Do you suffer from heartburn, and does eating food cause you to belch? Can't get rid of the bitter taste and bad breath? These may be the first signals indicating that there may be insufficiency of the gastric cardia (cardiac sphincter) - a disease that has become widespread recently. What is it and how to get rid of it, let's figure it out together.
The development of cardiac gastric sphincter can directly depend on a person’s lifestyle.
The essence of the disease
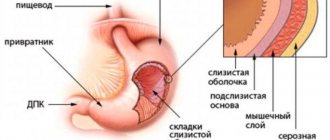
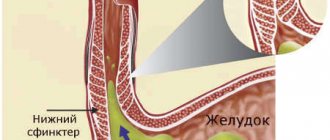
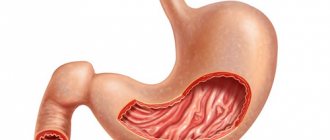
Gastric cardia insufficiency (cardiac sphincter, gastroesovagel reflux disease) is a disorder of the digestive system that occurs when acidic gastric juice enters the stomach or esophagus. Our body has sphincters. The sphincter is a valve through which the contents of one organ pass into another. One of them is the muscular sphincter of the esophagus, the pylorus of the stomach, a kind of valve separating the esophagus and the stomach, called the gastric cardia.
During normal digestion, this sphincter opens to allow food to enter the stomach and then closes to prevent acidic stomach acid from entering the esophagus. When the work of the sphincter (pylorus of the stomach) is disrupted, non-closure occurs and it does not close. Then the cardia of the stomach cannot contain gastric juice, as a result of which it enters the esophagus. This results in insufficient cardia and a condition of non-closure of the sphincter, called chalasia.
Causes
Cardia deficiency can occur in anyone. No one is immune from cardiac sphincter. Pyloric dysfunction can occur at any age, and it is sometimes difficult to determine what caused it. In addition, the occurrence is often associated with causes that cannot be prevented. However, most often the development of this disease is directly related to lifestyle. However, the most common factors that can cause the sphincter to not close are:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- high salt intake;
- low dietary fiber intake;
- passive lifestyle;
- irregular meals;
- overweight;
- eating heavy meals while lying on your back or bending at the waist;
- snacks before bed;
- frequent stress;
- side effect from taking certain medications;
- Sometimes cardiac sphincter can occur during pregnancy.
Causes of stomach cancer
The cause of stomach cancer in most cases is inflammatory diseases of the digestive system.
Let's look at some of them:
- Atrophic gastritis. It precedes gastric cancer in 70-80% of cases. Due to inflammatory processes, the gastric glands are destroyed, the ability to secrete acid decreases, and achlorhydria develops (sometimes pernicious anemia). This is followed by the colonization of the organ cavity by pathogenic microorganisms that are capable of synthesizing carcinogenic substances.
- Intestinal metaplasia. In this condition, the normal lining of the stomach is replaced by cells similar to the lining of the intestine. Often intestinal metaplasia develops against the background of atrophic gastritis, but how and why it progresses to cancer is not yet known.
- Adenomatous polyps (adenoma). With this disease, various dysplastic changes are observed in the mucous membrane around the polyps, and therefore the incidence of malignancy is 30-40%.
- Cardioesophageal cancer is possibly associated with a disease called Barrett's esophagus, where the cells in the lining of the esophagus undergo pathological changes and turn into columnar epithelial cells. Barrett's esophagus is closely associated with gastroesophageal reflux.
It is worth noting ,! The development of these diseases is closely related to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Some of its subtypes are capable of converting substances from food into chemical carcinogens that cause mutations in the DNA of cells in the gastric mucosa.
Scientists have identified several risk factors for gastric cancer with varying degrees of evidence:
- The first, most proven factor is nutrition. The consumption of semi-finished products, fats, smoked meats, and pickles has a negative effect. The disease is also associated with non-compliance with sanitary standards (for example, washing hands before eating, thoroughly washing vegetables and fruits) and improper storage of food.
- Smoking and alcohol. These factors most likely have a negative impact on the state of the digestive system and the entire body, although this has not been fully studied.
- In rare cases, hereditary stomach cancer has been observed.
- Operations. People with a resected stomach are several times more likely to develop cancer. This may be due to decreased stomach acid production and reflux of bile from the small intestine.
- Hereditary syndromes (Lynch syndrome, familial adenomatous polyposis, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, etc.). It has been noted that people with such abnormalities are more susceptible to DNA mutations.
- Overweight (not proven).
Read here: Causes of lung cancer in women
Risk factors sometimes contribute to the development of cancer, but many people who get it have no risk factors at all. However, some of them can be eliminated on your own and this will be the right choice.
Diseases that provoke the development
Sometimes developing non-functional functioning of the esophageal sphincter can occur as a result of a certain disease. The most common reasons are:
- Hernia. An anatomical anomaly when a hole in the diaphragm allows the upper part of the stomach to connect to the chest cavity, which sometimes leads to this disease.
- Obesity.
- Diabetes.
- Asthma.
- Adynamia (sharp loss of strength).
- Increased stomach acidity.
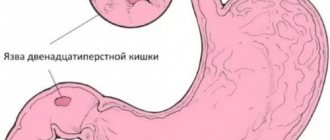
- Chronic stomach diseases (ulcers, gastritis).
- Connective tissue diseases, for example, scleroderma.
Treatment of gastric cardia cancer
Patients with cancer of the upper part of the stomach cause particular difficulties in treatment, the main reason being late diagnosis and, accordingly, involvement of the abdominal esophagus in the oncological process. According to various sources, from 4 to 26% of patients who underwent radical surgery survived the five-year mark.
Although surgery is a difficult task, it is the only way to overcome the disease. There are 2 main types of radical operations for gastric cancer - subtotal resection and gastrectomy.
In most cases, subtotal resection is used, which involves removing the proximal (upper) part of the organ. The resection margins must be at some distance from the boundaries of the tumor for the operation to be considered radical. Often, for cancer of the gastric cardia, surgery involves removing part of the esophagus, as cancer cells are disseminating along it.
As a rule, regional lymph nodes are also excised along with the stomach. There is still debate among scientists about the optimal degree of lymphadenectomy. The majority advocate resection of groups 1 and 2 lymph nodes (12 types of nodes in total). A more advanced approach involves complete lymph node dissection (all 3 groups of lymph nodes are removed). This technique of complete removal of the lymphatic system of the stomach is mainly used during gastrectomy.
But some doctors talk about the advisability of performing lymph node dissection in all patients, although there is no evidence of improved survival after such an operation, but the degree of trauma is very high. To choose the optimal treatment option for gastric cardial cancer, it is necessary to take into account many factors, including the size, stage and shape of the tumor.
In the USA and European countries, transpleural resection of the cardiac region is most often used. The method has many advantages over laparotomy. Transpleural surgery provides greater access to the object of removal, has a shallower wound depth and resects the esophagus as far as possible from the tumor. The only but important disadvantage of this method is the possibility of developing unilateral pneumothorax and its accompanying complications (pulmonary edema, shock, suppuration in the pleural cavity).
Patients with stage 1 disease (with a tumor size of no more than 2 cm and no metastases) may be candidates for endoscopic surgery. The tumor is removed using an endoscope inserted through the mouth. This technique is very simple and effective. This option is also suitable as palliative care for inoperable patients.
Read here: Classification of malignant tumors of the stomach: types, forms and types
If radical resection is not possible due to the extent of the process, then palliative interventions are performed to eliminate stenosis or prevent bleeding from the disintegrating tumor. Also, for inoperable patients, esophagojejunomastosis or gastrostomy is installed so that food enters the stomach and intestines.
Chemotherapy for cancer of the gastric cardia
Adenocarcinoma is relatively sensitive to chemotherapy. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is the most commonly used drug to treat stomach cancer, with a response rate of about 21%. In an attempt to improve this rate, drug combinations have been used; the most common is 5-FU, Doxorubicin and Mitomycin C (FAM) with a response rate of 33% and an acceptable degree of toxicity.
Other drug combinations have been tried, although duration of response and overall survival compared with 5-FU alone were not significantly different. In addition, such combinations had higher toxicity.
The patient is prescribed 3 courses before surgery and 3 courses after. Preoperative chemotherapy for stomach cancer can potentially stop the growth of the tumor and metastases, creating favorable conditions for subsequent surgery, and postoperative chemotherapy can reduce the risk of relapse. The positive result is evident in the improvement in 5-year survival from 23% to 36%, compared with patients who received surgical treatment alone.
Radiation therapy for cancer of the gastric cardia
Just like chemotherapy, radiation before surgery can improve survival and reduce the incidence of locoregional relapses. The doses used for gastric carcinomas are 30-40 Gy. The doctor divides them into 15-20 fractions.
Radiation therapy is often given once immediately after resection, for example, during non-radical surgery. The tumor bed is irradiated with a high dose of radiation (20 Gy) to destroy residual cells.
According to German researchers, the combination of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with radiation therapy improves the prognosis by 15-20%. Also, a combination of these methods is used for unresectable patients, which eliminates symptoms and stops tumor growth, thereby prolonging the patient’s life.
Degrees
The disorder has several degrees of development.
The severity of this disease depends on the level of dysfunction of the gastric cardia, dysfunction of the pylorus, as well as on the amount of gastric juice entering the esophagus. As a rule, there are three degrees of development of cardial failure:
- First degree. When the sphincter does not close completely. Accompanied by frequent belching.
- Second degree. When the sphincter closes halfway. She is accompanied by constant belching, heartburn, irritation of the stomach walls, and weakness.
- Third degree. When the pyloric closure does not occur.
Symptoms
The disease is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- heartburn, the most common symptom, a burning pain in the chest moving up to the throat, sometimes people feel the food come back completely, leaving a bitter or sour taste;
- burning in the stomach, a symptom that occurs some time after eating;
- sour belching;
- pain when swallowing;
- excessive secretion of saliva;
- chronic sore throat;
- hoarseness;
- weakness;
- inflammation of the gums;
- caries;
- bad breath;
- cardiopalmus;
- chest pain.
Complications
Failure to treat the disease can lead to serious consequences.
Most people do not feel drastic changes in their lives due to this disease. However, if left untreated, complications may arise as a result of the disease, in particular scars in places where the mucous membrane is damaged, ulcers, narrowing of the esophagus (stricture), complications in the swallowing process, and intestinal prolapse.
If acidic stomach juice gets into the throat, it can damage the lungs and cause difficulty breathing. Long-term pulp increases the risk of developing precancerous cells in the esophagus. This can lead to a condition called Barrett's syndrome, where tissue-like growths appear in the esophagus. This disease increases the risk of developing adenocarcinoma of the esophagus, a rare type of cancer.
Diagnosis of gastric cardia insufficiency
To diagnose cardia deficiency, you need:
- X-ray of the upper part of the digestive system;
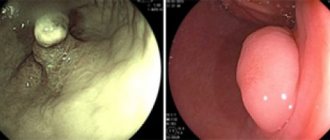
- endoscopy (examination of the inside of the esophagus);
- daily ambulatory pH-metry of the esophagus (test to determine the amount of acid in the esophagus);
- gastrofibroscopy (determines pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract);
- biopsy followed by histological examination;
- fibrogastroduadenoscopy (FGDS) - examination of the gastric mucosa.
Diagnostics
In the diagnosis of gastrointestinal pathologies, instrumental examination methods, which are highly informative and accurate, play an important role.
In the diagnosis of gastrointestinal pathologies, instrumental examination methods, which are highly informative and accurate, play an important role. In order to identify it, the following diagnostic measures can be prescribed:
- Fibrogastroscopy. It is assumed that a probe equipped with a video camera is swallowed, through which a picture of the internal state of the organ being examined is displayed on a computer monitor. Through such diagnostics, it becomes possible to identify pathologies of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
- Daily pH measurements. It is carried out to determine the acid level of gastric juice over a daily period. The data obtained during the survey process is recorded in the form of a graph.
- Radiography. A contrast agent is used, most often barium. This examination is carried out on an empty stomach in the morning. The essence of the procedure is to drink contrast and then record images in various body positions.
- Monometry of the esophagus. Various indicators are taken from special sensors in the esophagus while taking a sip of water. Allows you to determine the contractile function of the esophagus, the coordination of peristalsis with the work of the sphincter. The duration of relaxation, residual pressure, duration and speed of contraction are assessed.
Treatment
Treatment of insufficiency of the gastric cardia (sphincter) is carried out for the following purposes:
- eradication of the diagnosis itself;
- reducing internal abdominal pressure in the gastrointestinal tract;
- reduction and eradication of symptoms;
- regulation of the gastric cardia.
Medicines and diet for insufficiency of the gastric cardia help cure the disease. Weight is restored to normal. In some cases, surgery is necessary.
Drugs
Medications used to treat symptoms include:
- antacids that reduce gastric acidity and
The drug promotes healing of the gastric mucosa
and relieves heartburn (“Ranitidine”, “Almagel”); - drugs for healing the gastric mucosa (“Omeprazole”);
- antiemetic drugs (“Regidron”);
- analgesics (“Solpadeine”);
- Sometimes antibiotics are prescribed (subject to complications such as ulcers or gastritis).
Surgical intervention
When there is no improvement, surgical treatment becomes necessary. The following operations are performed: vagotomy, fundoplication, pyloroplasty and others.
Treatment with folk remedies
In addition to medical treatment, it is recommended to use folk remedies and treatment methods:
- To eradicate irritation of the gastric mucosa, a decoction of fennel, anise and dill is recommended.
- Potato juice, raspberry leaves, herbal tea or cabbage juice will help cure heartburn.
- Pharmacy infusions will be useful: chamomile, flax, motherwort, yarrow, calendula, St. John's wort. You need to drink 50 grams every hour for several days, 15-20 minutes before meals.
- To normalize the functioning of the digestive tract, plantain juice is recommended. It should be drunk on an empty stomach daily, 1 tbsp. spoon.
Prognosis and prevention
The 5-year survival rate for any type of CER averages 23.6%. Type III tumors have the most unfavorable course, since they are predominantly represented by poorly or undifferentiated neoplasms. The 5-year survival rate for this location is about 14%. The prognosis is significantly worsened by the presence of metastases in the mediastinal lymph nodes.
The European clinic employs doctors with extensive experience in treating stomach cancer. We are guided by current European standards. For this, the clinic has everything necessary - from the latest medications to modern equipment, thanks to which we are ready to provide assistance in the most severe cases.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Diet
- Fractional meals are recommended, in small portions 5-6 times a day.
- Overeating is prohibited. When you get up from the table, you should feel as if you would eat anything else.
- The last meal should be no later than 4 hours before bedtime.
- Eliminate tobacco use. Smoking leads to disruption of body functions.
- Avoid chewing gum and hard candies. They increase the amount of air swallowed, which consequently leads to belching.
- Don't lie down immediately after eating. This disrupts the process of digesting food.
- Avoid late-night snacking.
- Do not wear tight, narrow clothes or belts.
- Control your weight. Excess body weight leads to an increased risk of getting sick.
Fast food is the source of most gastrointestinal problems.
- Avoid eating heavy, fatty, fried foods. It complicates the digestion process.
- Avoid using butter, which immediately increases the amount of fat you consume.
- It is not recommended to eat chocolate containing a lot of caffeine and fats;
- Fast food is strictly prohibited.
- Do not eat citrus fruits, sour vegetables and juices (grapefruit, orange, pineapple, tomatoes), which corrode the walls of the stomach.
- Coffee (both regular and decaffeinated) is strictly prohibited;
- Of course, drinking carbonated drinks is not allowed.
- Do not eat hot, spicy foods with a lot of spices. It overloads the stomach, slows down the digestion process and destroys the stomach lining.
- Pineapples and watermelons are not healthy foods; their juice contributes to the destruction of the stomach walls.
- Cheese products, sour cottage cheese and whole milk are prohibited.
- Avoid eating fatty meats. The best option would be steamed cutlets or meatballs made from low-fat meat or poultry.
- Forget about lard, ham and other fatty meat products.
- The use of semi-finished products is prohibited.
- You will have to give up high-fat desserts, such as ice cream.
- Creamy sauces, gravies and creamy salad dressings are not recommended. It is better to replace them with olive oil.
- Cereal porridges (rice, oatmeal) are useful, enveloping the walls of the stomach and helping to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. It is recommended to consume them with water, without milk.
- Bananas, corn, apples and mangoes are healthy. Before eating them, you need to peel them. In addition to the fact that they promote digestion, coat the mucous membrane of the gastric tract, they remove toxins from the body and improve immunity.
- It is recommended to drink herbal and fruit teas as they combat acidity.
- Acidic vegetables (such as tomatoes) are not the best option when you are sick.
- Garlic, onions and spicy vegetables that cause heartburn are also strictly prohibited.
Treatment methods
If cardia deficiency is constantly present, this can lead to a number of dangerous health consequences. Ulcerative formations, possible when juice gets into the esophageal mucosa, act as the basis for the development of precancerous conditions. This means that treatment must be started immediately and approached with full responsibility.
Compliance with diet and nutrition
Already at the first stage of the development of the problem, there is an urgent need to correct the nutrition system. Initially, the correct regimen is established - food is taken several times a day (4-5), in small portions. At the same time, meal times every day should coincide as much as possible. After the next meal, lying down is prohibited for 2 hours.
It is also important to remove the factor of mucosal irritation, that is, all foods that can provoke it are excluded from the diet. This is too hot or cold food, fried, spicy, smoked, highly salted, coarse, seasonings, alcoholic drinks, coffee, chocolate, etc. The basis of the diet should be soups and tender foods, steamed, boiled or baked. Before eating anything, the patient needs to drink a glass of clean water. The emphasis is on plant foods (vegetables and fruits). The last meal should be at least a couple of hours before bedtime.
Photo gallery of prohibited products
Dishes with lots of spices
Smoked meats
Alcohol
Spicy dishes
Chocolate
Foods high in preservatives
Fried foods
Coffee
Medications
Specific treatment is difficult to describe as it largely depends on the underlying cause of the deficiency. Almost always, by correctly eliminating the cause, it is possible to influence the disturbances in the functioning of the cardia. Until this point, individual medications are used to eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease, namely heartburn medications, painkillers, and antiemetics. To combat the disease itself, drugs are prescribed that normalize acidity, gastric secretory function, as well as drugs to normalize the tone of the cardia and bring it to a normal functional state (cerucal, bimaral, raglan, metoclopramide, etc.).
Photo gallery of drugs
Metoclopramide
Raglan
Cerucal
Surgical intervention
The need for surgical intervention may be due to both the cause of cardia failure and the advanced stage of the disease. Surgery may be necessary if sphincter dysfunction is caused by a hernial formation (it needs to be eliminated by suturing the tissue) or if there was an error during a previous surgical intervention. When the muscle ring is completely opened at the last degree of insufficiency, the surgical method can be used to suturing the cardia muscles, but such actions are resorted to extremely rarely in the most difficult cases, when it is not possible to cure the disease by other means.
General tips to make you feel better and speed up recovery
In addition to correcting nutrition and following medical recommendations regarding treatment, for a successful recovery you will need to follow a few more rules:
- It is necessary to avoid heavy physical work and interaction with chemicals;
- physical activity is kept to a minimum;
- It is forbidden to wear clothes that are too tight or tight; you will have to give preference to loose options;
- inclined movements should be made as rarely as possible;
- Do not tighten the belt or belt too tightly;
- you need to prepare the sleeping area so that during the night's rest the upper part of the body is slightly higher than the lower part;
- You can resort to traditional methods of treatment (mumiyo, herbal preparations), but only after consultation with a specialist.
Lifestyle
If you have dysfunction of the gastric cardia, you need to quit smoking.
If you suffer from insufficient gastric cardia, this means that you will have to change your lifestyle:
- First of all, take care of your diet. Eat food in small regular portions 5-6 times a day. Watch your weight. Don't overeat.
- If you have a bad habit like smoking, you will have to give it up.
- Raise the pillow you sleep on so that it is slightly above body level. This will help eliminate heartburn and reduce pressure on the stomach.
- Do not wear restrictive, tight clothes or belts.
- Maintain a sleep schedule. Healthy sleep is the key to a healthy body as a whole.
- Reduce the amount of caffeine you consume.
- Try to keep stress to a minimum.
- Exercise. Avoid a sedentary lifestyle.
Prevention
Everyone is predisposed to a non-functional dysfunction of the sphincter and the fact that it does not close. Fortunately, the formation of cardiac sphincter can be prevented. To do this you need to take the following steps:
- The first and simplest thing to do is to eat regularly, even if you have not yet developed the disease. Small regular meals are beneficial for any person. This reduces the risk of acidic gastric juice entering the food cavity.
- Lead an active lifestyle and do physical activity.
- Drink a glass of water before meals in the morning on an empty stomach. Water helps remove toxins from the body and reduce the acidity of gastric juice.
- Limit your consumption of alcoholic beverages and products containing caffeine;
- Increase your consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables. The dish should consist of half vegetables or fruits.
Non-drug treatment of the disease
If a person is diagnosed with gastric cardia insufficiency, treatment should begin as early as possible. And first of all, it will begin with the following measures:
- reducing body weight if a person is obese (this can be achieved through diet);
- a decrease in intra-abdominal pressure if a person is diagnosed with ascites (dropsy);
- careful adherence to dietary nutrition.
The diet consists not only in the fact that the patient begins to eat properly at certain hours, but also in the fact that he will not overeat and eat at night. You should not lie down after eating for at least 2 hours. You need to include more pureed soups and cereals in your diet. Such food, accordingly, will protect the esophagus from physical irritation. You should avoid eating food that is too hot or too cold.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that are irritating:
- chips;
- all products during the preparation of which chemical preservatives and flavor enhancers were added;
- tea (strong);
- coffee;
- fatty and fried foods;
- tangerines, grapefruits;
- food containing a large amount of spices, salt, spices, as well as all smoked foods;
- homemade pickles and marinades.
You should have dinner approximately 3 hours before bedtime. It is not allowed to eat immediately before going to bed.
Other restrictions in the patient’s life are also shown:
- you need to give up clothes that squeeze your stomach;
- for the same reason, it is necessary to limit the wearing of tight belts;
- you need to sleep on a bed with a raised headboard;
- you don’t need to bend down often and you shouldn’t work very long and hard;
- if a person’s activity involves the need to work hard and often bend over, then it is advisable for him to change jobs.