What are tumor markers
A tumor marker of the gastrointestinal tract is a pathological protein. Intestinal markers indirectly indicate a tumor in the early stages of the disease, when there are no obvious symptoms. Pathological markers are tested in the early stages, when it is difficult to notice the neoplasm. Clinical manifestations have disappeared, but the tumor is growing. The division of altered cells in the body occurs with rapid metabolism. As a cancer tumor grows, pathogenic substances enter the bloodstream. A tumor marker shows intestinal cancer and gives doctors an idea of the severity of the process.
Colon and stomach cancer are the third most common malignant tumors. According to World Health Organization estimates, the disease caused 1.5 million deaths in 2021. To reduce the incidence of tumor diseases, early diagnostic methods are being developed. Detection of the early stages of cancer is the basis for treatment. One of the methods is analysis for tumor markers.
Preparation for analysis and its implementation
Since the determination of the level of tumor markers is carried out in the blood, the preparation for this test is practically no different from that for other blood tests. In order for the analysis to have the greatest diagnostic value, you must adhere to the following rules:
To diagnose tumors, venous blood is taken. To do this, the nurse pre-treats the injection site with cotton wool and an antiseptic. Then she takes a sterile disposable syringe and carefully draws blood from a vein. A label with the patient’s data is attached to the bottle of blood, and the blood is sent to the laboratory for further calculation of the number of tumor markers.
The result is given to the patient the very next day. In this case, the norm according to the data of a specific laboratory is indicated, and next to it is the level of the substance found in the patient’s blood.
The final interpretation of the result and diagnosis is carried out by the attending physician. It evaluates the analysis data for window markers, the results of instrumental examination methods and the clinical manifestations of the disease in a comprehensive manner. Only with this approach to diagnosis can a correct diagnosis be made.
What tumor markers exist?
Markers do not necessarily indicate malignant tumor processes. Such substances are natural to the body. The values increase during pregnancy, when the pregnant woman feeds the fetus. Intestinal tumor markers are usually divided into precise specific and rough nonspecific proteins.
Nonspecific markers
These substances are detected in cancer of the heart, kidneys, intestines and brain. With their help, they think about the presence of a malignant tumor, but it is impossible to indicate the exact location.
The group includes:
- Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) is a glycoprotein that also appears during gestation.
- LASA-P – liver antibodies to malignant tumors.
- Tu M2 PK – using Tu protein, the metabolic rate of cancerous tissues is determined. The indicator is considered a marker of choice; it is used to determine pathological growth in the body.
Such studies are not very specific. With their help, they determine the growth of cancer in the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and nervous system.
Remember, deviations from the norm do not provide complete confidence in malignant growth. If there is a suspicion of an increase in oncological values in the blood and body fluids, a thorough examination by specialists is required.
Specific markers
The group includes substances characteristic of the pathology of a particular organ. For example, for the stomach, liver or rectum. Their detection makes it possible to indicate the location of cancer with a high degree of probability. When the intestinal tract is damaged, the following indicators are most often detected:
- Carcinoembryonic antibodies (CEA) are a protein of cancer of the initial parts of the intestine. By assessing the results of the identified values, it is possible to predict and control the growth of small intestinal tumors. Decoding of CEA indicators is carried out to analyze the quality and success of treatment.
- CA 72-4 - this protein is often tested for detection in conjunction with cancer antibodies. The protein can be detected in tumor tissues of the large and sigmoid intestines in the small cell type. Increased antigen values also indicate colorectal cancer.
- CA 125 – The main indicator of cancer of the thick sigmoid part.
The detection of antibodies and proteins in the indicators indicates particularly malignant growths in the digestive tract.
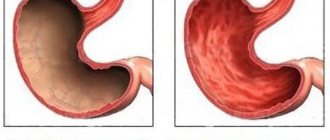
Cancerous tumor in the intestine
Objectives of the study
As in many other cases, the main goal is to monitor whether the treatment for stomach cancer was effective. Is there a recurrence of the tumor, or was the treatment successful? Is there a metastatic lesion, and how widespread is the tumor process? In this case, a blood test for tumor markers for stomach cancer will allow you to begin looking for metastases when the values increase. The oncologist will prescribe an MRI or positron emission tomography (PET) to identify “hot” metastases in which metabolism is increased.
Reference (normal) values of this tumor marker range from 0 to 6.9 U/ml. In healthy people, it is either not present in the blood at all, or its level is extremely low.
This tumor marker for stomach cancer has another important reason for research. Once a patient is diagnosed with cancer, tumor type and stage, from then on the carbohydrate antigen helps assess the chances of survival. If it increases, then the stage of the disease will also progress. This tumor marker value can be used even before treatment. But the diagnosis should already be made! After all, with intestinal cancer, for example, there is no such correlation, and it is difficult to make a prognosis, but with stomach cancer there is such a correlation.
However, this tumor marker is also not prescribed in isolation. And here CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) comes to his aid. Its task is to increase the diagnostic value of the carbohydrate antigen: it is safer to go for reconnaissance together.
The carcinoembryonic antigen itself can indicate many malignant tumors, but first of all it increases in intestinal neoplasms. But, unfortunately, its specificity in other cases is very low. It can reach high values, for example, in rheumatoid arthritis and many diseases of internal organs.
Therefore, we can say with confidence that the carcinoembryonic antigen is always taken together with the carbohydrate antigen to enhance the reliability of the result. If their concentration simultaneously increases or decreases, then the doctor has much more confidence in a particular treatment result, as well as in the prognosis of survival for stomach cancer.
How to take it
The study of gastrointestinal tumor markers is carried out using blood, urine and feces. You have to choose the most suitable option. If you do not want to donate blood, it is permissible to choose another medium. In this case, the diagnostic range of markers will be lower. The most common method is a blood test. For a good and accurate value, you should follow a diet for a number of days, and on the day of the procedure, come with an empty stomach in order to donate blood with the correct result.
The last meal is taken no later than 12 hours before the expected delivery. It is necessary to remember this rule. Many doctors recommend not eating the night before the test. A couple of days before the appointed date, give up sweet foods. Juice, sugary sodas and tea will compromise the accuracy of the test. The stress on the stomach will increase the malignant protein. Eating fatty fried foods incorrectly skews the results upward, but may have the opposite effect. You should drink more clean water. Such tests are a routine procedure, the results will be known on the day of delivery.
Blood is not suitable for analysis if a person takes B vitamins. This is critical if the test targets markers like 72-4. It is better to stop taking the drug the day before the test. In case of urgent need, the time is reduced to 8 hours.
The study of the Tu M2 PK marker is considered special. For research, the biological medium is stool analysis. Enemas and the use of laxatives are contraindicated. Due to its specificity, the result takes longer to determine than a blood test. The waiting time is 4 – 10 days.
Remember, the only type of marker for colon cancer is not a diagnostic criterion for diagnosing a malignant tumor. For a reliable analysis, it is recommended to study the list of types. Rectal cancer is studied for the presence of antigens CA 19-9 and highly specific CA 242. Studies on tumor markers of the stomach in combination with liver proteins are considered indicative.
Reliability and validity of indicators
In general, the analysis can be called a relatively reliable study, since it is usually performed with a diagnostic search for several markers of cancer in different organs. In this case, the main rule for making an accurate diagnosis is a repeated blood test for tumor markers. Observing the dynamics of the patient’s condition, the doctor makes a conclusion that based on a one-time increase in this indicator, one can only make an assumption about probable organ damage.
The English-language literature provides various statistical data regarding the diagnostic sensitivity of the CA 72-4 test for gastric cancer. According to these data, stomach cancer is detected in 28-80% of cases of this pathology. On average, in almost 100% of cases, the level of increase in the blood of CA 72-4 depends on the advanced stage of the disease.
Unlike other markers (CEA and CA 19-9), the tumor marker CA 72-4 has a slightly higher sensitivity to subsequent relapses of the disease. The joint administration of several tests for different tumor markers increases the reliability and reliability of diagnosis. In addition, the appointment of all these tests must necessarily be supplemented by the appointment of instrumental examination methods: ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract, gastroscopy, ultrasound of the ovaries. Genetic predisposition, previous manipulations and the patient’s personal history should also be taken into account.
RepostTweet
When to take it
Limitations in the use of the tumor marker method are highlighted. Examination of blood taken for nonspecific indicators gives incorrect ideas about the structure of morbidity. High values of individual indicators do not necessarily indicate tumor-like growths. Tumor markers for intestinal cancer are also isolated during inflammatory and structural changes in organs, and they are not associated with the spread of malignant neoplasms.
It is extremely difficult to identify a tumor in the digestive organs. The reason for the difficulties is the meager and vague symptoms of many clinical types of cancer at the initial stage. For laboratory determination, the values of cancer proteins are looked at. Determining the critical values of complex proteins at the beginning of the disease will increase the chances of successful treatment and longevity.
For individuals diagnosed with a malignant tumor, tumor markers are useful in assessing the effectiveness of therapy. During the therapeutic course, repeated measurements of oncotic proteins show the effect of the drugs used in a particular case. There are no identical diseases, just like there are no identical people. Therapy is required to be comprehensive and tailored to the patient.
Cancer oncoprotein shows intestinal cancer long before noticeable changes in the body begin. Various biological media and liquids are used for detection. Tests of saliva, urine, and stool can determine the presence of altered proteins.
Changes in the functioning of the digestive system are called dyspepsia. Similar phenomena include a feeling of heaviness after eating, heartburn, and nausea. These are stomach symptoms. Intestinal pathology causes bloating and constipation. The presence of flatulence and rare stools is considered a pathology of the intestinal canal. With such symptoms, it is recommended to conduct a comprehensive examination of the body. The presence of dyspepsia characterizes damage to the organs of the stomach and intestines.
Cancer carbohydrate antigen CA 72-4.
Indeed, malignant cells emerging from glandular tissue produce this antigen, and it is found in patients with stomach, ovarian and colon cancer. Its structure is also a glycoprotein, that is, a complex protein combined with a carbohydrate. It is produced normally in each of us even before birth, in the fetus, and in an adult its concentration is practically undetectable, or extremely low.
Its synthesis begins in patients with stomach cancer, but, unfortunately, it is not particularly helpful in the initial diagnosis. This tumor marker for stomach cancer has low specificity - any glandular tumor can cause its increase. And besides tumors, any pathology of glandular tissue.
Thus, in women, an ovarian cyst, which is never malignant, can cause an increase in the “tumor marker for stomach cancer.” Liver hepatitis and cirrhosis, inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, will also cause a surge in the “stomach tumor marker” in the blood. If you take it from a patient who has not yet been diagnosed, then doctors will wonder for a long time: yes, there is some kind of process, perhaps malignant, but where it is and what it is is unknown. But if a biopsy has already been performed and it is known exactly where the malignant neoplasm is located, then it begins to serve as a reliable beacon that helps the doctor guide the patient. So, stomach cancer cannot be diagnosed using a blood test. Why do they take a carbohydrate antigen test?
Organs of the gastrointestinal tract
The digestive system is the most massive in the human body. The length of the digestive canal in the body of an adult male reaches an average of 10 meters. The development of a malignant process in any part is accompanied by similar symptoms. Lack of bowel movements for 4 days, constipation, and bloating can be warning signs of many types of cancer. To determine the exact location, you need to understand the structure of the intestinal tract.
Small intestine
The first site of food absorption in the body is the small intestine. Conventionally, it is divided into duodenal, jejunal and sigmoid sections. The pathological process is localized in all areas equally, but tests for tumor markers give different results.
- CEA is the main marker of cancer of the small intestine, mainly the middle section. The values of this protein increase in cancer of the jejunum and, less commonly, of the ileum.
- CA 19-9 is an oncology antibody of the very first section of the intestine, the duodenum. It can also be detected by analyzing tumor markers of the stomach and esophagus.
Colon
The large intestine is the last section of the digestive tract. Here feces are formed and abundant enzymatic reactions occur. The large intestine contains a variety of microflora, so cancer in these sections is easily detected by the results of protein tests in the blood and stool.
The main structures of the large intestine are the cecum, colon, sigmoid and rectum.
- CA 125 – protein 125 is assessed for suspected sigmoid colon cancer.
- CYRFA 21-1 is the name given to the conditional brother of rectal cancer. A critical increase in indicators occurs precisely with this type of cancer.
- SCC - like the previous marker, signals the development of cancer in the last section of the intestine.
Stages of bowel cancer
Blood for stomach tumor markers
Tumor markers for cancer of the stomach and esophagus are used, first of all, to conduct a primary diagnostic study when the disease is suspected. In addition, it is used when it is necessary to develop a plan of therapeutic measures for an already identified malignant tumor.
The analysis is also prescribed for the purpose of assessing the effectiveness of the dynamics of the disease of already carried out therapy, especially after chemotherapy and to determine the process of spread of metastases several years after treatment.
Primary analysis is applied primarily to people who are at increased risk. These are patients with pathological processes such as gastric ulcers, severe atrophic gastritis, and adenomatous polyp. There is also an increased risk in patients who have undergone surgery to remove part of the affected anatomical structure.
In addition, laboratory testing to determine the presence of tumor markers is used when close relatives of the patient have had cases of cancer, regardless of its location.
Decoding the results
If the values of pathological proteins are increased, a detailed examination of all body systems is required. An integrated approach increases the reliability of the diagnosis. Below is what tumor markers of the gastrointestinal tract are present in the blood and their relative norm.
- CA 242 – 0-30
- PEA – 0-5.5
- SA 72 – 3.8-4
- Tu M2 PK – 1.5
- AFP – 15
- SA 19-9 – 3.4
- CA 125 – 2.5
- CYRFA 21?1 – 3.3
- SCC – 1.5
Such substances appear in pathological quantities in the blood and during benign processes. Informational value means analyzing dynamics, how indicators change depending on a change in diet, stress, and medications used. If metastases are suspected, proteins are examined monthly to assess tumor growth. Tumor markers in no way indicate the reason for the diagnosis. A single laboratory test is not enough. Altered proteins enter the bloodstream during aggressive tumor growth.
Cancer is not a death sentence. The sooner a problem is diagnosed, the sooner a solution will be found for it. In the first stages without metastasis, organ-preserving operations are used. Such techniques are complemented by radiation and chemotherapy. Do not delay going to the doctor and self-medicate. With its dangerous development and large volumes, cancer is difficult to treat. In such cases, partial removal of the affected organ is recommended. They resort to palliative care - alleviation of symptoms.
The treatment option depends not only on the speed of medical prescriptions, but also on the person’s mood. You can’t give up and give up; cancer can be cured. However, if you consider yourself a loser, it is much more difficult to do this.
Tumor markers for stomach cancer
There is such a thing as a tumor marker of the stomach and internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The antigen itself is the result of the formation of a tumor: cells begin to degenerate, but not into healthy ones, but into cancerous ones, forming a new tissue. In the process, a protein is produced or, as it is called in medicine, a tumor marker. Based on the level of this substance, you can determine whether there is cancer and where it is located.
Together with information about the presence of malignant tumors, the marker indicator can indicate the success or failure of therapy after operations to remove tumors. Although more than two hundred types of these substances are known, specialists use a tenth of them to determine the tumor process. Each type of tumor marker is responsible for a particular organ, and for the gastrointestinal tract, tests for the level of antigens of the SA group are used.
There is a risk group of people who are predisposed to this disease, namely:
- patients with chronic intestinal diseases;
- patients who have undergone gastrointestinal organ transplantation;
- people with genetic inheritance.
At the same time, it is worth contacting an oncologist in cases of frequent causeless fatigue, rapid weight loss and loss of appetite. This is another problem with the spread of cancer - people simply do not pay attention to such “minor” symptoms, try to cure themselves and thereby aggravate the state of affairs. Among the more serious reasons to conduct additional research on the level of markers are low hemoglobin, poor results of vitamin therapy and diets. In such cases, the specialist should pay attention to such indicators and take action.
When there is a suspicion of the formation of a malignant neoplasm, specialists prescribe an analysis to determine the following types of tumor markers for stomach cancer.
REA
Carcinoembryonic antigen refers to a group of special proteins that are produced by cancer cells.
Carcinoembryonic antigen refers to a group of special proteins that are produced by cancer cells. Normally, this antigen is absent in the human body. Only if a compaction begins to form, this indicator begins to increase and is released into the bloodstream.
This type of tumor marker belongs to the category of nonspecific. Its detection may indicate the presence of cancer affecting the stomach and intestines. If the study reveals an increase in the concentration of CEA in the blood fluid, the doctor conducts an additional diagnostic examination.
Alpha fetoprotein
This is another main method for identifying the development of cancer. Protein synthesis occurs during embryonic development. The liver, as well as the intestines of the fetus, are directly involved in its production.
If this antigen is detected in an adult, this indicates pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
In the case when its indicator significantly exceeds normal values, we can talk about cancer.
Analysis for the determination of alpha-fetoprotein is one of the primary diagnostic methods for suspected cancer pathology. Thanks to this indicator, it is possible to detect a malignant neoplasm in the stomach long before the first clinical signs begin to appear.
SA 19-9
This is a high molecular weight glycoprotein. An increase in its level is observed in cases of cancer of the stomach, pancreas and intestines. Tumor cells are directly involved in the production of this substance, after which it begins to be released into the bloodstream. In situations where its concentration exceeds 1000 IU/ml, in most cases we are talking about the presence of an inoperable neoplasm. In such cases, palliative therapy is carried out.
It is also worth noting that with a malignant lesion, normal or decreased levels of the substance may also be observed. This can happen mainly in the initial stages of the tumor process, when the isolation of this tumor marker is not yet available.
SA 72-4
This is an antigen that is a combination of protein and carbohydrates. Its high concentration is also observed in malignant neoplasms of the stomach. If a positive result was obtained during the study, then additional diagnostics of the body are carried out, which makes it possible to confirm or refute the primary diagnosis. Subsequently, this analysis is necessary in order to monitor the dynamics of the disease during therapeutic measures.
Indications for testing
The need for such tests does not always arise. Often, such specific proteins are only a confirmation or refutation of the data that the doctor already has, but only indirectly indicate the possibility of oncology. Indications for taking this screening test will be:
- the appearance in the patient of ambiguous signs of the onset of a cancerous formation in one of the sections of the gastrointestinal tract;
- monitoring the effectiveness of radical surgical treatment or chemotherapy;
- the need to obtain data to predict the course of the oncological process;
- systematic monitoring for precancerous diseases.
A test for gastrointestinal tumor markers should be carried out without fail if a person has any digestive problems with constant fatigue and elevated temperature. In addition, you should take tests for tumor markers in the following cases:
- with a prolonged period of dysphagia: nausea and aversion to certain types of food;
- the patient is over 40 years old and has a family history of cancer;
- duplicate causeless increases in temperature up to 37-37.5 degrees;
- significant reduction in body weight.
In addition, in addition to primary diagnosis, markers are often used to monitor the treatment process, in particular, to detect relapses, the appearance of secondary cancer or metastases.
Carrying out analyzes
To study tumor markers, venous blood is needed. For the convenience of patients, it is recommended to carry out the procedure in a lying position. The material is handed over in the morning. The duration of the diagnostic procedure is no more than 15 minutes. The resulting material is placed in a sterile container and sent for examination. Each marker requires specific reagents and implementation features. Therefore, the result is provided within 6-7 days.
The tumor marker for intestinal cancer Tu M2-RK is different from others. To conduct the study, the patient's stool is needed. Before this, you should not use laxatives or an enema to make the analysis more informative. Several particles are isolated from different sections of the material and the concentration of Tu M2-RK, a special substance that characterizes the metabolic processes of the tumor, is determined.
To diagnose a malignant process using tumor markers, special care is needed. The permissible error in the laboratory is 15-20%.