Briefly about the main thing
Thrombectomy is a minimally invasive (low-traumatic) operation that is performed to eliminate a blood clot formed in hemorrhoids.
This intervention is performed for acute hemorrhoids. Thrombectomy is performed under local anesthesia and takes no more than 10 minutes . The procedure has the shortest list of contraindications and does not require hospitalization of the patient. You can go home immediately after surgery .
The recovery period passes quickly and is not associated with serious restrictions. It will be necessary to follow basic hygiene rules: wash the anal area with warm water after each bowel movement. You should also follow all the doctor’s recommendations: ___• follow a diet, ___• limit physical and nervous stress, ___• avoid excluding thermal procedures, ___• take prescribed medications, ___• carry out local treatment of the postoperative wound.
Causes of thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins
Thrombosis can develop as a consequence of an acute, first-time attack of hemorrhoids, as well as as a complication of chronic hemorrhoids. The likelihood of developing thrombosis in chronic pathology increases with increasing “length” of the disease and the size of the nodes.
An attack can be triggered by: ___• chronic stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea, constipation alternating with diarrhea), ___• increased physical activity, ___• labor, ___• consumption of spicy food and/or alcohol, ___• hypothermia, overheating.
The development of acute hemorrhoids is promoted by all conditions accompanied by an increase in intra-abdominal pressure - from pregnancy to chronic cough and obesity.
Another factor in the occurrence of hemorrhoids is stagnation of blood in the veins of the pelvis, which often occurs as a result of a sedentary lifestyle and “sedentary” work.
Mechanism of blood clot formation
Thrombosis of external hemorrhoids occurs more often. It is extremely rare that the process spreads from external to internal nodes. Even less commonly, it occurs isolated in internal nodes.
Thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid occurs in both acute and chronic processes. In both cases, the pathology develops as a result of a combination of three factors: ___• slowing blood flow in the node, ___• blood thickening, ___• damage to the vascular network of the hemorrhoid.
Signs of thrombosis
___• The main symptom of thrombosis is acute, excruciating pain that prevents normal bowel movements. The pain syndrome intensifies many times over with straining, movement, and also in a sitting position. In severe cases, the pain takes on a pulsating character and, depending on the location of the node, can radiate to the leg, inside the rectum or to the external genitalia. ___• Bleeding often occurs, which varies in intensity - from individual drops on the surface of the stool to a trickle of blood during bowel movements. ___• Thrombosis of the internal node causes the sensation of a foreign body inside the rectum. Since the bleeding injured node comes into contact with feces, a secondary infection may occur. In such cases, mucous or purulent discharge appears and body temperature rises.
Removing a blood clot from a hemorrhoid
Knowing that hemorrhoids are a manifestation of varicose veins, it is easy to understand what complications it can have if proper and timely treatment is not undertaken.
One of the serious consequences of advanced hemorrhoids is thrombosis, the acute form of which poses a danger to the patient. To treat it, thrombectomy of the hemorrhoid is used.
This is an operation with a minimal degree of surgical intervention and the fastest possible results.
When and how does thrombosis occur?
The main cause of hemorrhoids is the genetic predisposition of the venous walls to thinning and the formation of nodes in places of blood overflow. And conditions that result in blood stagnation contribute to the development of thrombosis. Such conditions may include:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- increased pressure in the abdominal cavity;
- regular constipation;
- poor nutrition. regular constipation contributes to the formation of blood clots in hemorrhoids; unhealthy diet causes the formation of blood clots in hemorrhoids
There are three stages in the development of the disease:
- 1st is characterized by small nodes of a tightly elastic structure, which are painful upon digital examination;
- 2nd is expressed by acute pain, enlarged nodes that can fall out of the rectum, redness of the inflamed area;
- The 3rd does not allow digital diagnosis due to severe pain, swelling and inflammation of the nodes, which acquire a bluish-red color.
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node can occur at any time during the development of hemorrhoids.
The disease is of particular concern to the patient at stages 2 and 3, when the nodes are large and with the slightest straining with lifting heavy objects or bowel movements, they fall out of the rectum.
If after this the anal sphincter contracts, it will block the blood flow in the pinched node. This action leads to the formation of a thrombus - a clot of coagulated blood.
The site of the blood clot becomes inflamed, swelling appears, which is accompanied by severe pain. All this can lead to tissue necrosis and blood poisoning.
How to understand that node thrombosis has occurred
In case of complications of hemorrhoids, you should not postpone visiting a doctor; you should immediately seek qualified help from a proctologist. Without treatment, a blood clot may become infected or a bleeding ulcer may form.
A node thrombus can be identified by symptoms, which are the same at all stages of the disease, differing only in the degree of their severity:
- persistent pain;
- difficulty in bowel movement and gas release;
- swelling and discoloration to dark red or black in the area of the pinched node;
- discharge of mucus and blood from the anus;
- intoxication of the body after inflammation of the node;
- increased tone of the anal sphincter muscles was noticed.
After prolapse of thrombosed nodes, digital examination is impossible due to acute pain. Instrumental examination using a rectal speculum and rectoscope is carried out in any case using local anesthesia.
Indications for thrombectomy
After examination, diagnosis and assessment of the patient’s condition, the proctologist determines the method of treatment - conservative or surgical.
If the thrombosed node is small, you can try to relieve symptoms with medications with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and anticoagulant effects, as well as phlebotropic agents. This treatment helps restore blood flow in the node, increase the tone of the vascular walls and reduce capillary permeability.
In case of thrombosed nodes, surgical intervention is prescribed if:
- conservative treatment does not give positive results;
- the patient's condition worsens;
- the pain becomes unbearable;
- thrombosis manifested itself in a single external node, and there is a risk of necrosis.
Under these conditions, assistance is provided to the patient in the form of an operation, thrombectomy of the hemorrhoid is performed, which is the removal of a blood clot from a blood vessel.
How to prepare for surgery
After making a diagnosis and prescribing thrombectomy, the doctor refers the patient to a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- general blood analysis;
- tests for infectious diseases;
- Analysis of urine;
- fluorography;
- electrocardiography.
As with any operation on the rectum, it is necessary to carry out cleansing measures. This is done with laxatives or an enema 2-3 hours before surgery. The last meal should be 16 hours before surgery.
If you have chronic diseases, additional examination may be required.
How is thrombectomy performed?
The procedure is very simple, it takes only 10–15 minutes, so it is performed on an outpatient basis in a special clinic or proctologist’s office. The exception is cases complicated by increased inflammation and elevated temperature.
- The patient is placed in a proctology chair.
- The inflamed node and the surrounding area are treated with local anesthesia.
- Using a scalpel or laser, an incision is made on the surface of the prolapsed node no larger than half a centimeter in size to remove the blood clot.
- Usually, along with the blood flow, the clot comes out on its own. But it is possible to use a surgical instrument to remove it from the blood vessel.
- After suturing, the surgical site is cleaned and a sterile napkin is applied.
The pain caused by the formed blood clot goes away almost immediately when it is removed. Blood circulation in the node is restored after three minutes. After four to six days the wound heals.
During this time, it is necessary to carry out hygienic procedures after each bowel movement, treat the surgical site with an antiseptic and apply dry sterile wipes to it, and use medications prescribed by the doctor.
Prevention of thrombosis
In each case, the doctor, giving recommendations for the prevention of thrombosis, approaches the patient individually, taking into account the condition of hemorrhoids and the body as a whole.
Particular attention should be paid to such aspects of life as:
- nutrition, because it is important to avoid constipation and not create conditions for the formation of blood clots;
- physical activity - they must be excluded so as not to increase intra-abdominal pressure due to heavy lifting;
- hypothermia - avoid such temperature conditions when the lower part of the body freezes.
It is also important to understand that thrombectomy is not a treatment for hemorrhoids. It eliminates pain and the risk of blood poisoning, solving only a local problem. The further condition of hemorrhoids largely depends on the patient himself.
When is thrombectomy necessary?
Indications for surgery
Most cases of acute thrombosis of hemorrhoids (uncomplicated thrombosis, small size of the node) respond well to treatment with conservative methods. The main thing is to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Surgical procedures are performed if the period from the onset of the disease is 48-72 hours. If more time has passed since the onset of thrombosis, the doctor prescribes conservative treatment followed by surgical treatment. Surgical removal of a thrombosed node is carried out at a later stage from the onset of the disease in the following cases : ___• conservative therapy was unsuccessful, ___• acute pain syndrome, poorly controlled by standard painkillers, ___• symptoms of intoxication (general weakness, fever, headache), ___ • contraindications to the use of thrombolytic agents (pregnancy, lactation), ___• large size of the hemorrhoid.
The decision on surgical intervention is made by the doctor after an examination, which will reveal contraindications to surgery. Another goal of diagnostic manipulations is the choice of surgical intervention method.
Who is indicated for hemorrhoidal thrombectomy?
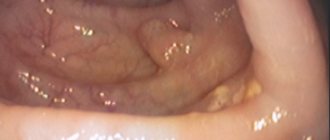
Thrombosis of hemorrhoids is one of the most unpleasant, very painful and difficult to tolerate complication of hemorrhoids. As a rule, thrombosis occurs when hemorrhoids prolapse from the anus, which is observed in the later stages of the disease. Thrombosis causes the patient significant physical suffering and completely knocks him out of the usual rhythm of life. Therefore, this situation requires urgent medical attention to help relieve acute symptoms. One way to quickly eliminate the symptoms of thrombosis is thrombectomy of the hemorrhoid, which is used for external hemorrhoids. This intervention is a surgical operation performed under local anesthesia. Its essence lies in the fact that through a small incision, no more than half a centimeter, a blood clot is removed from the thrombosed node. The pain goes away almost immediately, and within a few minutes the knot subsides.
The mechanism of thrombus formation in hemorrhoids
When a hemorrhoid prolapses from the rectum, part of it ends up outside the anal sphincter, which is a fairly strong muscle. The sphincter is capable of spontaneously contracting at any time and blocking the blood flow in the prolapsed node.
As a result of a violation of the venous outflow, a thrombus, that is, a clot of coagulated blood, forms inside the prolapsed and pinched node.
Symptoms of thrombosed hemorrhoids
- The main symptom of thrombosis is acute pain, which is the result of pinching and increasing swelling of the prolapsed hemorrhoid.
- The color of the node changes from bluish to deep purple or almost black. Severe swelling almost immediately spreads to the entire perianal area.
- Mucus is released from the anal canal, often with a strong, unpleasant odor.
- The passage of gases from the intestines becomes difficult, and defecation becomes almost impossible.
- In the case of inflammation, which is observed in most cases of thrombosis of nodes in hemorrhoids, symptoms of intoxication of the body are added.
Drug treatment of blood clots
In cases where the thrombosed node is small in size, you can try to solve this problem conservatively, that is, with the help of medications.
Since the main goal in this case will be to reduce pain and relieve inflammation caused by the formation of a blood clot in the lumen of the hemorrhoid, drugs with anticoagulant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects are used for conservative treatment. Sometimes this is enough to restore blood circulation in the node.
Surgical removal of a blood clot
Conservative therapy may not be effective enough and, as a result, the patient’s suffering may become literally unbearable. In such cases, thrombectomy is performed, that is, removal of a blood clot from the lumen of a thrombosed hemorrhoid. This operation is not a radical method of treating this disease, but can help quickly and effectively alleviate the patient’s condition. To perform a thrombectomy procedure from a hemorrhoid, there is usually no need to go to the hospital. As a rule, it is carried out on an outpatient basis, in a proctology clinic or a proctologist's office.
Thrombectomy technique
- First, the patient is injected into the area of the thrombosed node with an anesthetic drug. General anesthesia is not required to perform thrombectomy; local anesthesia is sufficient.
- Then, a small incision is made on the surface of the thrombosed hemorrhoid that has fallen out of the anal canal, sufficient to remove the blood clot.
- Through this incision, with the flow of venous blood flowing out, the thrombus usually comes out on its own. Sometimes it may need to be removed with a surgical clip.
- The patient's condition improves almost immediately: the swelling subsides, the pain decreases and soon disappears completely. After some time, the inflammation also stops.
- The incision wound heals completely in most cases within four to five days. During this period of time, it is necessary to apply a clean bandage to the knot and change it regularly after contamination.
Indications for thrombectomy
This intervention is indicated for thrombosis of single nodes. It is carried out in cases where conservative therapy is not effective enough or the pain tormenting the patient becomes unbearable.
It should be noted that thrombectomy is a quick solution to a local problem, but nothing more; this procedure does not radically cure hemorrhoids. In the future, the patient who has undergone thrombectomy needs complex treatment and compliance with all preventive measures.
OGemorroe.com>
Types of operations
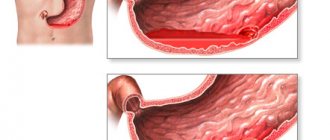
Removal of a blood clot for external hemorrhoids
Removing a blood clot for external hemorrhoids is a simple operation that lasts only a few minutes. The doctor makes a small incision over the blood clot. Then the blood clot is removed with tweezers or a clamp; the wound is not sutured. The inflammatory edema subsides almost immediately, the pain subsides, and the patient’s general condition improves.
According to indications, a more complex operation can be performed - excision of an external hemorrhoid with blood clots , which is also performed under local anesthesia and does not require the patient to be hospitalized. During excision, the pathological element is removed, which reduces the risk of recurrent thrombosis.
Removal of a blood clot for internal hemorrhoids
Thrombosis of internal hemorrhoids is much less common and, as a rule, develops in the later stages of the development of the process (III-IV stages of hemorrhoids).
Treatment in this case is conservative. After stopping the acute process, treatment is carried out aimed at removing internal hemorrhoids (hemorrhoidectomy).
Indications and contraindications for thrombectomy
Despite the fact that thrombectomy of the hemorrhoidal node is not a complex operation and in most cases does not require hospitalization, it requires the presence of absolute indications, which, first of all, include signs of thrombosis of the external hemorrhoidal node. You can recognize the beginning of such a process by the following symptoms:
- sudden appearance of a dense and painful formation in the anus;
- sharp pain in the perianal area;
- swelling of the soft tissues around the anus;
- spread of inflammation to the soft tissue around the hemorrhoid (sometimes with suppuration);
- increased body temperature (does not appear in all cases).
Patients are recommended to undergo surgical removal of a blood clot from the hemorrhoid if the listed symptoms cannot be eliminated by conservative methods, as well as if the condition rapidly worsens:
- with rapid progression of inflammation with suppuration and signs of tissue infection;
- when signs of tissue necrosis and abscess formation appear;
- if bleeding occurs that cannot be stopped with medications;
- with extremely severe pain that cannot be eliminated by conservative methods.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hemorrhoidal thrombosis is not difficult. The diagnosis is made by external examination of the anal area .
If the proctologist decides on surgical intervention, it will be necessary to take tests : ___• general blood test, ___• coagulogram, ___• blood glucose level.
It is necessary to tell the attending surgeon about all medications taken, since some medications (oral contraceptives, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.) affect blood clotting.
Prevention of blood clots
Many people believe that it is enough to follow a diet and such a problem will not happen. Yes, nutritional correction plays a big role, but the following recommendations from experts “work” specifically against the formation of clots:
- Do not stay in a sitting or lying position for a long time - hemorrhoids “love” physical inactivity. If you refuse minimal physical activity and do not take regular walks, this can cause prolapse and strangulation of the hemorrhoid.
- Avoid constipation. And this is where diet and regular exercise will help. If problems with bowel movements occur regularly, then you should inform your doctor about this. Most likely, laxative medications and cleansing/therapeutic enemas will be prescribed.
- Don't carry heavy things. If your work activity requires it, you will have to change it.
Contraindications
___• The operation is not performed if the patient’s condition is extremely serious (general exhaustion, complications of cardiovascular diseases, sepsis). ___• Surgical interventions are not prescribed for severe pregnancy (severe anemia, poorly controlled early toxicosis with dehydration, late toxicosis with generalized edema, etc.).
Since thrombectomy is a minimally invasive (low-traumatic) operation, the procedure can be prescribed after the patient’s condition has been stabilized. The decision about surgery or its inadmissibility is made individually, taking into account all risk factors.
Preparation for the procedure
If the doctor decides to undergo thrombectomy, the patient is prescribed a diet that excludes foods that cause gas formation in the large intestine (cabbage, legumes, fresh fruits and juices from them). The ban also includes products that cause a rush of blood to the rectum and/or have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane (smoked meats, spicy foods, alcohol).
Immediately before the procedure (in the morning and evening before the operation), you will need to cleanse the intestines using a Microlax microenema.
Preparation for thrombectomy is carried out when the patient's condition allows it. In case of severe pain and an impressive size of the node, bowel cleansing is not performed, and in the event of a threat of severe complications, surgical removal of the blood clot is carried out on an emergency basis.
How is the operation performed?
The procedure can be performed in a gynecological-style chair or on a couch and takes a few minutes. First, doctors give an anesthetic injection that “freezes” the tissue, just like in a dentist’s office. Therefore, the patient is conscious, but does not feel pain.
The surgical intervention takes several minutes and involves three manipulations: ___• opening the affected node (small incision), ___• removing the blood clot, ___• stopping the bleeding (the wound can be sutured, but more often it is not sutured)
After the procedure you can go home.
The exception is those cases of thrombosis when severe complications occur (gangrene of the node, paraproctitis, severe bleeding) that require hospitalization.
Complications after removal
Surgical treatment is the main way to get rid of complicated hemorrhoids. It allows in most cases to avoid progression of the disease. Just like any operation, removal and ligation of nodes cannot be completely safe.
Hemorrhoidectomy
Complete excision of hemorrhoids can be performed in several ways. With the Milligan-Morgan operation, complications are more common, but it is the most radical method, after which hemorrhoids rarely recur . More gentle techniques are easier to tolerate, but often require repeated interventions.
Early consequences of surgical treatment include:
- bleeding;
- pain syndrome;
- penetration of infection into the postoperative wound, paraproctitis;
- swelling of the tissue around the anus
- retention of feces and urine due to pain and swelling.
Long-term complications are:
- intestinal fistulas,
- narrowing of the anus,
- rectal prolapse,
- recurrence of hemorrhoids.
One of the possible disorders is incontinence of intestinal contents due to weakening of the muscles of the anal canal. These conditions significantly worsen the quality of life of patients and often require repeated corrective surgeries.
After ligation
With this method of treatment, a latex ring (ligature) is placed on the stem of the hemorrhoid. It prevents the flow of blood into the hemorrhoid, so after 10-15 days it becomes dead and comes out along with the contents of the intestines.
The most common complication of ligation is severe pain that is not relieved by pain medications. This can happen when a section of the dentate line gets into the latex ring (it is innervated by the spinal cord). This requires cutting the ligature and reinstalling it.
Also, the ring can come off the knot with strong efforts during bowel movements. Complications include thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins and bleeding when the ligature ring ruptures.
Rules of behavior in the postoperative period
If the evacuation of hemorrhoidal blood clots was carried out against the background of the patient’s satisfactory condition, then the postoperative period does not provide for significant restrictions.
The following are prohibited: ___• physical activity, ___• thermal procedures (bath, sauna, beach holiday), ___• prolonged stay in a sitting or squatting position.
Products that cause a rush of blood to the pelvic vessels or irritation of the mucous membrane are excluded from the diet: spicy, salty, smoked foods and alcohol.
Food should be rich in fiber, which stimulates intestinal function (prunes, apples). It is not recommended to eat foods that can cause constipation (rice and semolina porridge, potatoes, pasta). If stool retention occurs, a mild laxative (for example, Forlax) is prescribed.
After each bowel movement, wash the anal area with warm water and change the sterile napkin. If suspicious symptoms appear (pain, bleeding, discharge from the wound), you should immediately consult a doctor.
How does a blood clot occur in hemorrhoids?
When a hemorrhoid node falls out of the rectal cavity, some of it ends up beyond the anus. The sphincter, which is essentially muscle tissue, is capable of spontaneous contraction at certain moments, thereby disrupting the circulatory system in the part of the prolapsed node. The result of impaired blood circulation is a thrombus, which is a clot formed from coagulated blood.
From the formed blood clots in the external nodes, thrombosis develops, and the following factors can serve as the reasons for the formation of blood clots and the further development of thrombosis:
- dehydration of the body;
- errors in nutrition;
- rapid increase in intra-abdominal pressure;
- hypothermia;
- diarrhea and inflammation of the anus;
- physical effort when lifting heavy objects;
- long stay in a sitting or standing position, without changing posture;
- surgical interventions;
- exposure to viruses and pathogenic microorganisms;
- bad heredity;
- playing sports that involve physical activity.
When performing such actions, there is an unjustified excessive load on the veins that supply the rectum or stagnation of blood in them due to circulatory disorders. All this is the reason for the formation of blood clots in strangulated nodes, which in themselves are painless, but can disrupt the natural blood flow in the veins and damage the vascular wall in them. As a result of the resulting inflammation, phlebitis develops, blood flow in the veins increases and swelling of surrounding tissues occurs. Due to the changes that have occurred, the sensitive nerve receptors are compressed, which causes severe pain. At this stage, the veins running in the rectum suffer the most; they are deformed from excessive pressure in them, stretched, and their walls become very thin. Facilitates the formation of blood clots in them and slows down the movement of blood, which is typical for this form of the disease.
Reviews from patients and recommendations from doctors
We analyzed online reviews of patients who underwent removal of hemorrhoidal thrombosis. The vast majority of patients were satisfied with the procedure. The most common impression: “The procedure itself is not as unpleasant as waiting for it.”
No reviews of complications of the operation were found. The most common complaint is pain in the area of the postoperative suture, which disappears after a few hours, but may reappear during bowel movements.
A more serious drawback is the likelihood of relapse. In order to avoid recurrent thrombosis, you must follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Relapse after surgery to remove hemorrhoids
After surgery, a relapse of the disease may develop. Relapse often occurs due to non-compliance with doctor's recommendations, poor nutrition, physical inactivity, chronic stress, lack of personal hygiene, in people with heavy physical labor, and athletes. The risk of developing a relapse a short time after surgery depends on the patient’s age, the severity of the disease, and the method of treatment. After surgery, a few years later, most patients experience re-development of hemorrhoids.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Thrombectomy is a low-traumatic method of treating acute thrombosis of hemorrhoids, which has both advantages and disadvantages. The method involves surgical intervention, so it is prescribed if conservative methods are contraindicated or ineffective.
Positive aspects of thrombectomy: ___• a short list of contraindications, ___• does not require hospitalization, ___• the shortest recovery period with a minimum number of restrictions, ___• minor side effects of the operation (pain, weakness, swelling), ___• complications are extremely rare.
Disadvantages of the method. Thrombectomy does not involve removal of the hemorrhoid, so recurrent thrombosis may develop. For this reason, in case of recurrent thrombosis, a more radical operation to remove thrombosed nodes (hemorrhoidectomy) is indicated.
How is the operation performed?
Thrombectomy is not a reason for admitting a person to a hospital - the proctologist performs the manipulations in his consulting room on an outpatient basis. Before the clot removal procedure, the patient must go through the preparatory stage:
- the night before and one and a half to two hours before the scheduled procedure, you need to do a full cleansing enema;
- dinner the day before should be no later than 18:00;
- You must come directly to the operation hungry.
Of course, the proctologist does not perform thrombectomy immediately after diagnosing the problem; the patient will be prescribed an examination - urine and blood tests (general clinical and biochemistry), an x-ray and an electrocardiogram.
The algorithm for performing an operation to remove a blood clot is very simple and does not require any special knowledge or many years of experience:
- An anesthetic is injected directly into the area of the problematic hemorrhoid.
- Using a scalpel, the proctologist makes an incision into the thrombosed lump - blood begins to actively flow out of it and, in most cases, a clot comes out along with it. If this does not happen, the specialist removes the thrombus with a surgical clamp.
- The wound is treated with an antiseptic and a sterile bandage is applied.
As soon as the blood clot is removed from the affected area, the patient’s condition will immediately improve - pain will disappear, swelling will go away, and the affected area will acquire a normal color.
The wound after an incision heals in a maximum of 7 days; no washing or irrigation is necessary. The only thing required is to wear a sterile dressing and change it regularly after contamination.
Prevention of relapse
Basic principles of prevention
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node occurs as a complication of hemorrhoids, therefore, prevention of relapse consists in preventing the occurrence of enlarged hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids are a disease with a hereditary predisposition. Therefore, if there has already been one attack, there is a high probability of relapse. However, the implementation of a negative scenario is possible in the presence of additional risk factors: ___• pregnancy, ___• taking hormonal drugs, ___• overweight, ___• constant diet violations: eating spicy and fatty foods, alcohol, ___• abuse of thermal procedures (bath and sauna) or regular hypothermia, ___• work involving prolonged sitting or heavy physical work.
Necessary precautions
Most often, acute thrombosis occurs as a consequence of prolonged bowel dysfunction (chronic constipation). Therefore, you need to achieve daily bowel movements with a diet rich in fiber.
It is advisable to refrain from physical and nervous overload, as well as from hypothermia and overheating of the lower half of the body. You should not abuse alcohol, as well as spicy, smoked and salty foods.
When working “sedentarily”, you need to take regular breaks, during which you should perform hemorrhoid-preventing exercises. Many chronic diseases can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids, so taking care of your health is a reliable prevention of thrombosis of hemorrhoids.
Dangerous for the development of hemorrhoids and obesity. With this pathology, intra-abdominal pressure increases, the rheological properties of the blood change, problems with stool arise, and hormonal levels are disrupted. Therefore, normal weight is not only beauty, but also health.
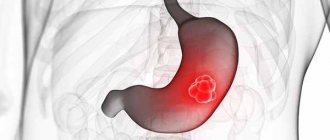
What is hemorrhoid thrombosis
Hemorrhoidal node
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node (hemorrhoidal thrombophlebitis) is a severe but common complication of hemorrhoids . Due to the delicacy of the clinical situation, patients develop the disease, hemorrhoids grow, fall out, become strangulated, and there are real risks of thrombosis and necrosis of rectal tissue.
Thrombosis is characterized by acute closure of the vascular lumen, obstruction or cessation of blood flow, and in the absence of emergency treatment leads to necrosis of intestinal tissue.
It is impossible to miss an acute condition, since hemorrhoidal thrombosis is accompanied by acute stabbing pain. Painkillers are ineffective, and patients are forced to see a doctor. Reduction and cessation of pain may signal the onset of necrotic changes.
Mechanism of occurrence
The occurrence of thrombosis in hemorrhoids is influenced by mechanical and vascular factors . In the first case, it is provoked by prolapse, displacement or compression of the hemorrhoidal node (bump), while in the second there is a disturbance of hemodynamics, a decrease in the elasticity and firmness of the venous walls, their stretching or damage.
Predisposing factors are not a direct cause of thrombosis , but significantly increase the risk of developing the clinical condition.
Provoking factors
It is impossible to reliably determine the reasons that could accurately and directly contribute to the development of acute blockage of the vascular lumen. Doctors believe that the preconditions are created by a number of main factors :
- lack of food discipline, violation of diet, alternation of fasting and overeating;
- pregnancy and lactation (especially gestation and childbirth with existing hemorrhoids);
- constipation and other stool disorders, difficulty defecating;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- intestinal infections;
- hypothermia.
, as well as other pathologies of the cardiovascular system, can provoke thrombosis of the veins of the rectum Excessive exercise, bad habits, varicose veins in the legs - all this can indirectly affect the development of thrombosis.
Is it possible to do without surgery?
If doctors recommended thrombectomy of the hemorrhoid, this means that conservative therapy is not indicated in your case. You should not try to treat thrombosis with “traditional” methods.
If treatment is inadequate or absent, complications may develop: ___• bleeding, ___• gangrene of the node, ___• paraproctitis (purulent melting of peri-rectal fatty tissue).
In some cases, the affected node may open on its own and free itself from the blood clot. At the site of the “bump,” a fold of skin is formed – an anal fringe, which causes unpleasant sensations (itching, weeping) and is an unpleasant cosmetic defect.
Indications for thrombectomy
After examination, diagnosis and assessment of the patient’s condition, the proctologist determines the method of treatment - conservative or surgical.
If the thrombosed node is small, you can try to relieve symptoms with medications with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and anticoagulant effects, as well as phlebotropic agents. This treatment helps restore blood flow in the node, increase the tone of the vascular walls and reduce capillary permeability.
In case of thrombosed nodes, surgical intervention is prescribed if:
- conservative treatment does not give positive results;
- the patient's condition worsens;
- the pain becomes unbearable;
- thrombosis manifested itself in a single external node, and there is a risk of necrosis.
Under these conditions, assistance is provided to the patient in the form of an operation, thrombectomy of the hemorrhoid is performed, which is the removal of a blood clot from a blood vessel.