10 October 2021, 21:52 0 1,961
A malignant tumor, or cancer, of the stomach is a formation growing on the epithelium of the gastric mucosa. In adult men and women, this disease ranks second in frequency of occurrence. As for children, this type of education is a rare occurrence for them. So, according to statistics, only one child out of a million is diagnosed with this diagnosis. Moreover, this disease occurs more often in boys than in girls.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Even “advanced” ulcers or gastritis can be cured at home, without surgery or hospitals. Just read what Galina Savina says and read the recommendation.
Very important! Savina G.: “I can recommend only one remedy for the quick treatment of ulcers and gastritis” read more.
Stomach cancer in a child
Children are characterized by so-called sarcomas - these are tumors that form on the connective tissues of the body (for example, on muscles or bones). As for stomach cancer, it can occur in any segment of the stomach and spread to nearby organs. It is immediately worth noting that treatment in children is more effective than in adults. This is explained by the fact that the structure, reasons and nature of education are different from those of older people. Due to these differences, tumors in children are much more sensitive to radiation and drug treatment.
Types of stomach cancer
Cancer cells differ in structure, growth rate, shape and location. Depending on these characteristics, there are two types of gastric cancer: poorly differentiated and signet ring cell. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Poorly differentiated gastric cancer. This form of stomach tumor is considered one of the most dangerous and aggressive. This neoplasm has an increased growth rate and an increased number of dividing cells. In this case, the tissues where the tumor began to form completely lose their primary signs. The danger of this type of cancer is explained by the structure of the cells. Thus, they are similar to primitive structures that perform two functions - they reproduce and consume nutrients. Features of this form of tumor include increased production of metastases and accelerated growth of malignant cells. As a result, the elements of the organ lose their properties.
- Signet ring cell cancer of the stomach is considered one of the most common in children. This name comes from the shape of the neoplasm cells. It is formed as a result of the accumulation of mucin, a special type of protein, in cells. This species is also characterized by the growth of neoplasms into the internal globules of the stomach. For unknown reasons, this cancer occurs more often in girls.
Types of cancer that are common in adults do not occur in children. This is due to the fact that a slow progression of the disease is not typical for a child’s body.
THIS IS REALLY IMPORTANT! Right now you can find out a cheap way to get rid of stomach pain. FIND OUT >>
Why is early diagnosis so important for stomach cancer?
Stomach cancer is a fairly common disease. Every year, just under 40 thousand new cases of this disease are diagnosed in the Russian Federation alone. Moreover, in most cases, it is detected already when the tumor tissue grows beyond the mucous membrane or even spreads beyond the organ. This greatly worsens the prognosis, makes treatment more difficult and complicated.
It is this tendency towards late diagnosis that explains the high mortality rate from stomach cancer: in terms of mortality, it ranks 2nd among all cancer diseases. And this situation, unfortunately, has remained unchanged in the Russian Federation over the last decade. In 2016, the officially registered incidence of stomach cancer was 38 thousand new cases, and the mortality rate was as much as 32 thousand! After all, the 5-year survival rate of patients with stage 3 cancer is no more than 15%.
But early diagnosis gives a completely different, much more favorable prognosis.
Among patients who consult a doctor with the first symptoms of stomach cancer, the 5-year survival rate is more than 80%. This is a very high indicator for cancer diseases affecting internal organs.
Main stages and symptoms of the disease
Stage 1 cancer
The neoplasm is small in size - only a couple of centimeters. Depending on the location and spread of the tumor, 1A and 1B forms are distinguished. Thus, form 1A is characterized by filling the gastric mucosa. In form 1 B, the neoplasm affects not only the mucous membrane, but also a pair of adjacent lymph nodes. In advanced cases, the muscle layer may also be affected. This stage of cancer does not have very pronounced symptoms. Therefore, the patient often simply does not pay attention to them. Survival rate is 80%. The most striking symptoms include:
- iron deficiency anemia;
- loss of appetite;
- increased fatigue;
- bloating after eating.
Return to contents
Stage 2 cancer
The size of the tumor is 4-5 centimeters. The neoplasm penetrates into all the balls of the stomach, affecting the lymph nodes. If cancer is detected at this stage, the survival rate is 56%. Symptoms at this stage include:
- depending on the location of the tumor, one or another part of the stomach begins to hurt;
- body temperature rises, up to 38 degrees;
- change in tastes;
- pain when swallowing food.
Return to contents
Stage 3 cancer
The neoplasm measures 6 centimeters. This stage is characterized by a continuously growing tumor, damage to more than 15 lymph nodes, and penetration of the tumor into all layers of the stomach. Survival rate is 35%. The following symptoms are present:
PAY ATTENTION! Do not prolong gastritis or an ulcer until stomach cancer, it is better to be on the safe side, but this will be necessary. read the story of Galina Savina >>
- significant weight loss, which develops into anorexia;
- periodic nausea and vomiting, often mixed with blood;
- stool disorder.
Return to contents
Stage 4 cancer
The last and most severe form of stomach cancer, which affects not only the digestive organ, but also other organs, regardless of the distance to the source. Added to the above symptoms are severe pain and a sharp enlargement of the abdomen, associated with the accumulation of excess fluid in it. The survival rate at this stage is low and is no more than 5%.
Early signs
Stomach cancer and the first main symptoms will be discussed below.
- Digestive problems
Loss of appetite is one of the main indicators of a stomach tumor, which affects middle-aged and older people. Simultaneously with this symptom, patients may experience attacks of nausea and heaviness in the stomach. Many patients say that they first noticed such discomfort after eating a large meal. Over time, they stopped enjoying food, and as a result, their appetite decreased. Early stomach cancer causes heaviness, belching, heartburn, and flatulence in patients. These symptoms accompanied the patients for many years, but they turned to the oncologist for more serious symptoms.
- Feeling of discomfort in the chest
The first symptoms of stomach cancer appear as unpleasant, painful sensations in the chest area. This is a feeling of fullness or squeezing, burning, heaviness, minor cramps. Signs at the initial stage appear after eating a large, difficult to digest, heavy meal. As the stomach tumor progresses, chest discomfort increases and worries the patient even when taking a small amount of dietary food. Patients at the initial stage of development of this pathology often complain to a specialist of pain behind the sternum, radiating to the heart and shoulder blades.
- Difficulty swallowing food
A sign of cancer is a problem with swallowing food, water appears only if the tumor has formed in the upper part of the stomach. It partially obstructs the movement of food, which explains this symptom. At the initial stage of the disease, difficulties with swallowing are caused only by eating rough food or large pieces. But as the disease progresses, it becomes increasingly difficult to swallow soft and liquid foods.
- Nausea and vomiting
The first symptoms of pathology and symptoms of stomach cancer at the initial stage can manifest themselves in the form of vomiting and nausea. And they are the ones who bring the patient to the doctor for examination. Vomiting can be one-time or repeated periodically, occur after eating or not be associated with food at all. The most dangerous manifestation of the disease is vomiting with scarlet or brown blood. Minor but recurring bleeding is accompanied by shortness of breath, fatigue, anemia, and pallor. Not all patients have early signs of stomach cancer in the form of blood that are permanent.
- Blood in stool
Early symptoms of stomach cancer also include the presence of occult blood in the stool. This indicates that gastric bleeding is occurring. It is in case of gastric oncology that stool tests for the blood content in it will constantly confirm its presence. If, after repeated studies, the result gives a positive answer, then this is a serious sign confirming the presence of a cancerous tumor in the stomach.
If gastric bleeding is regular, it will be accompanied by shortness of breath, fatigue, and pale skin. Recognition of stomach cancer by the presence of blood in the stool does not in all cases indicate the initial stage of the disease. The reason for the appearance of blood in feces or vomit can only be determined by a specialist after an examination. Bleeding can be caused not only by a neoplasm, but also by a duodenal ulcer and other gastrointestinal pathologies.
- Unreasonable weight loss and changes in well-being
After a patient has developed a stomach tumor, general clinical signs such as constant fatigue and sudden weight loss may also be observed. All this suggests that the patient has cancer. Those who have suffered from gastritis with low acidity for a long time should especially pay attention to them. For other people, weight loss occurs because they stop eating the amount of food they need due to lack of appetite and discomfort after eating.
All the signs and symptoms listed above answer the question asked - how to recognize stomach cancer. But there is another significant symptom with which patients most often come to the doctor - dyspepsia.
- Dyspepsia
Quite often, patients make an appointment with a doctor with a common symptom - dyspepsia. What it is? Dyspepsia is a disorder of gastric function, problems with digestion. The anomaly is manifested by the following symptoms:
- feeling of a full stomach;
- decreased or complete loss of appetite;
- food intake has decreased in portion;
- an aversion to your favorite food – protein products;
- attacks of nausea, vomiting;
- The food you eat is not enjoyable.
If you experience at least one of the above symptoms, you should not panic. But in combination with several others, you should be wary and seek help from a specialist who will prescribe the necessary examination.
Stomach cancer has several forms of the disease. Of these, there are three main ones:
- Asymptomatic or latent. A tumor in this form of pathology can be discovered completely by accident - during palpation or X-rays and other studies.
- Painless course of the disease. All signs are present, but the patient does not feel pain.
- The disease develops with pain. Stomach cancer can cause pain regardless of food intake. Discomfort can be long-term or short-term.
Gastric oncology is a malignant epithelial formation of the stomach. In medicine, it is classified into several forms.
Reasons for appearance
Despite advances in medicine, the exact cause of tumor formation remains unknown. This is mainly due to the fact that cancer can develop in the human body for years without showing itself in any way. However, despite this, scientists and doctors have identified the sources of this disease in children. They were divided into external and internal. So, external ones include: radiation, exposure to chemicals and some rare and dangerous diseases, against the background of which cancer can develop. Internal sources included: infection with carcinogenic microorganisms, genetic inheritance, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and congenital pathologies in the DNA structure.
Classification
Currently, specialists use several classifications of cancer; Lauren, Borrmann, TNM and ICD 10 are among the most common.
Classification according to Lauren or growth type implies the presence of two types of cancer - diffuse and intestinal. Diffuse is characterized by a genetic basis, which distinguishes it from intestinal, which develops on the basis of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Borrmann's classification is based on tumor types. Gastric cancer neoplasms are divided into polypoid, infiltrative, diffuse-infiltrative and unclassified. Each variety poses a great danger, so it is necessary to use a careful, individual approach to treatment.
TNM or degree of growth of formation. This classification is considered the most important in diagnosis. It indicates the spread of the tumor in the stomach, the depth of germination of the malignant tumor and the progression of the disease. This is the classification that most experienced oncologists use when diagnosing a patient.
The International Classification of Disease or ICD 10 designates gastric cancer with code C16. In addition to the main designation, doctors use certain subcodes.
The use of the term gastric cancer ICD code C16 allows specialists to conduct a dialogue about the patient’s pathology in his presence and not traumatize the psyche by voicing the diagnosis. Designating a disease with this code has enormous psychological significance.
But it should be borne in mind that the ICD 10 classification has a number of shortcomings, so in the near future the main gastric oncology code and its subsections will change in accordance with the latest research in the field of oncology and gastroenterology.
The use of classification codes helps specialists communicate with each other quickly and avoid errors when approving a diagnosis. This MK is used all over the world, so it is considered a standard and divides anomalies into types.
Treatment methods
It is worth noting that at the first suspicion of a tumor, parents should immediately consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you use traditional methods, as this will not bring results, but will only delay the start of effective treatment. There are several treatment options for stomach cancer in children. Depending on the stage of the disease, they can be used either separately or together.
- The first option is chemotherapy. For stomach cancer, this treatment method is ineffective. It can relieve symptoms and prepare the patient for subsequent surgery.
- The second option is radiation therapy. In the case of a child, this method is undesirable, since the body is exposed to radiation. During this process, not only infected cells die, but also healthy cells.
- The third option is surgery. It is considered the most effective method. During surgery, the tumor is removed. Both partial and complete removal of the affected organ is possible. A mandatory part of the operation is excision of the lymph nodes into which the metastases have spread.
Return to contents
Symptoms
First of all, the manifestation of the disease depends on the location of the tumor and its type. A malignant neoplasm can occur anywhere in the stomach - in the upper, middle and lower parts. A tumor located in the middle of this organ does not make itself felt for a long time.
Are common:
- Decreased performance, increased fatigue;
- Loss of body weight;
- Depression, lethargy;
- Anemia;
- Weakness.
Local symptoms:
- There is no pleasure from eating and no aftertaste;
- Loss of appetite, refusal of favorite foods and dishes;
- Systematic feeling of nausea, vomiting;
- Body temperature rises for no reason.
Special features:
- The patient's stool and vomit are the color of black gouache;
- Swallowing and moving food is difficult;
- Morning vomiting of yesterday's food.
These signs of the initial stage of stomach cancer are similar in their symptoms to gastritis and stomach ulcers. Therefore, if the symptoms listed above appear, you should consult a doctor.
The signs of stomach cancer at an early stage are so unexpressed and blurred that therapy is started very rarely and, as a rule, not for cancer. But the most likely symptoms of the disease can be identified. They are called “small sign syndrome in gastric cancer.”
Possible complications and prevention
Prevention methods are effective for any disease. In the case of stomach cancer, the recommendations are simple: lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid smoking and drinking alcohol, and have regular examinations with an oncologist. Complications after stomach cancer in children are common. The main ones:
- The appearance of a hole at the site where the tumor was removed. In this case, the contents of the stomach enter the abdominal cavity, causing pain and inflammation.
- Bleeding from a neoplasm. This is typical for advanced cases and can be eliminated by a doctor in a hospital.
- Stenosis. It appears when the tumor becomes large and occupies most of the stomach. In this case, food cannot move freely through the intestines. The only way out is surgery.
After recovery, the child will have to follow a diet and avoid bad habits for the rest of his life.
Not only doctors, but also parents should know that a child can get a malignant tumor.
The results of treatment of many malignant tumors of childhood are superior to the results of treatment of tumors in adults, since these tumors differ in structure, nature, and causes of occurrence. In children, sarcomas are more common - tumors of connective tissue (muscles, bones, kidneys, nervous system), their feature is high sensitivity to radiation and drug exposure. In the adult population, cancer predominates - malignant tumors from epithelial tissues (mucous membranes of various organs, skin, etc.). Unfortunately, recently, epithelial tumors have also been registered in children, especially in adolescence, for example, cancer of the kidney, liver, adrenal gland, stomach, and intestines.
The purpose of this publication is to show the main manifestations of malignant epithelial tumors of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) in children.
It should be noted that gastrointestinal cancer in children is an extremely rare pathology. According to world literature, children are most often diagnosed with colon cancer, while stomach and small intestine cancers are casuistically rare. Thus, the incidence rate is about 1 child per 1 million child population. Boys are more likely than girls to develop malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract.
Predisposing factors for the development of gastrointestinal tumors in children:
1. Familial polyposis of the colon is a dominantly inherited premalignant disease characterized by the presence of multiple polyps of the lower parts of the colon. It is an obligate precancer (transforms into cancer in almost 100% of cases) and usually becomes malignant in adolescence. 2. Gardner's syndrome is a rare disease, inherited in a dominant pattern, characterized by multiple polyps in the colon and the presence of tumors of soft tissues and bones. Polyps can be localized in any part of the digestive tract and become malignant (malignant). 3. Nonspecific ulcerative colitis. 4. Hypoacid gastritis, colitis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, surgical interventions on the stomach and intestines Children with this pathology constitute the main risk group for the development of malignant tumors of the gastrointestinal tract and should be under careful dynamic supervision by doctors of the general medical network.
Causes
The causes of stomach cancer are somewhat different from the generally accepted ones. The disease usually develops slowly, sometimes even over several decades, and is facilitated by an unhealthy lifestyle and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). But children cannot be subject to such disturbances due to the lack of proper life time, which means the influence of external factors is practically excluded.
Causes of gastric carcinoma in children:
- Genetic predisposition (in cases of stomach cancer in the family, the risk of future generations increases by 20%);
- Infection with Helicobacter pylori or any carcinogenic bacteria;
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, esophageal cancer, etc.).
The increased risk of childhood diseases is associated with an increase in alcohol consumption and smoking among the youngest age group.
Main signs and symptoms
The main symptoms of stomach cancer in children are similar to the signs of any gastrointestinal disease. Symptoms of carcinoma in children:
- Problems with eating and processing food (pain while eating, decreased or lack of appetite);
- Weakening of the body (unreasonable weight loss, constant weakness, decreased performance and increased fatigue);
- Depression and apathy;
- Inactive lifestyle.
Unlike diseases of the pancreas or esophagus, the symptoms of stomach cancer in children do not manifest themselves systematically and do not have a clearly defined character, so it is very difficult to determine that it is carcinoma. In addition, the frequency of occurrence of such a disease makes it unlikely that a doctor will correctly and timely diagnose stomach cancer in a younger age group.
The first signs of the disease in children appear late; even the dynamic course of the disease can pass without visible symptoms. The disease can be noticed after the tumor has invaded the mucous membrane of the stomach or intestines to one degree or another. The first pains can be very indicative.
What is the basis for preventing stomach cancer?
To prevent the appearance of malignant neoplasms, it is important to at least generally understand the nature of the changes that lead to pathological processes. According to statistics, inflammatory, hypertrophic and atrophic processes, polyposis and even banal gastritis lead to the formation of various types of tumors in the stomach. That is why it is first of all important to avoid any traumatic factors.
Among all the causes of stomach diseases, experts identify:
- Bad habits, especially smoking. Each cigarette contains a huge amount of carcinogens that have a devastating effect on the entire body. Tobacco has the most pronounced effect on the lungs and mucous membranes of the digestive tract.
- Alcohol is no less dangerous in terms of cancer risk. Even weak cocktails and drinks can cause serious changes in the mucous membrane and submucosal layer.
One of the predisposing factors for stomach cancer is smoking, so you should give up this habit
- Food products saturated with carcinogens - smoked meats, fruits and vegetables with nitrates, pickles and marinades with vinegar. In addition to the general negative impact on the body, they greatly irritate the mucous membranes of the stomach, leading to dysfunction of the digestive organs.
- Bacteria Helicobacter or others, as well as parasites and viruses that undermine the human immune system and become the main cause of the development of inflammatory and destructive processes on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Significant factors that very often lead to cancer include radiation. However, it remains insufficiently widespread, since there are not many places in the world where elevated background radiation is observed.
Cancerous tumors in the stomach can form as a result of the development of Helicobacter and other parasites
There is also a factor independent of a person that can become the main cause of a tumor in the stomach - a hereditary predisposition. This is precisely what is the main cause of the formation of malignant tumors in 80% of cases.
Unfortunately, even knowledge of the reasons that can provoke the formation of pathological cells in the body cannot 100% protect a person from stomach cancer. That is why the main way to avoid serious health problems remains timely detection of the disease and its elimination at an early stage.
Stages
There are several stages of the disease, each of them has its own indicators for diagnosis and treatment. The most important indicator at any stage of a carcinogenic disease is survival.
There are 4 stages of stomach cancer in children:
- Stage I (tumor size – up to 20 mm, absence of metastases, survival rate – 80%);
- Stage II (tumor size is from 40 to 50 mm, the appearance of metastases, germination of the submucosal and muscular layers of the stomach, survival rate is 56%);
- Stage III (tumor size becomes more than 60 mm, germination begins on neighboring intestinal organs, a moderate amount of metastases appears, survival rate is 35%);
- Stage IV (the tumor grows into neighboring organs, metastases spread throughout the body, survival rate is no more than 5%).
It is very important to determine the stage of stomach cancer in a child in advance, but practice shows that most often the disease is diagnosed at stage 3, but with the proper degree of treatment, even 35% is a lot, don’t despair and everything will work out.
Carcinoma in children is characterized by increased aggressiveness, rapid growth in the tissue of the intestine, pancreas or esophagus, and a high level of metastases. There are 2 main types of carcinoma that occur in childhood:
- Poorly differentiated gastric cancer. A very dangerous species, the main features of which are: increased production of metastases; high tumor growth rate; the cells of the organ turn into primitive cellular elements and lose their properties - they are only capable of dividing and feeding;
- Signet ring cell cancer of the stomach . Signet ring cell is the most common and malignant gastric cancer found in children. It is characterized by a high rate of tumor germination and produces a special protein (mucin) in the cells, the structure of which, when examined, resembles a ring (hence the name). Signet ring cell cancer of the stomach mainly affects girls for an unknown reason.
Typical adenocarcinoma and other “adult” types of stomach cancer practically do not occur in children, since the slow progression of the disease is unusual for children.
Symptoms and manifestations of stomach cancer
Clinical symptoms of stomach cancer depend on the stage of the process.
Stage O : carcinoma in situ, “cancer in situ” - there are no clinical manifestations, and the diagnosis in most cases is an incidental finding during a mucosal biopsy for other diseases.
Stage 1 of stomach cancer: characterized by localization of the tumor in the mucous membrane without growing into the muscular layer of the stomach wall, as well as possible damage to 1 - 2 lymph nodes located along the organ (T1 N0 M0 or T1 N1 M0). Already at this stage, early symptoms of stomach cancer appear, which include:
- unmotivated general weakness
- fast fatiguability
- lack of appetite
- anemia (decreased hemoglobin, see iron supplements for anemia)
- pronounced weight loss
- aversion to animal protein in food (meat or fish products, as well as to any one type of meat)
- a prolonged slight increase in temperature is possible (see causes of low-grade fever)
- depressive emotional background
Stage 2 : the tumor can either remain within the mucous membrane, but a larger number of lymph nodes are affected - 3 - 6, or grow into the muscle layer with damage to 1-2 lymph nodes (T1 N2 M0 or T2 N1 M0). The first symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract appear:
- heartburn (see heartburn pills)
- feeling of discomfort in the stomach
- nausea (anti-nausea pills)
- vomiting, which brings short-term relief
- belching air
- progressive weight loss
- increased gas formation in the intestines (flatulence)
- defecation disorders
These complaints are not permanent, and therefore patients do not attach due importance to their occurrence and hesitate to see a doctor.
Stage 3: the tumor grows not only into the muscle layer, but also through the outer lining of the stomach with damage to nearby tissues and organs, as well as the presence of cancer in seven or more lymph nodes. There are no metastases (T2 -4 N1-3 M0).
- the above complaints become pronounced,
- pain in the epigastric region intensifies and becomes constant,
- the patient practically cannot eat food, since it does not pass into the stomach,
- with cancer of the cardiac, “initial” part of the stomach, dysphagic phenomena occur - frequent choking, regurgitation, the need to wash down solid food with water or take only liquid food,
- with cancer of the pyloric, “exiting” part of the stomach, food is not digested and stagnates in the stomach for several days, a feeling of rapid satiety, constant fullness in the epigastrium, vomiting with stagnant contents, and belching with the smell of rotten eggs occur.
Stage 4 means complete germination of the stomach wall, destruction of neighboring organs, damage to a large number of lymph nodes (more than 15), metastasis to distant organs and lymph nodes - to the ovary in women, to the lymph nodes of the pararectal (around the rectum) fatty tissue, to the lymph node located in the fossa above the left collarbone.
- symptoms become permanent
- the patient is exhausted, unable to eat on his own, only through a tube
- experiences excruciating constant pain, relieved by taking narcotic analgesics with a short-term effect
- the body is poisoned from the inside by the products of metabolism and tumor decay, does not receive the required amount of nutrients from the outside, tumor cells capture nutrients from the patient’s blood, dystrophic changes occur in all organs and tissues of the body, and the person dies.
It is at stages 3 and 4 of stomach cancer - late stages - that 80% of patients consult a doctor when the diagnosis is no longer in doubt, which significantly worsens the prognosis of the disease.
Diagnostics and tumor markers
Diagnosis of the disease in children allows us to determine the nature of the damage and the set of symptoms. This is done in several ways:
- Fluoroscopy (using x-rays to identify a tumor);
- Blood test (general and biochemical - to identify protein metabolism disorders and anemia);
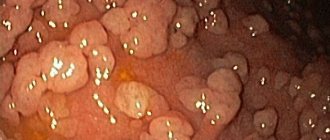
- Fibrogastroscopy (insertion of a long tube with a camera into the stomach, which allows the doctor to examine the mucous membrane of the organ);
- Carrying out a biopsy (samples) in areas suspicious for stomach cancer;
- In rare cases, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or CT (computed tomography) is used.
The accuracy of the diagnosis depends on the correctness of the chosen method and the qualifications of the specialist. An integrated approach (several methods are used simultaneously) is often used to determine carcinoma in children.
The most effective method for diagnosing diseases associated with cancer is the use of tumor markers.
Tumor markers are types of proteins that appear during cancer. Tumor cells produce tumor markers in the blood as soon as the child becomes ill; this process helps to quickly determine the nature and extent of the disease.
The following tumor markers are used to determine stomach cancer:
Tumor markers make it possible not only to determine, but also to control the process of treatment of carcinoma diseases of the intestine, pancreas or esophagus. At the same time, complex use helps to detect cancer at the earliest stages, but a more accurate diagnosis is possible only with the use of additional examination methods.
Treatment of carcinoma
Treatment of stomach cancer in a child is carried out in several ways:
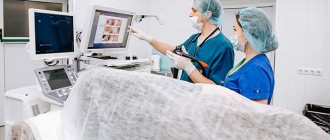
- Surgical intervention . The main method of treating carcinoma is gastric surgery, namely removal of the tumor, both part and all of the organ. During the procedure, lymph nodes containing metastases are also excised. Removing part or all of the stomach is called a gastectomy;
- Chemotherapy . Chemotherapy for stomach cancer plays a supporting role: it alleviates the symptoms and signs of carcinoma, prepares for upcoming surgery, and prevents relapses of carcinogenic diseases. Taking potent drugs is fraught with consequences for the body, but they can be overcome, unlike death.
- Radiation therapy . It is used extremely rarely due to its low efficiency.
Treatment of stomach cancer with folk remedies, even at an early stage, does not bring results, so it is recommended to use traditional medicine methods.
The best way to treat carcinoma, and other diseases, paradoxically, is to prevent stomach cancer. Prevention of stomach cancer consists of simple truths: lead a healthy lifestyle, undergo regular examinations with an oncologist, monitor your health and the health of your loved ones.