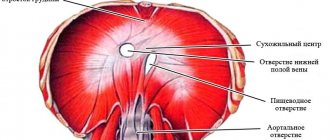
The esophagus is a tubular organ consisting of muscle tissue. It passes through the lumen of the diaphragm from the chest into the peritoneal cavity. When exposed to unfavorable conditions, the anatomical location of the esophagus changes, and the organ from the peritoneum completely enters the chest. In this case, we are talking about such a serious pathology as a hiatal hernia.
Expert opinion
Shoshorin Yuri
General practitioner, site expert
This disease significantly reduces a person’s quality of life and poses a serious danger to his health, because with the development of pathology, not only the digestive system, but also the respiratory system, and the heart suffer. In addition, disruption of the outflow of gastric juice entering the esophagus significantly increases the risk of developing oncological tumors of the organ.
Characteristics of the pathology
Normally, the lumen of the diaphragm is a rather narrow opening, however, under the influence of certain reasons, this lumen can expand, allowing the peritoneal organs to pass into the chest. In this case, the anatomically correct location of the organs of the digestive system, in particular the esophagus, is disrupted. In this way, a hernia develops, the chest organs are compressed, and specific symptoms characteristic of this pathology appear.
The following types of hiatal hernia are distinguished:
- Paraesophageal form, in which the position of not only the esophagus, but also the fundus of the stomach, intestinal loops, and omentums changes;
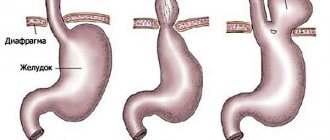
- Axial form, in which the displacement of organs occurs in a vertical manner. In this case, the esophagus and stomach emerge into the chest (in whole or in part);
- A sliding form, which is characterized by a dynamic position of the organs that make up the hernia (they are located in a special hernial sac and change their location, being either in the abdominal cavity or in the chest).
What causes a hiatal hernia?
The following reasons are identified:
- Congenital anomaly of the esophagus. A hernia is diagnosed immediately after birth or in young children. The percentage of its development is not significant.
- Age-related relaxation and sprain of the esophagus and diaphragm.
- Obesity, overweight. At the same time, intra-abdominal pressure increases, internal organs are displaced, which causes hernial protrusions.
- Dramatic weight loss. Over 20 kg per month is considered critical.
- Chronic processes in the liver with changes in its size: hepatitis, cirrhosis.
- Excessive overeating.
- Strength physical activity.
- Surgical interventions on internal organs, especially the esophagus, stomach, trachea, heart.
- The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity is ascites.
- Sometimes during pregnancy.
- Constipation.
- Organic lesions of the esophagus.
- Burns of the insides with salts and acids.
- Post-stroke condition.
- Blunt abdominal injuries.
Causes and development factors
A hiatal hernia develops as a result of exposure to such unfavorable factors as:
- Congenital anomalies of the development of internal organs (in this case it is customary to talk about a congenital form of pathology);
- Age-related changes leading to weakening of the ligamentous apparatus of the esophagus (this problem occurs mainly in people over 60 years of age);
- Liver atrophy (decreased size and weight of the organ, decreased functionality);
- Rapid weight loss, which destroys the fat layer located just below the diaphragm;
- Previous surgical operations in the esophagus;
- Accumulation of pathological exudate in the peritoneal cavity (ascites);
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Systematic disturbance of stool (constipation);
- Excessive physical activity;
- Impaired motor function of the organ;
- Excess body weight;
- Damage to esophageal tissue (thermal or chemical burns, traumatic damage to the organ);
- Chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a hiatal hernia depend on the degree of hiatal hernia. The modest size of the anomaly does not give any external manifestations. A person discovers signs of hiatal hernia during an examination for cardiovascular or pulmonary diseases, during which a chest x-ray is taken. Signs of a hernia include:
- heartburn after eating, worsening when bending over or other sudden changes in body position, for example, if you lie down after lunch. There is a burning sensation in the throat and esophagus;
- difficulty swallowing, food retention, pain and lump in the throat;
- a specific symptom of an esophageal hernia is a dull pain of moderate intensity behind the sternum (in the lower third) or in the hypochondrium that bothers you after playing sports or lifting weights;
- indirect signs of hiatal hernia are pain in the cardiac region, radiating to the left shoulder and scapula. Patients have been treated for angina and ischemia for a long time. Sometimes there is an increase in rhythm, uncoordinated work of the ventricles;
- symptoms in adults include a hacking cough accompanied by shortness of breath;
- often a hernia is manifested by sour belching, attacks of convulsive contraction of the diaphragm - hiccups.
The greatest danger is the complication of a strangulated hernia. Blood circulation slows down, the passage of a food coma is inhibited. Pinching makes itself felt by signs:
- fever up to 38°C, pain in the center of the sternum;
- pain in the solar plexus area, aggravated by pressing on the abdomen;
- anemia as a result of bleeding from ulcers of the esophagus and stomach;
- digestive disorders - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation.
A hernia is dangerous because its long-term progression has an extremely negative impact on the functioning of the digestive system. Regular irritation of the esophagus with hydrochloric acid and bile enzymes leads to its inflammation. Dysfunctions of the digestive tract result in gastritis, peptic ulcers, pancreatitis, inflammation of the gallbladder
.
Symptoms and stages of formation of a hernia in the esophagus
There are 3 stages of development of a hernia in the esophagus, each of them is characterized by certain manifestations. At the initial stage, symptoms are most often absent; the patient may complain only of minor discomfort after eating. At stages 2 and 3, characteristic signs appear, the intensity of which may vary (depending on the stage of development of the pathological process and the form of the disease).
| Stage of development | Characteristic signs |
| initial stage | In most cases, the pathology is asymptomatic; sometimes the patient is bothered by heaviness and discomfort after eating. |
| Stage 2 | Symptoms such as:
|
| Terminal stage | At this stage, the symptoms mentioned above intensify, the clinical picture becomes more detailed, and additional signs appear such as:
|
With an advanced form of the disease, the risk of hernia strangulation increases. This problem is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Sudden sharp pain localized in the lower chest or upper abdomen. In this case, the pain can spread to the area of the shoulder blades and collarbone;
- Nausea and active vomiting;
- Bloating, a feeling of painful fullness inside.
Classification
There are more than 50 classifications of hernias localized in the diaphragm. In practice, the most acceptable are those that take into account anatomical changes, the characteristics of the formed hernia, the size of the hernia opening and the role of the subphrenic part of the esophagus.
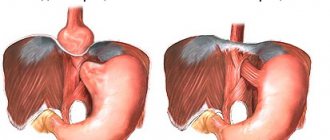
The most popular division of hernias according to mobility is sliding (axial, axial) and fixed paraesophageal (paraesophageal). Additionally, mixed hiatal hernias with a complicated course are distinguished.
The share of paraesophageal hernias accounts for no more than 5% (in children 0.3), non-fixed hernias occupy almost 95% (in children 99.4)
Sliding hernias have the possibility of fixation, most often against the background of shortening of the esophagus. Their main symptom is the free movement of the upper part of the stomach and the subdiaphragmatic portion of the esophagus into the chest cavity and back. Able to adjust independently when a person is in an upright position.
Types of axial hernias are distinguished depending on the portion of the stomach that passes into the chest cavity:
- cardiac - a small section of cardia emerges from the esophageal opening;
- cardiofundal - the hernia consists of the cardia and the body of the stomach;
- subtotal - the stomach is displaced into the chest cavity up to the pylorus;
- total - the hernia includes the entire organ with the pyloric section.
Usually, with a fixed cardiac section, the fundus of the stomach or the entire organ, a loop of intestine, the omentum, and rarely part of the spleen emerges into the distended esophageal opening. This species may be disadvantaged. Among fixed hernias, depending on the contents, the following types are considered:
- fundal - the body of the stomach moves into the chest cavity;
- antral - part of the antrum is displaced;
- intestinal - passes through a loop of the small or large intestine;
- gastrointestinal - the intestines and part of the stomach move at the same time;
- omental - the hernia contains an omentum.
There is a division according to the degree of expansion (size) of the hernial opening:
- 1st degree - only the abdominal segment of the esophageal tube lies in the supradiaphragmatic space, the stomach is pulled up to the diaphragm;
- 2nd degree - the vestibule and cardiac part move upward, gastric folds protrude into the diaphragmatic opening;
- 3rd degree - in addition to the abdominal part of the esophagus, the body and antrum of the stomach pass into the chest cavity.
It is possible to classify hiatal hernias in detail only with the help of additional studies.
Why is a hernia in the esophagus dangerous? Possible complications
In the absence of therapy and the rapid development of a hernia, there is a risk of developing health-threatening complications, such as:
- Development of erosions affecting mucous membranes;
- Strangulated hernia with the appearance of symptoms characteristic of this problem;
- Esophageal ulcer caused by systematic exposure of aggressive gastric juice to the walls of the organ;
- The appearance of scars on the walls of the organ, narrowing of its lumen, leading to the impossibility of normal movement of food;
- Perforation of the walls of the esophagus;
- Development of internal bleeding in the digestive organs;
- Disorders of the heart and respiratory system.
What complications does a hiatal hernia lead to?
The more severe the hernia and the longer targeted treatment is delayed, the more the risk of complications increases. The most commonly observed:
- pinching of organs that have moved from their anatomical location by the muscles of the diaphragm;
- reflux esophagitis - inflammation of the esophagus, as a result of constant reflux of the acidic contents of gastric juice, leading to ulcers on the surface of the mucosa, perforation;
- formation of adhesions, scars, narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus;
- stomach ulcer;
- acute or chronic bleeding from varicose vessels of the esophagus and stomach, anemia;
- attacks of angina pectoris, which are difficult to combat with nitro drugs;
- Barrett's esophagus is a precancerous disease.
The likelihood of malignant degeneration of mucosal cells increases
Diagnostic methods
To make a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the following diagnostic measures:
- Questioning the patient, assessing the symptoms that bother him;
- Contrast radiography (special contrast agent - barium, administered through the mouth);
- Fibrogastroscopy using a special probe equipped with a miniature video camera;
- Ultrasound of the chest organs, peritoneum;
- pH-metry, which allows you to determine the acidity of gastric juice in order to identify the risk of developing burns to esophageal tissue.
Why is this hernia difficult to recognize?
It is often really very difficult to suspect a hiatal hernia.
- In half of the cases, the pathology does not manifest itself at all.
- In 35% of cases, the main complaint of patients is interruptions in the functioning of the heart and chest pain, which are often very similar to those that occur with coronary heart disease.
- The majority of patients are elderly people, who usually already have a whole “bouquet” of health problems.
- The presence of a hiatal hernia does not at all exclude the presence of cardiovascular pathology.
All this creates serious diagnostic problems. Many patients continue to undergo treatment with a cardiologist for years, all to no avail, while the actual disease continues to progress.
Treatment regimen
Therapy for an esophageal hernia can be conservative or surgical (the choice of treatment method depends on the stage of development of the pathology, the risk of complications, the health status and age of the patient). The most commonly used therapeutic treatment includes 4 main points. This:
- Taking medications prescribed by a doctor;
- Performing special exercises;
- Compliance with a special diet developed by the doctor;
- Use of traditional medicine (after consultation with a specialist).
Drug treatment
Drug therapy involves taking medications to relieve pain, reduce the production of gastric juice, reduce its acidity, and protect the walls of the esophagus from the negative effects of aggressive elements.
Expert opinion
Shoshorin Yuri
General practitioner, site expert
That is, drug therapy is symptomatic in nature and eliminates the unpleasant manifestations of a hiatal hernia, improving the patient’s quality of life.
Physiotherapy
The complex of classes includes breathing and physical exercises. Breathing exercises must be performed on an empty stomach. Exercises that are often prescribed include:
- Starting position – lying on your back. While inhaling, it is necessary to tense the abdominal muscles as much as possible, stick out the stomach, while exhaling, the abdomen relaxes and retracts;
- Lying on your back, you need to turn to the sides, taking a deep breath (alternating turns to the right and left).
Physical exercise can be different. This includes raising the upper body from a lying position, raising the legs in a horizontal position (as an option, the “scissors” exercise).
Diet therapy
Therapeutic nutrition involves the exclusion of all foods that are difficult to digest, increase the production of gastric juice and increase its acidity. This includes white cabbage, spicy foods and spices, pickles, pickled and fatty foods, carbonated drinks, and alcohol.
Surgery
Surgery is required in the following situations:
- Low effectiveness of conservative treatment;
- Significant size of the hernia;
- Sliding form of hernia (with this form of pathology, the claim for strangulation increases);
- Threat of developing dangerous complications;
- Significant damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus (formation of erosions, dysplastic changes).
For esophageal hernia, the following types of surgical operations are used:
- Fundoplication is an operation aimed at protecting the esophageal mucosa from the aggressive effects of gastric juice;
- Belsi's operation, which consists of fixing the abdominal organs in an anatomically correct position (the lower part of the esophagus and the sphincter area are attached to the diaphragm, the fundus of the stomach is connected to the esophagus);
- Laparoscopy, which allows you to reduce the size of the diaphragm opening.
Treatment of hiatal hernia
Treatment of hiatal hernia depends on the degree of the disease and is divided into conservative and surgical.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment of a hiatal hernia involves relief of unpleasant symptoms - pain, bloating, heartburn, belching. This means lifelong use of antacids, prokinetics, antispasmodics, antihistamines and sedatives. The patient also constantly limits his diet. Strong coffee, chocolate, citrus fruits, tomatoes, onions, garlic, mint, and soda are excluded. It is worth deviating from the course of therapy - not taking a remedy that helps with heartburn, allowing errors in nutrition, burning, pain and spasms to return with renewed vigor. Regular decrease in acidity makes it difficult to digest food.
A poorly processed food lump enters the intestines, where it becomes prey for putrefactive microflora. Long-term use of antacids has side complications: stomach polyps, mucosal atrophy, impaired motility, and cancerous lesions. It is not possible to cure a hernia using a conservative method. You can treat with folk remedies for a small defect and mild symptoms.
Medications
| Name | Description | Admission rules | Price |
| Nizatidine | The drug in the form of a concentrated solution for intravenous administration helps reduce the production of gastric juice and reduces the concentration of hydrochloric acid. | 0.15 gr. of the drug 2 times a day, or 0.3 g. 1 time per day. The duration of treatment is determined individually. | 850 rub. |
| Almagel | An antacid that can bind hydrochloric acid, neutralizing its negative effect on the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus. Available in the form of a suspension for oral administration. | 1 tbsp. l. the drug 3-4 times a day. Duration - until the onset of the remission period. | 220 rub. |
| Omeprazole | The drug in the form of capsules with a dense shell reduces the secretory function of the stomach and the acidity of gastric juice, neutralizing its aggressive effect on the mucous membrane. | 20-18 MG of the drug per day (divided into 2-3 doses). Duration of treatment is 2-8 weeks. | 30-40 rub. |
| Metoclopramide | The drug normalizes the motor function of the esophagus and helps eliminate the symptoms of heartburn. | Dosage: 5-10 MG 3 times a day. The duration of treatment is individual. | 20 rub. for 2 ampoules |
Useful and prohibited foods
Diet is an important point in the treatment of hiatal hernia. The basis of the diet should be dishes that are easy to digest. Does not burden the digestive system. Heavy, fatty foods must be avoided.
In addition, it is very important to pay attention to the portion size: overeating is not allowed, you must stop eating before you feel completely full.
| Allowed | Forbidden |
|
|
Example of a diet for a hiatal hernia
It is important to eat small meals, at least 5 times a day. It is recommended to choose one of the following options:
- Breakfast: Protein omelet or boiled egg, milk cereal porridge, cottage cheese casserole;
- Lunch: Baked or fresh fruit (excluding sour varieties), low-fat yogurt, carrot and beet juice;
- Lunch: Vegetable soup, boiled meat with vegetable side dish, steamed cutlets with pasta;
- Kissel, drinking yogurt, low-fat kefir;
- Dinner: Vegetable stew, baked fish and potatoes, milk porridge.
Diagnostics
In order to determine the required range of studies and make an accurate diagnosis, you should contact a qualified specialist. First, the doctor questions the patient and examines him. This helps to detail complaints and collect the necessary information.
When palpating the abdomen, a protrusion of the hernia can be immediately detected. After this, general clinical tests are prescribed: general urine test, general blood test, stool test for coprogram.
There may be anemia and minor inflammatory changes in the blood. In the coprogram, the digestive and enzymatic functions of the organs are assessed. Next, we begin instrumental research methods.
X-ray with the introduction of a contrast agent. An x-ray allows you to evaluate the location of structures and detect a hernia.
Signs of a hernia will be:
- Displacement of the abdominal esophagus.
- High diaphragm dome.
- Presence of a hernial sac.
- Expansion of the diaphragmatic ring.
To detail the signs, endoscopic methods are prescribed. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy for esophageal hernia allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membranes, the movement of organs, the size of the protrusion, the expansion of folds and holes. Based on this, a final diagnosis can be made.
Laparoscopy
Applies to both diagnostic and therapeutic methods. It is prescribed when there is insufficient collection of information about the patient’s health status.
Laparoscopy is a type of surgical technique that involves making small punctures in the abdomen. Through these punctures, cameras and the necessary instruments are inserted, all in the form of metal tubes.
The image from the cameras is displayed on a computer monitor. If a hernia is detected, it is dissected, examined and sutured. The operation is not long, minimally invasive, non-traumatic.
After it there are no complications or huge scars, the recovery period is short. This method is actively used in surgery.