Aerophagia is a specific disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, that is, spontaneous swallowing of air when eating and not only, followed by regurgitation. Swallowing excess air puts pressure on the surface of the stomach and causes pain.
According to established data, when a person eats, he normally swallows about half a teaspoon of air in volume with each sip. Because of this, there is always an air bubble in the stomach with a volume of 2/3 of a standard glass. It gradually moves into the small intestine, where the main amount is absorbed, the remaining air leaves through the anus. A small amount of air in the stomach may be expelled by belching.
Aerophagia is divided into two types:
- Organic . It appears due to the pathological development of the gastrointestinal tract, dysfunction of the central nervous system, due to genetic disorders;
- Functional or physiological – considered normal. It occurs in premature babies.
Causes of aerophagia
They are divided into three categories:
- Neurological;
- Psychogenic (neurotic);
- Due to pathologies of internal organs.
Neurological - progresses due to the development of an incorrect conditioned reflex.
With hasty eating, insufficient chewing, talking while eating, increased salivation, smoking, chewing gum. Psychogenic aerophagia occurs if: nervous work or frequent shocks; disturbed psyche; hysterics, stressful situations. In this case, a person may swallow air outside of meals. Aerophagia refers to gastric neurosis and gastrocardial syndrome. More than 2/3 of the population experienced neurosis. Most people had never heard of this disease, but mistook it for gastritis, a stomach ulcer or poisoning. Neurosis develops due to many psychological and physiological reasons. Psychological ones include:
- Hard work with constant stress;
- Recent nervous breakdown;
- Frequent lack of sleep;
- Shattered psyche;
- Intensive course of life.
In stressful situations, a large dose of adrenaline enters the human blood, which inhibits the natural functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and provokes gastric neurosis.
Physiological are:
- Frequent consumption of unhealthy foods;
- Abnormal diet;
- Use of low quality products;
- Viral pathologies;
- Gastritis;
- Diseases of other internal organs.
Airbrushing is a form of gastric neurosis in which air enters the stomach not during food intake. Whether a patient has airbrushing can be determined using an x-ray of the stomach and intestines. At the same time, you can see how much excess gases there are and the high position of the diaphragm.
Gastrocardiac syndrome appears when the stomach is full and is expressed by the following symptoms:
- Breathing heavily with a feeling of heaviness in the chest area;
- In the area of the heart, a growing pain is felt, similar to an attack of angina pectoris;
- Sudden onset of anxiety;
- Significant delay in heart rate;
- Right after the delay, increased heart rate.
There is also a sudden drop in blood pressure, profuse sweating, dizziness, fear, and unexpected weakness.
Those who have experienced such symptoms should know that gastrocardiac syndrome disappears immediately after belching or vomiting (vomiting must be induced).
Diseases leading to aerophagia:
- Respiratory tract diseases that impair breathing through the nose;
- Protracted gastritis;
- Stomach ulcer;
- Narrowing of the primary zone of the duodenum;
- Deterioration in the activity of the stomach muscles;
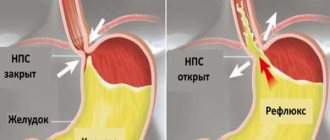
- Weakness of the muscles at the point where the esophagus passes into the stomach;
- Failure of the instinctive passage of food through the lower esophageal valve;
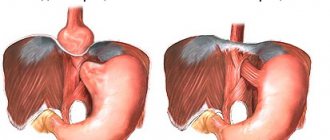
- Hiatal hernia;
- Prolonged colitis (swelling of the abdomen due to excess gases, resulting in severe flatulence);
- Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity;
- Damage to heart vessels;
- Insufficient blood supply to the stomach and intestines;
- Fusiform stretching of the lower region of the cardiac aorta.
Causes
The main causes of bloating in cats are:
- aerophagia, that is, swallowing air while greedily swallowing food;
- food with a high content of soy and dietary fiber;
- spoiled food;
- food intolerance (may also cause vomiting and diarrhea);
- malabsorption syndrome (impaired absorption of nutrients in the intestine);
- inflammatory bowel diseases;
- oncological diseases of the tract (for example, lymphosarcoma);
- viral, bacterial and parasitic intestinal diseases;
- constipation.
Contact your veterinarian immediately if your pet's bloating is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, or worsening general condition (restlessness, shortness of breath, weakness, etc.).
Diagnostics
The fact of the disease is verified based on:
- Data from the patient, where the doctor clarifies: under what circumstances the first symptoms appeared (when they swallow saliva, when rushing while eating, etc.);
- A kind of belching, when the sick person pulls his head forward, squeezes his chin to his chest and makes swallowing movements;
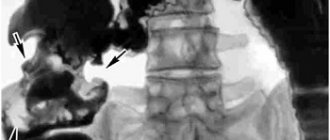
- Radiographs. In the image you can see a large concentration of accumulated gas in the stomach, in some cases, a transformation of the configuration of the stomach.
To find out the causes of the pathology, the following is carried out:
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- Endoscopy of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
Sometimes a consultation with a psychiatrist is necessary.
Aerophagia
Aerophagia is the systematic swallowing of air during or outside a meal, which leads to subsequent regurgitation.
ICD-10ICD-9MeSH
| F45.3 |
| 306.4 |
| D000334 |
Leave a request and within a few minutes we will find you a trusted doctor and help you make an appointment with him. Or select a doctor yourself by clicking on the “Find a Doctor” button. Find a doctor
- general information
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Forecast
- Prevention
Normally, while eating, a person swallows air - 2-3 cm3 with each sip. As a result, there is always an “air” or “gas” bubble with a capacity of 200 ml in the stomach. From the stomach it passes into the small intestine, where most of it is absorbed, and the remainder is released through the anus. The small amount of air remaining in the stomach may be released as a belch.
If a person swallows an excessive amount of air, it cannot quickly and completely pass into the small intestine, as a result, it puts pressure on the walls of the stomach and causes a number of unpleasant sensations. This is how aerophagia occurs. It is believed that infants and young women are most prone to it.
In addition, aerophagia can occur due to swallowing air, when a person is drowning, or is just learning to swim.
The causes of aerophagia can be divided into three groups:
- neurological;
- psychogenic (neurotic);
- associated with diseases of internal organs.
Neurological aerophagia develops as a result of a formed pathological conditioned reflex - a person, out of habit, swallows air while eating, talking, or constantly (along with saliva). As a rule, it leads to:
- violation of the rules of eating - hasty eating, poor chewing, talking during meals;
- hypersalivation (increased secretion of saliva) due to smoking, chewing gum or sucking on lozenges.
Psychogenic (neurotic) aerophagia is the result of nervous shock, stress, phobias, and hysteria. In this case, a person “grasps for air” regardless of meals.
Diseases that can lead to excessive swallowing of air:
- pathologies of the respiratory tract that impede nasal breathing or are accompanied by mucus flowing down the back wall of the pharynx;
- gastrointestinal diseases - chronic gastritis with low acidity, high-position gastric ulcer, pyloroduodenal stenosis, gastric hypotension, cardiac sphincter insufficiency, achalasia, hiatal hernia, colitis;
- pathologies of the dentition and oral cavity, incorrectly installed dentures;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels - coronary disease, venous congestion in the stomach and intestines, aneurysm of the descending aorta.
Aerophagia in infants occurs as a result of swallowing air while eating or crying. Basic prerequisites:
- improper attachment to the breast or incomplete latching of the nipple;
- Milk flow is too slow or fast.
The main symptoms of gastric aerophagia:
- belching – loud, “empty” (no smell), “multi-story”;
- bloating (especially in the upper segment), a feeling of heaviness, fullness in the epigastric region after eating;
- periodic hiccups (not in all patients);
- tachycardia, extraordinary contractions of the heart, angina after eating, feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath.
All unpleasant sensations become less pronounced after belching.
The main symptom of neurotic (psychogenic) aerophagia is belching, independent of food intake, which in many patients is accompanied by screaming. Often, episodes of belching bother a person throughout the day, disappearing only during sleep.
Aerophagia in newborns is accompanied by:
- screaming while eating;
- bloating and colic;
- regurgitation;
- in severe cases - refusal to eat, lack of food or weight loss.
Usually, after the excess air is released, the child calms down.
Aerophagia is diagnosed based on:
- patient complaints and medical history;
- identifying tympanitis - a loud high-pitched sound when tapping over the stomach;
- X-ray examination - shows a large amount of gas in the stomach and colon, a change in its shape (the stomach is shaped like an “hourglass”, “snail”, “horn”), an upward displacement of the diaphragm contour (not always).
In addition, the doctor asks the patient to provoke a burp - pull his head forward, press his chin to his chest and make swallowing movements.
During the examination, not only the fact of the presence of aerophagia is established, but also the diseases that led to it are identified. For this purpose the following is carried out:
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy.
In some cases, consultation with a psychiatrist is required.
How to get rid of aerophagia? Directions for assistance are determined by the causes of the disease. For dental pathologies, gastrointestinal dysfunctions, diseases of the respiratory or cardiovascular systems, systemic therapy is required.
Treatment of neurotic aerophagia is based on physiotherapy, rational psychotherapy and the prescription of sedatives: antidepressants or antipsychotics (chlorpromazine) in small doses.
Regardless of the reasons that caused the symptoms of aerophagia, its treatment should include correction of human behavior. Basic recommendations:
- meals in small portions in a calm environment without rushing;
- Chew solid foods thoroughly and drink enough liquid;
- limiting foods that contribute to increased gas formation (legumes, carbonated water);
- spitting saliva;
- breathing exercises, abdominal massage, warm baths.
Treatment of symptoms of aerophagia with folk remedies may include the use of herbal preparations - chamomile, valerian, fennel. Herbal medicine should be discussed with your doctor.
Aerophagia in infants does not require drug treatment. If the child is restless while eating, you should put him in an upright position and wait until the air comes out.
In most cases, aerophagia has a favorable prognosis if treated. Without correction it can lead to:
- weakening of the sphincter between the stomach and esophagus due to its constant stretching;
- development of a hiatal hernia as a result of pressure exerted by the stomach.
Since the cause of aerophagia in a newborn is the physiological immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract and nervous system, it goes away over time without treatment. However, efforts must be made to minimize the child's swallowing of air while eating.
Measures to prevent aerophagia:
- compliance with nutritional rules;
- correction of habits that lead to excessive air entering the gastrointestinal tract;
- adequate treatment of somatic diseases and psychological disorders;
- proper attachment of the baby to the breast or bottle.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
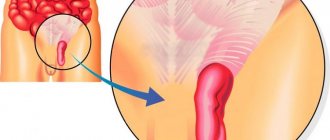
Barrett's esophagus (Barrett's syndrome or Barrett's metaplasia) is a serious complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), in which the squamous stratified epithelium of the esophageal mucosa is replaced by columnar epithelium, which is uncharacteristic of the esophagus. Cell metaplasia occurring in the terminal esophagus is considered to be a condition caused by chronic acid damage.
Hairy leukoplakia is white thread-like formations on mucous membranes covered with flat or transitional epithelium, the appearance of which is associated with hyperkeratosis (increased keratinization).
Tenesmus is a clinical symptom characterized by a painful and ineffective urge to defecate or urinate.
Acholia (acholic state, acholic disease, fistulous disease, bile leakage, biochemical depletion) is a condition in which there is a partial or complete cessation of the flow of bile into the duodenum.
As a result of prolonged bile loss in the human body, a complex of disorders arises associated with the cessation of the participation of bile in the digestive process, and subsequent disruption of the functional activity of various organs and systems.
Acholia is an important symptom of biliary tract diseases (blockage of the common bile duct, external biliary fistula, etc.)
Whipple's disease (mesenteric lipogranulomatosis or intestinal lipodystrophy) is a rare systemic disease of an infectious nature, in which disorders of cellular and humoral immunity are observed.
The causative agent of the disease primarily affects the small intestine, also affecting the mesenteric lymph nodes and synovial membranes of the joints.
As the disease develops, other organs are also involved in the pathological process.
Source: https://liqmed.ru/disease/aerofagiya/
How to get rid of aerophagia?
Treatment is selected individually depending on the source of the disease and first of all it is necessary to treat the underlying disease. All patients with aerophagia, regardless of the cause of the disease, need to:
- Adhere to hygienic standards for eating - eat without haste, silently, if the food is dry, drink with the required amount of water;
- Eat frequently throughout the day (250 g up to 5 times a day);
- Do not drink carbonated drinks, do not eat foods that increase gas formation;
- Perform a light abdominal massage after meals, take warm sitz baths;
- Do not swallow saliva while eating, but spit it out;
- Do breathing exercises;
- Quit smoking and alcohol;
Patients with neurotic disorders are prescribed courses of psychotherapy and small doses of antidepressants.
Physiological aerophagia in infants disappears after a certain time without treatment. After feeding him, you need to hold him in an upright position until excess air comes out.
Symptoms
The disease causes unpleasant symptoms. Patients with this diagnosis are embarrassed to be in crowded places, because belching can occur anywhere.
With aerophagia, everyone should know the symptoms and treatment in order to provide timely help to themselves or others.
Interesting! Foam belching appears (happens after eating) - ways to eliminate it
How to recognize pathology? It is important not only to understand the meaning of aerophagia and what it is, but also to know its manifestations.
Symptoms of the disease:
- frequent belching;
- flatulence;
- bloating;
- dry mouth;
- abdominal discomfort;
- periodic hiccups;
- feeling of fullness in the epigastrium;
- dyspepsia;
- chest pain;
- cardiopalmus;
- rumbling in the intestines.
The most common signs of indigestion are belching and excess gas.
In newborn babies, the pathological condition is accompanied by crying during breastfeeding, colic, refusal to eat and weight loss.
Aerophagia can also be treated with folk remedies.
Among them:
- Reflexology . Acupuncture with moxibustion is performed daily. Course 7 days. Conduct 2-3 courses. Break for a week.
- Phytotherapy.
The infusion is restorative and calming.
Take: 20 g each: Echinops leaves, lemon balm leaves, hop cones; 30 g each: - St. John's wort flowers, chamomile baskets; 25 g valerian root. Grind all dried ingredients in a mortar. Pour 2 tablespoons of the mixture into half a liter of boiled water. Leave for 2 hours, express. Use 50 g. 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. Herbal medicines with peppermint extract and artichoke herb are used. They help liver function and minimize digestive dysfunction.
Fennel fruit extract helps a lot with excess gases.
Drinking 150 grams of goat's milk is of great benefit from belching. 3 times a day immediately after meals.
Mix half a glass of cranberry juice and half a glass of aloe juice in a separate bowl, add a tablespoon of honey, and pour in a glass of boiled warm water. Take a tablespoon 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. Store in a cool place. Course 7 days. Repeat in a month.
50 gr. Mix potato and carrot juice and drink three times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Video on the topic: Causes of burping
Treatment
First of all, the correct therapy for aerophagia is determined by the cause of the occurrence and further development of the pathology. The important point is that if the disease is caused by disorders of the nervous system, treatment should be carried out under medical supervision in accordance with all instructions. In such a situation, self-medication can worsen the patient's condition, negatively affecting his health.
Causal aerophagia can be cured independently at home, since it is episodic in nature and, by and large, is not a disease as such. Those patients who suffer from this type of illness need to carefully plan their diet and not eat foods that cause excessive gas formation and further belching. For a while, it is worth giving up any carbonated drinks altogether, and eliminating chewing gum, which promotes the release of excess saliva.
To eliminate this pathology, you need to avoid physical activity immediately after eating. In addition, it is not advisable to drink water or tea immediately after eating. This also has a negative effect on the body, and therefore it is advisable to wait a while after eating (from half an hour), setting aside a cup of tea for this period of time.
In general, all habits that adversely affect the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, outlined above, should be strived to be eliminated and not forgotten about their negative impact.
After a short time of abstaining from undesirable habits, aerophagia of the cause-and-effect type will no longer bother the patient. The most important thing is not to provoke your body into excessive gas formation in the future.
How else to get rid of air accumulation in the stomach?
Nutrition
An incorrect diet very often becomes the cause of the appearance and development of a wide range of diseases, and not only of the gastrointestinal tract. In this section we will try to highlight the most common products that cause excess air to accumulate. Experts include these products:
- Soft carbonated drinks;
- Champagne;
- Bread and rolls;
- Cabbage;
- Fruits;
- Chewing gum;
- Legumes.
All of the listed products, entering the stomach, begin to produce gases. Therefore, excessive consumption of the above drinks and foods can contribute to the formation of air in the stomach.
Prevention
To prevent a child from burping air, parents should help him with this:
- The child must adhere to nutritional rules.
- The use of chewing gum and hard candies should be minimal.
- If psychological disorders occur, the child should be taken to a psychiatrist to begin timely treatment. Parents should protect their child from stressful situations.
- An infant must be properly placed on the breast or bottle, and not fed while crying. After feeding, the baby should be kept in an upright position for some time. Belching of air usually occurs.
Aerophagia - the word comes from the Greek. aerophagia - air, phagein - eat, absorb. The disease consists of swallowing air in large quantities and regurgitating it afterwards.
Not every swallowing of air is pathological. First, there is the physiological swallowing of air that is necessary to create a certain level of pressure. Such swallowing is not accompanied by belching. Secondly, belching can occur due to the consumption of carbonated drinks, soda or beer.
Carbonated drinks can cause belching
The diagnosis is made based on examination and medical history. Often, directly during the examination, you can observe how preparation for belching occurs. The movements are quite characteristic. The patient pulls his head forward, then presses his chin to his chest and makes empty swallowing movements.
Percussion can determine the enlarged Traube space. X-ray images show the diaphragm at a fairly high level. It is brought into this position by a large air bubble located in the stomach. This effect can also be achieved by detecting a functional cascade in the stomach.
In this case, the patients' complaints boil down to belching, which is accompanied by loud sounds, but it has no smell. If the patient is prone to hysteria, then during belching he also screams. This type of belching is almost permanent. It disappears in most cases during sleep.
If aerophagia is neurological in nature, then swallowing air has nothing to do with the process of eating.
Patients complain of discomfort in the stomach: pain, heaviness, bloating. The abdomen of such patients may be distended. If a person’s condition is complemented by ischemic disease, then gastrocardial syndrome develops: angina pectoris, extrasystole. True, this condition can also appear in patients with a healthy cardiovascular system. Sometimes a condition occurs that was previously called asthma dyspepticum. It consists of difficulty breathing.
Poor nutrition is the main cause of aerophagia
Aerophagia in childhood can occur in infants. This happens when the baby sucks a lot on the nipple or breast, where there is little milk. Moreover, the pathology can be threatening. After all, persistent regurgitation leads to weight loss.
Aerophagia in a baby can be determined by crying while sucking, a voluminous tummy, and a reluctance to suck further. When the child changes position, he burps. This calms the baby, and he can then behave calmly and continue to eat.
The diagnosis must be confirmed by x-ray examination. Swallowing air in children can be a bad habit. It needs to be weaned off. This can be done by carefully monitoring the eating process. In extreme cases, tube feeding is used. Also, aeorophagia may be due to the immaturity of the processes of nervous regulation of the digestive organs. In this case, it goes away on its own with age.
Other reasons for the appearance
There is also a list of reasons that are, in their own way, habits that provoke intense gas formation in the body. For example, smoking after eating negatively affects the stomach in two ways. Firstly, during smoking, additional air is swallowed. Secondly, nicotine has a negative effect on the stomach, which leads to pain and belching.
The process of eating food and its absorption in the body should be treated with the utmost care, because trouble can await any person when nothing predicts it. Taking a bath after eating helps increase blood flow in the extremities by reducing the flow in the stomach area. Those who like to sleep after eating should also be on guard, since during sleep the body slows down the digestion process, which ultimately causes discomfort.
Let's highlight a few more causes of aerophagia:
- Quick meal;
- Conversations over food;
- Excessive amount of food taken;
- Exercising after meals;
- 2nd trimester of childbearing.
Due to the above reasons, an excessive amount of air enters the stomach, so you should be careful and responsible about the process of eating and refrain from some activities immediately after eating.