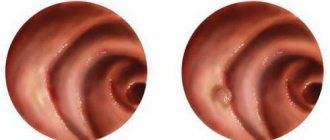
A pancreatic polyp is a benign neoplasm with slow growth that develops exclusively in the ducts.
Sometimes a pancreatic polyp is used as a conventional name, implying a cyst, hemangioma, fibroma, lipoma. This use of the term is used incorrectly, since a polyp is a growth of mucosal cells inside a hollow organ. It has different histological structures depending on the type of cells from which it originates.
A polyp cannot develop in the tissues of the gland itself, since it is a parenchymal organ consisting of glandular tissue. It lacks cavities and mucous epithelial cells, which are the basis of formation. The polyp occurs in the Wirsung duct of the pancreas, but given the size of the canal, the neoplasm cannot always be detected, and it does not manifest itself symptomatically.
Causes and types of polyps in the pancreas
The impetus for the development of benign formation can be factors of different types:
- Hereditary . Neoplastic tissue degeneration is a phenomenon that most often has a genetic pathogenesis.
- Traumatic . Internal bleeding, bruises, pressure, and tissue ruptures can occur due to injury to a person, injuries sustained in an accident, or falling from a height.
- Purchased . Abuse of fatty and spicy foods, as well as systematic poisoning of the body with nicotine, alcohol and chemicals causes failure of pancreatic fermentation and inflammation of the pancreas. As a result of the gradual death of cells and tissue injury, cysts, swelling and polyps are formed.
- Secondary . Since all body systems are interconnected, pathological changes inside the pancreatic ducts can occur against the background of any other protracted illness. In addition to chronic pancreatitis, danger lurks in hepatitis, cholelithiasis, hormonal dysfunctions, complications after infections and viruses.
The danger of polyps to health
Polyps can remain unnoticed for several years or a lifetime, without manifesting themselves in any way, and do not cause concern to a person. In some cases, they are diagnosed accidentally during a general examination.
The disease has a number of features:
- lack of rapid growth;
- absence of pronounced symptoms at the development stage.
The formations themselves do not cause harm. The danger lies in the occurrence of complications if adequate treatment is not prescribed. The pathogenic effect manifests itself as:
- degeneration into a malignant tumor;
- internal bleeding;
- the appearance of dangerous purulent clots;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- pancreatitis;
- liver diseases;
- peritonitis;
- anemia;
- fistulas
We recommend reading: Failure of the menstrual cycle at 49 years 3 months
Timely diagnosis, immediate treatment, and compliance with doctor’s recommendations help to avoid complications.
Pancreatic polyps: features and difference from cysts
Polyp in the pancreas is not a completely correct definition. It’s just more convenient to denote pathology in colloquial speech. In fact, in organs such as the liver or pancreas, the parenchymal tissue is a “spongy” pulp that leaves no room for formation. And polyps can only form inside cavities.
The only place where polypous formations appear in the pancreas is in its duct. Specific localization is one of the features of pancreatic polyposis.
Other distinctive features of the disease include its extreme rarity and the absence of pronounced clinical symptoms.
A polyp is sometimes confused with another formation - a cyst. But these two pathologies have significant differences:
- Anatomical . A polyp is a “fleshy” growth consisting of connective tissue. A cyst is an autonomous cavity enclosed in a membrane and containing liquid or a thickened mass.
- Localization . The polyp grows inside a cavity that has a mucous wall to which it is attached. A cyst forms anywhere in an organ, often from its own tissues.
What are polyposis formations
Pancreatic polyps are benign neoplasms that grow slowly and develop only in the ducts. Sometimes a polyp is used as a symbol, meaning a pancreatic cyst, hemangioma, lipoma, fibroma. This use of terminology is inappropriate, because this neoplasm is represented by the proliferation of mucosal cells inside a hollow organ. It has different histological structures based on the type of cells from which it arises.
The appearance of such neoplasms is impossible in the tissues of the pancreas, since it belongs to a parenchymal organ and consists of glandular tissue. It does not contain a cavity and mucous epithelial cells, which are the basis of the formation.
The appearance of polyps is observed in the Wirsung duct of the organ, but when taking into account the size of the channel, the growth is not always detected, and symptomatically it does not make itself felt.
- The formation of neoplasms in the pancreas is detected only in its duct; growth is impossible in any other area.
- The course is asymptomatic at the developmental stage and at an early stage.
- Development is slow.
- Fixed in rare cases.
Cysts are conventionally classified as organ polyps, which is incorrect. In turn, cysts are divided into:
- true;
- pseudocysts;
- cystadenomas - formations of a benign course from the epithelium of the canal;
- adenocarcinoma - with malignant growth.
A pseudocyst is a consequence of changes in pancreatic tissue, or the result of household, iatrogenic trauma. Pancreatic growths also include malignant growths inside the gland. This will be the proliferation of one of the types of cells of the islets of Langerhans, which synthesize certain types of hormones. Each of them will have certain characteristics. Their diagnosis is carried out using laboratory and functional examination methods.
If you feel unwell, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms and signs of pancreatic polyp
Up to a certain point, polyposis can develop asymptomatically. Very small formations are quite difficult to diagnose even with a full comprehensive examination.
The basic clinical picture consists of the following signs:
- permanent low-grade fever;
- frequent urination;
- gastrointestinal dysfunctions (constipation, diarrhea, bloating);
- nausea after meals;
- general weakness;
- sleep disorders.
Enlarged polyps begin to put pressure on the walls of the organ, block the pancreatic duct and increase symptoms:
- sudden sharp pain occurs in the right hypochondrium;
- vomiting may occur after eating;
- constant dryness and bitterness in the mouth.
Signs of the presence of polyps are becoming more and more similar to acute pancreatitis. This is understandable. If the pancreatic duct is blocked, pancreatic enzymes begin to corrode the organ tissue, which directly leads to inflammation.
Symptoms upon appearance
In the early stages of development, neoplasms do not manifest themselves and are detected only during instrumental studies. Obvious symptoms are observed when a pancreatic polyp provokes pancreatitis, interferes with the outflow of secretions, or reaches a large size and puts pressure on nearby organs.
The patient complains of:
- weakness;
- malaise;
- constant aching pain in the upper abdomen;
- periodic abdominal cramps;
- increased urination;
- bowel disorders;
- flatulence;
- nausea;
- thirsty;
- swelling.
Symptoms and signs become more pronounced if the growths are larger and produce hormones. In this case, there is an increased level of insulin, glucagon and gastrin.
Against the background of hormonal hypersecretion, increased sweating, tachycardia, dizziness, anemia appear, and diabetes mellitus develops. A sharp weight loss is possible, and the person’s general condition worsens.
Complications of polyps are likely, which lead to the development of intestinal obstruction, which occurs due to compression of a segment of the small intestine and obstructive jaundice - if a large growth puts pressure on the liver. Possible internal hemorrhages, suppuration, fistulas, splenic rupture or peritonitis.
What complications can there be?
As with the development of pancreatitis, the pathology of the pancreas is “overgrown” with concomitant diseases:
- jaundice;
- cholecystitis;
- duodenitis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- peritonitis.
In addition to exacerbation of pancreatitis, a polyp in the pancreatic duct threatens with other complications:
- internal bleeding;
- spread of suppuration;
- fistula formation;
- exacerbation of infections;
- development of malignant tumors;
- splenic rupture.
Dangerous consequences can be avoided by promptly consulting a doctor if you feel unwell and having a thorough examination.
Diet for illness
The diet for pancreatic polyps involves table No. 5 according to Pevzner. After the operation, you need to follow a strict diet for a long time: food should be chopped and thoroughly pureed, too hot or cold dishes are excluded - it is recommended to eat food warm, 5-6 times a day in small portions. This allows you to significantly reduce the functional load on the organ.
Fatty, spicy, fried, smoked foods are excluded. For any pathology of the pancreas, it is necessary to completely abandon alcohol-containing drinks, even low-alcohol drinks. The diet includes vegetables and fruits - during the period of pronounced clinical manifestations they are consumed in processed form.
Dietary nutrition is an important component of complex treatment for any pancreatic pathology, so it must be strictly observed until discontinued by a doctor. If diabetes mellitus develops, a diet (table No. 9) with limited carbohydrates is prescribed by an endocrinologist. In this case, you sometimes have to adhere to dietary restrictions for the rest of your life.
Diagnostics
It is difficult to accurately make a diagnosis confirming the presence of polyps in the pancreas. Therefore, doctors insist on simultaneous research using three methods:
- clinical;
- laboratory;
- instrumental.
Only after assessing all the data can you confidently differentiate the disease and decide on the actions necessary to eliminate the problem.
Clinical diagnostic method
Clinical examination of the patient includes:
- studying the hereditary background to identify the prerequisites for pathology;
- a detailed survey of the patient about all suspicious symptoms and discomfort, the frequency of their occurrence, intensity and duration;
- external examination and study of the epigastric region of the abdomen by palpation.
Abnormal formations can be suspected at this stage of diagnosis, but only if they are significant in size. In any case, the diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory tests.
Laboratory diagnostic method
Any damage to the pancreas is accompanied by characteristic changes in the biochemical composition of blood, urine and feces. Their traditional general analysis is mandatory.
If polypous formations are suspected, the following additional studies are preferred:
- measuring the amount of insulin production;
- determination of cancer markers;
- detection of fats and proteins that are not broken down during the digestion of food;
- assessment of fecal elastase.
Studies of pancreatic juice and enzymatic disorders are also important in clarifying the picture as a whole.
Instrumental diagnostic method
Instrumental methods are widely used in modern medicine. This is the most reliable way to informatively describe all the nuances of a polyp:
- its exact localization in the pancreas duct;
- its size;
- the degree of proliferation in a quantitative aspect (new emerging polyps);
- the nature of the inflammatory process in the surrounding tissues;
- the degree of destruction of the mucosa to which the polyp is attached.
Such detailed information is obtained from one method or in a cumulative study in several instrumental ways:
- ultrasound examination;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance;
- endoultrasonographic;
- fluoroscopic;
- retrograde endoscopic;
- cholangiopancreatographic.
The most common method is ultrasound. With sufficiently large polyps, this type of hardware research can reveal both the exact localization of formations and the size of their growths.
Endoultrasonography is informative and convenient in the study of the upper gastrointestinal tract. This is a method that uses a special endoscope with an ultrasound scanner at the tip. The method gives a visual picture of the condition of the tissues and walls of internal organs. When prescribing such a procedure, the patient is prepared for it for at least 10 hours. The main preparation is to refuse to eat.
Diagnostic measures
When a patient comes to a medical facility with complaints of pain in the left upper abdomen or has other symptoms indicating a pathology of the pancreas, in addition to general tests, he undergoes an ultrasound examination (ultrasound). It should be taken into account that this examination method is not always able to detect the presence of a cystic neoplasm, especially if it is small in size. Therefore, the patient may additionally be prescribed magnetic resonance or computed tomography (MRI or CT). Such diagnostic methods also make it possible to distinguish a gland tumor from a cyst. In case of doubtful results, another examination may be performed - laparoscopy. During its implementation, pathological tissues are taken for examination. A biopsy will provide accurate confirmation of whether there are cancer cells in the tumor.
We recommend reading: Pulling on stitches after episiotomy, how to relieve pain
Finding out the cause of the cyst is also included in the diagnosis. This information will help prevent the recurrence of growths.
After a complete diagnosis has been made, the patient is prescribed appropriate treatment.
Treatment
Polyps are practically not amenable to traditional treatment. Homemade folk recipes will also be useless. Unfortunately, no medications or herbal remedies are able to “dissolve” polyp-like growths. They can only be physically removed.
If the formations are very small, there are no indications for immediate surgery. On the contrary, doctors themselves do not recommend rushing in such cases. They register the patient and select medications that slow down the growth of tumors.
There is a possibility that if polyps are detected in a timely manner and their growth is “preserved” using medication, surgical intervention will not be required at all. The person will live normally with the pathology, follow a diet and undergo preventive examinations from time to time.
But most often, polyps are noticed in a sufficiently expanded state, when their presence impedes the outflow of pancreatic juice and bile. To prevent complications and the development of chronic processes, surgical removal of the formations is prescribed.
Surgical intervention
Operations to remove benign tumors can be of different variations:
- enucleation polypectomy;
- resection;
- endovascular embolization.
The essence of arterial embolization is to block the blood vessels feeding the formation. As a result, its tissues die and the polyp dries out. This is the least traumatic method in surgery to remove various tumors and benign formations.
Resection is prescribed only in complicated cases, when the growth of the formation has destroyed the surrounding tissues and the further development of the disease is life-threatening. Cutting off part of an organ or even its complete removal has always been a last resort.
Enucleation is used to remove small polyps. They are “husked” with special instruments, and to prevent bleeding, electrocoagulation is used - cauterization of the site of the former attachment of the polyp.
The likelihood of recurrent polyps, even after a successful polypectomy (removal of previous ones), is very high. Therefore, prevention of neoplasms is of great importance.
Preventive measures
It is possible to resist benign neoplasms if you strictly follow all the instructions of your doctor and undergo periodic examinations.
We also need to reconsider our lifestyle:
- give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- adhere to a balanced diet and completely exclude everything fatty and spicy from the diet;
- Take warm food (not scalding or cold), do not eat it dry or at night.
Dietary nutrition is one of the strongest preventive ways to influence the health of the pancreas as a whole.
It is also important to pay attention to improving the tone of the body: toughen up, walk a lot in the fresh air, take care of the immune system and promptly cure all infectious diseases.