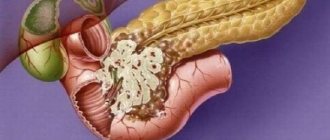
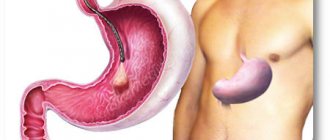
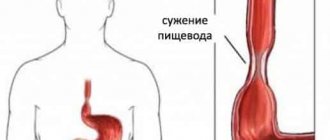
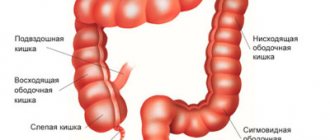
Gastric obstruction is a disease that is characterized by disruption of the movement of food and liquid throughout the digestive tract. Stagnant processes develop, blood circulation is disrupted, and the walls of the organ are stretched. Symptoms of intoxication appear.
Pathological processes in adults are complicated by other gastroenterological diseases. It is important to go to the hospital in a timely manner, undergo examination and treatment. Otherwise, the likelihood of serious complications increases.
Reasons for development
The main reasons for the development of obstruction from the stomach to the intestines include:
- infectious/inflammatory processes in the intestines/stomach;
- neoplasms that develop as a result of cancer of the gastrointestinal tract, regardless of their nature and the nature of the cancer;
- narrowing of the exit section of the internal organ. Most often, this condition is provoked by an intestinal ulcer;
- eating inedible, hard, large objects that cannot be digested and absorbed by the body;
- intestinal atresia (a condition in which natural channels and openings in the body become overgrown or absent from birth);
- coprostasis (clogging of the hernia, closure of the intestinal loop with feces);
- intussusception (a disease in which one part of the intestine invades the lumen of another);
- gastrointestinal tuberculosis;
- formation of adhesions;
- esophageal diverticulum;
- disturbances of normal blood circulation in the body (occurs when organs protrude/herniation);
- the presence of foreign bodies in the stomach/intestines;
- formation of fistulas (fistulas).
Causes
Gastric obstruction occurs against the background of various provoking factors:
| Name | Description |
| Internal reasons |
|
| External factors |
|
A gastroenterologist will help determine the main cause of the pathological condition by prescribing a comprehensive examination for the patient. It is important to immediately go to the hospital when the first signs of gastric obstruction appear.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease are ambiguous and depend on the following factors:
- nature of the disease;
- the degree of damage to the body by infection;
- localization of the affected organ;
- individual patient indicators;
- presence of cancer, oncological pathologies.
The main symptoms appear as follows:
- nausea/vomiting (in case of cancer, vomit contains blood clots, a large amount of mucous matter, and emits a rotten odor);
- unpleasant odor from the mouth during belching;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- constant feeling of oversaturation;
- discomfort, pain in the intestinal area;
- intense spasmodic pain in the abdomen;
- retention of stool and gases;
- intoxication;
- asymmetrical bloating;
- relaxation of the anal sphincter;
- sudden uncontrolled tension in the abdominal wall;
- accumulation of gas in the colon;
- bloody feces;
- the sound of splashing over the intestines.
Pyloric stenosis
Pyloric stenosis is the name given to obstruction of a certain part of the stomach (pyloric), which occurs as a complication of gastric ulcer. The ulcer becomes scarred, the internal organ becomes deformed, and the stomach cavity narrows (a special channel through which, using diagnostics, the level of obstruction is determined). The lumen of the stomach is closed by membrane tissue. This tissue has an uneven structure, covered with small holes of different sizes (the gaps can be more than half the size of the membrane).
The membrane located in the pyloric canal consists of a thin mucous membrane, submucosal coating, and fragments of muscle tissue. In the absence of proper treatment, the membrane increases in size (the wall thickens) and becomes identical to the tissues that make up the walls of the stomach.
The symptoms of pyloric stenosis are no different from those of an ulcer. The pain does not affect the general condition of the patient; it is spasmodic in nature and of low intensity. Rare attacks of nausea or vomiting are attributed to eating poor quality food or overeating. You should pay attention to the composition and smell of the vomit. It has a specific acidic taste and large mucous secretions.
Normalization of patency with pyloric stenosis occurs with the help of probing, pumping out contents from the internal organ that have undergone oxidation. The patient is prescribed systematic gastric lavage. After such manipulations, the patient’s condition improves. In the absence of medical manipulations, the following occurs:
- increased inflammation;
- decreased tone in the muscle tissues of internal organs;
- sudden weight loss;
- distension of the normal size of the stomach;
- manifestation of profuse vomiting;
- development of atony;
- dehydration;
- general exhaustion of the body;
- metabolic disease;
- constipation
Types of operations for intestinal obstruction
There are several types of medical intervention for intestinal obstruction. The choice of treatment depends on several factors - the individual characteristics of the patient, the course of the disease and the method of pain relief.
If the disease develops against the background of cholelithiasis, then medical intervention is carried out by laparotomy. This method involves making a large incision on the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, through which the stones are completely removed. In cases of an inflammatory process in the area of obstruction, intestinal perforation is performed.
In situations where intestinal obstruction has formed against the background of adhesions in the abdominal cavity, the operation is aimed at separating the adhesions.
Often the formation of the disease is caused by intussusception, i.e. the process of penetration of the large intestine into the cavity of the small intestine or vice versa, which is quite often diagnosed in children. The situation is corrected by straightening the intestine. This is done in several ways - manually, through an incision in the abdomen, or by introducing air into the peritoneum. The second technique is used for minor intussusception. If for some reason it is not possible to perform disinvagination, they resort to removing the affected area of the intestine. This operation involves the application of enteroanastomosis or enterecoloanastomosis. In such cases, the postoperative period is characterized by a long recovery and the occurrence of complications, but over time the body gradually returns to normal.
In addition, a diaphragmatic hernia can cause intestinal blockage. In such cases, surgery for intestinal obstruction is aimed at removing this cause of the formation of the disease. It is worth noting that this type of obstruction is extremely rare.
In some disorders or in the acute stage of such a disorder, intestinal patency can only be restored by installing a special probe designed to unload the intestines.
Not in all cases is it possible to eliminate the cause of such a disorder the first time, for example, in the case of oncology or a serious condition of the patient. Then specialists perform a unloading stoma immediately after surgery to eliminate intestinal obstruction. A stoma is an external fistula intended for emptying. It is installed temporarily or for life. In the first case, its removal occurs during a repeat operation, after eliminating the factor of origin and restoring patency.
Classification
Classification according to functional characteristics:
- Dynamic obstruction. Impairment of intestinal motor function, which is not provoked by mechanical stress. Reasons: decreased muscle tone/sharp increase in muscle tone.
- Mechanical obstruction. Impaired movement of food mass, the causes of which are: volvulus, organ strangulation, mechanical obstruction (gallstones, fistulas, feces, helminths, foreign bodies), tumor, cyst.
- Mixed type. Characterized by intussusception and the formation of adhesions.
Diagnosis of gastric obstruction
In order to determine the patency of the stomach, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Fibrogastroscopy. With this diagnostic method, a contrast agent is introduced, which detects the root cause of the disease and examines the structure and surface of the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract. After fibrogastroscopy, a subsequent microscopic analysis (biopsy) is performed. It allows you to determine the presence of a tumor or cancerous tumors.
- X-ray examination. X-ray examination helps determine the degree of narrowing of the gastric openings, detect an object that interferes with the patency of the organ and retains food mass. Using X-rays, cancer and the formation of tumors in the digestive system are detected.
Why is intestinal obstruction dangerous?
Intestinal obstruction leads to dehydration of the body, pronounced shifts in the water-electrolyte and acid-base balance of the body. It is based on a violation of food intake, its digestion and absorption, as well as the cessation of secretion of gastric and intestinal juices into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract.
Since the tissues and cells of the body are sensitive to the slightest changes in the chemical constancy of the internal environment, such changes cause dysfunction of almost all organs and systems. Along with fluid and electrolytes, in case of intestinal failure, due to fasting, vomiting, and the formation of inflammatory exudate, a significant amount of proteins is lost (up to 300 g/day), especially albumin, which plays an important role in homeostasis. The presence of metastases in the liver, which inhibit the protein-synthetic function of the liver, further reduces the level of protein in the blood, reduces the oncotic pressure of the blood plasma, which causes the development of persistent edema.
Treatment
After an accurate diagnosis of the disease, the patient is urgently hospitalized in a surgical hospital. The operation is expected to be carried out immediately (as already stated, with each passing hour the body is exposed to more intense pathogenic effects). Before proceeding with surgery, the patient undergoes special training, which takes up to 4 hours.
If the diagnosis is not established or is not definitively established, treatment consists of conservative (medicinal) methods and additional diagnostics of the patient’s condition.
Is it possible to help a patient without surgery?
Often in severe cases and inoperable tumors in critically ill patients with partial intestinal obstruction, decompression of the gastrointestinal tract is achieved by endoscopic placement of a stent in the colon. In this case, the surgical operation is performed through the natural lumen of the intestine - under the control of a colonoscope, a balloon is initially inserted into the lumen of the colon per rectum, expanding the narrowed (stenotic) area, and then a stent is installed.
Timely preventive installation of a stent in the intestinal lumen can prolong life and significantly improve its quality by reducing intoxication, as well as avoid possible surgical intervention in patients with stage 4 cancer. Stenting of areas of the duodenum can be performed in a similar manner.
We install stents in the large intestine in patients with intestinal cancer and with a high class of anesthetic risk due to the presence of concomitant diseases, including coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus and a number of others. This will allow you to maintain intestinal patency for a long time and avoid surgical intervention.
Conservative therapy
Enema technique.
Conservative treatment is aimed at:
- providing an analgesic effect;
- normalization of the processes of self-regulation of organisms;
- additional protection against cancer of affected organs;
- freeing the digestive tract from remnants of stagnation (undigested food).
Treatment consists of taking medications prescribed by your doctor, following a strict diet, and normalizing physical activity. An additional method of cleansing the body is enemas. After conservative treatment, the patient’s condition should improve, and the symptoms should dull or disappear:
- Abdominal pain will disappear;
- the feeling of nausea/vomiting will stop;
- the passage of feces and gases is normalized;
- bloating will disappear;
- removal of stagnant substances from the body;
- the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract is normalized.
After proper conservative therapy, the patient will not require surgery.
Surgery
Surgery is indicated only in cases where conservative treatment has not produced any results. An additional factor that influences the time frame for the operation is the current condition of the patient (symptoms of the disease, the patient's condition, which may be life-threatening). In some cases, there is no time to carry out therapeutic measures, since this threatens the death of the patient.
Diet
Patients with gastric obstruction should adhere to a special diet to quickly normalize the body’s condition and avoid relapses of the disease. A person should change their own diet and switch to healthy foods:
- Organize split meals in small portions every 2-3 hours. On average, this amounts to 5-6 meals per day.
- Refusal to eat fatty, carbohydrate, smoked, seasoned, pickled foods. It is recommended to eat food that has undergone minimal heat treatment.
- Use of vitamin complexes/biological supplements.
- Increase your consumption of fruits and vegetables.
- Increase your protein intake.
Treatment methods
Gastric obstruction (symptoms in adults will help the gastroenterologist determine the area of localization of the pathological focus) is recommended to be treated using complex methods, taking into account the patient’s complaints, examination results and the individual characteristics of the human body.
Patients are prescribed medications and are advised to adhere to a special diet. If there are no medical contraindications, you can use folk remedies. In emergency situations, surgery is performed.
Drug therapy
The gastroenterologist selects medications for gastric obstruction for the patient, taking into account the research results.
Gastric obstruction is treated with the following remedies:
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs | Zinnat, Cefix | Medicines slow down the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. The dosage of the drug depends on the person’s condition and is 40-250 mg 2 times a day. The tablets should be taken after meals for a week. |
| Antispasmodics | No-Shpa, Atropine | The drugs relieve pain and eliminate spasms. The medicine should be taken orally, 1-2 tablets 3 times a day. |
| Medicines to eliminate intoxication | Refortan, Poliglyukin | The drugs eliminate the symptoms of intoxication of the body and restore the water-salt balance. The medicine is administered intravenously through a drip. Adults are prescribed 33 ml/kg per day. The course of therapy lasts 5-10 days. In severe situations, therapy is carried out for 3-6 weeks. |
| Enzymes | Mezim, Festal | The drugs stimulate the motility of the stomach and intestines. It is recommended to take the medicine 1-3 tablets 1 time per day before meals. |
| Prokinetics | Cerucal, Domperidone | It is recommended to take the medicine 10 mg 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 1-2 months. |
Cerucal
Additionally, patients need to take vitamin complexes to support the functioning of the immune system. It is important to strictly adhere to the prescriptions, since medications can cause side effects.
Folk remedies
Recipes from witch doctors and healers can be used at home if there are no medical contraindications. If the patient is indicated for surgical treatment, folk remedies will not help eliminate gastric obstruction. The recipes used should be discussed with a gastroenterologist; there is always a risk of an allergic reaction or individual sensitivity.
Effective folk remedies:
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Sea buckthorn | Wash the berries of the plant (1 kg) well, chop and squeeze out the juice. | It is recommended to drink the resulting nectar every morning before meals, 100 ml, 30 minutes. Sea buckthorn has an anti-inflammatory effect and a mild laxative effect. |
| Dried fruits | Mix 10 tbsp. raisins, figs, prunes and dried apricots. Rinse all components well, add hot water and leave overnight. In the morning, grind the dried fruits using a meat grinder. Add 50 g of natural honey to them. Mix everything well. | It is recommended to consume the resulting mass 1 tbsp orally. on an empty stomach every day. |
| Blackberry | Pour boiling water (1 tbsp) over the leaves of the plant (1 tbsp) and leave for 4 hours. Strain and take the medicine orally. | A decoction of blackberry leaves has a laxative effect. It is recommended to take the medicine in ¼ tbsp. before meals throughout the day 3-4 times. |
A simple decoction prepared from flax seeds will help restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and eliminate periodic constipation. They are filled with hot water, left overnight and taken in the morning. The decoction not only has a laxative effect, but also reduces the development of the inflammatory process.
Diet
Gastric obstruction (symptoms in adults appear and intensify as pathological processes progress) in complex therapy requires the patient to follow a specially selected diet. A nutritionist will help you create a menu. It is necessary to exclude from the diet all foods that can aggravate a person’s condition or negatively affect the functioning of the stomach.
| Recommended Products | Prohibited Products |
|
|
You need to eat small meals throughout the day. Food should be consumed warm, preferably mashed. It is also important to maintain a drinking regime. Patients are additionally recommended to take vitamin complexes and mineral supplements.
Physical exercise
Therapeutic exercises for gastric obstruction will help improve the functioning of the digestive organs and enhance peristalsis. It is recommended to do the exercises every day for 30 minutes.
A physiotherapist will help you choose a set of exercises:
- While lying on your back, while exhaling, pull one knee towards your head. Stay in this position for a few seconds. Then return to the starting position. Repeat the exercise with the other leg. It is recommended to repeat the movement 20 times, changing legs.
- Lying on a flat surface, pull both lower limbs towards your chin, hold for a few seconds and return to the starting position. Repeat the exercise 10 times.
- Lying on your back, bend one leg at the knee and try to touch the floor through the other leg. At the same time, do not lift your back and shoulders off the floor. It is recommended to repeat the exercise with each leg 10 times.
Correctly performed gymnastics in the morning or before bed for a certain period of time will help cope with numerous disorders in the functioning of the digestive tract.
Operation
Gastric obstruction (symptoms in adults require a full examination) in severe situations, when the patient has complications, is treated surgically. The same applies to the lack of a positive result after using medications.
The doctor selects the method of surgical treatment based on the person’s condition and the reason that caused the gastric obstruction:
- gastric resection;
- pyloroplasty;
- vagotomy;
- gastroduodenostomy.
After surgery, patients are prescribed medications that will help prevent the development of the inflammatory process and the occurrence of complications.
Possible complications/consequences
Poor cross-country ability is fraught with the following:
- death;
- the patient's state of shock (requires additional medical measures);
- formation of paralytic obstruction;
- severe pain syndrome;
- development of additional oncological and infectious diseases;
- movement restrictions;
- deterioration of the body's condition;
- destruction of internal microflora, inhibition of the protective function of the immune system, its weakening.
Forecast
Destruction of human microflora is a consequence of gastric obstruction.
Experts say that the probability of death from this disease is 25%. At the same time, every hour of delay has a detrimental effect on the body. In the presence of obstruction, its transition to paralytic obstruction is possible, and the risk of shock is high. Doctors make a prognosis based on the following factors:
- age;
- gender;
- timing of the operation, degree of damage to the body;
- type of obstruction;
- presence/absence of shock. Measures to relieve shock are taken into account;
- presence/absence of pain relief;
- general indicators of the body (temperature, pressure, water level, level of consumption and digestion of proteins/fats/carbohydrates/useful microelements);
- presence/absence of cancer, oncological neoplasms.
The forecast depends on the above factors. Cases of death are common, but if you consult a specialist in a timely manner and follow medical instructions, the operation will be successful.
What is acute intestinal obstruction?
Acute intestinal obstruction is a serious, life-threatening complication of many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including tumors of the intestine itself, as well as tumors of other organs of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
Despite the advances of medicine, if timely medical care is not provided in the first 4-6 hours of development, up to 90% of patients die from acute intestinal obstruction.
For patients with cancer of the colon and small intestine, especially in the later stages of the disease, in the presence of massive metastases in the area of the porta hepatis, it is important to know the first signs of the development of acute intestinal obstruction in order to promptly seek medical help at a medical institution.
The essence of acute intestinal obstruction is the rapid cessation of the normal physiological passage (passage) of food through the digestive tract.
Intestinal obstruction can be complete or partial. With partial obstruction, the passage of food is sharply limited. For example, with stenosis (compression) of the colon by a tumor conglomerate, its diameter can decrease to 1-3 mm. As a result, only a small amount of food can pass through such an opening. Such a lesion is diagnosed by gastroscopy or colonoscopy, depending on the location of the narrowing of the intestine.
To predict the treatment and outcome of this acute complication of cancer, it is extremely important to know whether the disruption of food passage occurred before or after the ligament of Treitz, formed by the fold of peritoneum that suspends the duodenum. Accordingly, therefore, high (small intestinal) and low (colon) obstruction are distinguished.
Also, the prognosis for treatment of acute intestinal obstruction is determined by the presence or absence of a mechanical obstruction. If there is no obstacle to the passage of food in the form of complete compression of the intestinal tube, intestinal obstruction is called dynamic, which in turn can be paralytic or spastic.
If there is a mechanical obstruction in the path of food (usually a tumor, swelling of adjacent tissues caused by a tumor, or adhesions, including those arising as a result of previously performed surgical treatment of cancer), such intestinal obstruction is called mechanical (synonymous with obstructive).
When there is compression of the mesentery (folds of the peritoneum that support the intestine, through which blood vessels and nerves pass), intestinal obstruction is called strangulation.
In case of dynamic intestinal obstruction, conservative treatment is prescribed in a surgical hospital. For mechanical and strangulation intestinal obstruction, treatment is only surgical.
Preventive measures
To prevent poor patency, do the following:
- cure the root cause. which caused obstruction;
- promptly treat gastrointestinal diseases;
- undergo routine diagnostics with your attending doctor;
- normalize physical activity. It is recommended to perform physical therapy, pay attention to exercises in the pool, and spend more time outdoors;
- change your diet. Bad (fatty, carbohydrate, solid) foods should be excluded from the diet. It is recommended to eat more protein foods. Include plenty of fruits and vegetables in your diet. It is allowed to take vitamin complexes and dietary supplements;
- control the development of worms. Parasite prevention should be carried out twice every six months;
- regularly take tests for the presence of cancer and oncological diseases;
- if necessary, take medications prescribed by your doctor;
- refuse self-medication.
Reviews from our patients
- Feedback on hemicolectomy
Review of hemicolectomy May 11, 2021The patient was admitted to us in critical condition. The diagnosis is intestinal obstruction due to cancer. The illness came unexpectedly. The only hospital in the community was repurposed to fight coronavirus. The patient went to a paid medical center, but they could not help. The condition gradually worsened. When contacting us, the patient promptly underwent surgical intervention involving a left-sided hemicolectomy. The patient tolerated the operation well. Recovery period...
read more
- Patient's review of the treatment of intestinal obstruction
Patient's review of the treatment of intestinal obstruction August 23, 2021
Intestinal obstruction is a serious pathology that often develops with metastatic damage to the intestine. The pathology is manifested by such severe symptoms as: vomiting, dehydration, high fever, sudden weight loss, intoxication. The patient was admitted to the clinic in a state of extreme exhaustion due to intestinal obstruction. The weight at the time of hospitalization dropped to a critical 35 kg. At the place of residence…
read more
- Let me sincerely thank the medical staff for the professional attitude shown to my mother on April 7, 2021.
Dear clinic staff! Let me sincerely thank the medical staff for the professional attitude they showed towards my mother, who was admitted to the clinic for a serious problem - intestinal obstruction. The matter was complicated by the fact that my mother suffers from cancer. In this situation, doctors and nurses showed the main human qualities: sensitivity, care and of course professionalism...
read more
Surgical removal of intestinal obstruction
During surgery, as much tumor tissue as possible is removed. Often, a resection of the affected area is performed with an anastomosis - connecting the remaining ends of the intestine. If an anastomosis cannot be performed, for example, due to the risk of developing peritonitis, then a stoma is performed - the upper end of the intestine is brought out onto the skin so that feces pass through it. In some cases, a second operation can be performed in the future to close the stoma and restore the integrity of the intestine.
In late stages of malignant tumors, such operations are palliative in nature: the surgeon does not completely remove the cancer, his task is to restore intestinal patency and improve the patient’s condition.
Such surgical interventions are not possible for all patients. In some patients they are accompanied by too high risks. The main factors limiting the indications for surgical treatment of intestinal obstruction in oncology:
- elderly age;
- severe exhaustion, cachexia;
- peritoneal carcinomatosis - damage to the peritoneum by cancer cells;
- several blocked areas in the intestine;
- ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity) that cannot be eliminated or that quickly recurs after treatment;
- metastases outside the abdominal cavity that cause symptoms;
- severe concomitant diseases;
- renal, liver failure;
- recent abdominal radiation therapy;
- inability to prescribe specific antitumor treatment.
The optimal candidates for surgical treatment of intestinal obstruction in oncology are patients with early stages of cancer, in satisfactory condition, whose intestine is blocked in only one place.
Enduring pain is life-threatening!
Take care of yourself, schedule a consultation today
Stoma placement
A stoma is an opening that connects the lumen of an internal organ to the surface of the skin. Intestinal stomas are placed to ensure the passage of stool if low intestinal obstruction cannot be eliminated by other means.
There are colostomies - when the hole is removed from the large intestine, and ileostomy - an opening from the ileum, the final part of the small intestine.
The main indications for intestinal ostomy for cancer are:
- if it is impossible to perform surgery and remove the part of the intestine affected by the tumor;
- if during the operation it was not possible to connect the ends of the intestine after resection , in such cases the stoma can be temporary or permanent;
- if you had to remove the entire rectum.
Some patients undergo a gastrostomy - an opening from the stomach is brought to the surface of the skin. This type of palliative treatment helps solve two problems:
- Removal of stomach contents, liquid and gases. This helps relieve nausea and vomiting.
- Administration of drugs into the stomach.
A tube is inserted into the stomach through the stoma and its outer end is connected to a special bag with a valve.
In modern clinics, such operations are performed without incisions, using a percutaneous endoscopic method. A fiber endoscope is inserted into the stomach, its end is pressed against the abdominal wall - a glow through the skin becomes noticeable. An incision is made in this place and a hole is created using a special sharp instrument - a trocar. The advantages of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy are that it takes only 15–30 minutes, can be performed under sedation (“medicated sleep”—without general anesthesia), and can be used in patients with high-risk surgical procedures.
Endoscopic surgery
The most modern and minimally invasive way to eliminate intestinal obstruction in cancer patients is stenting. This is a completely endoscopic procedure and does not require any incisions or punctures in the abdominal wall. During a colonoscopy, the doctor finds a blocked area in the colon and places a stent, a short tube with a mesh wall made of metal or polymer material. The stent keeps the intestinal lumen open and restores its patency. If obstruction occurs at the junction of the stomach and duodenum, a stent is installed during gastroscopy.
Stenting can effectively relieve intestinal obstruction, and most patients tolerate the procedure well. It can be performed for different purposes:
- For operable cancer to temporarily restore intestinal patency. Subsequently, a radical operation is performed, during which the stent is removed along with the tumor.
- As a palliative procedure for advanced, inoperable cancer.
At the Medicine 24/7 clinic, intestinal stenting is performed by experienced endoscopists using the latest endoscopic equipment from leading manufacturers. We use modern models of stents. Our clinic is ready to receive cancer patients at any time of the day, including in an emergency.
The material was prepared by oncologist, endoscopist, chief surgeon of the Medicine 24/7 clinic, Konstantin Yuryevich Ryabov.