If a significant part of the organ is damaged (total or subtotal pancreatic necrosis), despite timely and adequate assistance provided in full, the best prognosis may be survival with subsequent disability of the patient. The gland, according to various authors, fails in cases of large-focal infection of the pancreas by more than 80%, even when treated in specialized clinics. Cell necrosis occurs at lightning speed: after an emergency operation, it is not always possible to achieve a positive result, and the chance of saving life is reduced to zero. With small focal pancreatic necrosis of a separate part of the pancreas (head, body or tail), mortality rates range from 11 to 40%.
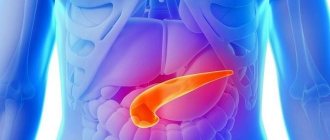
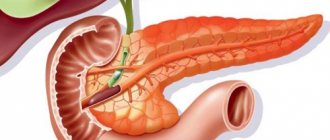
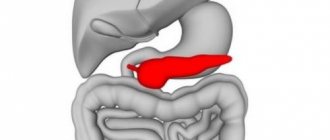
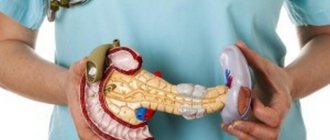
Where is it located in a person, where is it located?
Considering the anatomical structure of the abdominal cavity of a person standing upright, we can describe how the organs are located in it:
- immediately below the diaphragm are the liver and stomach (the main part of the liver is on the right, the stomach is on the left);
- on the left side, near the stomach, there is another organ, small in size, the spleen;
- the gallbladder is placed in front of the liver, next to the stomach;
- behind the stomach, pressed against the back wall of the abdominal cavity, the pancreas is located;
- below - the large and small intestine begin.
Thus, the organ we are interested in lies not under the stomach, as is mistakenly thought based on the name, but behind it. If a person is in a horizontal position, then the pancreas actually appears exactly under the stomach.
From the back, the location of the pancreas is determined by the vertebrae: the organ rests from the inside in the area between the first and second vertebrae belonging to the lumbar region. From the side of the abdomen, they are guided by the navel: approximately 6–9 cm above it.
If we talk about size, then the norm for an adult is considered to be approximately 20 cm, weighing about 75 grams of the pancreas.
The pancreas regulates glucose levels
The pancreas controls blood glucose levels using the hormone insulin. It is produced by beta cells concentrated in the islets of Langerhans. In type 1 diabetes, immune cells begin to attack beta cells, and they stop producing the required amount of insulin. This type of diabetes is also called insulin-dependent because insulin is artificially administered to the person.
In type 2 diabetes, the body simply does not perceive insulin - it develops resistance to it (insulin resistance). This type of diabetes usually develops due to overweight and obesity. It is accompanied by hypertension (high blood pressure), fatty liver disease and atherosclerosis.
We prove that the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is the main defense of the body. Research shows that increased permeability of the mucous membrane underlies most diseases of the digestive system. read in full »
What functions does the organ perform?
The functions of the pancreas are conventionally divided into two main ones:
- Endocrine (or internal).
- Exocrine (or external).
The first is responsible for the production of hormones and regulation of metabolism. The second is for the secretion of pancreatic juice.
Exocrine secretion is important in order to properly digest food that passes from the stomach to the duodenum. The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice, which includes a sufficient amount of the following enzymes:
- lipases, which break down fats;
- lactases and amylases that digest carbohydrates;
- trypsins and chymotrypsins, so necessary for the digestion of proteins.
Enzymes are not all the valuable substances that pancreatic juice contains. It also contains elements that can protect the intestinal mucosa from excessive acidity. These important substances neutralize acid from gastric juice and thereby regulate the alkaline balance of the gastrointestinal tract.
Internal secretion involves the balanced production of hormones such as glucagon and insulin. The first one increases the glucose level in the blood, the second one decreases it. The result is an adequate carbohydrate metabolic process. If something goes wrong in it, diabetes develops.
Classification of cystic lesions of a parenchymal organ
According to morphological indicators, all types of cystic lesions of the pancreas are divided into two main typologies:
- Formed during complications, formed during the development of an inflammatory disease of a parenchymal organ, without an epithelial lining, referred to as pseudocysts.
- Formed during obstructive processes in the cavity of the ducts, glands with a characteristic epithelial lining are called true cysts, or retention cysts.
In most cases, to assess cystic lesions of the pancreas, which has formed as an aggravation of the development of acute pancreatic pathology, the Atlanta classification is used, according to which the following varieties of this pathology are distinguished:
- acute fluid injury,
- subacute form with accumulated fluid,
- development of gland abscess.
Rapidly developing cysts with an acute course have incompletely formed walls of their cavity, which may include parapancreatic tissue, pancreatic ducts and the pancreatic parenchyma itself. But cystic formations formed during the chronic course of pancreatic pathology have walls made of fibrous and granulation tissue structures.
An abscess is a cavity filled with purulent contents formed during the development of pancreatic necrosis or suppuration of a cystic lesion.
Cysts can be localized both in the area of the head of the gland, its body, and in the tail area. Among other things, there is also an uncomplicated development of a pancreatic cyst and a complicated one. Cystic lesions can be complicated by the development of processes such as:
- perforation,
- suppuration,
- fistula formation,
- hemorrhage,
- progression of peritonitis,
- malignancy.
Where does it hurt, on which side?
Very often it is difficult for a person to describe the pain syndrome that engulfs him during a pancreatic attack. The sensations may have the following variations:
- sharp pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the lower back;
- aching pain under the diaphragm with tingling in the left arm;
- severe pain around the navel, which is slightly relieved by bending forward.
An inflamed pancreas, as a rule, begins to hurt from its main part - from the head. Therefore, pain is more likely to occur in the area located just above the navel, to the right of the midline. If a sharp pain resonates in the back, in its lumbar region, we are talking about the spread of inflammation to the tail of the organ and to more serious pathologies.
Why does it hurt?
Pain syndrome can be caused by pathological processes occurring in the pancreas:
- when internal pressure in an organ increases;
- if the bile duct is compressed;
- perhaps the effect on sensory nerves of fibrotic changes in tissues;
- due to ischemia of blood vessels that enrich the organ with blood;
- the appearance of a cyst or cancer.
The inflamed, swollen pancreas increases in size and puts pressure on neighboring organs. Because of this, the pain can intensify and spread throughout the abdominal area.
There are quite a few reasons why pancreatic pain can occur. The most basic primary factors due to which the pancreas fails to cope with its functions and fails include:
- systematic overeating and passion for fatty foods;
- poisoning of the body with nicotine, alcohol, chemicals, medications;
- cholelithiasis.
Pancreatitis often occurs against the background of long-term mental or physical stress. Almost all causes of pancreatic pain are long-term systematic neglect of health, failure to treat chronic diseases, and weakened immunity.
Causes of pancreatic swelling
Swelling of the pancreas is evidence of the development of acute pancreatitis in a mild version of its course. Occurs in 80-85% of cases. Develops with excessive alcohol consumption, reflux of bile into the biliary ducts, injuries, autoimmune processes, acute infectious diseases, use of toxic drugs and chemicals. In some cases it occurs for no apparent reason.
The swelling is inflammatory in nature and is the result of damage to the pancreas tissue by its own enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin). It also develops with pancreatic necrosis, but here the first place is taken by deep damage to the glandular tissue with its death. The enzymes of the gland digest it itself. The accumulation of fluid during edema is diffuse, spreading over the entire area of the organ. Proliferation of liquid fractions occurs due to changes in vascular permeability against the background of the inflammatory process.
Separately, the peripancreatic infiltrate that occurs as a consequence of acute pancreatitis (in phase IB) should be considered. In this case, fluid accumulates both in the tissues of the gland itself and near it. The infiltrate does not have walls of fibrous tissue, is located freely, and can transform into a cyst or pseudocyst.
How to understand that it is she who is hurting?
Sometimes it is easy to confuse pancreatic pain with another pathology. For example, with radiculitis, discomfort occurs closer to the left side and can resonate in the hypochondrium. Therefore, you need to pay attention not only to how the pancreas hurts, but also to the accompanying symptoms:
- If continuous vomiting is added to the sharp pain, food poisoning may be suspected. Acute pancreatitis is characterized by the fact that the pain becomes more and more intense, and vomiting does not bring even temporary relief.
- Frequent pressing discomfort in the upper abdomen and a feeling of overeating from small portions indicate chronic pancreatitis. Additionally, this may be indicated by weight loss, dryness and bitterness in the mouth.
Serious problems of the pancreas can also be judged by stool. The masses become shiny in appearance, stick to the walls of the toilet bowl and may contain visible pieces of undigested food.
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most dangerous
Pancreatic cancer is well treated in its early stages, but due to the lack of symptoms, the disease is diagnosed late in most cases. That is why pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest - the advanced form is fatal in most cases.
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer include smoking, excess weight and physical inactivity, diabetes mellitus and chronic pancreatitis. Age plays a role: people over 55 years of age have a higher risk of developing a tumor in the pancreas, so preventive screenings are necessary. There is also an increased risk in familial cases of pancreatic cancer.
To prevent the development of such a serious disease, you need to undergo a full check-up of the body at least once every two years - an examination that gives an overall picture of your health. If signs of illness are detected, you can easily and quickly deal with it.
Main symptoms
Impaired secretion of pancreatic juice causes a typical symptomatic picture for both men and women:
- Pain syndrome. Unbearable cutting pain above the navel, extending into the left hypochondrium or aching, growing. Sitting forward or "fetal position" may provide some relief.
- Dyspeptic disorders. Nausea, vomiting with bile, diarrhea, bloating, belching - all these signs accompany a failure of fermentation of pancreatic juice.
- Intoxication. Enzymes blocked in the pancreas begin to destroy surrounding tissue, and food in the duodenum, not receiving the necessary elements for breakdown, decomposes. All this poisons the body and manifests itself in tachycardia, cold sweat, increased body temperature, headaches, severe weakness, and dizziness.
Chronic pancreatitis leads to even more serious pathological processes in the body. For example, due to an imbalance in insulin production, diabetes mellitus begins. And metabolic disorders affect the liver. As a result, yellowness of the skin and eye sclera appears.
Causes of fluid accumulation in the pancreas
A condition where fluid accumulates in the pancreas can be a consequence of the following problems:
- diseases of the duodenum;
- infectious processes in the liver, for example, viral hepatitis;
- metabolic problems;
- severe obesity;
- cholelithiasis;
- the presence of a benign or malignant tumor;
- inflammation in the pancreas – acute pancreatitis;
- helminths;
- diabetes;
- injuries in the abdominal area.
Sometimes swelling is observed due to alcoholism or as a result of banal overeating. The accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the gland is provoked by the consumption of carbonated drinks, foods high in protein, and fast food. Such a diet is the cause of acute pancreatitis, which often causes swelling.
You can understand what it is by considering the state of the organ in the event of an inflammatory process. In the absence of timely assistance, a significant amount of enzymes is constantly released. But the ducts of the gland are not able to remove fluid; they are compressed and blocked. Pancreatic juice gradually accumulates in the tissues and digests them. Pancreatic cells die, necrosis of individual areas develops. Decay products are carried through the bloodstream throughout the body, causing intoxication.
The situation is no less dangerous when the swelling is caused by a tumor. The first stages of cancer are not necessarily detected in the gland itself. Often, mutated cells penetrate into the pancreas through the lymphatic system from another organ affected by a malignant tumor.
Primary pancreatic cancer is a rare phenomenon and is practically asymptomatic. Therefore, the disease is often detected when the tumor metastasizes.
When examining such patients, doctors note that the pancreas is swollen, as if filled with fluid, and its size is greatly increased.
At the first signs of pancreatic edema, it is advisable to contact an endocrinologist. The sooner the doctor determines the problem with the gland, the more successful the therapy will be.
What are the symptoms and signs of organ pathologies?
Based on the clinical picture and the nature of the pain, doctors can determine this or that organ pathology.
The presence of a cyst that grows and increases pressure on pancreatic tissue is indicated by characteristic symptoms:
- aching pain after or during a meal;
- attacks of nausea with dizziness;
- vomiting without relief of the general condition.
Symptoms indicate swelling and enlargement of the inflamed gland:
- heaviness and bloating of the upper abdomen;
- loss of appetite and nausea;
- taste of bile in the mouth;
- unstable stool.
Diagnosis of diseases
To select effective complex therapy, first of all, an accurate diagnosis is necessary. For its qualified differentiation, a set of diagnostic measures is carried out, including several stages:
- Visual examination by a doctor of the skin and eye sclera. Probing painful areas using palpation.
- Studying the patient’s medical history, genetic predispositions, and other chronic diseases.
- Laboratory study of blood, feces and urine parameters. The level of pancreatic enzymes is measured in the blood serum. Biochemical analysis reveals the degree of activation of bilirubin and liver fermentation, as well as glucose content. The amylase level in the urine is analyzed. The content of undigested fats is determined from feces.
- An abdominal ultrasound shows the contours of the pancreas and the degree of its enlargement, the presence of stony formations or scars in the bile ducts. For the same purposes, radiography or layer-by-layer computed tomography may be prescribed.
Only all the data taken together can give a clear picture of the pathology and help find the most effective treatment strategy.
Treatment
A conservative treatment method consists of medications and providing maximum rest to the pancreas (hunger followed by a strict diet). Some home remedies and traditional medicine recipes can be added to therapy, but only after prior agreement with the doctor.
Antacids
Drug treatment necessarily includes taking antacids - medications that can suppress gastric acid. Strength of action, duration of effect and composition are the main characteristics of drugs that are distinguished in this group.
Absorbable antacids are among the most effective and fastest-acting. Preference is given to simple connections that have been tested many times:
- magnesium oxide;
- sodium phosphate or sulfate;
- sodium bicarbonate.
In inpatient treatment, these substances are administered in pure form intravenously. In outpatient treatment, pharmaceutical preparations are popular, the composition of which is based on the listed antacids (we are talking about Bourget's mixture, Rennie or Tams mixtures).
Non-absorbable antacids act for a longer period, although their effect occurs more slowly. These elements (aluminum salt of phosphoric acid, magnesium hydroxide, alginate) are the basis of pharmaceuticals that produce such drugs as Almagel, Phosphalugel, Maalox.
Enzyme preparations
Due to enzymatic dysfunctions, food is poorly digested, and a person suffering from inflammation of the pancreas is prescribed enzyme preparations. Therefore, on what substance the medicines are based, they are divided into groups:
- their animal proteins;
- vegetable.
In the production of the former (for example, pancreatin, mezim, creon) pork protein is used. It improves digestion and fermentation of pancreatic juice. But it can cause allergies. Especially in children and pregnant women. The second group acts softer and weaker, but is based on non-allergenic papain or rice fungus (somylase, pepphys, unienzyme).
Gastroenterologists warn about the dependence of the body, accustomed to artificial fermentation. Over time, the pancreas refuses to produce the necessary elements on its own.
Therefore, if the pathology has not yet gone too far, doctors themselves recommend considering traditional medicine recipes (herbs, decoctions, infusions) - those that improve gastric motility and the production of enzymes naturally.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of the pancreas is used infrequently, only if traditional therapy fails to cope with the tasks and the pathology progresses rapidly. Indications for surgery include cysts, cancers, necrosis of pancreatic tissue, and large stones in the bile ducts.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. During the intervention, the surgeon can cut off part of the organ (resection of a separate affected area) or remove only a dangerous formation (cyst, tumor). In exceptional cases, a pancreas transplant is possible. During the operation, the inflammatory process is stopped, pain is eliminated, and bile is drained and removed.
First aid for pain in the pancreas
If you suspect that the cause of abdominal pain is inflammation of the pancreas, you should immediately seek qualified help. Before consulting a doctor, you can alleviate the patient’s condition by doing the following:
- Completely avoid eating any food for at least 24 hours. This will reduce the load on the gland, reduce the production of enzymes and relieve the organ.
- Apply cold (ice, a heating pad with cold water) to the sore spot. This will slow down the development of edema in the pancreatic tissue.
- Provide plenty of fluids (at least 2 liters of fluid per day). It is advisable to drink non-carbonated alkaline mineral water. This will help improve the outflow of bile and pancreatic juice.
- It is allowed to take medications that have an antispasmodic effect, preferably intramuscularly. This is necessary to relieve spasm of the sphincter of the main bile duct and restore the flow of juice produced by the gland into the intestinal lumen. Thanks to such actions, the likelihood of self-digestion of pancreatic tissue is significantly reduced.
- Any other medications and therapies should be prescribed only by a specialist.
How to care for the organ?
Treatment of the pancreas is always a complex and long process. It is much easier to prevent new inflammation of the organ by following simple advice from gastroenterologists:
- Avoid alcoholic beverages and nicotine. Nothing destroys the pancreas and liver as much as these two dangerous habits.
- Maintain a healthy diet. Eating a lot of fatty foods leads to the fact that the pancreas can no longer cope with the production of enzymes in sufficient quantities to digest all the junk food.
- Periodically you need to cleanse your body of waste and toxins. Once a month, it is advisable to have a fasting day, completely refusing food, taking only healing herbal decoctions.
Healthy juices prepared at home help strengthen the health of the pancreas: carrot, potato, parsley and aloe vera. It is very useful to start the day with a glass of clean water, to which one tablespoon of lemon juice and one teaspoon of honey have been added.
Diagnostics
After collecting anamnestic data, examination and palpation, which can reveal a large pseudocyst, the doctor orders the patient to go to the laboratory for tests.
Elevated levels of amylase in the urine and blood confirm the presence of an inflammatory process in the pancreas. But it is possible to detect false cysts, determine their location and stage of development only by carrying out diagnostic procedures using special equipment:
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy . The introduction of a probe with a camera attached to the end makes it possible to detect erosions in the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum at the site of compression by the enlarged pancreas and false cysts.
- X-ray of internal organs located in the abdominal cavity makes it possible to identify shadows of pseudocysts and displacement of organs adjacent to the pancreas.
- Ultrasound of the pancreas allows you to visualize the tumor, assess its condition and determine the exact location.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is performed only before surgery to select a treatment method.
- MRI of the gland helps to most fully assess the condition of the organ and make a final diagnosis.
Ultrasound is the most common and accurate method for diagnosing pancreatic pathologies
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor develops a conservative treatment regimen or decides on the advisability of surgical intervention.
The role of diet in the treatment of the organ
Dietary nutrition is a fundamental factor in a healthy pancreas. The goal of a proper diet is to load the gastrointestinal tract as little as possible with heavy foods oversaturated with fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
Having survived an acute pancreatic attack, a person is prescribed fasting for complete rest of the pancreas and the opportunity to cleanse itself of intoxication. Normal fermentation will not be restored without a strict diet.
Without it, neither medicines nor folk remedies will help. Only strict adherence to the advice of nutritionists can truly cure pancreatic diseases.