general description
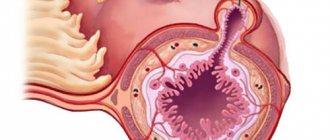
Achalasia cardia is a chronic disease characterized by the absence or insufficient reflex relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter, resulting in an intermittent obstruction of the esophagus caused by a narrowing of its section before entering the stomach (called “cardia”) and expansion of the upstream areas.
It can develop at any age. The essence of achalasia is discoordination of the processes of esophageal peristalsis and relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter.
The causes of achalasia are currently not completely clear. Particular attention is paid to the state of the patient’s nervous system - often achalasia develops after suffering stress. The presence of chronic diseases of the esophagus and stomach - gastritis, esophagitis - is also important.
Clinical symptoms
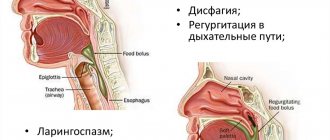
The clinical condition of achalasia cardia is characterized by a slowly progressive course of the disease, the main signs and symptoms of which are expressed in esophageal dysphagia. This sign of the disease is considered the most persistent symptom of achalasia cardia and has distinctive features:
- feeling of a food lump in the chest;
- after swallowing, 3-5 seconds from the beginning of the act, difficulties appear in the passage of food;
- patient complaints about the sensation of food getting into the nasopharynx.
Typically, these symptoms of esophageal dysphagia are activated by eating solid foods. To enhance the act of swallowing, a person needs to drink some warm water.
Pain and feeling of heaviness with achalasia cardia
The next symptom is regurgitation, when there is a passive return of the contents of the stomach or esophagus back into the oral cavity. The process of regurgitation, or regurgitation, can occur even several hours after eating food. All this time, the food mass can remain in the lower part of the esophagus without causing nausea or a gag reflex in a person. Such symptoms can be aggravated by uncomfortable body position, fast walking or running, bending the body, and so on. In most cases, symptoms of achalasia cardia after esophageal congestion are associated with chest pain radiating to the cervical, shoulder and scapular areas. Frequent manifestations of pain, which provide the body with an uncomfortable state, cause in a person a conscious feeling of limiting food intake, which affects his appearance. A person begins to lose weight, and at the same time experiences a constant feeling of hunger. Alachazia of the esophageal cardia is accompanied by other symptoms characteristic of many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- belching of rotten contents;
- bad breath;
- heartburn and feeling of heaviness;
- uncontrollable nausea and gag reflex;
- increased salivation;
- general condition disturbance (weakness, dizziness, cardiac arrhythmia).
The complexity of clinical pathology lies in the fact that the symptoms of achalasia cardia do not have a constant course and can occur spontaneously with varying frequency and intensity. Any painful discomfort in the esophagus should be carefully studied and appropriate therapeutic measures taken.
Treatment of achalasia cardia
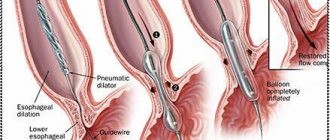
Treatment of esophageal achalasia is initially conservative - pneumomodulation of the lower esophageal sphincter is performed with a balloon, which gives good clinical results. If the process is neglected and there is no effect from pneumodilatation, a surgical intervention is performed in which the muscle fibers of the esophageal sphincter are dissected.
Essential drugs
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
- Nitrendipine (second generation calcium antagonist). Dosage regimen: sublingually at a dose of 10-30 mg over 30 minutes. before meals.
- Isosorbide dinitrate (vasodilator, antianginal agent). Dosage regimen: sublingually at a dose of 5 mg over 30 minutes. before meals or orally at a dose of 10 mg 2 times a day.
- Botox (muscle relaxant). Dosage regimen: administered in a dose of 50-100 units directly into the area of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Esophageal achalasia - treatment
Achalasia cannot be completely cured, but symptoms can be relieved. If diagnosed early, medications can help widen the narrowed part of the esophagus so food can pass through normally. Examples include calcium channel blockers and nitrates. After a few months, some drugs stop helping. For achalasia of the esophagus, pneumatic expansion is used. A small balloon is passed into the narrowed area of the esophagus and inflated to widen the space. This may need to be done several times. Complications include chest pain immediately after the procedure and a small risk of esophageal perforation, which requires further treatment.
Myotomy
- an operation in which a muscle is cut - this usually helps prevent obstruction. It has a success rate of 70 to 90%. Symptom reduction lasts 10 years in 85% of cases.
Endoscopic myotomy - the surgeon uses an endoscope to make an incision in the lining of the esophagus and create a tunnel in the wall of the esophagus. This procedure appears to be safe and effective, but its effects are unknown since it is a relatively new treatment.
Botox
- the injection is given to relax the muscles in the lower part of the esophagus. Botox injections can help those who are unable or unable to undergo surgery. One injection provides relief for 3 months in 65-90% of patients, but then it must be repeated.
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
How is the disease treated?
Treatment of achalasia cardia of the esophagus Medicines are the basis of therapy for achalasia cardia
Treatment of achalasia cardia is prescribed by a specialist after making an accurate diagnosis. Depending on the stage of development of the disease, therapy can be non-drug, that is, aimed at adjusting lifestyle and diet, conservative (medicines) or surgical. Traditional medicine offers its own remedies for the treatment of this pathology, but they can only be used as part of comprehensive measures.
Treatment of achalasia cardia with medications is most often prescribed. The following groups of drugs are used for this:
- Nitroglycerin preparations. Helps relax the smooth muscles of the esophagus.
- Sedatives. They help relieve nervous tension and stress and can be used in tablets or suspensions. Used for achalasia caused by psycho-emotional factors.
- Prokinetics. These medications help normalize gastrointestinal motility.
- Calcium antagonists. Help relieve spasm and return the esophageal sphincter to its normal state.
- Enveloping agents. These drugs prevent the development of inflammation in the later stages of cardiospasm development.
You cannot take pills without the knowledge of your doctor; only a specialist can prescribe the appropriate medicine in the correct dosage. It should also be taken into account that all medications have contraindications and side effects, and therefore can harm the body if there are restrictions on their use.
If drug therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment of achalasia is prescribed. A minimally invasive treatment method, that is, one that slightly damages healthy tissue, is pneumocardiodilation. This is a procedure in which the esophageal sphincter is artificially dilated by installing balloons of the required size.
Direct surgical treatment of achalasia cardia is carried out at stages 3 and 4 of the disease. Surgical intervention consists of excision of the muscle tissue of the esophagus and its subsequent suturing. This allows you to restore the natural structure of the organ, in which there will be no problems with swallowing food.
Folk treatment of achalasia of the esophageal cardia Folk treatment involves the preparation of decoctions and tinctures
Doctors do not recommend using traditional treatment for achalasia cardia as the main method; it must be combined with the main drug therapy. Otherwise, you may not only fail to achieve the desired effect, but also aggravate the situation, since the disease is serious and requires no less serious measures to be taken.
The following remedies are most often recommended:
- Tincture of ginseng root. It is necessary to grind the dry root to a powder, pour 30 g of this raw material with a liter of high-quality vodka and leave for a month in a dry, dark place. Strain the product and consume 2 ml three times a day before meals.
- Schisandra tincture. It is necessary to pour 100 g of Chinese lemongrass fruits with 0.5 liters of alcohol and leave for 10 days. Strain the product and take 30 drops 3-4 times a day for 2 weeks.
- Herbal decoctions. If there is an inflammatory process and pain in the esophagus, you can take decoctions based on oregano, flax seeds or marshmallow. The product is prepared at the rate of 2 tbsp. raw materials per glass of water.
- Sedatives. If cardiospasm is caused by psycho-emotional reasons, you must take valerian or motherwort according to the regimen prescribed by your doctor.
The patient can alleviate his condition himself. To do this, it is necessary, firstly, to normalize the daily routine, clearly defining the time for work, rest and eating. Secondly, you need to spend more time in the fresh air, taking walks for at least half an hour every day. Thirdly, you need to sleep in a well-ventilated area with your head slightly elevated. Fourthly, it will be necessary to adjust the principles of nutrition, eating food often, but in small portions, avoiding overeating.
—
Possible complications
Most often, if sphincter insufficiency is present, gastroesophageal reflux and esophageal stricture subsequently develop.
Lack of treatment can lead to the development of cancer, the statistics in this case are disappointing - from 2% to 7%.
It is also possible as a complication the appearance of megaesophagus, that is, a dramatic increase in the width of the size of the esophagus. This diagnosis is made in approximately 20% of patients.
Interesting! GERD: causes and clinical manifestations
Individual signs
If gastric cardia insufficiency is diagnosed, doctors distinguish several syndromes:
- Dysphagia syndrome. Clinical manifestations in this case are as follows: a feeling as if there is a “lump” in the chest;
- hard to swallow;
- The patient constantly chokes while eating.
It is easier for the patient to eat solid than liquid food. This is due to the fact that solid foods put a lot of pressure on the pyloric sphincter and promote its opening. Simply put, there is a violation of the passage of food. These symptoms are very important for a correct diagnosis; for example, in the presence of cancer or stenosis, the clinical picture is the opposite, and it is difficult for the patient to eat solid food.
If the cardiac sphincter loses its functionality, then in addition to the syndromes described above, the patient also experiences other symptoms:
- unpleasant odor from the mouth due to changes in the diameter of the valve and the constant retention of food particles in the esophagus. Over time, this can cause erosions and ulcers on the mucous membrane;
- heartburn, the patient feels that the pain is burning and moves from bottom to top;
- some patients even feel how food moves through a valve that does not close, leaving behind a sour taste;
- belching with a sour taste;
- excessive salivation;
- hoarseness in the throat;
- problems with teeth and gums, caries;
- increased heart rate.
This pathology is a progressive condition, so exhaustion and deterioration are increasing.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
To identify achalasia, you should be examined by a doctor, take blood tests, do an ultrasound of the esophagus and endoscopy. Doctors also recommend manometry.
After identifying the disease, individual therapy is prescribed (it depends on the degree of neglect of the pathology).
Traditional treatment is aimed at restoring sphincter patency and eliminating pain. It provides the following:
- Prescribing medications that reduce pressure in the esophagus. The best of these are Cerucal and Nitrosorbitol.
- Prescription of sedatives (Novo-passit, valerian, motherwort extract).
- Compliance with dietary nutrition.
If drug therapy does not help, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment.
Nutritional features and diet
To ensure that food enters the stomach and does not stagnate in the esophagus as a result of obstruction and narrowing, it is necessary to consume foods in a liquid or thoroughly ground state.
It is important that all products are at the optimal temperature; cold and too hot causes spasm of smooth muscles and helps accelerate degenerative processes.
Eat 5-6 times a day, but in small portions. You need to take your time and try to chew your food as thoroughly as possible.
To improve peristalsis, after finishing a meal, drink one small sip of warm boiled water.
Dinner should be 2-3 hours before bedtime so that the food bolus does not collect in the esophagus and begin to decompose.
Recommendations regarding nutrition for achalasia:
- Completely eliminate fried, spicy, salty, pepper and fatty foods;
- Eat only small portions, at least 5 times a day;
- Take food with water;
- Avoid alcohol, coffee and carbonated drinks;
- Eat only food that is quickly digested and stimulates the gastrointestinal tract;
- You can't eat before bed.
If the process has already started and achalasia has led to nutritional deficiency, the patient is transferred to artificial nutrition.
Differential diagnosis of pathology
Passes in the presence or suspicion of malignant tumors. They will cause secondary achalasia.
During diagnosis, it is important to exclude ulcerative stenosis, especially in patients with scleroderma and Raynaud's syndrome, which is combined with gastric reflux.
Diagnosis is carried out using x-rays, which can differentiate tumor processes. On an x-ray, you can see uneven contours in a segment of the distal portion of the esophagus.
A test with nitroglycerin is informative; if the cardia does not open when taking the drug, and a gas bubble is visible in the stomach, the diagnosis is confirmed.
The presence of malignancy is confirmed by targeted biopsy. A piece of tissue taken using endoscopic instruments is sent for cytological examination. The results of the analysis confirm or refute the presence of cancer cells.