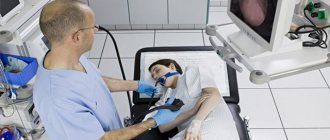
Questioning the patient
The first thing a patient begins to question is the symptoms. It is important to establish when signs of the disease appeared, whether self-medication was carried out, and if so, how. People with esophageal diseases typically complain of difficulty swallowing and pain behind the chest or back.
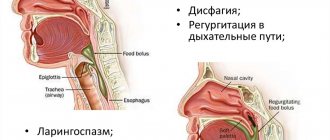
Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing). Discomfort can occur every time you try to swallow something, regardless of the structure of the food. Sometimes even swallowing saliva becomes impossible. Preesophageal dysphagia (lump in the throat) is a consequence of muscle diseases and disorders of the central nervous system. Most often characterized by a sensation of a lump in the throat. Esophageal indicates impaired motility of the esophagus; any movement of food is difficult, regardless of its consistency. Patient complaints of dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) when eating solid food sometimes indicate possible infectious, chemical, fungal, bacterial, or physical damage. Progresses gradually.
Odynophagia (pain in the chest or back). More often appears when there is difficulty swallowing. The cause may be not only impaired motility of the esophagus, but such an unpleasant phenomenon as damage to the mucous membrane in the form of ulcers and erosion. Esophageal cancer and gastroesophageal reflux disease cannot be excluded. For a healthy person, the problem is solved by simply drinking water; for a sick person, this will only aggravate the problem.
Imaging diagnostic methods
Instrumental methods in making a diagnosis are of primary importance. There are several of them, and the doctor chooses which method to prescribe after suspecting a particular pathology of the esophagus.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound (ultrasound) is the most common method for diagnosing the whole body. Examination of the esophagus in this way is not only effective, but also does not in any way threaten the patient’s health. In addition, as a result, the doctor receives the most accurate visualization compared to other diagnostic methods.
The following examination is performed using ultrasound:
- lymph nodes are analyzed (their structural changes, size, location);
- the walls of the esophagus and tissue structure are studied;
- the condition of the blood vessels is determined;
- a violation of the motility of the organ walls is visible.
An ultrasound will help identify not only the disease, but also the stage of its development. There are a number of indications for which the doctor will prescribe this research method:
- heartburn of unknown cause;
- achalasia (weakening of the sphincter between the esophagus and stomach);
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- cancerous tumors;
- polyps;
- hernias;
- ulcerative lesions.
Ultrasound examination is recommended not only when a disease of the upper digestive system is suspected, but also as a preventive measure.
We recommend finding out why gluten is used in baked goods and why it is dangerous.
Read: what are the symptoms of dyspeptic syndrome?
Esophagomanometry
Esophagomanometry or manometry is a diagnostic test method that allows you to evaluate the coordination and contractile strength of the walls of the esophagus. During the diagnosis, the doctor will gradually examine and evaluate the interaction of the functioning of the muscles of the esophagus during swallowing.
Using manometry, the doctor will be able to determine:
- lesions of the esophageal mucosa;
- organ abnormalities;
- weakening of the motility of the sphincter and the organ itself;
- development of diaphragmatic hernia.
In addition, the diagnostic method will help to identify the possible involvement of esophageal pathologies in the development of diseases such as diabetes and scleroderma.
Indications for the procedure:
- disturbances in the swallowing process;
- heartburn on a constant basis;
- uncontrollable drooling;
- belching air;
- pain when swallowing;
- chest pain;
- suspicion of erosion, neoplasms, ulcers, polyps;
- when you feel a lump in your throat;
- severe cough (especially at night).
To make the procedure painless, local anesthesia is used in the form of a spray or lubricant containing xylocaine. Diagnosis is carried out in two ways: through the oral cavity or nasal passages. The probe is inserted until the sensors are in the esophagus.
We advise you to read how rotavirus infection is treated in children.
Read: what is achlorhydria.
Find out what are the symptoms of dirty hand diseases.
Objective methods for examining the esophagus
An initial examination and palpation allow the doctor to decide on further diagnostic measures for the diseased esophagus.
Diagnosis of esophageal diseases begins with a general examination and local examination. During the general physical examination of the patient, attention is paid to the larynx. The color and condition of the mucous membrane are important. Often an alarming signal is the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth, which we habitually ignore. It is necessary to check whether there are any deviations in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system. Additional signs that may be detected during a general examination: exhaustion, roughening or discoloration of the skin, the presence of bulges, temperature, facial expression disturbances, nervous disorders, swelling and venous patterns.
Local examination of the esophagus consists of palpation of the lymph nodes, palpation of the neck, radiography, esophagoscopy, percussion (tapping and listening). When the esophagus is narrowed, auscultation (listening to the sound as it passes through the esophagus) is effective.
List of the most informative examination methods
The most relevant examination methods today in gastroenterology:
- visual survey and examination of the patient;
- X-ray examination;
- gastroscopic examination;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound examination of the esophagus.
Each of these methods has its pros and cons. Many patients have a question about how to check the esophagus and larynx in such a way that there is no discomfort or even pain. In fact, modern examination methods are quite painless, and if the basic rules of the procedure are followed, only mild discomfort may occur.
X-ray examination of the esophagus
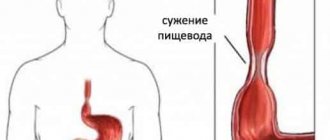
It is a common means of diagnosing the esophagus. Thanks to radiation examination, it is possible to identify pathological changes in the structure of this organ and draw conclusions about the motor disorders present. There are many radiography techniques, such as orthodiagraphy (used to detect deformation of the esophagus), teleradiography (the radiograph is viewed using a fluorescent screen), teleradiography (monitors the avoidance of foreign body deformation), stereoradiography (achieves a three-dimensional picture, determines the location of pathologies), X-ray kymography ( notes peristaltic movements) and others.
Before taking an x-ray, it is necessary to consume barium sulfate in the form of a solution, sometimes iodine lipol is added to it. This makes it difficult for X-rays to penetrate. The procedure is preceded by careful preparation. It is carried out exclusively on an empty stomach. During the x-ray, the patient's lower body is raised slightly higher. It would be prudent to prepare accurate local photographs in case of dyspepsia, suspected induration, malignant tumors, achalasia or foreign bodies.
Computed and spiral tomography of the esophagus
Indispensable for identifying tumors, metastases, deviations in the thickness of the walls of the esophagus or enlarged lymph nodes. Computed tomography is also a radiation scan, but unlike conventional fluoroscopy, thanks to scattered x-rays, it provides a detailed image. The rotating scanner looks like a large ring, inside of which there is a special table. Before the procedure, it is necessary to use special contrast liquids externally or externally; as a rule, they contain iodine.
Spiral tomography is also based on the radiography method, but it is more modern and high-tech. The method consists of synchronous movement of the tomograph in a spiral, with simultaneously moving sensors. The devices convert the received information into digital information. The specialist independently sets the speed and movement parameters of the scanner. Its main advantages are accurate 3D models, accelerated scanning process, minimal radiation and detection of the most subtle changes. Using this method, almost all internal organs are examined and checked for diseases.
Esophagofibroscopy allows you to see the condition of the esophageal mucosa and take biomaterial.
Examination of the patient
Examination of the esophagus consists of general examination and palpation. In this case, special attention is paid to examining the larynx, its condition, and the smell from the oral cavity. A general examination is of no less diagnostic importance: the patient’s degree of fatness, skin color and texture, facial expressions, body temperature, swelling.
Local examination of the esophagus includes palpation of the lymph nodes, neck, auscultation and percussion, as well as instrumental diagnostic methods:
- radiography;
- daily pH measurements;
- computed and spiral tomography;
- esophagofibroscopy.
With painful shock, pale skin is observed, with oncology and hypochromic anemia there is yellowness, with esophagitis there is hyperemia, and with large formations that cause hypoxia there is cyanosis.
The presence of pain is indicated by a grimace on the face and anxiety of the patient. An unnatural position of the body or head with a forward tilt indicates a possible diverticulum or foreign body. The patient in these conditions tries not to make body movements that cause him pain.
The lethargic and indifferent state of the patient signals septic or traumatic shock (for example, with a burn or mechanical perforation of an organ by a foreign body, massive bleeding, a state of severe intoxication).
X-ray of the esophagus
The manipulation is carried out on an empty stomach. Before undergoing radiography, the subject must take a contrast agent (barium sulfate solution). This is explained by the fact that not all organs of the gastrointestinal tract are capable of blocking X-rays, and barium makes it possible to visualize motor functions and contours of organs.
This method is necessary if the presence of neoplasms or foreign bodies is suspected, as well as with achalasia. The procedure for radiography of the esophagus and stomach does not require lengthy preparation. You should refrain from eating for about eight hours or skip breakfast.
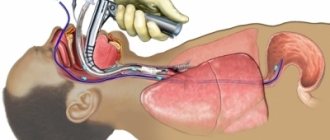
Esophagofibroscopy
This highly informative research method helps to find out the cause of pain, dyspepsia and dysphagia of the esophagus. It can be used to determine the presence of varicose veins, tumor formation, and bleeding from the esophagus. It is carried out both for the purpose of diagnosing the esophagus and for providing emergency assistance. Thanks to the method, it is possible to diagnose cancer formations on the walls of the organ and pathological changes in the lymph nodes.
The method makes it possible to determine the condition of the inner lining of the esophagus and obtain material for histology. The manipulation is carried out by qualified specialists under local or general anesthesia. The method requires preliminary preparation of the patient.
Diagnosis occurs by introducing an ultrasound sensor through the larynx to visually examine the mucous membrane and collect biological material for histology. The endoscope has high ultrasound frequencies that detect minimal deviations from the norm, which makes esophagoscopy one of the most highly informative research methods.
Daily pH-metry
The method helps, by measuring the pH level, to determine the nature and severity of esophageal reflux. To do this, a probe with a sensor of one to three electrodes is inserted through the larynx and fixed in a certain place.
The sensor records changes in pH in the lower part of the esophagus during the day. The data is subjected to computer analysis, and on its basis, its compliance with the norm is established.
Bernstein test
Acid perfusion is used when other methods do not show changes in the mucous membrane, but the patient feels dyspepsia, odynophagia, and dysphagia. The method consists of introducing saline and HCl solution into the larynx through a probe alternately at the required speed. In the presence of reflux esophagitis, discomfort and pain in the chest occurs due to irritation by acid.
Esophagotonokymography of the esophagus
The essence of the method is to obtain images that record decreased tone and contraction of the esophageal muscles. In this way, the initial form of dysphagia, hernias and muscular pathologies of the esophagus without severe symptoms is diagnosed.
During the study, a multichannel probe with a catheter or rubber balloon is used to measure intraesophageal pressure. The gastroscopy method allows you to obtain complete information about all possible decreases in the muscle tone of the sphincters.
Computed and spiral tomography
The study is used to diagnose neoplasms and metastases, enlarged lymph nodes, and determine wall thickness. This diagnostic method is also radiation, but unlike X-rays it allows you to obtain a higher quality image. The procedure involves preparing the patient for the study, which consists of administering externally and internally contrast solutions containing iodine.
Spiral tomography is a method of x-ray examination. During it, the tomograph moves in a spiral, creating highly accurate 3D models. The devices automatically convert the received data into digital form. With the help of such a study, pathologies of almost all internal organs are diagnosed. The method is characterized by high information content and accuracy of research with a minimum degree of radiation from devices.
It is used for a comprehensive diagnosis of the esophagus, determining the exact location and boundaries of the lesion or the presence of a foreign body. It is used as an additional research method if previous measures did not give the desired result.
Chromoendoscopy method
The method reveals pathological changes in the esophageal mucosa using staining with Lugol's solution, phenol, and methylene blue. The procedure helps determine the location of the lesion by changing the shade of the tissue. It is used primarily for the diagnosis of oncological tumors.
Esophagofibroscopy
It is carried out both for the purpose of diagnosing the esophagus and for providing first aid. The gastroscopy method is reliable. Helps to accurately determine the cause of dysphagia and odynophagia. Determine pathologies and locations of lesions and bleeding. Esophagofibroscopy will make it possible to view the condition of the esophageal mucosa, conduct histological studies, biopsy, and obtain smears. The procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia and only by a highly qualified specialist. Requires preliminary preparation of the patient.
Gastroscopy of the esophagus - is it really that scary?
This test usually frightens patients. The very fact that a tube with a tiny camera will be pushed into the larynx all the way to the stomach causes psychological rejection. Therefore, patients often ask the question of how to check the esophagus without gastroscopy. In most cases, the doctor manages to persuade the patient to perform it, since EGDS is by far the fastest and easiest way to assess the condition of the esophagus and stomach.
Carrying out an endoscopy takes only about 10-15 minutes, taking into account all the preparations. If the patient follows the instructions of the gastroenterologist, the procedure will be painless and will not entail negative experiences.
Endoscopic ultrasound examination of the esophagus
Only thanks to this method can one judge the appearance of neoplasms on the walls of the esophagus, stomach or duodenum. Its results help determine the degree of membrane damage and adverse changes in the lymph nodes. This study is carried out by inserting a sensor into the esophagus through the larynx, which is necessary for visual inspection of the mucous membrane and sampling of biomaterial, which makes it possible to conduct histological and bacteriological studies. The endoscope has ultra-high frequency ultrasound that penetrates deep into tissue and shows minute changes in detail, which is an incredible achievement compared to other methods. Endoscopy, as a type of gastroscopy, is recommended to detect bleeding from the upper lobe of the esophagus, varicose veins, and malignant tumors. Prescribed for chest pain, dyspepsia, and dysphagia.
The rigid method of esophagoscopy is used to remove foreign bodies, neoplasms in the esophagus, and to stop bleeding.
Esophagoscopy with a rigid esophagoscope
A rigid esophagoscope during gastroscopy is used to remove foreign bodies, stop bleeding, divide tumors (for example, by using a laser), as well as to influence the membrane or, if necessary, undergo surgical interventions. Before the procedure, the patient is given pain relief with special medications. The patient's head is tilted back and he is asked to swallow if possible. And although esophagoscopy is an effective method, it is not suitable for everyone. People suffering from narrowing of the esophagus, chemical burns, aortic aneurysm, cardiovascular diseases, goiter, hemophilia, nervous disorders, and diseases of the respiratory system will have to think about other methods.
Esophagotonokymography of the esophagus
The essence of esophagotonocymography is to record graphic images of contractions and changes in the tone of the walls of the esophagus. Diagnoses achalasia at an early stage, other muscle diseases, hiatal hernia, the symptoms of which may not yet have fully manifested themselves. To do this, use a multichannel probe with a rubber balloon or catheter that measures the pressure inside the esophagus. Can provide comprehensive information about any violations of muscle tone and esophageal sphincters, regardless of their condition. Refers to gastroscopy methods.
Acid measurements in the esophagus are made to monitor gastric secretion and its effect on the organ.
Causes of development of esophageal pathologies
The reasons why certain pathologies of the esophagus develop:
How is the esophagus checked if for some reason access directly to the larynx is difficult? For this, there are methods of external examination - for example, computed tomography or radiography do not require direct access to the organ. Many patients are afraid of endoscopy and are interested in how to check the esophagus and stomach without gastroscopy. In fact, endoscopy can be completely painless if the procedure is performed by a competent specialist and the patient follows all the rules of the examination.
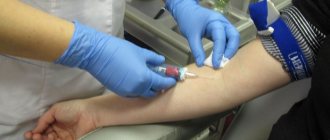
pH-metry of the esophagus
Allows you to determine the intensity and nature of esophageal reflux using pH level measurements. A special probe with a sensor, having from one to three electrodes, is inserted through the larynx and stops 5 cm before the cardiac part of the stomach. The sensor's task is to record daily changes in pH in the lower part of the esophagus. Next, they are processed by computer, and the obtained data is checked for compliance with standard indicators. A decrease in pH levels increases pain. To make the procedure more comfortable, a special electrode paste is applied to the patient’s skin.
Bernstein test
In other words, acid perfusion. It is used when changes in the mucosa are not noticeable visually, but the patient experiences dysphagia, odynophagia, and dyspepsia. Through a nasogastric tube, an isotonic saline solution and a weak solution of hydrochloric acid are alternately injected into the larynx at a set rate. As a result, a contrasting sensation of pain appears when exposed to an acid solution. A sign that esophageal reflux esophagitis is present will be the appearance of pain and burning sensation in the back and sternum. Sample error up to 3%.
Instrumental research methods
Esophagoscopy
This is the most reliable method for diagnosing the causes of dysphagia or pain and identifying structural changes in the esophagus and the location of bleeding. At the same time, a biopsy of mucosal areas is performed for histological examination. Esophagoscopy is also used as a treatment method to remove foreign bodies, coagulate bleeding areas, target tumors with laser radiation or bipolar electrocoagulation, and widen narrowings of the esophagus.
Bernstein test
Used for the diagnosis of esophagitis, it is carried out by alternate perfusion of the esophagus through a nasogastric tube with saline and a neutral 0.1% hydrochloric acid solution at a rate of 6 ml/min. The appearance of a burning sensation in the lower third of the sternum at the time of perfusion of an acidic liquid indicates a pathology of the esophagus.
X-ray examination
An X-ray examination, carried out according to a standard technique with the use of a barium mixture, video and cine-radiography, allows us to identify pathological changes (for example, strictures, congenital esophageal membranes) and establish motor disorders (achalasia, spasm of the upper esophageal sphincter).
Esophageal manometry (esophagomanometry)
Allows you to determine the pressure in the sphincter area and the coordination of propulsive movements of the esophagus, and detect changes in contractile activity. The method is used for dysphagia, heartburn and chest pain to diagnose achalasia, diffuse esophagospasm, hypo- and hypertension in the lower sphincter area. Use 3-4 thin catheters filled with water, attached to a pressure recorder, which are inserted through the nose or mouth into the lumen of the esophagus and further into the stomach. The probes are then gradually withdrawn by 1 cm each time and the pressure from each centimeter of the esophagus and pharynx is recorded between and during swallowing. The highest pressure is recorded in the area of the upper and lower sphincters, which relax when swallowing. During the swallowing movement, a wave of peristalsis of the sphincter and esophagus occurs. Esophageal manometry can also identify neuromuscular abnormalities of the upper esophagus and the motor response of the lower sphincter in reflux esophagitis.
Radioisotope research
The method is not so widely used, but it has advantages, because it helps to obtain clear contrast data that is not available with other methods and is at the same time relatively harmless. Another advantage is the lack of preliminary preparation. Radioisotope research is based on the use of radioactive phosphorus, which accumulates in malignant tumors and is detected by specially designed sensors. This is a differential method for diagnosing cancer.
The appearance of unpleasant symptoms during the digestion process, such as pain when swallowing, dyspepsia, odynophagia, indicates the presence of diseases of the esophagus. Don't expect them to go away on their own. It is better to contact a specialist who will examine and prescribe a diagnosis.