What is it - esophageal diverticulum?
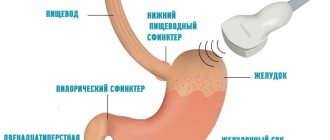
An esophageal diverticulum is a change in the walls of the organ that results in a protrusion. That is, the wall is deformed and a pouch forms on it in the mediastinum. The process may involve one layer of esophageal tissue or all three.
The protrusion can be located anywhere in the tubular organ, but is more often observed in the thoracic region. The most common carriers of the disease are men who have crossed the 50-year mark and suffer from other diseases of the digestive system:
- cholecystitis;
- gastritis;
- peptic ulcer;
- cholelithiasis and others.
Zenker's diverticulum affects the pharyngoesophageal part of the gastrointestinal tract, but belongs to the esophageal group because it has similar symptoms and development mechanisms. With a traction diverticulum, constant stretching of the walls of the esophagus occurs, which causes a weakening of the muscle layer. The mechanical factor is adhesions with neighboring organs and lymph nodes. With pulsion, there is an external influence, for example, the pressure of a bolus of food.
Causes of manifestation
Factors that cause esophageal diverticula to develop:
- primary/congenital muscle weakness (the esophageal canal is weakened in a certain area, where diverticulitis and subsequent neoplasms form);
- long-term damage to the gastrointestinal tract (play the role of a concomitant disease that reduces the level of immune protection);
- abdominal trauma;
- the effect of the pulsation mechanism on the lymph nodes, fastening the inflamed lymph nodes and the walls of the esophagus;
- long-term use of drugs/tobacco products/alcohol;
- poor nutrition of a breastfeeding mother can be one of the most important factors due to which esophageal diverticula develop in a child;
- stressful state, constant nervous overstrain.
Why does protrusion of the esophageal wall occur and why is it dangerous?
The causes of esophageal diverticulum are very diverse and are associated both with the anatomical characteristics of a person and with the action of external factors. Thus, the congenital type of pathology occurs due to the weakness of the muscle tissue that forms the walls of the organ. The incorrect lifestyle of the mother during the period of bearing the baby contributes its share, which does not allow his developing body to form correctly.
But more common is an acquired diverticulum, which forms as a consequence of:
- inflammatory processes in the esophagus;
- mechanical damage to the walls;
- development of fungal diseases;
- narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus;
- poor nutrition;
- ulcers of the stomach and duodenum;
- achalasia;
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- formation of tumors on the mediastinal organs.
When exposed to any of these factors, a change occurs in the walls of the esophagus: spastic contractions of the walls and an increase in internal pressure contribute to the formation of protrusions.
Among the factors that provoke the development of pathology are:
- alcoholism and smoking;
- unfavorable working conditions (inhalation of dust, toxic substances);
- imbalance in metabolic processes that develops against the background of illness or malnutrition;
- regular consumption of hot and spicy foods;
- eating large amounts of food at night.
If left untreated, the disease progresses, contributing to the development of complications:
- abscesses – localized purulent processes;
- wall erosion;
- stenosis (narrowing of the lumen);
- perforation (rupture) of the walls of the organ;
- phlegmon - diffuse purulent process;
- the appearance of aspiration pneumonia, which occurs as a result of the contents of the esophagus entering the respiratory tract;
- malignant neoplasms.
As complications develop, a person’s general well-being decreases, quality food intake becomes impossible, and the patient begins to lose weight (a symptom that signals the beginning of exhaustion of the body). In addition, the pathology affects nearby organs, causing structural and functional changes in them.
Prevention measures
To prevent the formation of diverticula or relapse of the disease, you must constantly adhere to the following rules:
- control your diet;
- do not overeat;
- avoid dry food and snacks;
- chew food thoroughly;
- take regular walks in the fresh air;
- perform physical exercises;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- undergo a medical examination, visit a gastroenterologist.
We recommend: What is the peculiarity of the transition of the esophagus into the stomach?
Classification
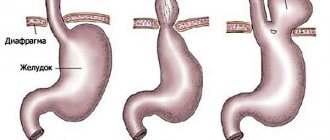
In addition to dividing into congenital and acquired, esophageal diverticula are distinguished by location:
- pharyngoesophageal;
- suprabronchial;
- supradiaphragmatic;
- abdominal.
Depending on the participation of the mucous membrane, the following types are distinguished:
- true, affecting all three layers of the walls of the esophagus;
- false, formed only due to protrusion of the mucous membrane.
All these varieties belong to the same disease, which has an ICD code - Q 36.9, respectively, their treatment and symptoms are similar, but have their own characteristics.
Esophageal diverticulum: symptoms and signs
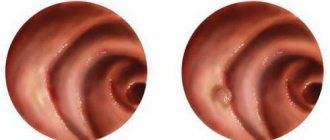
Let us now consider the symptoms of esophageal diverticulum. If the protrusion is less than 2 centimeters in size, it usually does not appear in any way. Larger sizes reveal themselves with the following signs:
- belching with an unpleasant odor;
- difficulty passing food through the organ;
- sensations of soreness and scratching in the throat;
- production of large amounts of saliva;
- nausea and vomiting after eating;
- constipation;
- heartburn;
- a sharp increase in temperature is a symptom of infection;
- severe cough, not accompanied by sputum production;
- in a horizontal position, food can move in the opposite direction;
- feeling of a lump in the throat and others.
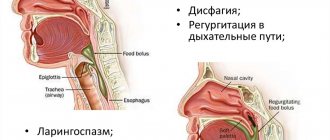
The most striking symptoms of a diverticulum are in the area of the pharyngoesophageal junction. With it, food accumulates in the protrusion, causing constant regurgitation and bad breath.
In addition to the classic clinical picture, other signs may be observed. So, a person’s voice may change, and after eating, the face turns red, there is a feeling of suffocation and even fainting. Patients often experience shortness of breath, chest pain, tachycardia, and snoring. Such symptoms make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. For verification, a number of additional instrumental examination methods are prescribed.
Diagnosis of diverticula
A preliminary diagnosis is made when collecting anamnesis, and is clarified using instrumental methods. The doctor performs palpation - feeling the esophagus, during which the protrusion is clearly felt. Listens to complaints, prescribes blood and urine tests. Tests make it possible to obtain information about the presence of symptoms of the inflammatory process.
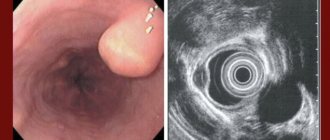
The best way to confirm the presence of esophageal diverticula (and determine the type, size, location of the defect on the wall) is to visualize the organ using:
- X-ray with the addition of a contrast agent, which allows you to determine not only the location of the defect and size, but also the presence of complications, destructive changes above and below the formation;
- esophagoscopy, in which the examination is carried out “from the inside” using optical instruments; as a result, the doctor can examine the walls of the organ, take part of the tissue for laboratory tests, for example, if a tumor is suspected;
- computed tomography;
- esophageal manometry or study of esophageal motility (studies allow us to assess the severity of functional changes);
- Holter monitoring (disturbances in heart function are determined).
If there are complaints about the heart (an organ adjacent to the esophagus), cardiac ultrasound, ECG and other procedures are additionally prescribed. The acidity of the stomach is examined and a cytological analysis is performed.
The main goal of diagnosis is to determine the location of the protrusion and find out the cause of its formation. After verification of the diagnosis, you can begin to select a treatment regimen for the disease.
Treatment of diverticula
Treatment of diverticulosis with folk remedies is ineffective. Only a doctor who can accurately determine the condition of the defect, its characteristics and choose a treatment method should prescribe therapy. It can occur in a conservative way, that is, in the form of taking medications and following a diet, or surgically.
The conservative method of treating esophageal diverticulum is to eliminate irritating factors, which means:
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- treatment of diseases that provoked this pathology;
- following a diet based on avoiding spicy, fried and hot foods, eating baked or steamed foods, preparing various purees and soups;
- using fractional meals 5-6 times a day;
- drinking large amounts of water - from 2 liters per day, and after each dose it is necessary to strain the esophagus;
- conducting gymnastics;
- Regular rinsing of the esophagus with water.
Antiseptic drugs are used as medicines to help eliminate the symptoms of inflammation and prevent the decomposition of food accumulated in the sac-like formation. They are sprayed as a solution along the esophagus. Drugs that reduce gastric acidity, normalize peristalsis, and antibiotics can be used.
ethnoscience
In the treatment of esophageal diverticulum, folk remedies can also be used. However, drugs should be used carefully and after consultation with a doctor. The use of folk remedies does not exclude treatment with traditional medical methods, but only complements it.
The most effective traditional medicine is an infusion of medicinal plants.
You need to mix finely chopped fruits: rose hips, motherwort, dill, chamomile flowers, stinging nettle. One tablespoon of crushed and mixed plants is poured into a glass of boiled, non-hot water. After 1.5 hours, strain the infusion and consume 100 g in the morning and evening. The infusion relieves inflammatory processes and improves the general condition of the patient.
A couple more interesting folk recipes are given below. The use of any traditional medicine is permissible after consultation with a doctor.
Decoction of oak bark: a handful of dry ground bark, walnut leaves, cinquefoil roots, oregano and St. John's wort flowers (10 g each). For 30 g of mixture – 1 liter of boiling water. Fill with water and place in a warm place for two hours. Then boil the infusion and cook for another 10 minutes. Cool, strain and consume 50 ml before each meal. The decoction is considered healing.
Bran perfectly speeds up the passage of food through the digestive tract and has a cleansing effect. Brew one spoon of bran in 100 ml of boiling water and take on an empty stomach, starting with six teaspoons a day, gradually increasing to eight tablespoons. Six months of use will cleanse the body, increase intestinal tone and help heal diverticulum.
Surgery
Surgery for esophageal diverticulum is inevitable if the disease is severe or complications arise:
- wall perforation;
- bleeding;
- esophageal stenosis and others.
It is carried out in two ways:
- complete excision of the damaged area and subsequent plastic surgery;
- turning the diverticulum inside the esophagus and suturing the walls, which is effective for small wall defects.
Patients after diverticulum removal are fed using a gastric tube for 10-14 days.
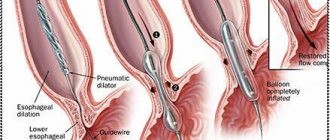
Removal of esophageal diverticulum by endoscopic method
Modern medicine makes it possible to remove esophageal diverticulum using endoscopy. The peculiarity of this technology is the absence of large incisions and a short recovery period after surgery. Small incisions are made in the skin through which special surgical equipment equipped with a camera is placed inside. The doctor sees all his actions on the screen. As a result, the intervention is minimal and the healing period is much faster.
Postoperative period and prognosis
The prognosis after surgical treatment is favorable, provided that the cause of the disease is eliminated. After surgery for esophageal diverticulum, sick leave is issued for a period of 7 to 21 days, depending on the type of intervention.
With the endoscopic method, the patient can leave the clinic within a couple of days.
Attention! Throughout the entire recovery period, it is necessary to follow a strict diet based on chemical, thermal and physical sparing of the organ. It is advisable to adhere to nutritional recommendations for life.
If you follow the recommendations of your doctor, the likelihood of recurrence of esophageal diverticulum is very low.
Physical exercise
A good addition to the main treatment of the disease is physical activity. An inactive lifestyle, on the contrary, contributes to the development of the disease. Physical activity speeds up the passage of food through the digestive system. Walking and running are the most useful exercises for preventing diverticulosis. But other sports activities also have a beneficial effect on the body. It is worth choosing any type of physical activity and devoting at least a little time to it. Frequent exercise will guarantee the health of the whole body.
Do not despair if specialists have diagnosed diverticulum. The pathology lends itself well to traditional therapy and even treatment with folk methods and remedies. Perhaps this illness will serve as an incentive to permanently change the previously habitual harmful lifestyle. During the treatment period, the habit of eating right will be developed, and the potential of physical activity will be properly appreciated.