Stomach diseases occur in almost every third person. First of all, these are various types of gastritis and peptic ulcers. However, more serious diseases can also occur, for example, tumor damage to the organ wall with the development of metastases. The gold standard in diagnosing stomach diseases is fibroesophagogastroscopy, which allows the doctor to visually assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the organ and draw a conclusion about the necessary treatment. But such a procedure cannot always give an accurate answer about damage to the stomach. Then gastroscopy with biopsy is used - a method of morphological examination of the organ after preliminary staining of the obtained gastric sample.
Fiber gastroscope with biopsy tip
General description of the procedure
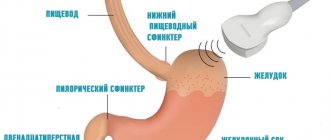
FGDS with biopsy is a combination of two diagnostic methods - fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGS, FGDS) with fine-needle biopsy and subsequent morphological analysis of the obtained sample of the gastric mucosa. When performing FGS, a thin flexible probe with a video camera and a light source is inserted through the esophagus into the stomach. This allows you to visually assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, identifying pathological processes in their wall: inflammation, ulcerative defects, tumor growth, etc.
The main advantages of conducting this survey:
- Thanks to a good video camera, the image has a high degree of detail, which makes it possible to identify even minor changes in the walls of the organ.
- It is possible to detect erosions and small polyps that are invisible during X-ray examination.
- FGDS is the best method for identifying the source of intragastric bleeding with the possibility of stopping it during the procedure.
- A biopsy during FGDS allows you to quickly diagnose tumor diseases due to the possibility of their morphological examination.
A biopsy consists of a minimally invasive procedure involving the collection of a small fragment of the gastric mucosa (sample diameter is several millimeters). After this, the sample is passed through a series of special stains, which allows individual cells to be visualized and their condition assessed. Biopsy during FGDS is an indispensable method in the diagnosis of benign and malignant tumors, especially in the initial stages of their growth.
Morphological examination of the mucous membrane allows us to identify pathological processes at the earliest stages of their development.
The doctor monitors the progress of gastroscopy on the monitor
Performing a gastric biopsy
Endoscopic examination of the stomach with biopsy is widely used to diagnose various diseases. There are two methods of performing a biopsy:
- fine-needle, which involves excision of a small fragment of the mucosa;
- aspiration, when organ cells are obtained through special suction.
In each specific case, a certain type of method is selected individually.
There are two types of gastric biopsy: targeted and blind. In the first case, the attending physician visually monitors the procedure and can select the appropriate area of the organ mucosa for further analysis. As a rule, the tissue area with the most pronounced pathological changes (erosions, bleeding vessels, etc.) is selected. In the blind method, a fragment of the mucous membrane is taken without visual control.
The patient undergoes FGDS with biopsy
Indications and contraindications for the study
FGDS with biopsy is performed only if the patient has certain indications:
- The need for differential diagnosis of the ulcerative process and tumor growth in the form of an ulcer.
- Early detection of precancerous and tumor changes in the cells of the gastric mucosa.
- Difficult diagnostic situations (Crohn's disease with damage to the stomach, malignancy of the edges of an ulcer, etc.).
- Determination of Helicobacter pylori infection using morphological examination.
The procedure should be carried out only after consultation with the attending physician and a gastroenterologist.
Despite the high information content of the procedure, FGDS and biopsy are contraindicated in the following situations:
- Decompensated state of any diseases of internal organs (respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary system, etc.).
- Blood clotting disorders.
- Conditions and diseases leading to obstruction of the esophagus or intestines.
- Mental disorders in the patient.
- Acute infectious diseases and exacerbations of chronic infections.
- Inflammatory processes in the larynx, nasal cavity and pharynx.
If the patient has no contraindications, then preparations for the study begin.
Indications for use
FGDS with biopsy is prescribed primarily for the purpose of differential diagnosis if an ulcer or tumor formed in the stomach is suspected.
The procedure is also carried out for previously identified precancerous conditions or tumor changes in the cells of the intestinal mucosa.
Indications for gastroscopy with biopsy include diseases such as Crohn's disease, in which the digestive tract is affected.
The procedure also allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis and features of the course of the pathology in the presence of an infectious lesion, in particular Helicobacter pylori.
Preparing for the study
Your attending physician will tell you about proper preparation for FGS.
Preparation for EGD of the stomach with biopsy does not require special measures, however, there are several recommendations for patients. The attending physician must prepare the patient psychologically for the procedure - explain the risks and possible complications, describe the course of the study and the necessary measures.
Regardless of the duration of the procedure, a number of general tips can be identified:
- A few days before the study, stop drinking alcoholic beverages, spicy and hot foods.
- Do not take food or liquid 3-4 hours before the test.
- The evening before the test, the patient may take sedatives to reduce stress levels.
- Do not take medications that can reduce the effectiveness of hemostasis (Aspirin, etc.).
- If the patient has an increased gag reflex, local anesthetics may be used.
FGDS with biopsy: what is it and why do it?
FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) is a method of examining the digestive organs (esophagus, stomach, duodenum) using a flexible device - an endoscope. Specialists refer the patient for a study with a biopsy - taking a tissue sample for analysis to clarify the diagnosis.
This means that a small piece of tissue will be taken from the surface of the stomach (another organ) for examination.
Almost every third person suffers from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. These are various types of reflux (reflux of contents into the esophagus and pharynx), gastritis, peptic ulcers, and, finally, neoplasms. FGDS is the most accurate diagnostic method and makes it possible to make the correct diagnosis and, accordingly, prescribe effective treatment.
Advantages of conducting FGDS:
- — Availability of a video camera. The image from the camera has a high degree of detail, which makes it possible to detect even minor changes in the walls of the organ.
- — It is possible to identify erosions and small polyps that are invisible during X-ray examination.
- — FGDS is best suited for identifying the source of intragastric bleeding and has the ability to stop it during the procedure.
- — FGDS with biopsy allows you to quickly diagnose tumor diseases due to the possibility of their morphological examination.
The FGDS procedure should be carried out only after consultation with a doctor if the patient has certain indications:
- — If necessary, differential diagnosis of the ulcerative process and tumor growth in the form of an ulcer.
- — Early detection of precancerous and tumor changes in the cells of the gastric mucosa.
- — Difficult diagnostic situations (damage to the stomach, the appearance of neoplasms in the area of the edges of the ulcer, etc.).
— Diagnosis of infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori using morphological examination.
It is very important to prepare psychologically, since the study is interpreted by many as unpleasant.
The doctor can give a number of general recommendations:
- — Avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, spicy and hot foods a few days before the test.
- — Do not take liquid 3-4 hours before the test.
- - Do not eat 12 hours before the test.
- - You can take anti-anxiety medications to reduce stress the evening before the test.
- — Do not take medications that can reduce the effectiveness of hemostasis (aspirin, etc.) in the morning before the procedure.
- — If the patient has an increased gag reflex, local anesthetics may be used.
— To conduct an FGDS with a biopsy, you will need modern medical equipment. The medical clinic is equipped with the latest endoscopic devices, which allows procedures to be carried out quickly and almost painlessly.
Photo: yandex.ru
Call and make an appointment by phone: 8 (343) 300-8432,
or write to us on WhatsApp/Viber/Telegram +79222030450
Stay up to date with events, subscribe to our channels: Vkontakte / Facebook / Instagram / YouTube
Description of the procedure
Gastroscopy with biopsy examination is performed in an endoscopy room by specially trained doctors. A special flexible endoscope is used, equipped with a light source and a small video camera that allows visual control of the procedure.
It is very important to follow the procedure to minimize the risk of complications.
The probe is carefully inserted into the esophagus through the mouth and carefully advanced into the stomach. As a rule, already at this stage the attending physician carefully monitors the resulting image and evaluates the mucous membrane of the organs. When it enters the stomach, the probe allows you to examine all its walls, and, if necessary, assess the condition of the duodenum. In this case, the biopsy is performed in a targeted manner, i.e. a “suspicious” area of the mucous membrane is removed.
A biopsy is performed to clarify the diagnosis or monitor treatment
Upon completion of the study, the probe is removed and the patient can immediately leave the hospital if anesthesia was not used. If anesthesia was used, the patient is left in the hospital for a certain time for observation.
Possible complications of the procedure
Complications after gastroscopy occur extremely rarely, however, in a number of situations, the following conditions may occur:
- As a result of inflating the stomach with air, nausea, belching, flatulence and bloating in the epigastric region are possible. Such discomfort goes away within a few hours without treatment.
- If sterility conditions have been violated, various bacteria are likely to enter the stomach.
- If the technique of the procedure is violated, the walls of the esophagus and stomach may be injured, resulting in bleeding.
If complications develop, it is necessary to stop the procedure and begin therapeutic measures.
Gastroscopic examination with biopsy is the “gold” standard in the diagnosis of diseases affecting the stomach, in particular, various precancerous and tumor processes. Proper preparation of the patient and adherence to the procedure allows obtaining informative results while maintaining a low risk of complications. Additional morphological assessment of mucosal biopsy increases the accuracy of diagnosis and improves the long-term prognosis of treatment.
Procedure for performing a gastric biopsy
No lengthy preparation for endoscopy is required. It is important not to eat or drink much fluid at least 8-10 hours before it starts. If a biopsy is included in the procedure, you should stop smoking and drinking liquids rich in coloring substances (tea, coffee, juices, carbonated drinks).
The biopsy is performed as follows:
- The patient is placed on his left side.
- The larynx and oral cavity are treated with an antiseptic.
- A plastic mouthpiece is placed in the mouth.
- An endoscope is inserted and air is injected to inflate the walls of the esophagus and stomach to ensure a good view.
- Based on the image from the device’s camera, the doctor looks for suspicious areas and takes tissue samples with a special device.
Endoscopy with biopsy is completed by removing the endoscope and sending the resulting samples for detailed histological analysis. The entire procedure lasts 20-40 minutes, the results of the biopsy analysis will be ready in a few days.