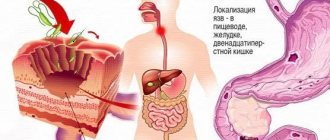
Erosion of the esophagus is caused by a disorder - the reflux of hydrochloric acid into the esophagus with subsequent destruction of the epithelium.
The harsh rhythm of life, constant nervous tension, and improperly organized nutrition sharply reduce the ability of city residents to protect themselves from infections. A drop in the level of immune defense does not allow the body to effectively counteract environmental aggression. Many diseases take on a chronic form and people try to control them, unaware that no less serious pathologies develop against their background, which for the time being do not manifest obvious symptoms.
Such diseases include erosion (inflammation and destruction) of the esophageal mucosa. This disorder develops as a concomitant pathology in many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or as an independent pathology.
Description of the disease
Normally, the stomach is separate from the esophagus, and food moves in only one direction - down into the stomach. Reverse movement in a healthy body is almost impossible.
With some violations of the structure of the organ or due to injury, the normal activity of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted and caustic gastric juice enters the esophagus. The organ mucosa, which is not adapted to the effects of a caustic substance, becomes inflamed and destroyed.
The danger of erosion lies in the vagueness of its manifestation - a person attributes painful symptoms to deficiencies in nutrition. Discomfort rarely occurs, the patient does not attach any importance to it, and does not go to the doctor - this does not allow the pathology to be diagnosed in time.
Esophageal erosion, like all diseases of this type, is well treated in the early stages of diagnosis. In the later stages, the consequences of the disease are deep destruction of the walls and bleeding. At this level of development of the pathology, a visit to the doctor is inevitable and treatment becomes complex and lengthy.
Erosion is not as common a disease as inflammatory diseases of the stomach and intestines, but its impact on the general condition of the body is just as serious.
The complexity of the disease is also that it:
- not recognized by the patient in a timely manner;
- Diagnosed only by hardware.
Erosion is considered as a concomitant disease of diaphragmatic hernia, which occurs due to pathological displacement of the abdominal organs.
What does it look like
When visualizing esophageal erosion, it is possible to record the severity and phase of the disease and determine the specific type.
The picture is as follows: the mucous membrane is inflamed, hyperemia and irritation are observed, you can clearly see foci of erosion, which in places are fused. In later stages, penetration of erosive lesions into the deeper layers of the mucosa and the formation of ulcers are observed. On the surface of the esophagus you can see scars after erosive lesions and ulcers, which cause narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus, its deformation and difficulty in swallowing.
Causes
Pathologies that provoke the disease (diaphragmatic hernia, traumatic injury to an organ or burn) are too general reasons. The true causes of destruction and inflammation of the walls of the esophagus are:
- inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract caused by viral or other infections;
- lack of vitamins and low immune threshold of the body, which causes tissue damage;
- disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- injuries caused to mucous membranes by the habit of eating too hot food;
- burns caused by the entry of caustic chemicals into the esophagus;
- disturbances in the functioning of the sphincters;
- previous surgical treatment;
- long-term treatment with certain medications (dopamine blockers, strong analgesics).
A diaphragmatic hernia (provoking erosion) occurs when the lower part of the esophagus with part of the stomach, and sometimes other abdominal organs, are displaced through a hole in the diaphragm, upward into the chest cavity.
Pathology occurs due to the following reasons:
- congenital or acquired high elasticity of tissues and ligaments of the esophageal opening;
- congenital malformation, in which the esophagus is too short and the stomach is in an incorrect physiological position;
- increased cavity pressure due to excessive physical labor and obesity, multiple pregnancies, age;
- neoplasms;
- weak muscle tone;
- diaphragm opening enlarged for various reasons;
- curvature of the spine (hump).
Erosion of the esophageal tube occurs as a concomitant disease with:
- inflammation of the duodenum 12;
- bile duct stenosis;
- cholelithiasis, caused by difficulties in the outflow of bile.
Important provoking factors for the occurrence of erosion are alcohol and smoking, which destabilize the state of the body.
Consequences
Esophageal erosion is a serious disease. Neglect is fraught with serious consequences and the occurrence of secondary pathologies. There is a possibility of developing:
- Bleeding. It is the most dangerous complication of esophageal erosion. Bleeding in an organ cavity occurs when a blood vessel in the organ wall is damaged. The pathological condition is revealed by vomiting mixed with scarlet blood. The condition is typical for young patients who abuse tobacco and regularly drink alcohol.
- Peptic ulcer disease. The disease can be acute or chronic with periodic relapses. This type of complication often develops in older people.
- Neoplasms. Erosion of the esophagus is often a prerequisite for the appearance of a tumor disease. There is a possibility of the formation of both benign and malignant tumors.
Esophageal erosions, if left untreated, develop into hyperplasia (increased cell growth). As a result, the cells begin to change internally, which leads to their degeneration into malignant tumors.
- Blood flow failure. As a result of erosive processes, thrombosis of the esophageal vessels, disruption of cell nutrition, and necrosis of tissue structures are possible.
- Disorders of the structure of the esophagus. Erosion of the esophageal tube often leads to the formation of connecting scars. Scars disrupt the normal structure of the esophagus, complicate the swallowing process, and cause problems with digestion of food.
Symptoms
Due to insufficiently manifested symptoms of esophageal erosion, it is difficult to diagnose the disorder in a timely manner, although some symptoms indicate it. Very often, patients complain of chest pain that resembles heart pain. Often unpleasant sensations of varying strength are localized in the abdominal cavity.
The pain gets worse:
- after eating and is combined with a feeling of fullness inside;
- when changing the position of the body (bending, running).
Additionally, the following symptoms appear;
- pain when swallowing;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor in the mouth;
- heartburn and belching;
- hiccups;
- increased nausea;
- bouts of vomiting.
None of them are clear signs of esophageal erosion, the symptoms of which are similar to inflammation of the stomach or duodenum, and therefore the disease is difficult to qualify.
Therefore, it is important for the patient to contact a specialist at the first signs of gastrointestinal disease and perform a hardware examination.
Types of erosion
A defect in the esophageal mucosa is an insufficiently studied disease that does not have a coherent classification. There are erosions, divided according to the causes of occurrence:
- primary, distinguished as independent diseases of the esophagus;
- secondary, which arise as concomitant disorders that occur against the background of the disease.
In relation to tissue changes, there are:
- non-malignant erosions;
- lesions associated with neoplasms.
Erosion according to the type of flow is divided into:
- spicy;
- chronic.
Additional erosions are distinguished:
- polypoid;
- linear;
- superficial;
- multiple;
- flat.
The study and systematization of types of disease continues.
Linear erosions of the esophagus
A lesion of this type should be understood as damage to the upper layer of the mucous membranes of the esophageal tube, which then form into small ulcers. With the development of mucosal lesions, the ulcers merge into larger lesions.
Linear erosion occurs due to the development of superficial erosion, which was not diagnosed and treated in time. This happens in most cases - superficial erosion is difficult to diagnose.
Linear erosion is easier to detect due to the large affected area.
- linear erosion leads to strong changes in the mucosa;
- inflammatory processes, when healing, form scars that deform the esophageal tube;
- its narrowing and deformation makes digestion difficult.
The most common cause of the development of linear erosions is damage to the esophagus by spicy and rough foods, and burns of the mucous membrane.
Can it develop into cancer?
Esophageal erosion is a disease without a clear clinical picture. Often the patient learns about his illness by chance during gastroenteroscopy. Minor symptoms on the part of the patient are accepted as a consequence of a violation of the diet, and that is why in most cases a doctor is consulted in the later stages of the pathology, when severe, sometimes even irreversible changes in the mucous membrane of the esophagus are recorded.
Erosion is a superficial defect in the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube, which does not extend to the deeper layers of the esophageal wall. Foci of erosion can be single or multiple, varying in location and size. The consequences of erosion pose a serious danger.
Erosion can eventually turn into a deeper defect - an ulcer. There is a risk of infection with the development of esophagitis or heavy bleeding. When the disease is advanced, the erosive defect may undergo cellular transformation, which is a precancerous condition; the patient is diagnosed with leukoplakia or Barrett's esophagus.
In some cases, the changes are quite profound (esophageal cancer), and it is not possible to correct the condition even with surgery.
What are the risks of erosion?
Erosion is a disease against which various pathologies develop, leading to serious illnesses. One of the most dangerous complications is damage to the wall of the esophagus with rupture of blood vessels and bleeding.
Symptoms of complications are:
- abdominal pain;
- vomit is red.
The main “candidates” for this complication will be young men:
- alcohol and tobacco abusers;
- who are exposed to severe and frequent stress.
In older people under such circumstances, stomach ulcers occur.
In addition, the following complications are possible:
- development of deep mucosal ulcers;
- damage to the vessels of the esophageal tube;
- neoplasms on the mucous membranes.
To prevent the development of complications, treatment should be prescribed as early as possible.
Why is pathology dangerous?
Erosive processes are far from harmless. What is dangerous about erosion of the esophagus and stomach is its complications. Untimely or illiterate treatment can lead to very dangerous conditions:
- Esophageal stricture more often occurs with unreasonably short courses of treatment (up to 4 weeks) or with insufficient therapy to reduce gastric secretion. Strictures of the esophagus lead to disruption of the nutritional process, cachexia, and require surgical intervention, which is difficult for the patient.
- A peptic ulcer of the esophagus is a deep defect in the wall of the esophagus, leading to deformation and shortening of the organ.
- Barrett's esophagus is a metaplasia of squamous epithelium into columnar epithelium, which greatly increases the risk of cancer.
- Periodic or constant bleeding from ulcerative defects.
- Threat of esophageal perforation with deep peptic ulcers.
With gastric erosions, there is also a danger of bleeding, deformation and malignancy (development of tumor diseases). These two diseases are similar in morphological changes, symptoms and treatment.
Diagnostics
Erosion of the esophageal tube is usually detected during preventive hardware examinations by a specialist. Therefore, if possible, the examination should be carried out annually, and in case of parallel pathologies – once every 6 months.
When a patient visits a doctor:
- interviews the patient, collects information about complaints about the condition;
- during the interview, the doctor pays attention to atypical pain (in the chest, spine or upper abdomen);
- clarifies the nature of the pain in the patient;
- conducts an examination of the upper abdomen, determining swelling and the presence of inclusions and inflammation;
- assesses the condition of the skin and chest.
The following examinations are prescribed:
- general clinical blood test;
- blood chemistry;
- Analysis of urine;
- stool examination to detect occult blood.
From hardware diagnostics the following is used:
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity as the main research method. The contrast agent used for the study is barium sulfate or a substance that dissolves in water. During the examination, the doctor examines the contours of the organ, the features of the mucous membrane, and the functioning of the sphincters. To study the functioning of the lower esophageal sphincter, the patient is placed on a special table with the lower end raised; a loose sphincter will allow contrast to pass into the esophagus;
- study of contraction and tone of the walls (esophagotonokymography) to determine diaphragmatic hernia.
The purpose of the survey is to determine:
- possible diseases of the esophagus;
- the condition of the internal organs located in the abdominal cavity.
After comparing the results of all studies, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes how to treat esophageal erosion.
Treatment
The lesion is complex, so treatment of the pathology is quite complex and must be prescribed by a doctor. The use of traditional methods of treatment must be coordinated and carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Drug treatment
In case of esophageal erosion, medication treatment is prescribed exclusively by a specialized doctor. For therapy, 2 groups of drugs are used:
- neutralizing the effect of the negative effects of hydrochloric acid, which is part of the gastric juice, as a result of which the symptoms of destruction of the mucous membranes of the esophageal tube are eliminated (antacids). Medicines reduce pain and burning, restore damaged mucous membranes. These include Maalox, Phosphalugel, Almagel; drugs that form a thick layer on the walls of the stomach
- foam, create a thick protective layer that does not allow gastric juice to enter the esophagus (alginates). The main properties of drugs in this group are the ability to eliminate bleeding and absorb secretions; seaweed extract is used for production. Medicines from this group – Gaviscon, tablets;
- improving gastric motility and allowing to reduce the period of contact of gastric juice and mucous membrane (prokinetics). The drugs in this group include Motilium, Ganaton, Cisapride. Dosage regimen – 4 times a day;
- Proton pump inhibitors, which inhibit the secretion of gastric juice, reduce the load on the walls of the esophagus. The drugs in this group include Omez, Omeprazole, Nexium, Zantac, Pariet.
If erosion is secondary to:
- stomach and duodenal ulcers (if infected with Helicobacter pylori) are simultaneously prescribed a course of antibacterial therapy;
- for calculous cholecystitis, choleretic agents and sedatives are additionally prescribed.
Treatment for erosion without consultation with a doctor, with self-prescribed drugs is dangerous and should not be practiced.
Folk recipes
In parallel with medication, treatment of esophageal erosion with folk remedies should be used. Many of the traditional methods have found recognition in official medicine:
- potato juice – juice from fresh potato tubers is used, which is drunk before meals, 50 grams (up to 4 times a day). You need to be treated for at least two months, then it is recommended to take a break for 10 days, then continue treatment again. Duration of treatment – at least 4 times a year;
- Carrot juice is included in the diet in a volume of at least a glass; you can mix it with potato juice in equal parts and drink it before meals;
- eat a tablespoon of honey on an empty stomach, before breakfast and lunch. the antibacterial property of the product allows you to accelerate the healing of mucous membranes during erosion of the stomach and esophagus;
- sea buckthorn oil, which is taken after meals 15-20 minutes for at least 45 days and at least 20 days after healing. The treatment uses the antibacterial effect of the oil and its vitamin composition;
- flaxseed oil, a teaspoon after meals at least 4 times a day;
- infusion of a mixture of herbs (take equal parts linden blossom, marigold and fireweed, horsetail, dill (seeds), valerian root, chamomile, St. John's wort, immortelle). Pour 2 teaspoons of the mixture into ½ liter of boiling water and leave in a thermos for at least 3 hours. Drink 100 grams before meals at least 4 times a day;
- To improve your condition, you can drink tea from oregano, calamus, hawthorn, corn silk at the rate of 1 tablespoon of the product per glass of boiling water, you need to drink tea for at least 60 days.
Herbal teas should be brewed every day; You cannot drink infusions that have been brewed for three days - you can get poisoned from this. Erosion of the esophagus, its treatment with folk remedies should be supplemented by a properly organized diet.
Nutrition
Nutrition for esophageal erosion is one of the components of treatment. The diet and preparation of dishes depends on the patient’s condition - a strict diet during an exacerbation and a softer one during remission. The diet and composition of foods and dishes are selected by a doctor.
For erosion, one of the therapeutic diets (tables) is used:
- No. 1A for acute disease;
- No. 1B – during the period of remission 15 days after the main treatment;
- No. 1 – must be adhered to constantly.
The principle of using the diet is prohibited and permitted foods. Permitted ones include:
- milk and dairy products;
- boiled or steamed lean meat;
- pureed vegetable soups and light vegetable puree.
Dishes must be pureed, warm, and have a uniform structure. Meals should be frequent, small portions - you need to eat at least six times a day. It is recommended to drink a glass of warm milk at night.
The list of prohibited foods is much larger and more extensive - these include all traditional fried, spicy, and fatty foods, hot and sour vegetables, sauces and spices.
You should not eat very hot and cold drinks, carbonated water, alcohol, solid foods, or sweets. Sour fruits are prohibited for the entire period of exacerbation, it is necessary to exclude cigarettes from habits.
Failure to follow a diet for this disease is a guaranteed exacerbation of the disease.
Diet for gastric erosion: menu
To speed up the healing process and increase its effectiveness, you need to eat the “right” foods, which include:
- first: soups on lean broth with pureed vegetables;
- second: cereal porridge, milk porridge and boiled pasta;
- lean meats. For example, cutlets, meatballs and steamed meatballs;
- steamed lean fish;
- soft-boiled eggs or steamed omelettes;
- fermented milk products: milk, fermented baked milk, kefir, cheese, cottage cheese, sour cream, cream, yogurt (low fat);
- butter and vegetable oil;
- sweets: sugar, jelly, honey, jam, marshmallow, soufflé, jam;
- bakery products: stale wheat bread, biscuits, biscuits, pies and buns made from unleavened dough (up to 2 times a week);
- drinks: fruit jelly, compotes with pureed fruit, weak herbal teas, natural fruit juices diluted with water.