of the signs of this disease is an enlarged gallbladder. It is felt upon deep palpation.
The following symptoms are also observed:
- pain in the right hypochondrium, which sometimes radiates to the lower back, right shoulder blade, right half of the chest;
- increased body temperature;
- nausea, vomiting that does not bring relief;
- bitter taste in the mouth in the morning;
- change in appetite;
- disruption of intestinal function (constipation, bloating).
Dropsy is another answer to the question of why the gallbladder is enlarged. With this pathology, the length of the internal organ is 10 cm, the thickness (height) is 4-5 cm, and the volume reaches 200 ml. Dropsy occurs when the flow of bile is disrupted. In most cases, this occurs due to pinching of a stone in the area of the bladder neck (i.e., the pathology is a complication of urolithiasis).
With dropsy, patients may complain of intense pain. Attacks of biliary colic occur due to the fact that the contractile function of the internal organ is preserved in pathology. During the examination, specialists note that their patients’ gallbladder is tense. It is filled with a light liquid and has a pear shape.
The digestive organs of children are not ready for serious stress. However, adults do not think about the fact that children and teenagers need to create a special menu and exclude from it dishes for adults (too fatty, spicy, sour, salty foods).
If this recommendation is not followed, the functioning of the digestive system in children is disrupted. They begin to develop various diseases of internal organs (gastritis, pancreatitis). Poor nutrition negatively affects the gallbladder. It becomes inflamed and increases in size.
How to carry out therapy directly depends on the reasons for the enlargement of the gallbladder.
For chronic cholecystitis
If, during the diagnostic measures carried out, chronic cholecystitis is discovered, occurring in an acute form, the sick person is hospitalized. During remission, specialists prescribe outpatient treatment.
In both cases, nutritional recommendations are given, designed to prevent bile stagnation and reduce inflammation in the gallbladder:
- In case of exacerbation of the disease, you need to adhere to diet No. 5a. Fried foods, extractives, and refractory fats are excluded from the diet. Small meals, steamed and pureed food will help improve your condition.
- During the period of remission, diet No. 5 is indicated. Patients should eat boiled food. Vegetables and fruits are desirable. Foods containing extractives and cholesterol can be included in the diet, but in minimal quantities.
Drug therapy for chronic cholecystitis depends on the phase and course of the disease and the symptoms that appear. As a rule, if the gallbladder is enlarged, doctors prescribe treatment with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, choleretic and antispasmodic drugs.
If necessary, surgery can be performed. Indications for it are:
- conservative treatment, which over a long period of time did not produce a positive result;
- severe deformation of the gallbladder;
- diagnosing diseases such as pancreatitis, cholangitis.
With hydrocele of the gallbladder
In case of this pathology and the patient has no contraindications, surgical intervention is performed. Elderly and weakened people are prescribed drainage and puncture of the gallbladder. These procedures are performed by specialists under ultrasound and laparoscope control.
Treatment
A slightly curved gallbladder does not cause functional disorders of the biliary system. This condition is equivalent to a manifestation of a physiological norm and does not require treatment. Such children are under constant supervision until they “outgrow” the functional problem.
Congenital inflection cannot be cured. Therefore, therapy is carried out to combat bile stagnation, as well as prevent the development of dangerous complications. In case of a strongly curved form, double torsion, if it is impossible to correct the general condition, radical measures are used - removal of the gallbladder.
If a bend in the child’s gallbladder causes disruption of the functioning of the biliary system, an effective treatment regimen is chosen. For this purpose, the baby is examined in detail to identify concomitant diseases. Often, a bend of the gallbladder is combined with dyskinesia of the bile ducts. This means that the underlying disease also needs to be treated.
Drug therapy
Therapeutic measures with the prescription of medications are aimed at eliminating and preventing bile retention in the bladder, ensuring its timely evacuation, improving general well-being, and enhancing immunity.
In case of gallstone inflection, children are prescribed the following medications:
| Pharmacological group | Effect on the body | Drugs |
| Antispasmodics | Relieves spasms and eliminates pain. They are used for pain attacks, with a pronounced curved form of the gall bladder. | Papaverine, No-Shpa |
| Choleretic | They enhance the outflow of bile, improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and restore the correct shape of the gallbladder in case of functional disorders. | For children under 5 years old - Flamin, Holaflux, for schoolchildren - Holenzim, Odeston, Barberine, herbal teas |
| Antibiotics | Used to treat the bending of the gallbladder in a child due to infection of the bile to eliminate the inflammatory process. | Amoxicillin |
| Agents that normalize intestinal microflora | Prescribed in combination with antibiotics to prevent dysbiosis, as well as to eliminate diarrhea and restore the body's immune defense. | Acipol, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Normobact |
| Sedatives | Sedatives begin to be used in severe cases of the disease. In combination with antispasmodics, they help reduce the severity of pain during double and other forms of bending. | Herbal tea |
In addition to the main treatment, pediatricians recommend giving children multivitamin preparations. For babies up to one year old - Multi-tabs baby in drops, it can be drunk by newborns from the first days of life. After a year - Pikovit, Multi-tabs Baby.
Physiotherapy
In case of slight bending or twisting of the gallbladder, the pediatrician selects a set of exercises. Light physical activity will help:
- relieve tension in muscle tissue;
- improve the contractile function of the bladder and biliary tract;
- improve the quality of metabolic reactions and digestion.
The doctor prescribes the frequency and duration of use of the exercise therapy complex, and teaches parents how to correctly perform therapeutic movements. To improve the flow of bile, perform the following exercises:
- Walk for 2 minutes, raising your knees high.
- In a standing position, rotate your torso in different directions for 4 minutes, keeping your hands on your belt.
- Without changing the starting position, do shallow squats. Duration – 1 minute.
- The child is asked to lie on his back, inhale, slowly raise his arms up, and while exhaling, lower them down.
Young children do therapeutic exercises under adult supervision. If you experience pain, dizziness, or “floaters” flashing before your eyes, stop doing the exercise and inform your doctor.
Diet therapy
If a child's gallbladder is bent, treatment includes nutritional correction. Following a diet relieves the biliary system, improves digestion, and prevents dangerous consequences. The diet is based on compliance with the rules and norms of healthy eating:
- split meals – 6–7 times a day every 2–3 hours;
- light dinner 1.5 hours before bedtime;
- diet – balanced, food – easily digestible;
- Before serving, food must be warmed until warm;
- preference is given to food prepared by boiling or steaming;
- Fatty, spicy, salty foods are excluded.
Products should not cause fermentation and heaviness in the stomach. Children are fed well-cooked cereals, lean meat, fish, and soups with vegetable broth. The diet includes fermented milk products, compotes, jelly, fresh vegetables and fruits. Sweet carbonated water, chips, hot crackers, baked goods, cakes, and fast food are strictly prohibited.
Other diseases
Young children often put dirty hands in their mouth. This may be the cause of infectious inflammation and infection of the child with helminths (ascariasis, giardiasis, opisthorchiasis). If the body is intoxicated, immediate medical attention is required. Prevention of this disease consists of following the rules of hygiene, timely dental treatment, hardening the child and taking vitamins in the spring.
Another disease, hepatomegaly, is determined using ultrasound and stool and urine tests. For pathological hepatomegaly, a liver biopsy is indicated.
Complex treatment is carried out subject to a special diet, antibiotics, choleretic agents (Allohol, Sorbitol), antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine) and probiotics. For hepatomegaly, hormones are used. It is necessary to lead an active lifestyle, do gymnastics and douches, and spend more time with the child in the fresh air. This helps strengthen the nervous system and reduce bile stagnation.
Possible gallbladder diseases
Changes in organ size, pain and other symptoms may indicate the development of the disease. What gallbladder diseases are most common in children?
Biliary dyskinesia
This is the most common disease among children. Its reasons lie in the transition from home meals to school meals, changes in the daily routine and emotional overload that may be associated with the start of school.
Biliary dyskinesia is of two types: hyperkinetic and hypokinetic.
Hyperkinetic dyskinesia consists of increased motor function of cholecystitis and, as a consequence, the inability of sphincters (muscular openings) to open to a sufficient width. This causes sharp pain, but it is usually short-lived (passes within an hour).
Hypokinetic dyskinesia is characterized by insufficient tone of the gallbladder and its weak contractions. The pain is not sharp, but dull, aching in nature.
Chronic cholecystitis
Chronic cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder, often caused by infectious agents: from E. coli to staphylococcus. The disease leads to disruption of the outflow of bile and changes in its composition, as well as the formation of stones. The pain is very reminiscent of hepatic colic and radiates (spreads) to the back muscles. This is accompanied by vomiting, which does not bring relief.
Since children very often put dirty hands into their mouths, the development of infectious inflammation is more likely. For prevention, require them to wash their hands before eating.
Tumors of the gallbladder and ducts
The most dangerous pathology of the gallbladder is tumors. They are divided into benign and malignant (gallbladder cancer). In the early stages of the disease, it is quite difficult to determine the presence of a tumor; the doctor may make an erroneous diagnosis of “cholecystitis” and only then discover benign formations – “polyps”. Treatment is only possible through surgery.
What to do if your child has an enlarged gallbladder
Any organ that a person has cannot be superfluous, and the pancreas plays its role by collecting bile, which is important for digestion and removal of products from the body. It’s not the most pleasant thing if a child has an enlarged gallbladder. All responsibility in this case falls not only on doctors, but also on parents, who must monitor the condition of their baby and his normal functioning.
Why does the gallbladder enlarge in children?
If a child has an enlarged gallbladder, this may mean the presence of pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas.
- Lack of diet, abuse of junk food.
- If the gallbladder is enlarged in infants, then this is lactose deficiency or an allergic reaction to foods consumed by the mother.
- Due to a fall - bruises on the back or abdomen. Strong physical stress on the child’s body.
- Abnormal development of the gallbladder, digestive system, most often this is a congenital phenomenon.
- Blockage of the biliary tract. Impaired functioning of the gallbladder.
- Inflammatory processes in the intestines, in the gall bladder.
- Consequence of drug treatment.
- Overdose of vitamin D or calcium.
- Heredity. Infectious diseases.
How to help if a child has an enlarged gallbladder
After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a number of medications necessary to normalize the outflow of bile, dilute it and eliminate other pathologies. Treatment is prescribed individually, depending on what and how enlarged the child’s gall bladder is.
In addition to medications, doctors are inclined to believe that such a disease is best treated in combination with traditional methods, which is why, if there is no intolerance to certain medicinal herbs, decoctions and infusions are prescribed.
If the child is hysterical and nervous, sedatives are prescribed, and the baby is sent to a child psychologist
Parents should pay special attention to the child’s physical activity and not allow him to sit for a long time in front of the TV or computer
Nutrition and diet #8212; this is the most important thing in treating an enlarged pancreas. All processed foods, chips, colas, foods with dyes and preservatives, fried and spicy foods should be excluded. Everything is only fresh, steamed or boiled. Meals should be strictly on schedule, six times a day and in small portions.
Complications after gallbladder removal
Improper outflow of bile, the formation of stones or sludge in the gallbladder lead to surgery to remove this organ - cholecystectomy. This is not considered a complex operation for humans, but it is possible.
Signs of gallbladder disease
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ of small size, but very important for the liver. After eating food, the gallbladder contracts, and oily, viscous bile enters the liver, as well.
Signs of gallstones
The gallbladder acts as a container for accumulating bile. Bile, in turn, is an important element for the proper functioning of the liver and for the normal digestion process. The pear-shaped organ is greenish.
No comments yet!
The structure of the gallbladder in a child
The gallbladder is considered an important element of the digestive system and serves as a reservoir for constantly produced bile. Normally, the liver is located above it, and below and to the right is the hepatic flexure of the ascending segment of the colon.
The histological structure of the organ is presented:
- mucous membrane with many folds;
- muscular membrane, thanks to which it contracts;
- serous membrane that covers it from the outside.
Through the cystic and common hepatic ducts, bile enters the lumen of the duodenum, where it helps digestion.
Children's ways of expressing pain
Infants and small children express their painful state by frequent crying after feeding, especially when complementary foods are introduced.
Children under 3 years old point with their hand at the painful area of the abdomen; their pain is accompanied by nausea after eating, rapid breathing, salivation, and frequent crying.
Older children can explain what is happening to them and describe how they feel.
If a deviation from the norm is detected, parents should not hesitate to seek help, otherwise the disease will become chronic and difficult to treat. The fact that the gallbladder is enlarged negatively affects the functioning of nearby organs and the entire digestive system.
Why does the gallbladder increase?
Periodic changes in the size of the gallbladder during the day are a process of normal functioning of the organ, as it contracts, pushes bile into the duct and becomes empty, and then fills up again and increases in size.
But there are reasons why an organ cannot take on physiological dimensions. This condition causes certain symptoms: epigastric pain, heaviness, bitter taste in the mouth. A child tolerates these symptoms more easily than adult patients, since the manifestations of the disease in children are less pronounced. Such attacks are associated with eating fatty, spicy foods, as well as irregular (with long breaks) meals.
But there are reasons why an organ cannot take on physiological dimensions. This condition causes certain symptoms: epigastric pain, heaviness, bitter taste in the mouth. A child tolerates these symptoms more easily than adult patients, since the manifestations of the disease in children are less pronounced. Such attacks are associated with eating fatty, spicy foods, as well as irregular (with long breaks) meals.
Normal sizes of the gallbladder in children on ultrasound, depending on age
The organ is measured using a longitudinal scan from under the right hypochondrium. Measurements are taken of its length and width, in some cases the volume is measured using three indicators and a special formula.
The dimensions of the gallbladder according to ultrasound are normal in children:
- children under 1 year : width – 6-10 mm, length – 11-25 mm;
- children 1-3 years old : width – 8-20 mm, length – 20-51 mm;
- children 4-6 years old : width – 10-24 mm, length – 28-61 mm;
- children 7-10 years old : width – 11-28 mm, length – 33-72 mm;
- children over 10 years : width – 12-32 mm, length – 38-82 mm.
In infants, the average volume of the organ is 3.0 ml. In preschool age, this figure doubles or triples; in adolescents, the normal volume of the gallbladder does not exceed 34 ml.
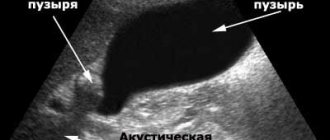
On ultrasound, the bile reservoir is visualized as a pear-shaped or round formation with thin hyperechoic (bright white) or isoechoic (equal to the liver) walls. Its lumen is filled with bile, which is normally anechoic - black. When its physicochemical characteristics change, an echo suspension appears - small light grains against the background of the dark contents of the organ.
Sometimes children undergo dynamic cholecystography - the contractility of the biliary system is examined. To do this, measurements are taken on an empty stomach and 40-50 minutes after taking a special breakfast - choleretic (2 chicken yolks, heavy cream or banana). Normally, the organ should shrink by 50-70%, otherwise they speak of a slow or accelerated contraction of the biliary tract.
In addition, in children, the normal size of the gallbladder depends on their age, body weight and its shape. So, with an S-shaped deformation, the organ has an optimal volume, but on ultrasound its width and length will be slightly less than normal.
Features of mixed form
There is also a mixed form, in which the walls of the gallbladder either become too tense and contract, or relax. A chaotic change in motor skills naturally affects the condition of the whole organism.
In this case, the above-described symptoms are accompanied by other disorders - for example, severe swelling occurs on the face and body (in particular, on the limbs). Despite the fact that the child has no appetite and eats little, his body weight is constantly increasing. A small patient is bothered by constant belching with a very unpleasant smell of rotten eggs, which indicates the presence of serious digestive disorders.
General signs of anomaly
If the baby has an enlarged gallbladder, he is tormented by pain in the side or hypochondrium on the right. They are paroxysmal or aching in nature, intensifying after eating fatty and spicy foods, and sweet carbonated drinks. With dyskinesia, attacks can last up to 20 minutes, and additionally there is a feeling of heaviness in the right side. The baby tries to lie down and tuck his legs, but any movement increases the discomfort.
Other symptoms may indicate an increase in the size of the bile sac:
- nausea;
- belching;
- flatulence;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- stool disorder;
- decreased appetite;
- vomiting with and without bile.
When the temperature rises to 40°C, the child gets chills and sweats. Skin itching may occur. The peritoneum shows signs of irritation. Minor or pronounced muscle tension is detected in the right hypochondrium.
Symptoms
With a slight increase, the symptoms are almost invisible. There is mild nausea, slight bloating; less often - gas formation. A clear manifestation of symptoms is the root cause of another disease of the gastrointestinal tract of the liver and or pancreas.
- Pain in the right hypochondrium, if the root cause is liver enlargement, muscle spasms.
- Nausea, heartburn, flatulence - pancreas, increased acidity of gastric juice, pancreatic disease; pain can radiate to the left hypochondrium, heart.
- Severe girdling pain, pulsating in nature, colic radiating to the back - cholecystitis, cholangitis.
- Significant gas formation, wandering pains from the stomach to the bottom, a pressing feeling in the right hypochondrium - dysbacteriosis.
- Dyspepsia, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, burning sensation - dysbacteriosis, helminthiasis.
- An increase in temperature of 37.8-39, pus in the stool - inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract with significant complications - a reactive inflammatory process with subsequent destruction of soft and muscle tissue.
- Nervousness, aching bones, swelling of soft tissues, increased volume of joints, reactive inflammation of a congenital nature - an autoimmune disease.
- Periodic nausea and slight vomiting are a complication after taking antibiotics, colds, and infectious diseases.
Associated symptoms
Since bile is involved in the absorption of a number of fat-soluble vitamins, a child with cholecystis diseases has a pale appearance, a grayish skin tone, and vegetative disorders are common. He becomes lethargic, inactive, “jams” are visible in the corners of his mouth, and the whites of his eyes acquire an unhealthy yellowish tint.
Depending on the nature of the disease, the following symptoms may appear:
- stabbing or aching pain in the right hypochondrium;
- pain intensifies with food intake;
- there is a bitter taste in the mouth;
- tongue is “covered”;
- emotional stress increases negative symptoms;
- unpleasant sensations are diverse and changeable.
Rarely are ailments accompanied by nausea, and even more rarely by vomiting. Nausea and vomiting are dangerous symptoms that may indicate the development of cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder).
Symptoms of a bent gallbladder
There are three main types of inflection, depending on which one or another clinical manifestation can be observed.
Thus, an inflection between the bottom and the body of the gallbladder, which is the most common type, causes the following manifestations:
- pain radiating to the right side;
- nausea and vomiting;
With this form, children may experience stool instability and may require additional treatment for diarrhea.
In the inflammatory form of this type, the symptoms are supplemented by the following manifestations:
- increased sweating;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- earthy complexion.
A bend in the neck of the gallbladder is characterized by elongation of the neck of the organ or sagging of the body. This defect can have consequences in the form of necrosis of the cervix, which can lead to bile entering directly into the abdominal cavity.
When the neck is bent, symptoms may be:
- the child has a stomach or left hypochondrium pain;
- bloating;
- nausea;
- increased body temperature;
If inflammatory processes are present in the body, the same symptoms as in the previous case may be observed.
Twisting of the gallbladder in several places is a fairly rare pathology.
Among the causative factors of this disease may be the increased size of the organ itself or the presence of stones in it. Symptoms include intermittent pain and nausea.
Very often, the defect is congenital and can be completely asymptomatic until it becomes noticeable during ultrasound examination. If the pathology is acquired due to any factors, it is subject to treatment.