How is bougienage of the esophagus done?
The bougienage procedure is quite complex, its duration is on average several weeks and is determined by the severity of the narrowing of the esophagus.
To do this, a bougie is inserted into the esophagus every day for a period of from several minutes to one hour. With each subsequent session, the number of the bougie (determines the diameter of the probe) and the time for which it is inserted into the esophagus gradually increase.
Then a so-called plateau is established - for about a week, the maximum bougie number is entered every day for the maximum time (half an hour - an hour). The end of the bougienage procedure is determined by the doctor individually, depending on the results.
Technique for bougienage of the esophagus
Patients often ask their doctor how bougienage of the esophagus is done. It begins to be carried out only after esophagoscopy (insertion of an optical probe into the esophagus) to determine the location, nature and degree of narrowing of the esophagus. Then the bougie of minimal size is lubricated with medical Vaseline for better passage through the esophagus. Its introduction is carried out under visual control, without much effort. Next, the number (determines the diameter) of the bougie is increased until difficulty is felt during its insertion. The bougie remains in the esophagus for about 2-5 minutes, then it is increased to 10-15 minutes.
The next largest bougie number begins to be inserted into the esophagus only after the previous number is inserted without difficulty.
The maximum is number 15, which is injected into the esophagus for several weeks (usually 2-3) for half an hour or an hour every day or every other day. The passage of this bougie number into the esophagus without difficulty indicates the effectiveness of lumen expansion. Possible complications are monitored by measuring body temperature every day. Its increase above 37.5 C is an indication for temporary termination of the procedure.
Bougienage of the esophagus in children
Since bougienage of the esophagus is an invasive procedure, its implementation in children has a number of features:
- The procedure uses soft probes with a rounded tip to prevent possible damage to the walls of the esophagus.
- The minimum initial bougie number for the first session is selected depending on the age of the child - the lower the age, the lower the bougie number.
- During bougienage, a small child is wrapped in a sheet, an assistant holds his head - this is necessary to avoid sudden movements and the possibility of damage to the esophagus.
- The maximum one-time time for introducing a bougie into a child’s esophagus should not exceed half an hour.
- It is not recommended for a child to carry out the procedure every day; it is usually performed 3 times a week.
- The entire course of bougienage sessions for children averages 1.5-2 months.
- During the entire course of the procedure for dilating the esophagus, the child must be in the hospital with constant monitoring of his general condition and the absence of complications of bougienage.
- During bougienage, it is recommended to take antibacterial drugs to prevent infectious complications.
These features of bougienage in children are common. The selection of the bougie number, the time of its administration, and the duration of the entire course are determined by the doctor on an individual basis.
General execution process
Bougienage of the esophagus requires some time, so the manipulation is performed in several sessions, and the treatment itself is complex.
The course of therapy is individual, based on the symptoms and stenosis of the organ. One session averages 10-50 minutes.
After the diagnosis, the doctor selects the size of the bougie and the main method. After several sessions, the diameter of the probe is increased, and at the very end of the treatment, the maximum diameter and period of the procedure are used.
Even after manipulation, the lumen may begin to narrow again.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
- An endoscopic examination is performed to assess the degree of narrowing, the type of disease and the condition of the esophagus itself.
- Oil or Vaseline is applied to the bougie for easy insertion.
- After insertion, the probe is left for 2 minutes at the very beginning of the course, and at the end the time is increased to half an hour.
- After inserting a thin bougie, its number changes, which indicates a larger diameter of the tube.
- The effectiveness of treatment can be determined when bougie No. 15 is inserted without difficulty and is easily removed.
To avoid complications, after each session you need to monitor your general condition and measure your temperature.
If the indicator is more than 37.5 degrees, then the course stops or stops altogether.
Carrying out the procedure
Gastroscopy (FGDS) in Nizhny Novgorod
The procedure is preceded by preparatory measures:
- The patient is placed on his back (urethral dilation in men is carried out on a urological chair, and in women - on a gynecological chair) and the external genital organs are disinfected with antiseptic solutions to avoid infection in the urinary tract.
- If necessary, local anesthesia is injected into the lumen of the urethra. Pain relief is not provided in all cases. For young children, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia. For older children - under local anesthesia.
- The bougie is treated with Vaseline for better glide.
- Since the patient must be relaxed during the procedure, he may be given sedatives.
In general terms, the procedure is carried out approximately the same for all patients:
The bougie is carefully inserted into the urethra to the narrowed area or bladder - the metal tube is left at the beginning of the narrowing, and the synthetic tube is slowly pushed further, and then filled with water (to expand the channel). Depending on the indications, the bougie is left in the urethra for 5–15 minutes (for the first procedure, the time is minimal) or is removed and replaced with a thicker tube, repeating the manipulation and each time introducing a bougie of a larger diameter. At the end of the procedure, the urethra is washed with an antiseptic solution.
The procedure, depending on the degree of narrowing and structural features of the patient’s organs, can last from 15 minutes to several hours. It is impossible to expand the urethra to its original size at one time - there is a high risk of rupture of the urethral mucosa. The procedures are repeated every 8–24 hours. The number of sessions and duration of treatment depends on the degree of narrowing and its cause. Therapy can be carried out over several days or several months. On average, 3 to 14 procedures are required.
Due to anatomical features, bougienage in men and women is carried out slightly differently:
- The procedure is easier for women because they have a shorter and less tortuous urethra.
- For men, a flexible bougie is used, which is inserted with rotational movements up to the urinary canal.
- For women, a steel bougie is used, pushing it to the narrowed area: the size of the bougie head is slightly larger than the diameter of the narrowing.
Despite the fact that bougienage is a simple procedure, it cannot be called absolutely safe. Therefore, after it is performed, if there is severe pain in the lower abdomen and genital area, purulent discharge or significant bleeding, the patient should definitely consult a doctor. Discomfort, burning, and a little blood in the urine in the first days are considered normal.
Usually, to avoid complications after bougienage, antibiotics are taken on the recommendation of a doctor. If the patient finds it difficult to tolerate discomfort in the lower abdomen, he may also be prescribed painkillers.
Bougienage methods
Classification of strictures (narrowings) of the esophagus
What method is used for such a complex medical procedure? There are several of them, and the doctor chooses the one recognized as the safest depending on the degree of stenosis and the individual characteristics of the human body.
Early bougienage gives better results, since stenosis is easily corrected. Currently, the following procedure methods are used in practice:
- Blind bougienage. The size of the probe is selected during the procedure itself. Currently, it is used quite rarely, because it is very dangerous due to the occurrence of injuries.
- Endoscopic manipulation is performed if there are expansions in front of the narrowed area. This equipment is necessary to bypass hard-to-reach areas of the esophagus.
- Bougienage with fluoroscopy. This method is carried out using contrast agents and under the control of an X-ray machine. The risk of perforation, however, increases with this technique, but there is also a greater risk of radiation exposure.
- Bougienage by the thread is carried out subject to the patient's preparation. A week before the procedure, a gastrostomy tube is installed - an opening in the esophagus. Next, the patient swallows the thread and drinks a liter of water, which pushes out the bougie.
- Bougienage along a string is carried out similarly to the method described above, but the probe is inserted into the esophagus along a string. The device may deviate due to the thread not being stiff enough. This method is used mainly for scar changes and narrowings characterized by a high degree of rigidity.
Thus, none of the bougienage methods is completely safe for the patient and is always associated with certain risks.
Bougienage of the esophagus: when indicated, methods, course, result
All materials on the site were prepared by specialists in the field of surgery, anatomy and specialized disciplines. All recommendations are indicative in nature and are not applicable without consulting a doctor.
Averina Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, pathologist, teacher of the department of pathology. anatomy and pathological physiology, for Operation.Info ©
Bougienage is a method of studying the patency and expansion of hollow tubular organs and natural communications in the body using special probes. Bougie (French bougie) – probe, thin flexible rod. In practical medicine, the most common are bougienage of the esophagus, urethra, cervix, auditory tube and some other organs.
The essence of the method: under the influence of bougie pressure, the lumen of the narrowed areas gradually expands.
Indications for bougienage of the esophagus
Bougienage of the esophagus is used when it is narrowed (stricture). This situation occurs:
- With congenital narrowing of the esophagus.
- After burns with caustic substances (acid, alkali).
- After thermal burns.
- When the lumen of the esophagus is deformed by scars due to injury from foreign bodies or medical devices.
- For scars formed after ulcerative esophagitis.
- For tumors of the esophagus or mediastinum.
- Consequences of previous infectious diseases (tuberculosis, actinomycosis, syphilis, etc.)
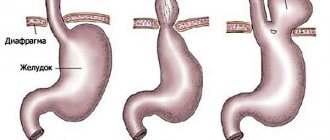
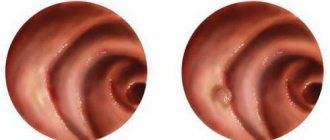
Narrowings of the esophagus can be single or multiple. They are mainly localized in places of physiological narrowing (above the diaphragm, at the junction of the pharynx with the esophagus, at the bifurcation of the trachea). They can be linear, ring-shaped, or tunnel-shaped.
Stenosis after chemical or mechanical damage forms within 6-10 weeks. At this time, symptoms begin to appear (difficulty swallowing food). If measures are not taken, the process can be complicated by complete obliteration of the esophagus and its obstruction not only to food, but also to liquid.
Bougienage of the esophagus, when performed correctly, is effective in 80-90% of cases.
Diagnostics
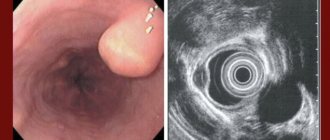
There are two main methods for diagnosing esophageal stenosis: fluoroscopy of the esophagus with contrast and esophagoscopy.
Fluoroscopy allows you to determine the diameter of the stenotic area, its shape and extent. Fluoroscopy is performed vertically in two projections (direct and right oblique).
esophagoscopy
Esophagoscopy in case of stenosis sometimes cannot be carried out completely; in cases of severe narrowing, it is carried out only to the site of stenosis; it allows one to determine the diameter of the entrance to the narrowed part, the condition of the mucous membrane, the presence of ulcers, scars.
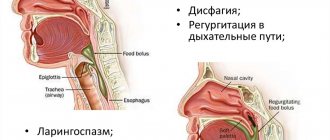
Esophagoscopy is performed not only if there are symptoms of dysphagia (difficulty swallowing). After burns of the esophagus, by 7-9 days the patient may experience improvement in swallowing as swelling decreases. But this is the so-called “period of imaginary well-being,” doctors know about this, and during this period endoscopic monitoring of the condition of the mucous membrane is very important.
If there is only superficial catarrhal inflammation of the epithelium, there is no risk of developing stenosis and the patient can be discharged home. If the submucosal layer is involved, erosions, ulcers, and fibrinous plaque are detected, then such a patient is indicated for early preventive bougienage due to the risk of developing cicatricial stenosis.
Types of bougienage
- Preventive bougienage. It is carried out to prevent the development of stenosis when the scar is just beginning to form. It is advisable to start it from the 7th to the 10th (maximum 12th) day from the burn.
- Therapeutic bougienage. It is carried out when stenosis has already formed (two months after the injury).
It is not recommended to start bougienage after the 12th day after the burn, since during this period there is a massive rejection of necrotic tissue and the formation of ulcers, because of this there is a high probability of perforation of the esophagus. If symptoms of esophageal obstruction develop during this period, this is a direct indication for gastrostomy.
Preparing for bougienage
In itself, treatment of a burn of the esophagus can be called preparation for bougienage. Pain relief, detoxification, antibiotic therapy, enveloping agents are administered, and steroid hormones are prescribed to reduce the formation of granulations.
If renal failure develops after taking acetic acid, hemodialysis is performed.
Nutrition during this period is usually parenteral, if swallowing is possible - intake of liquids and liquid food.
If symptoms of complete obstruction of the esophagus develop, a gastrostomy tube is placed.
Late therapeutic bougienage usually does not require special preparation; only a preliminary endoscopic examination is necessary. When erosive-ulcerative esophagitis worsens, it is treated.
scheme of bougienage of the esophagus
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications:
- Esophageal-tracheal and esophageal-bronchial fistulas.
- Perforation of the esophagus.
- Bleeding.
- Sepsis.
- Complete obstruction of the esophagus
- Blood clotting disorders.
Relative contraindications:
- Exacerbation of esophagitis.
- Development of mediastinitis.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Mental disorders.
- Severe somatic diseases.
- Esophageal diverticula.
Techniques for bougienage of the esophagus
- Bougienage “blindly” without x-ray and endoscopic control.
- Bougienage on a conductor string.
- Bougienage under endoscopic control.
- Bougienage “endlessly” by the thread.
- Retrograde bougienage through a gastrostomy tube.
What is an esophageal bougie?
An esophageal bougie is a tube 70-80 cm long, made of various materials. Currently, metal bougies are used, as well as plastic bougies.
Bougies are produced as a set. The set includes bougies of various diameters (from 3 mm to 1.5 cm), conductors, and cleaning devices. The included bougies are calibrated according to the Charrière scale, where each number is 0.3 mm greater than the previous one.
The bougie has a conical shape or has replaceable tips (olives) of various diameters.
Currently, elastic radiopaque bougies made of polyvinyl chloride, which have a channel inside for a conductor, are mainly used. When heated, such bougies soften, become quite flexible and carry less risk of damage to the walls of the esophagus.
Such bougies are sterilized by immersion in an antiseptic solution.
There are bougies that have a cuff around the perimeter that is inflated with air.
Blind bougienage
Before bougienage, an endoscopic examination is performed again.
Bougienage is done in the morning on an empty stomach every other day. The first few procedures involve local anesthesia of the pharynx with lidocaine spray or gel. Subsequently, anesthesia, as a rule, is not required, since the patient quickly gets used to this procedure.
Before use, the bougie is immersed in hot water to soften it, moistened with vegetable oil or glycerin for better glide.
The patient sits on a chair, head slightly tilted forward, breathing through the nose.
The doctor presses the fingers of his left hand on the root of the tongue and smoothly inserts the bougie into the esophagus and stomach.
The procedure begins with a bougie, which freely passes into the lumen of the stenosis, then a bougie of a larger diameter is inserted. It is recommended to enter no more than 2-3 bougies per procedure, with a difference of no more than 2 numbers. If the new bougie gauge passes with difficulty, they return to the previous number.
The bougie is left in the esophagus for 2-3 minutes, then smoothly removed.
So, with each procedure, the diameter of the inserted probes is gradually increased, as well as the time they remain in the esophagus (up to 10-15 minutes).
Control fluoroscopy with barium is periodically performed.
Blind bougienage is convenient because the patient (in the absence of neurological and mental disorders) can learn to do it independently, which greatly facilitates planned outpatient bougienage.
If pain, bleeding, or increased body temperature appear, bougienage temporarily stops.
Bougienage on a conductor string
This is the most common and safest way to dilate esophageal strictures. It is used in persons with an eccentrically located, tortuous canal stenosis, pronounced suprastenotic expansion. In such patients, blind insertion of a flexible probe is difficult and may result in perforation of the esophageal walls.
The conductor string is a steel wire with a diameter of about 0.7 mm, which has a spring with a smooth tip at the end.
The essence of the method: a guide string is first passed along the stenosis channel, and then a hollow plastic bougie is passed along it. The rigid metal conductor prevents the flexible bougie from bending or moving to the side.
The string can be entered in several ways:
- Under X-ray control without the use of an endoscope.
- Through the biopsy channel of a fiber endoscope.
- Using a flexible conductor with a diameter of 0.7 mm, previously passed through the endoscope.
- Tied to the end of a previously swallowed thread.
Bougienage on a thread
Bougienage of the esophagus along a thread requires the preliminary application of a gastrostomy tube.
First, a silk thread is inserted into the stomach. It can be entered in several ways:
- By swallowing.
- From above through an endoscope.
- Retrograde through gastrostomy tube.
Usually the thread is swallowed. To do this, a weight (bead) is tied to the end of the thread, the patient swallows it, washes it down with plenty of water. The water pushes the bead with the thread into the stomach, and it is taken out through the gastrostomy tube.
A bougie is tied to the oral end of the thread and the gastric end is pulled. The diameter of the bougies is also gradually increasing. The thread is left in the esophagus for these purposes for a long time; its end is usually secured behind the ear.
Sometimes, according to indications, the bougie is tied to the gastric end of the thread and pulled by the oral end. This is a retrograde (oppositely directed) bougienage.
Bougienage schemes
The frequency and duration of bougienage is individual for each patient.
The scheme of preventive bougienage is approximately as follows: 3 months - 3 times a week, 3 months - 2 times a week, 3 months - 1 time a week, 3 months - 1 time every 2 weeks. The total is a year.
There may be other schemes; they depend on the patient’s condition, the severity of the stenosis, and the doctor’s experience and preferences.
Some doctors prescribe bougienage daily; the probe can remain in the esophagus for up to 2-3 hours; some practice techniques of leaving the bougie in place all night.
The patient remains in the hospital for about 6 months under the supervision of medical staff, then can be discharged for outpatient treatment.
Nutrition for a patient with esophageal stenosis is carried out in accordance with its patency. At first it will be only liquid and semi-liquid food. As the lumen of the esophagus expands, it is possible to add solid food in small portions. Solid food serves as an additional factor for bougienage of the esophagus.
In some cases, nutrition is provided through a gastrostomy tube.
After expanding the lumen to the diameter of the maximum bougie, patients are transferred to maintenance bougie with a maximum bougie once every 2-3 months for 2-3 years.
Complications during bougienage of the esophagus
The following complications are possible:
- Perforation and rupture of the esophagus (up to 11% of cases). Most often it occurs when using metal bougie, during blind probing with flexible probes, when wounded by a metal guide string, during forced bougienage.
- Bleeding. Occurs when the bougie injures the ulcerated walls of the esophagus.
- Exacerbation of esophagitis. At different periods and to varying degrees of severity, this complication occurs in almost all patients. If symptoms of inflammation of the esophagus appear, bougienage should be stopped for a while.
- Restenosis. Against the background of constantly recurrent or sluggish esophagitis, new scar tissue develops, which leads to repeated narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus. Esophageal stents, both absorbable and metal, are sometimes used to prevent restenosis.
- Chronic sclerosing mediastinitis.
Bougienage in children
The most common causes of narrowing of the esophagus in a child are:
- Congenital anomaly.
- Thermal or chemical burns.
Features of bougienage of the esophagus in children.
- Bougienage in children is carried out only with soft elastic probes.
- The minimum diameter of the first bougie is chosen in accordance with the age of the child.
- In children, bougienage is almost painless, so anesthesia is usually not required.
- To secure the child, wrap him in a sheet and hold his head.
- You cannot bougie children every day. Maximum frequency – 3 times a week.
- The child remains in the hospital under the supervision of doctors for the entire course of bougienage.
- Early preventive bougienage in children, started in a timely manner, has an almost 100% effect.
Main conclusions
- Bougienage remains the main method of treating esophageal strictures, especially post-burn ones.
- Bougienage of the esophagus when it narrows is a fairly effective procedure; if started correctly and on time, the effectiveness reaches 90%.
- Bougienage is prescribed to everyone if there is minimal patency of the esophagus and there are no contraindications.
- The procedure itself is quite simple and does not require expensive equipment, but the experience and qualifications of the doctor are very important.
- The bougienage process is quite lengthy, up to a year or more. It is necessary to tune in, since preserving the esophagus is in any case better than its plastic surgery.
Source: https://operaciya.info/abdominal/buzhirovanie-pishhevoda/
Possible complications of bougienage
Burn of the esophagus by gastric juice
A serious complication of this procedure is exacerbation of esophagitis. Symptoms of this phenomenon are pain in the back, behind the sternum. The patient may experience some difficulty in swallowing food and liquids, and may be concerned about minor bleeding from the esophagus.
The most serious complication of bougienage is perforation of the esophagus. The patient experiences a sharp aggravation of the above symptoms. They are accompanied by high temperature. Such complications can be prevented by gently inserting the probe into the esophagus or by placing it using esophagoscopy. Sometimes it may be necessary to reduce the number of the probe so as not to provoke rupture of the epithelial tissue or bleeding.
So, bougienage is a very serious procedure that requires a well-trained doctor. The patient should always remember that it can cause serious complications
At the same time, if it is carried out carefully, it will be possible to achieve complete disappearance of strictures. Naturally, this requires time and patience from the patient, since such treatment is associated with some restrictions and unpleasant sensations
Stenosis or stricture is a pathological condition in which the wall of the esophagus narrows, interfering with natural physiological processes (including swallowing). The condition requires medical intervention. The patient is prescribed bougienage of the esophagus, during which the doctor gradually expands the tubular organ using a probe.
Contraindications
General restrictions on the procedure:
- mediastinitis, accompanied by inflammation of the tissue in the mediastinum;
- esophagitis and periesophagitis in the acute phase - inflammation of the digestive tract or the tissue around it;
- somatic disorders of internal organs in an acute chronic form;
- systemic diseases of the hematopoietic apparatus with a decrease in coagulability;
- oncology of any localization;
- infection of the body, accompanied by intoxication, fever;
- severe mental disorder with hallucinations, speech and motor disorders.
Bougienage may be delayed for the time required to treat the identified pathology that has become a contraindication. Dilatation of the esophagus after surgery is performed after the wound has healed and there is minimal risk of suture dehiscence. Contraindications from the gastrointestinal tract are represented by the presence of:
- diverticulum;
- perforations;
- complete scarring of strictures;
- fistulas.
When is urethral dilation used?
Bougienage can be diagnostic and therapeutic.
Diagnostic bougienage is carried out for the purpose of:
- Determining the location of the narrowing and the approximate size of the lumen of the narrowing.
- Determining the location of the stone in the urethra.
- Calibration of urological instruments before any endourethral examinations or operations.
stricture (narrowing) of the urethra
The causes of narrowing of the urethra can be:
- Consequences of pelvic trauma.
- Consequences of injury to the urethra itself (after medical procedures, studies, after the introduction of foreign bodies into the urethra).
- Cicatricial narrowing of the urethra after inflammatory diseases.
- With narrowing of the urethra, the main symptom is difficulty urinating. Urine has difficulty passing through the narrowed area, the bladder is not completely emptied and is overstretched. Stretched bladder walls contract worse, which only worsens urine output.
Strictures can be:
- Congenital.
- Acquired.
- Short (up to 2 cm).
- Long.
- Primary.
- Secondary (developed after primary bougienage).
This procedure is quite simple, does not require general anesthesia or special preparation, and can be performed on an outpatient basis.
Types of bougienage
- Preventive bougienage. It is carried out to prevent the development of stenosis when the scar is just beginning to form. It is advisable to start it from the 7th to the 10th (maximum 12th) day from the burn.
- Therapeutic bougienage. It is carried out when stenosis has already formed (two months after the injury).
It is not recommended to start bougienage after the 12th day after the burn, since during this period there is a massive rejection of necrotic tissue and the formation of ulcers, because of this there is a high probability of perforation of the esophagus. If symptoms of esophageal obstruction develop during this period, this is a direct indication for gastrostomy.
Bougienage in children
Since the procedure is invasive, bougienage of the esophagus in children requires compliance with certain measures.
Among the main features it is worth highlighting:
- For the operation, only soft devices with a rounded tip are used. This eliminates mechanical damage to the organ mucosa.
- Based on the child’s age, the minimum bougie number is selected. The younger the children, the lower the number of bougies they use.
- If the child is very small, during the procedure he will need to be wrapped in a sheet, and the health worker will need to hold his head. This eliminates possible sudden turns of the head, thereby eliminating the possibility of injury to the esophagus.
- A single device insertion time should not exceed 30 minutes.
- It is not recommended to bougienage the esophagus in children every day. The acceptable norm would be 3 times during the week.
- The course is determined individually for each child, but on average it lasts up to 2 months.
- During treatment, expansion of the lumen of the esophagus, children must constantly be in the hospital, where doctors monitor them. This eliminates the possibility of negative consequences and complications that may occur after the procedure. Even when similar symptoms appear, the symptoms quickly stop.
- During the procedure, antibiotics should be used to prevent secondary infection and complications from occurring.
The described features are generally accepted, but some features of the procedure are determined individually for each child.
These include the choice of bougie number, the time of insertion into the esophagus, and the course of treatment.
Description
Bougienage of the esophagus is a complex medical technique used for the prevention, treatment, and diagnosis of pathological narrowing of the lumen of the stenotic alimentary tract. To carry out the procedure, special instruments are used - a bougie in the form of a probe, equipped with optics and a lighting device or without auxiliary equipment. The shape of the expander is cone-shaped, that is, gradually expanding towards the top.
With the gradual introduction of a special device into the lumen of the alimentary tract, a slow expansion of the narrowed areas occurs. Different types of bougies are used: flexible or rigid, which vary in size. The choice of instrument depends on the nature of the stenosis.
Before the procedure, the amount of narrowing of the esophagus is determined by radiopaque or esophagogastroduodenoscopic examination . The following bougienage methods are used:
- Blind expansion. Then the size number of the probe is selected. Two probes are used in one procedure lasting 30 minutes. The manipulation begins with a smaller number, then a larger one is taken. When repeating a bougienage session, use the last bougie, and then a new one - the next one by number. The method has a high risk of injury, so it is rarely used.
- Endoscopic bougienage. Used if there are eccentric or stricture narrowings, “pockets” or other dilations of the esophagus in front of the stenotic area. With the help of an optical device, it becomes possible to bypass difficult areas without injuring the digestive tract.
- X-ray bougienage. To carry out the manipulation, X-ray-opaque bougies with a steel conductor string are used. At the first stage, a string is inserted. The process is controlled by x-rays. Then the bougie attached to the string is advanced. The procedure is dangerous due to the risk of perforation of the esophagus and exposure of the patient and the doctor to radiation.
- Bougienage by thread. The method requires preparation. 7 days before the procedure, the patient is given a gastroma - an opening in the stomach through the anterior abdominal wall. Bougienage of the esophagus is based on the patient swallowing a nylon thread with a bead at the end, drinking 1 liter of water, which pushes the bougie through the gastroma. But complications are possible that accompany the creation of a gastrostomy, unwanted deformation of the stomach and digestive dysfunction.
- Bougienage along the thread. The patient swallows a thread with a bead at the end, which is firmly fixed in the gastrointestinal tract. A probe is inserted along the thread. The risk of this method is the high possibility of bougie deflection due to insufficient rigidity of the thread used as a conductor.
Complications
A frequent negative consequence is exacerbation of background inflammation, for example, esophagitis. This is accompanied by back pain behind the thoracic region, difficulty swallowing food and liquids, and spotting on the tube.
Another equally serious consequence is perforation or perforation of the esophagus. The process is accompanied by an intensification of the above symptoms with an increase in temperature and increasing leukocytosis. Perforation can occur above the stricture or in the narrowing itself, which is especially important for curved stenoses. As a result, saliva with infiltration of the esophagus will enter the nearby tissue through the hole, which will cause the development of mediastinitis, pleural empyema. To prevent complications from occurring, you should:
carefully insert the bougie device; if pain occurs, you should take a probe of a smaller diameter; if simple bougienage is unsuccessful, it is recommended to use a method with vision control (using an esophagoscope).
Stenosis or stricture is a pathological condition in which the wall of the esophagus narrows, interfering with natural physiological processes (including swallowing). The condition requires medical intervention. The patient is prescribed bougienage of the esophagus, during which the doctor gradually expands the tubular organ using a probe.
Stricture of the esophagus, narrowing of the esophagus, burn of the esophagus, stomach, bougienage of the esophagus
Definition, etiology. A burn stricture of the esophagus is a scar narrowing of the esophagus, formed as a result of accidental or intentional ingestion of thermal (hot water, etc.) or chemical (acid, alkali, heavy metal salts, solvents, etc.) aggressive substances through the mouth. The department provides specialized care to patients with formed scar strictures of the esophagus, after 1 month. and more after receiving a burn.
Classification. A stricture of the esophagus can be complete (no lumen) or incomplete, short (up to 5.0 cm long) or extended. The latter can spread to the entire esophagus - total strictures. Often, damage to the esophagus is combined with strictures of the pharynx and stomach.
The symptoms of cicatricial stricture depend on the severity of the esophageal lesion. The main symptom is dysphagia, the degree of which most often correlates with the length and diameter of the narrowed portion of the esophagus. Impaired patency of the esophagus is accompanied by salivation, regurgitation, nausea and esophageal vomiting. Nutritional deficiency causes progressive weight loss in patients, quickly leading them to exhaustion, which can reach an extreme degree - cachexia.
Diagnostics. X-ray of the esophagus reveals uneven narrowing of the esophagus up to its complete obliteration in combination with a disturbance in the relief of the mucous membrane, rigidity of the walls and expansion of the lumen of the esophagus above the narrowing of the esophagus. In addition, this study determines the boundaries of the burn lesion and its extent. X-ray can detect cicatricial deformation of the pharynx and stomach, esophageal-respiratory fistulas. Esophagoscopy allows you to identify changes in the mucous membrane of the esophagus and exclude its cancerous transformation. If possible, examine the stomach and duodenum in order to diagnose a combined burn lesion and concomitant diseases.
Treatment. There are two main methods of treating burn strictures of the esophagus - plastic surgery and bougienage of the esophagus.
Main conclusions
- Bougienage remains the main method of treating esophageal strictures, especially post-burn ones.
- Bougienage of the esophagus when it narrows is a fairly effective procedure; if started correctly and on time, the effectiveness reaches 90%.
- Bougienage is prescribed to everyone if there is minimal patency of the esophagus and there are no contraindications.
- The procedure itself is quite simple and does not require expensive equipment, but the experience and qualifications of the doctor are very important.
- The bougienage process is quite lengthy, up to a year or more. It is necessary to tune in, since preserving the esophagus is in any case better than its plastic surgery.
Types of bougies
Let's talk about the tools for the procedure, because they often inspire fear in those who see them for the first time. A bougie is a medical instrument that is used to examine or, in some cases, treat the urethral canal. There are different types of tools that differ in shape and technical characteristics. Bougies are made from metal or synthetic materials. The first ones are used if it is necessary to remove constrictions. Synthetic bougies are used to treat narrowing of the urethra and diagnose pathology of the urethra.
Bougies also vary in shape. Available with smooth surfaces, additional extensions at the end of the tool or in any part of it. Short and long bougies are necessary in order to carry out the procedure at different depths. Bougienage of the urethra in women is most often performed with short bougies. There are straight and curved instruments. Straight ones are necessary for the diagnosis and treatment of intraurethral constrictions in women, and curved ones are necessary for the treatment and diagnosis of cervical canal obstruction in males.
Each type of tool has certain advantages and disadvantages. Experts believe that synthetic bougies are much more comfortable and safe, especially when performing the procedure on men. Such instruments are elastic and do not lead to injury to the urethra, which can happen when using metal bougies (in case of sudden insertion of the instrument).
Preparing for urethral dilation
To clarify the choice of treatment method for urethral stricture, it is necessary to have the best possible understanding of the location and extent of the narrowed area. For this, the following examination methods are used:
- Retrograde urethrography (injection of contrast into the urethra followed by radiography).
- Ultrasonography.
- MSCT.
Before bougienage, general blood tests, urine tests, blood sugar tests, bacterial culture of urine or urethral discharge are performed.
Bougienage is not shown:
- In inflammatory processes in the genitourinary tract. The manipulation is carried out after the course of treatment.
- For fresh injuries of the urethra.
- For narrowings more than 2 cm in length.
- With phimosis.
- If a tumor is suspected.
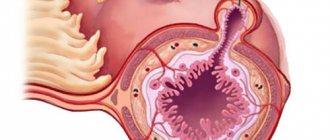
What is cervical atresia
The term atresia or stenosis of the cervical canal refers to an anomaly in the structure of the cervix, consisting of narrowing or complete obstruction of the cervical canal. In the medical literature, the term means complete fusion of the walls of a hollow organ. Atresia can be partial or absolute. If the canal is not passable along its entire length, its complete fusion is diagnosed. If pathology is observed in the area of the external or internal pharynx, partial stenosis is diagnosed.
The main task of the gynecologist is to distinguish stenosis and atresia of the cervical canal from stricture. With stricture, cervical obstruction occurs due to scar deformities. The disease is detected based on the patient’s complaints and simple diagnostic procedures. The diagnosis of complete stenosis is determined when it is impossible to enter the uterine cavity with a probe with a diameter of 12 mm. The main danger of such a deformation is that it may have an oncological basis. To exclude the possibility of developing cancer, the patient undergoes an endometrial biopsy.
If the woman does not have atypical cells or negative symptoms, surgery is performed. It is worth noting that stenosis detected during menopause cannot be treated; patency of the cervical canal is restored only to women of childbearing age. In some cases, pelvic ultrasound and MRI are performed to diagnose the disease. It should be taken into account that atresia may be accompanied by structural disorders of the genitourinary system. To clarify the diagnosis, urethrocystoscopy is performed.
In medical practice, a distinction is made between acquired and congenital atresia. With congenital pathology, fusion of the cervical canal occurs at the stage of embryonic development. The reasons that provoke such deformation are as follows:
- infection of a pregnant woman with toxoplasmosis, chlamydia or syphilis;
- taking certain medications in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- exposure of a woman to ionizing radiation.
With congenital fusion, the symptoms do not bother the woman until puberty, or more precisely, until the first menstruation. Acquired atresia appears due to age-related changes or due to injuries to the cervical canal. Normally, the menopause period is accompanied by a significant decrease in the size of the uterus and cervix, a change in the structure of all tissues and organs that provide reproductive function. Such changes occur against the background of the cessation of estrogen secretion and cell insensitivity to follicle-stimulating hormone. Against the background of a decrease in the intensity of production, thinning of the epithelium occurs, resulting in a partial narrowing of the lumen of the canal. Over time, the stenosis progresses and complete fusion occurs.
The main causes of atresia that manifests itself during reproductive age may be the following:
- transferred electrocoagulation of the canal;
- chemical treatment of the cervix;
- violation of curettage technology during abortion;
- complicated course of endometritis or endocervicitis;
- cancer of the cervix or uterine body;
- consequences of past infections (tuberculosis, gonorrhea, chlamydia).
When atresia of the cervical canal appears in a woman, menstrual bleeding stops or its intensity significantly decreases. Such a symptom should be a cause for concern; the girl should urgently consult a doctor. The main danger is that menstrual blood accumulates in the uterine cavity and can cause infection.
The video and photos in this article will help the reader understand exactly how the operation occurs.
What is bougienage of the esophagus, who is it prescribed for and how it is performed
Stenosis or stricture is a pathological condition in which the wall of the esophagus narrows, interfering with natural physiological processes (including swallowing). The condition requires medical intervention. The patient is prescribed bougienage of the esophagus, during which the doctor gradually expands the tubular organ using a probe.
Indications for bougienage of the esophagus
The procedure is indicated for people who have narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus as a result of injury:
- chemical burn caused by ingestion of alkaline or acidic compounds (the formed coarse fibrous scar blocks the food tract);
- thermal burn (scar formation due to ingestion of hot food and drink);
- mechanical damage (penetrating type injuries);
- the presence in the esophagus of a foreign body attached to the walls of the organ;
- infectious infections of the esophagus (with the formation of granuloma);
- streptococcal, staphylococcal damage and damage to intestinal microbes (complicated by infiltrate sediment);
- peptic ulcer (acidic acid from the stomach rises into the esophagus, causing scarring);
- chronic esophagitis in acute form (inflammation);
- tumors blocking or compressing the esophagus.
The condition of stenosis is also congenital. Partial or complete infection of the esophagus in children also requires a bougienage procedure.
Types of bougienage
Before the procedure, the doctor identifies the degree of narrowing of the esophagus using radiopaque or esophagogastroduodenoscopic analysis techniques. Based on the data obtained, the bougienage method is selected.
- Blind expansion. The method is used extremely rarely, as it can cause damage to the organ cavity. The probe is inserted in two stages - first a small bougie is used, and then a large bougie.
- Endoscopic extension. The method is indicated in the presence of eccentric and stricture narrowings, in the presence of extensions in front of the stenotic part of the esophagus. Optical equipment allows you to carefully bypass damaged areas.
- X-ray expansion. To carry out the procedure, a bougie with a steel conductor (thin string) is used. First, the guidewire is inserted, and then the bougie attached to it is advanced. The progress of the operation is monitored using x-rays. The method is quite dangerous due to the threat of radiation and perforation of the esophagus.
- Extension by thread. The method requires preliminary preparation. A week before the procedure, the patient is given a gastroma (access to the stomach through the outer anterior part of the abdominal region). After this, the patient swallows a nylon thread with a medical bead at the end and drinks at least a liter of liquid to push the probe through the gastroma. The method is associated with risks (deformation of stomach tissue is possible).
- Expansion along the thread. The patient swallows a nylon thread with a medical bead attached. Subsequently, the thread creates a trajectory for the movement of the probe.
Bougienage can be therapeutic or preventive. Preventive sessions are carried out when the scar is just beginning to form (7–10 days after injury).
Technique
Before bougienage, an optical probe is inserted into the esophagus to identify the features of the narrowing site and its localization.
Then the doctor individually selects the dilator, treats it with Vaseline for easy sliding and inserts it into the esophagus (the insertion force should be minimal).
ATTENTION! Each bougie has a number corresponding to the size. The largest is expander number 15
The tool has a cone-shaped shape. Sometimes it is performed in the form of a probe equipped with optical and light elements.
The patient's condition is monitored by daily temperature measurement. This helps to prevent complications in time. The reason for stopping bougienage sessions is a temperature above 37.5C.
Complications after surgery
The risk of complications is minimal and adverse effects after treatment are rare, but they must be taken into account:
- violation of the integrity of the esophageal wall (perforation);
- damage to the mucous membrane;
- damage to small vessels and subsequent bleeding;
- infection of the esophagus with the concomitant development of esophagitis and periesophagitis;
- tract commissure ruptures;
- restenosis
Complications are also possible after an operation to form a gastroma (the operation accompanies one of the bougienage methods).
Relapse refers to complications only indirectly. But even with a positive outcome of treatment, over time the lumen of the esophagus may decrease again.
Complications after surgery
Bougienage of the esophagus is a simple and low-risk operation. The risk of complications is minimal and adverse effects after treatment are rare, but they must be taken into account:
- violation of the integrity of the esophageal wall (perforation);
- damage to the mucous membrane;
- damage to small vessels and subsequent bleeding;
- infection of the esophagus with the concomitant development of esophagitis and periesophagitis;
- tract commissure ruptures;
- restenosis
Complications are also possible after an operation to form a gastroma (the operation accompanies one of the bougienage methods).
Relapse refers to complications only indirectly. But even with a positive outcome of treatment, over time the lumen of the esophagus may decrease again.
Bougienage methods
The bougienage method is a diagnostic and treatment procedure that helps expand the lumen of the esophagus. It is sometimes the only available method of treating narrowing (or otherwise stenosis, stricture). The effectiveness of bougienage of the esophagus has been experimentally proven, so this method is used quite often for stenosis.
The bougie has a cone-shaped shape and is usually equipped with a light source and an optical device, but can be used without additional devices. The shape of the instrument is determined by the need to gradually expand the lumen of the organ during insertion. The procedure takes about half an hour, and two sizes of probe are used. A small instrument is used first, followed by a larger probe.
During the preparation, the patient is explained why instruments come in different sizes and types of rigidity and why it is necessary to select an instrument in accordance with the severity of the disease and the severity of symptoms.
The following bougienage methods are used:
- Blind expansion. This method is rarely used due to the high probability of injury to the walls of the organ.
- Endoscopic dilation method. The method is used for complex structural narrowings, as well as if the patient has depressions in the wall of the organ. With the help of optical equipment, a specialist can confidently bypass the affected areas without the risk of injuring the esophageal canal.
- X-ray method. In this case, contrast X-ray instruments equipped with a steel wire are used. First, the string is inserted, and then the process occurs under X-ray control. The bougie is propelled by attaching it to a steel string. There is a risk of perforation of the esophagus.
- Bougienage is retrograde for the thread. This method involves preliminary preparation of the body for the procedure. 7 days before the procedure, the patient should have a gastroma, which is a small hole in the stomach cavity and anterior abdominal wall. After this, the patient is asked to swallow a thread made of durable nylon with a bead at the end, and then drink at least a liter of water to push the probe out of the gastroma. The method is also fraught with possible complications, especially at the stage of creating the hole. In addition, the retrograde bougienage method can be complicated by accidental deformation of the stomach and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Bougienage along the thread. Before the examination, the patient must swallow a nylon thread with a bead fixed at the end. A probe is inserted along the thread, trying not to deviate from the given trajectory.
Almost 40% of patients with scarring strictures require surgical treatment, in which case there is a possibility of tissue rupture. In some cases, the method does not produce results and after manipulation the lumen may narrow again.
Basic techniques
The bougienage procedure is a medical procedure for treatment or diagnostics, which allows the doctor to expand the narrowed esophagus without surgical treatment.
The effectiveness of manipulation has been proven over the years and through many experimental studies, due to which the technique is widely used.
Before performing the procedure, doctors measure the lumen of the esophagus, which makes it possible to assess the degree of stenosis.
For this purpose, radiography and endoscopy are used. The procedure is carried out using a bougie, which comes in different types, but generally resembles a regular probe.
A bougie is a cone-shaped device with a tip that contains optics and light, but may not require additional equipment.
The shape of the bougie is such that it allows you to gradually increase the lumen of the organ, without the use of an auxiliary instrument.
One session lasts about 30 minutes, during which 2 types of bougie are used. Initially, a small probe is inserted, after which thicker equipment is used.
There are several main methods; they are selected individually for each patient.
Blind bougienage
Before performing this method, a diagnosis must be made using an endoscope.
The procedure itself is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach every other day. The first manipulations are carried out using an anesthetic.
For this purpose, local anesthesia is used, which is used to treat the pharynx. Lidocaine-based sprays or gels may be used.
After a few manipulations, pain medication will not be required, as patients begin to get used to the technique.
Before inserting the bougie, it is immersed in hot water to make the probe softer, after which everything is lubricated with oil or glycerin for easy insertion.
Sitting on a chair, the patient's head is tilted slightly forward, and during the operation breathing is carried out through the nose.
The doctor presses on the tongue and slowly inserts the bougie, which passes through the esophagus and into the stomach.
The beginning is carried out using a bougie, which can easily pass through the lumen of the narrowed esophagus, after which a larger probe is used.
At a time, the doctor can use up to 3 bougies of different types, but no more than 2 numbers.
If choosing a new probe is difficult, then you need to return to the old number. After inserting the device, leave it in for a couple of minutes and slowly remove it.
Each time the lumen begins to increase, and the doctor gradually changes the size of the probe, using a larger diameter. The time for keeping the probe in the esophagus also changes, maximum – 15 minutes.
From time to time, between sessions, the doctor needs to take x-rays using contrast agents.
The blind technique is convenient, because the patient will be able to independently learn how to perform the procedure if there are no contraindications or mental disorders, which can significantly facilitate the planned procedure in a hospital setting.
If there is blood, pain or other disturbances, the procedure is stopped and not carried out for some time.
Bougienage on a conductor string
This one is used most often and is one of the safest. It is recommended to use the method for people with an eccentrically located, tortuous lumen, as well as obvious suprastenotic expansion.
For such people, using a blind method with flexible bougies is almost impossible, and there is also a risk of organ perforation.
The conductor string is a small steel wire, the thickness of which is up to 0.7 mm, and at the end there is a smooth tip.
The essence of the manipulation is that initially a string is inserted into the esophagus, and a plastic bougie is launched along it.
Due to the string, the bougie will not bend; it follows a clear direction. The string is inserted using different methods:
- Without the use of an endoscope using x-ray control.
- Through a fiber endoscope.
Bougienage by thread
To carry out this manipulation, the use of a gastrostomy tube is initially necessary.
First of all, a silk thread is inserted into the esophagus and stomach:
- Through normal ingestion.
- Through an endoscope.
- Retrograde through gastrostomy tube. This technique requires preparatory steps. The patient is given a gastrostomy a week before, and after the thread gets inside, he needs to drink 1 liter of water to push the tube out. The method can cause complications, especially during the period of the hole. In addition, there may be disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract and deformation of the stomach. Due to the described complications, the method is almost never used.
Typically, the thread is swallowed, so there is a small weight at the end, namely a bead. During swallowing, the patient drinks plenty of water, which allows the load to travel all the way and go straight into the stomach.
After surgery, it is removed through a gastrostomy tube. At the end that remains in the mouth, a bougie is put on, and through the end in the stomach it is pulled.
The thickness of the bougie gradually increases during such manipulation, and the thread itself can remain for a long time; as a rule, it is attached behind the person’s ear so that it does not dangle and does not interfere with everyday activities.
There are other ways to carry out the operation. Among them, endoscopic bougienage can be distinguished.
The method is used for complicated narrowing of the esophagus or if the patient has depressions in the walls.
Using a device with optics, doctors can pass through diseased parts without damaging the lumen of the esophagus itself.
Types of tools
Suitable for bougienage:
- probes with olive;
- simple conical;
- hollow radiopaque.
Probes can be made of plastic or metal. Radiopaque dilators made of polyvinyl chloride are more often used. They contain powdered bismuth oxide, which absorbs X-rays. X-ray contrast bougies are supplied as a set of 17 numbers (No. 8-40), of which:
- No. 8, 10, 12 are solid;
- No. 14-40 - probes with a longitudinal channel of 1-2 mm in the center.
The probes are equipped with metal guide strings equipped with a spring tip. The advantage of probes is the ability to change the direction of movement when approaching a stricture.
Bougienage of the esophagus: what is it, indications, implementation and complications
Narrowing of the esophagus is a dangerous condition that occurs for various reasons and requires medical attention.
If the narrowing is insignificant, then an artificial dilation of the esophagus is prescribed using bougienage or dilatation. Despite the fact that medicine is offering more and more new ways to treat gastrointestinal diseases, not every patient knows what bougienage of the esophagus is. This is a method based on the introduction of a special hollow instrument into the organ, which does not allow it to narrow. Bougienage is used for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes and has already proven its high effectiveness.
Description
Bougienage of the esophagus is a complex medical technique used for the prevention, treatment, and diagnosis of pathological narrowing of the lumen of the stenotic alimentary tract.
To carry out the procedure, special instruments are used - a bougie in the form of a probe, equipped with optics and a lighting device or without auxiliary equipment.
The shape of the expander is cone-shaped, that is, gradually expanding towards the top.
With the gradual introduction of a special device into the lumen of the alimentary tract, a slow expansion of the narrowed areas occurs. Different types of bougies are used: flexible or rigid, which vary in size. The choice of instrument depends on the nature of the stenosis.
Before the procedure, the amount of narrowing of the esophagus is determined by radiopaque or esophagogastroduodenoscopic examination . The following bougienage methods are used:
- Blind expansion. Then the size number of the probe is selected. Two probes are used in one procedure lasting 30 minutes. The manipulation begins with a smaller number, then a larger one is taken. When repeating a bougienage session, use the last bougie, and then a new one - the next one by number. The method has a high risk of injury, so it is rarely used.
- Endoscopic bougienage. Used if there are eccentric or stricture narrowings, “pockets” or other dilations of the esophagus in front of the stenotic area. With the help of an optical device, it becomes possible to bypass difficult areas without injuring the digestive tract.
- X-ray bougienage. To carry out the manipulation, X-ray-opaque bougies with a steel conductor string are used. At the first stage, a string is inserted. The process is controlled by x-rays. Then the bougie attached to the string is advanced. The procedure is dangerous due to the risk of perforation of the esophagus and exposure of the patient and the doctor to radiation.
- Bougienage by thread. The method requires preparation. 7 days before the procedure, the patient is given a gastroma - an opening in the stomach through the anterior abdominal wall. Bougienage of the esophagus is based on the patient swallowing a nylon thread with a bead at the end, drinking 1 liter of water, which pushes the bougie through the gastroma. But complications are possible that accompany the creation of a gastrostomy, unwanted deformation of the stomach and digestive dysfunction.
- Bougienage along the thread. The patient swallows a thread with a bead at the end, which is firmly fixed in the gastrointestinal tract. A probe is inserted along the thread. The risk of this method is the high possibility of bougie deflection due to insufficient rigidity of the thread used as a conductor.
Bougienage of the esophagus - what is it?
Probing or bougienage of the esophagus is a rather complicated medical procedure that is used to detect, prevent and treat pathological narrowing of the alimentary tract. During the manipulation, a separate instrument is used - a bougie (probe), equipped with optics and a lighting device or without them. It is endowed with a cone-shaped shape, gradually expanding upward.
How is bougienage of the esophagus performed? As the device is slowly inserted into the tract, the walled areas gradually expand. The procedure uses different types of bougies - elastic and hard.
It is also possible to vary their sizes. The selection of instrumentation will be determined by the nature of the stricture.
That is why, before bougienage, the degree of narrowing of the esophagus is recorded using a radiopaque technique.
Indications
Bougienage of the esophagus is indicated for narrowing of its lumen, which occurs when damaged. The technique is used if:
- chemical exposure with burns due to ingestion of acids or alkalis, as a result of which a coarse fibrous scar was formed at the site of damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, leading to narrowing;
- thermal effects with burns after ingesting very hot drinks and food;
- mechanical injury caused by penetrating wounds or foreign body entrapment;
- infection of the esophagus, provoked by specific diseases, for example, tuberculosis, syphilis, as a result of which a narrowing in the form of a granuloma is formed;
- infection with streptococcal, staphylococcal and intestinal microbes, as a result of whose vital activity an infiltrate is formed, narrowing the esophagus;
- damage to a peptic ulcer, caused by the backflow of acidic contents from the stomach into the esophagus, resulting in the appearance of a coarse fibrous scar;
- exacerbation of chronic esophagitis with aggressive inflammation due to constant exposure to irritating factors.
And also when diagnosing:
- tumors, the growth of which compresses the esophagus;
- congenital stenosis (atresia) with partial or complete fusion of the esophagus.
conclusions
Bougienage of the esophagus is the main method of treating its strictures, especially after severe burns. The effectiveness of the procedure reaches 90% if it is carried out correctly and started on time. It lasts a long time - up to a year.
But in many cases it helps to avoid expensive and even more complex surgery for esophagoplasty. Therefore, if there are no contraindications and there is at least a small gap in the esophagus, only bougienage will help.
It is very important to find a competent, experienced specialist to carry out this manipulation.
We recommend: The most effective drugs for the treatment of reflux esophagitis
Methodology
The procedure is considered complex and lengthy. Bougienage is carried out gradually in several sessions. The course of treatment is selected depending on the severity of stenosis of the alimentary tract. The duration of one session varies from 10 to 60 minutes.
Based on the results of a preliminary examination of the esophagus, the number of the dilator that will be used first is determined. As the manipulations progress, the diameter of the probe, as well as the time of its insertion, gradually increases. In the last sessions, a “plateau” is established, which involves the introduction of a large-diameter bougie for 30-60 minutes. Rules for introducing an expander:
- Bougienage begins after esophagoscopy. This method of optical examination of the esophagus allows you to find a stricture, determine its type and degree.
- Before insertion, the dilator is lubricated with Vaseline, which will facilitate swallowing and passage.
- The first sessions involve installing a dilator in the esophagus for 2 minutes. Subsequently, the time increases to 15-30 minutes.
- Wider bougies are inserted only after lightly inserting smaller probes.
- The maximum possible number is entered daily for 30-60 minutes for 2-3 weeks.
- The effectiveness of bougienage is determined by the ease of passage of the dilator No. 15 into the esophagus and back.
- Adverse effects are monitored by daily temperature measurements. The procedure stops when it rises to 37.5°C.
How is bougienage carried out?
Expansion of the lumen of the esophagus is carried out using a set of several probes - bougies of various diameters. They are introduced one by one, gradually increasing the diameter of the bougie; the difference between their sizes is usually 0.3 mm (Charrière scale).
A bougie is a thin metal or plastic tube 75-80 cm long, conical in shape or with replaceable tips. In addition to them, the set includes cleaning accessories. Modern probes are made of polyvinyl chloride with inclusions of a contrast agent to facilitate the fluoroscopy process.
The bougienage procedure is complex and lengthy, takes several weeks, even months, and requires special care to avoid complications.
Bougienage of the esophagus is preceded by a preparatory process, which consists of treating burns or mechanical damage to the esophagus. In case of a chemical burn, detoxification, pain relief, antibiotic therapy are carried out, and if necessary, hemodialysis.
If the patient has retained the ability to swallow, then he eats liquid food and drinks water. If it is impossible to swallow due to complete obstruction of the esophagus, then a gastrostomy is placed - a special hole in the anterior abdominal wall and stomach with a tube removed for feeding through it.
There are two types of bougienage:
- early bougienage - to prevent the formation of scars with subsequent stenosis, carried out on the 7th day after the burn or on the 10th day after surgery;
- late bougienage - 2-3 months after a chemical burn, when there is already a stricture due to the scar.
After surgery, you need to make sure that during the manipulation there is no risk of sutures coming apart.
There are several methods for performing bougienage, depending on the patient’s condition and endoscopy results:
- Blind - to a patient standing or sitting on a chair, the first bougie is introduced through the mouth without anesthesia or in the first days with lidocaine spraying the pharynx, lubricated with glycerin or oil for ease of sliding, the size of which is selected based on the results of an endoscopic examination and which fits freely into the lumen. After 2-3 minutes, it is removed and a probe of a larger diameter is inserted. So use 2-3 sizes at a time. If the larger diameter is not suitable, return to the previous one. The procedure is carried out every other day for a month or longer. Next time they start with the size of the bougie that they finished with the day before. This method is rarely used and is dangerous due to complications. Although it is convenient in that some patients can eventually carry out the bougienage procedure on their own.
- Using a conductor in the form of a string is the most common and safe method for expanding the lumen of the esophagus, especially in cases of complex narrowing. Its essence lies in the fact that first a rigid metal string with a diameter of 0.7 mm with a spring at the end is inserted into the esophagus, and along it, as if along a guide, is a flexible hollow bougie. Due to the rigidity of the string, it does not deviate to the side. The string can be inserted in different ways - using an endoscope channel, tied to a swallowed thread, under X-ray control.
- Along the thread, a gastrostomy tube is first applied. Then the patient swallows it or inserts it through the gastrostomy tube with a weight on one side. A bougie is tied to the second end of the thread. If the thread is removed from the hole in the abdominal wall, then it is pulled, and the bougie moves along the esophagus. They can also pull in a retrograde (reverse) direction. The thread remains in the esophagus for a long time, depending on the duration of the bougienage process.
Doctors are developing various manipulation schemes - from 3 times a week at the beginning, reducing the number to once every two weeks. In total, this process can take a year. In this case, the duration of stay of the probe in the esophagus gradually increases to 60 minutes. Bougienage is considered complete when a probe of maximum size passes freely into the lumen.
Schemes depend on the doctor’s decision, examination results and the degree of damage to the esophagus. For the first six months, it is recommended to carry out bougienage in a hospital, then on an outpatient basis, under the supervision of a doctor.
Types of tools
Suitable for bougienage:
- probes with olive;
- simple conical;
- hollow radiopaque.
Probes can be made of plastic or metal. Radiopaque dilators made of polyvinyl chloride are more often used. They contain powdered bismuth oxide, which absorbs X-rays. X-ray contrast bougies are supplied as a set of 17 numbers (No. 8-40), of which:
- No. 8, 10, 12 are solid;
- No. 14-40 - probes with a longitudinal channel of 1-2 mm in the center.
The probes are equipped with metal guide strings equipped with a spring tip. The advantage of probes is the ability to change the direction of movement when approaching a stricture.
Bougienage for prevention purposes
Manipulation is used to prevent the formation of strictures due to mechanical and chemical damage to the esophagus. Rules:
- before using the technique, the patient undergoes an x-ray and endoscopic examination;
- the first procedure is carried out in the subacute period, that is, from the 7th day after injury. If the manipulation is caused by an operation on the esophagus, the first procedure is carried out on the 10th day;
- frequency - up to 3 times weekly;
- duration 45-60 days.
Bougienage of the ureter. How does ureteroplasty differ from other operations?
In addition to ureteroplasty, other operations are used that also solve problems of the functionality of the urinary system, but differ in technical terms.
One type of such intervention is bougienage, which is used for pathological narrowing of the urethra. This disorder can occur against the background of autoimmune reactions, the activity of pathogenic microorganisms and due to hypothermia.
Bougie is the physical expansion of the urethra using a bougie - a special catheter with a thickening of different shapes at the end.
This procedure can be performed not only to expand the canal, but also as a diagnostic procedure, during which a specialist can identify the degree of fusion of the walls of the urinary canal and determine the presence of various formations and scars on its walls.
Another type of surgical intervention is reimplantation, which is done for a pathology called “megaureter”.
Source: https://bugmk.ru/diagnostika/buzhirovanie-pishchevoda-u-detej.html
Indications for testing
The bougienage method is used for narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus, which can be congenital, or also occurs due to a burn or injury.
The method is used if:
- exacerbation of the chronic form of esophagitis, provoked by aggressive influence;
- chemical burn of the gastrointestinal mucosa caused by ingestion of irritating substances and leading to the formation of keloid tissue and narrowing of the esophageal tube;
- mechanical trauma to the esophagus caused by ingestion of a foreign body or penetrating injury;
- thermal burn of the inner lining of the esophagus caused by the consumption of scalding drinks and food;
- infection of the organ lining with specific infections followed by narrowing of the lumen in the form of a granuloma;
- infection of the esophagus by nonspecific microorganisms with the formation of an infiltrate that narrows the lumen of the organ;
- ulcerative lesion of the esophagus, the cause of which is the reflux of irritating stomach contents with the further formation of a coarse fibrous scar.
In addition, endoscopic bougienage is used to diagnose neoplasms that progress over time and cause compression of the esophageal tissue, as well as for atresia with complete or partial closure of the organ lumen.
Indications
Bougienage of the esophagus is indicated for narrowing of its lumen, which occurs when damaged. The technique is used if:
- chemical exposure with burns due to ingestion of acids or alkalis, as a result of which a coarse fibrous scar was formed at the site of damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, leading to narrowing;
- thermal effects with burns after ingesting very hot drinks and food;
- mechanical injury caused by penetrating wounds or foreign body entrapment;
- infection of the esophagus, provoked by specific diseases, for example, tuberculosis, syphilis, as a result of which a narrowing in the form of a granuloma is formed;
- infection with streptococcal, staphylococcal and intestinal microbes, as a result of whose vital activity an infiltrate is formed, narrowing the esophagus;
- damage to a peptic ulcer, caused by the backflow of acidic contents from the stomach into the esophagus, resulting in the appearance of a coarse fibrous scar;
- exacerbation of chronic esophagitis with aggressive inflammation due to constant exposure to irritating factors.
And also when diagnosing:
- tumors, the growth of which compresses the esophagus;
- congenital stenosis (atresia) with partial or complete fusion of the esophagus.