If gastritis, ulcers, inflammation of the gastric mucosa, esophagus and duodenum are suspected, the pediatric gastroenterologist decides to perform fibrogastroduodenoscopy. FGDS is prescribed to children regardless of age. This is an informative type of examination, during which the doctor receives data on the condition of the mucous membranes of the alimentary canal. Further treatment is prescribed based on the results of the examination.
What does the procedure help to identify?
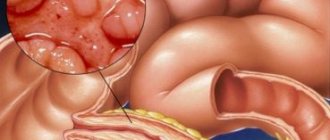
During an endoscopic examination, ulcers, polyps, and other diseases of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum can be identified.
In children, gastroscopy is often used to diagnose mucosal burns caused by chemicals, congenital pathologies of the esophagus, digestive organs, and diaphragmatic hernia.
The latter pathology is a hereditary disease, which can be diagnosed using gastroscopy . Also, during the examination, the specialist may detect foreign objects in the esophagus that the child has swallowed.
Indications for use
The examination can take place on a scheduled or emergency basis. A routine examination is carried out if the child exhibits symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases for a long time.
A planned gastroscopy procedure is prescribed for the following indications:
- sudden weight loss or lack of weight;
- regular spasmodic pain in the abdominal area;
- constant vomiting, regurgitation;
- pathologies of the pancreas and biliary tract.
If symptoms recur regularly, it is necessary to undergo a routine examination.
In emergency cases, gastroscopy is performed for children if there is a suspicion of serious pathology of the digestive organs. The risk of complications after EGD in children is higher than in adults.
FGDS on an emergency basis
Urgent gastroscopy is required for the following pathologies:
- stomach bleeding;
- cauterization of a damaged vessel that is bleeding;
- there is a possibility of a foreign object entering the esophagus;
- burn of the mucous membrane with acid or alkali;
- if there is a suspicion of malformations of the digestive organs.
In this case, the procedure is performed without preparation, often under general anesthesia.
Indications
At what age do endoscopic examinations begin for children? What are the indications for its use? Indications for gastroscopy of the stomach are the following complaints:
- Repeated vomiting, regurgitation. This symptom is a common reason for performing gastroscopy in children.
- Frequent, recurrent abdominal pain.
In addition, the following indications for emergency fibrogastroscopy are distinguished:
- Gastrointestinal bleeding (is an indication for FGS, regardless of age). In this case, it is possible to diagnose the cause of bleeding in a timely manner and eliminate it immediately.
- Suspicion of high intestinal obstruction.
- Detection of foreign bodies in the esophagus and the need to remove them.
Such a study also becomes necessary in the differential diagnosis of diseases occurring with a similar clinical picture, for verification of erosive and ulcerative changes in the mucosa, and in the diagnosis of malformations of the esophagus.
In addition to the above reasons, gastroscopy is widely used for medicinal purposes ─ to stop bleeding, remove polyps, and administer medications.
Where to do the procedure? If you have complaints, you should contact a therapist or gastroenterologist, who will determine the indications and set a date for the study.
Features of the procedure for young children
Until recently, when the examination was carried out without anesthesia, it was difficult to do a gastroscopy. The child developed panic, and it was almost impossible to insert a probe into the gastrointestinal tract.
How to prepare for the procedure
Before probing, children are not given food for at least 8 hours (better - 12, infants - 6 hours). The day before gastroscopy, mineral and alkaline water should be excluded.
On an empty stomach, the study is more informative, and the risk of vomiting is minimized. If the examination is urgent, the stomach is emptied before surgery.
Psychological preparation is no less important. Children over 3 years of age must be set up for examination and the importance of the procedure explained. You can give your child his favorite toy.
It is important to explain to your child how to breathe correctly during gastroscopy if it takes place without anesthesia.
At home, you can practice calm, even breathing through your nose. They do this to avoid psychological trauma so that the baby’s procedure goes without complications.
When visiting a doctor, you must have with you a medical card, results of tests and other examinations (if carried out), a diaper, a towel, and disposable napkins.
To use anesthesia or not
The need for anesthesia before the procedure is discussed with the doctor. The examination can take place under local or general anesthesia.
Currently, before gastroscopy, children under 7 years old are given an injection with sedatives. Infants under 3 months of age are given anesthesia for medical reasons . During the procedure, the child is in a state of sleep and does not resist.
Additionally, atropines are used. These drugs allow you to painlessly insert a probe into the esophagus. Anesthesia can be either general or local depending on the condition.
The age of the child should also be taken into account . Anesthetics allow you to “freeze” the larynx area and suppress the gag reflex.
Features of carrying out under anesthesia and without
While under anesthesia, the baby does not experience fear and does not see the progress of the entire operation. This greatly facilitates the doctor’s work and allows the examination to be carried out quickly and efficiently.
If, due to age or illness, the use of sedatives is impossible, the procedure is performed without them. However, the examination does not always go smoothly. In this case, the child’s psychological mood, the closeness of the parents, and the degree of trust in the doctor are important.
How does the procedure work?
After the preparatory process, the child is placed on the couch, placed on his side - this makes it easier to insert the probe. The oral cavity, pharynx, and esophagus should be located at the same level.
A nozzle is inserted into the mouth, which does not allow the jaw to close during the entire examination.
For pediatric gastroscopy, a flexible probe is used. It does not injure the food tract and mucous membranes .
During insertion of the probe into the esophagus, the small patient does not experience any discomfort or pain. If the gastroscope is inserted correctly, the baby breathes easily, there is no coughing or asthma attacks.
Diagnosis of the digestive organs occurs in the following order:
- esophagus;
- fundus of the stomach, cardia;
- body of the stomach;
- pylorus;
During the examination, the doctor examines the mucous membranes of the esophagus and stomach, and the duodenum is also examined. During the procedure, pictures and videos are taken using a gastroscope.
According to indications, bleeding can be stopped, a tissue sample taken for biopsy, and a polyp removed. The manipulation is carried out within 15 minutes.
Indications for gastroscopy
Gastroscopy for a child is not such a rare procedure. Gastrointestinal disorders are very common among children. Indications for FGDS may be:
- Ulcer;
- Colitis;
- Intestinal cramps;
- Tumor of the esophagus;
- Stomach tumor;
- Bleeding inside the digestive tract, manifested as vomiting blood;
- Severe abdominal pain;
- Nausea and frequent vomiting;
- Sudden loss of body weight;
- Retarded physical development;
Indications for pediatric gastroscopy are much more serious than for adults. Since the risk of developing serious complications in a child after such manipulations is higher than without them.
Possible complications
After gastroscopy, you may experience discomfort and burning in the throat, unpleasant sensations, dry mouth, bloating, and belching of air. This goes away within a day.
The endoscope, passing through the food tract, may slightly damage its mucous membrane. After the examination, the baby feels a burning sensation while eating.
It is important to give young children warm, pureed food during this period . Sweets, crackers, chips should be avoided for several days after gastroscopy.
After anesthesia, there may be slight malaise, dizziness, and rarely redness of the eyelids. This occurs from overexertion during the procedure. Inflammation can be easily relieved with chamomile infusion (wet cosmetic pads and apply to the area of redness).
If after gastroscopy there are sharp abdominal pains, vomiting, fever, or other complications, it is necessary to leave the child in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor.
How to prepare a child for FGDS
But the most important thing during the study is the correct mood of the patient. But how to prepare your child for such an unpleasant procedure? Fgds for children over 5 years of age are usually done by inserting a device into the oral cavity. Therefore, it is important to tell the child the entire sequence of the doctor’s actions, explain that this is not at all frightening and, with correct behavior, the unpleasant sensations will be reduced to zero. Try to keep your voice even and calm during a conversation. Kids clearly pick up on changes in mood, so remain calm during the explanation.
The child should be made to understand that many children undergo gastroscopy, and this does not at all indicate a serious illness. That this is a standard procedure and you shouldn’t be afraid of it. You should especially not be ashamed of increased salivation and belching during administration, as this is a normal reaction of the body to an irritant.
A couple of days before the FGD, rehearse proper breathing with your baby. It should be smooth and nasal.
In addition to psychological comfort, it is important to take care of physical preparation:
- Avoid fried, salty, spicy and smoked foods 10 hours before the procedure;
- It is necessary to give up alkaline mineral water for a few days;
- Check with your doctor at what time in the morning you are prohibited from drinking distilled water. This parameter is often purely individual.
After an FGD of the stomach, the child may experience redness on the eyelids. This is not scary - the result of overvoltage. Such consequences quickly pass without leaving a trace. It is recommended to apply cotton pads soaked in cooled chamomile infusion or tea leaves to the child’s eyes.
Contraindications to the procedure
There are a number of contraindications to gastroscopy.
If a child has these disorders, the study is carried out using ultrasound or MRI:
- lung diseases;
- heart pathologies;
- phlebeurysm;
- aortic aneurysm;
- mental disorders;
- blood diseases, blood clotting disorders.
Instead of FGDS, less traumatic alternative types of diagnostics are performed.
Performing a gastroscopy on a small patient is risky due to the anatomical features of the growing organism. If the baby has a narrowing of the esophagus, this is a direct contraindication to the study.
When passing a probe through the esophagus, there is a risk of minor damage to the mucous membranes, therefore, in case of hemophilia (incoagulability of blood), the procedure is prohibited.
Preparing for the study
The child must be brought to the examination on an empty stomach.
Further on how to prepare a small patient for FGDS. Fibrogastroscopy is performed 8 hours after the last meal. It is advisable not to drink water 4 hours before the examination. If the patient constantly takes medications, then this can be done after the examination or washed down with a few sips of water before it.
If a child has increased anxiety and does not tolerate stress well, then this should be taken into account when preparing for an FGDS of the stomach and the use of sedatives (in children, as a rule, these are herbal preparations). But if the child is calm, you can do without medication. Some parents, in order to avoid possible psychological trauma for the child, may ask for the examination to be performed under general anesthesia.
Gastroscopy is performed using special children's gastrofibroscopes of smaller diameter when compared with instruments intended for adults. Sometimes it becomes necessary to use larger diameter devices for gastroscopy in a child under 4 years of age, and intubation anesthesia may become a prerequisite due to the danger of tracheal compression.
Before the study, the doctor must be aware of the presence of all possible allergic reactions in the patient, as well as all his concomitant diseases.